2003 Oldsmobile Alero tow
[x] Cancel search: towPage 2 of 354

The 2003 Oldsmobile Alero Owner Manual a
Seats and Restraint Systems ........................... 1-1
Front Seats
............................................... 1-2
Rear Seats
............................................... 1-8
Safety Belts
.............................................. 1-9
Child Restraints
....................................... 1-32
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS)
...................................... 1-53
Restraint System Check
............................ 1-60
Keys
........................................................ 2-2
Doors and Locks
....................................... 2-7
Windows
................................................. 2-1 4
Theft-Deterrent Systems ............................ 2-1 6
Starting and Operating Your Vehicle
........... 2-17
Mirrors
.................................................... 2-32
Siorage Areas
......................................... 2-34
Sunroof .................................................. 2-35
Instrument Panel Overview
.......................... 3-4
Climate Controls
...................................... 3-1 9
.w .arning Lights, Gages and indicators ......... 3-23
Audio System(s) ....................................... 3-38
Features and Controls
..................................... 2-1
Instrument Panel
............................................. 3-1 Driving Your Vehicle
....................................... 4-1
Your Driving, the Road, and Your Vehicle
..... 4-2
Towing
................................................... 4-31
Service
..................................................... 5-3
Fuel ......................................................... 5-5
Checking Things Under
the
Hood ............................................... 5-9
Headlamp Aiming
..................................... 5-47
Bulb Replacement .................................... 5-49
Windshield Wiper Blade Replacement
......... 5-52
Tires
...................................................... 5-53
Appearance Care
..................................... 5-72
Vehicle Identification
................................. 5-80
Electrical System
...................................... 5-81
Zapai;iiit=s at-tii ~J~LIIIL~LIUI I> 5-w~
Normal Maintenance Replacement Parts ...... 5-88
Maintenance Schedule ........................... ... 6-1
Maintenance Schedule
................................ 6-2
Customer Assistance Information
.................... 7-1
Customer
Assistance iniorrnation .................. 7-2
Index ................................................................. 1
Service
and Appearance Care
.......................... 5-1
n.- - -:I: - -1: - .- - .....................
Page 10 of 354
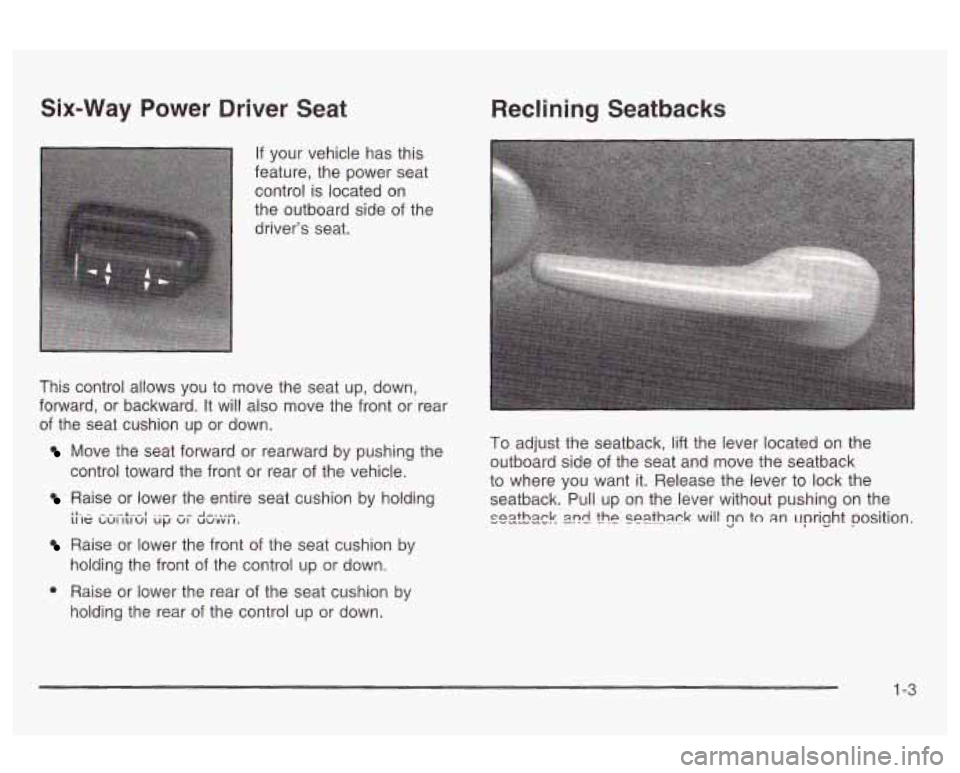
Six-Way Power Driver Seat Reclining Seatbacks
If your vehicle has this
feature, the power seat
control is located on
the outboard side of the
driver's seat.
This control allows you to move the seat
up, down,
forward, or backward. It will also move the front or rear
of the seat cushion up or down.
Move the seat forward or rearward by pushing the
control toward the front or rear of the vehicle.
Raise or lower the entire seat cushion by holding II- - - -.-1..-I . "- ^- A -...- 11 le LUI ILIUI up VI UUVVI I.
Raise or lower the front of the seat cushion by
holding the front
of the control up or down.
To adjust the seatback, lift the lever located on the
outboard side of the seat and move the seatback
to where you want it. Release the lever to lock the
seatback. Pull up on the lever without pushing on the
snrthzck IPC! !he seafhack will 20 to an upright position.
0 Raise or lower the rear of the seat cushion by
holding the rear of the control up or down.
1-3
Page 40 of 354

Never do this.
Here two children are wearing the same belt.
The belt can’t properly spread the impact
forces.
In a crash, the two children can be
crushed together and seriously injured.
A belt
must be used by only one person at
a time.
Q: What if a child is wearing a lap-shoulder belt,
but the child is so small that the shoulder belt
is very close to the child’s face or neck?
A: Move the child toward the center of the vehicle, but
be sure that the shoulder belt still
is on the child’s
shoulder,
so that in a crash the child’s upper
body would have the restraint that belts provide.
If the child is sitting in a rear seat outside position,
see “Rear Safety Belt Comfort Guides” in the
Index.
If the child is so small that the shoulder belt is still
very close to the child’s face or neck, you might
want to place the child in the center seat position,
the one that has only a lap belt.
1-33
Page 45 of 354
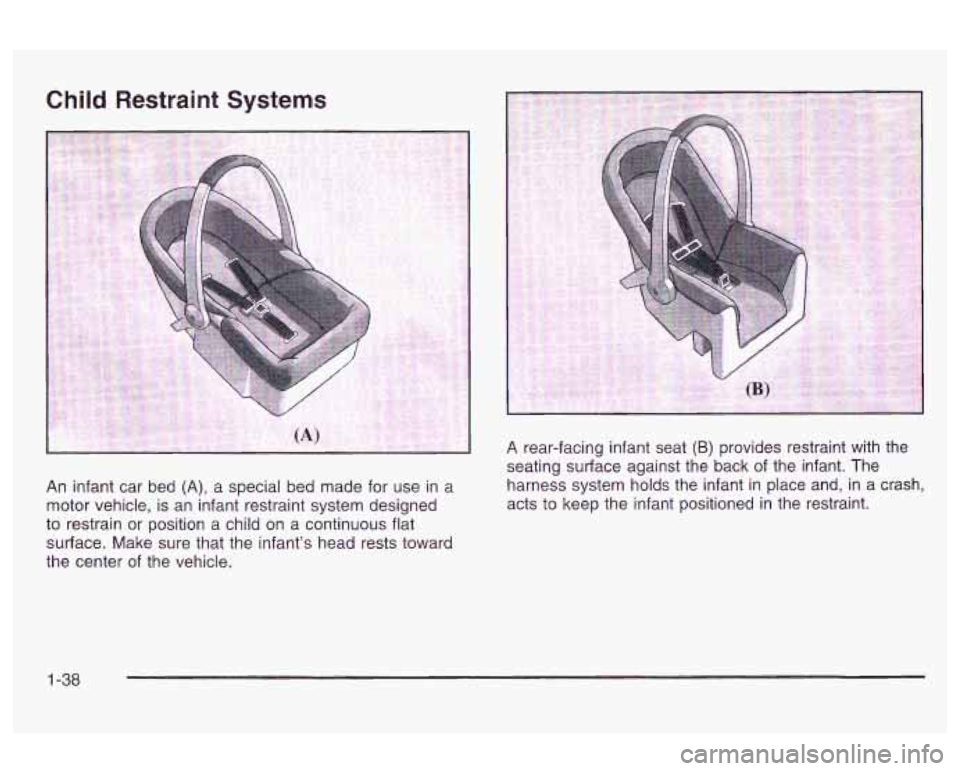
Child Restraint Systems
I
An infant car bed (A), a special bed made for use in a
motor vehicle, is an infant restraint system designed
to restrain
or position a child on a continuous flat
surface. Make sure that the infant’s head rests toward
the center of the vehicle. A
rear-facing infant seat
(B) provides restraint with the
seating surface against the back of the infant. The
harness system holds the infant in place and, in a crash,
acts to keep the infant positioned in the restraint.
1 -38
Page 64 of 354

If your vehicle strikes something that will move or
deform, such as a parked car, the threshold level will be
higher. The air bag is not designed to inflate in
rollovers, rear impacts, or in many side impacts because
inflation would not help the occupant.
In any particular crash, no one can say whether an air
bag should have inflated simply because of the damage
to a vehicle or because of what the repair costs were.
Inflation is determined by the angle of the impact
and how quickly the vehicle slows down in frontal and
near-frontal impacts.
What Makes an Air Bag Inflate?
In an impact of sufficient severity, the air bag sensing
system detects that the vehicle is in a crash. The
sensing system triggers a release of gas from the
inflator, which inflates the air bag. The inflator, air bag
and related hardware are all part of the air bag modules
inside the steering wheel and in the instrument panel
in irorli ui ine rigni ironi passenger.
How Does an Air Bag Restrain?
In moderate to severe frontal or near-frontal collisions,
even belted occupants can contact the steering wheel or
the instrument panel. Air bags supplement the
protection provided by safety belts. Air bags distribute
the force of the impact more evenly over the occupant’s
upper body, stopping the occupant more gradually.
But air bags would not help you in many types
of
collisions, including rollovers, rear impacts and many
side impacts, primarily because an occupant’s motion is
not toward those air bags. Air bags should never be
regarded as anything more than a supplement to safety
belts, and then only
in moderate to severe frontal or
near-frontal collisions.
What Will You See After an Air Bag
Inflates?
After an air bag inflates, it quickly deflates, so quickly
that some people may not even realize the air bag
iniiated. some components
of the air bag module - the
steering wheel hub for the driver’s air bag or the
instrument panel for the right front passenger’s
bag
- will be hot for a short time. The parts of the
bag that come into contact with you may be warm,
but not
too hot to touch.
1-57
Page 86 of 354

Starting and Operating Your
Vehicle
New Vehicle Break-In
Nofice: Your vehicle doesn’t need an elaborate
“break-in.” But
it will perform better in the long run
if you follow these guidelines:
0
0
0 Don’t drive at any one speed - fast or
slow
- for the first 500 miles (805 km).
Don’t make full-throttle starts.
Avoid making hard stops for the first
200 miles
(322 km) or so. During this time your new
brake linings aren’t yet broken
in. Hard stops
with new linings can mean premature wear and
earlier replacement. Follow this breaking-in
guideline every time you get new brake linings.
Don’t tow a trailer during break-in. See “Towing
a Trailer”
in the Index for more information.
Ignition Positions
With the key in the ignition switch, you can turn it to four
different positions.
A
hB
A (OFF): This is the only position from which you can
shift lever must be in PARK (P) with the ignition in
OFF
to remove the key. With a manual transaxle, the shift
lever must be in
REVERSE (R) with the ignition in OFF
to remove the key.
I~IIIUV~: iP~t: key. VVIU I 21-1 huiei-fi&ic tTSiTsZ26, th~ 8 18!1l-
2-1 7
Page 87 of 354

A warning chime will sound if you open the driver’s door
when the ignition is
off and the key is in the ignition.
Notice: If your key seems stuck in OFF and
you can’t turn it, be sure you are using the correct
key;
if so, is it all the way in? Turn the key only
with your hand. Using
a tool to force it could break
the key or the ignition switch.
If none of this
works, then your vehicle needs service.
B (ACCESSORY): This position unlocks the transaxle.
It also lets you use things like the radio and windshield
wipers when the engine is not running. To use
ACCESSORY, turn the key clockwise to the first
position. Use this position
if your vehicle must be pushed
or towed, but never try to push-start your vehicle.
C (ON): This position is where the key returns to after
you start your engine and release the key. The
ignition switch stays in ON when the engine is running.
But even when the engine is not running, you can
use
ON to operate your electrical accessories and to
display some instrument panel warning lights.
D (START): This position starts the engine. When the
engine starts, release the key. The ignition switch
will return to ON for normal driving.
Retained Accessory Power (RAP)
Your vehicle is equipped with a Retained Accessory
Power (RAP) feature which will allow the radio to
continue
to work up to 10 minutes after the ignition is
turned to OFF.
Your radio will work when the ignition key is in ON or
ACCESSORY. Once the key is turned from ON
to OFF,
the radio will continue
to work up to 10 minutes or
until the driver’s door is opened.
Starting Your Engine
Automatic Transaxle
Move your shift lever to PARK (P) or NEUTRAL (N).
Your engine won’t start in any other position
- that’s a
safety feature. To restart when you’re already moving,
use NEUTRAL (N) only.
Notice: Don’t try to shift to PARK (P) if your
vehicle
is moving. If you do, you could damage the
transaxle. Shift to PARK (P) only when your
vehicle is stopped.
Manual Transaxle
The gear selector should be in neutral and the parking
brake engaged. Hold the clutch pedal to the floor
and start the engine. Your vehicle won’t start
if the clutch
pedal is not all the way down
- that’s a safety feature.
2-1 8
Page 91 of 354

4. Before starting the engine, be sure to unplug and
store the cord as it was before to keep it away
from moving engine parts.
If you don’t, it could be
damaged.
How long should you keep the coolant heater plugged
in? The answer depends on the outside temperature, the
kind of oil you have, and some other things. Instead
of trying to list everything here, we ask that you contact
your dealer in the area where you’ll be parking your
vehicle. The dealer can give you the best advice for that
particular area.
Automatic Transaxle Operation
Your automatic transaxle
has a shift lever located
on the console between
the seats.
PARK (P): This position locks your front wheels. It’s the
best position to use when you start your engine
because your vehicle can’t move easily.
It igerous to get out of your vehicle if the
shift lever
is not fully in PARK (P) with the
parking brake firmly set. Your vehicle can roll.
Don’t leave your vehicle when the engine is
running unless you have to.
If you have left the
engine running, the vehicle can move
suddenly. You
or others could be injured. To
be sure your vehicle won’t move, even when
you’re on fairly level ground, always set your
parking brake and move the shift lever to
PARK (P). See “Shifting Into Park (P)” in the
Index. If you’re pulling a trailer, see “Towing a
Trailer”
in the Index.
Ensure the shift lever is fully in PARK (P) before starting
the engine. Your vehicle has an automatic transaxle shift
lock control system. You have to apply your regular brake
before you can shift from PARK
(P) when the ignition key
is
in ON. If you cannot shift out of PARK (P), ease
pressure on the shift lever and push the shift lever all the
way into PARK (P) as you maintain brake application.
2-22