2003 DODGE RAM torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 171 of 2895

(8) Install anewcollapsible spacer on the pinion
shaft (Fig. 63).
(9) Lubricate rear pinion bearing and install pin-
ion gear into the housing.
(10) Install companion flange with Installer
C-3718 and Holder 6719.
(11) Install bolts into two of the threaded holes in
the companion flange 180É apart.
(12) Position Holder 6719 against the companion
flange and install a bolt and washer into one of the
remaining threaded holes. Tighten the bolts so the
Holder 6719 is held to the flange.
(13) Install companion flange washer and anew
nut on the pinion and tighten the nut until there is
zero bearing end-play.
(14) With a torque wrench tighten the nut to 285
N´m (210 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 64).
CAUTION: Never loosen pinion nut to decrease pin-
ion rotating torque and never exceed specified pre-
load torque. If preload torque or rotating torque is
exceeded a new collapsible spacer must be
installed.
(15) Slowly tighten the nut in 6.8 N´m (5 ft. lbs.)
increments until the desired rotating torque is
achieved. Measure pinion rotating torque frequently
to avoid over crushing the collapsible spacer.(16) Check pinion rotating torque with an inch
pound torque wrench (Fig. 65). The pinion rotating
torque should be:
²Original Bearings: 1 to 3 N´m (10 to 20 in. lbs.).
²New Bearings: 2 to 5 N´m (15 to 35 in. lbs.).
Fig. 63 COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
1 - COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
2 - REAR PINION BEARING
3 - PINION DEPTH SHIM
Fig. 64 PINION NUT
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - HOLDER
3 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 65 PINION ROTATION TORQUE
1 - COMPANION FLANGE
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
3 - 98 REAR AXLE-91/4DR
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR/TONE RING (Continued)
Page 172 of 2895

(17) Position exciter ring on differential case. With
a brass drift, slowly and evenly tap the exciter ring
into position.
(18) Position ring gear on the differential case and
start two ring gear bolts. This will provide case-to-
ring gear bolt hole alignment.
(19) Invert the differential case in the vise.
(20) Installnewring gear bolts and alternately
tighten to 156 N´m (115 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 66).
CAUTION: Never reuse the ring gear bolts. The
bolts can fracture causing extensive damage.
(21) Install differential in housing and verify gear
mesh, backlash and contact pattern.
(22) Install axle shafts.
(23) Install differential cover and fill with gear
lubricant.
(24) Install propeller shaft with reference marks
aligned.
Fig. 66 RING GEAR BOLTS
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - RING GEAR BOLTS
3 - RING GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
DRREAR AXLE - 9 1/4 3 - 99
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR/TONE RING (Continued)
Page 176 of 2895

Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern. Adjust backlash or
pinion depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a lifting device under the axle.
(3) Secure axle to device.
(4) Remove wheels and tires assemblies.
(5) Remove RWAL sensor from the differential
housing.
(6) Remove brake hose at the axle junction block
and axle vent hose.
(7) Disconnect parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(8) Remove brake calipers and rotors.
(9) Mark propeller shaft and companion flange for
installation alignment reference.
(10) Remove propeller shaft.
(11) Remove shock absorbers from axle.
(12) Remove U-bolts from axle.
(13) Separate the axle from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise axle with lifting device and align to the
leaf spring centering bolts.
(2) Install axle U-bolts and tighten to 149 N´m
(110 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install shock absorbers to axle and tighten to
specification.
(4) Install the RWAL sensor to the differential
housing.
(5) Connect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(6) Install brake calipers.
(7) Connect brake hose to the axle junction block
and axle vent hose.
(8) Align propeller shaft and pinion companion
flange reference marks and tighten companion flange
bolts to 115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install the wheels and tires.
DRREAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA 3 - 103
REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 177 of 2895

(10) Fill differential to specifications.
(11) Remove lifting device from axle and lower the
vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim. The shim is located
between the rear pinion bearing and the pinion gear
head.
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 1).
(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 8899 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 1).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 2).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and install the
Cone-nut 6740 hand tight. Then check tool rotating
torque with an inch pound torque wrench. The rotat-ing torque should be 1.7-2.26 N´m (15-20 in. lbs.)
(Fig. 1).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 3).
(5) Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs
and snug the bearing cap bolts. Then cross tighten
cap bolts to 165 N´m (122 ft. lbs.).
NOTE: Arbor should rotate freely in the arbor discs.
(6) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(7) Position Scooter Block/Dial Indicator flush on
the pinion height block. Hold scooter block and zero
the dial indicator.
Fig. 1 PINION GEAR DEPTH GAUGE TOOLS
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 2 PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 3 GAUGE TOOLS IN HOUSING
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
3 - 104 REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AADR
REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 179 of 2895

(12) Tighten bearing cap bolts to 115 N´m (85 ft.
lbs.).
(13) Tighten adjuster lock bolts to 33 N´m (24 ft.
lbs.).
(14) Measure ring gear backlash with a Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 and Dial Indicator Stud L-4438 at eight
points around the drive side of the ring gear (Fig. 7).
The backlash should be 0.08-0.25 mm (0.003-0.010
in) with a preferred backlash of 0.13-0.18 mm (0.005-
0.007 in).
NOTE: Backlash measurement should not vary
more than 0.05 mm (0.002 in) between measuring
points. If measurement does vary inspect the gears
for burrs, the differential case flange and ring gear
mounting.
GEAR TOOTH CONTACT PATTERN
Gear tooth contact pattern is used to verify the cor-
rect running position of the ring and pinion gears.
This will produce low noise and long gear life. Gears
which are not positioned properly may be noisy and
have shorten gear life.
(1) Wipe clean each tooth of the ring gear.
(2) Apply gear marking compound to all of the ring
gear teeth.
(3) Verify bearing cap bolts are torque specifica-
tion.
(4) Apply parking brakes lightly to create at 14
N´m (10 ft. lbs.) pinion rotating torque.
(5) Rotate the pinion/pinion yoke 4 full revolutions
in each directions.
(6) Read gear tooth contact pattern:²Gear contact pattern correct (Fig. 8). Backlash
and pinion depth is correct.
²Ring gear too far away from pinion gear (Fig. 9).
Decrease the backlash, by moving the ring closer to
the pinion gear using the adjusters.
²Ring gear too close to pinion gear (Fig. 10).
Increase the backlash, by moving the ring away from
the pinion gear using the adjusters.
Fig. 7 RING GEAR BACKLASH
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - RING GEAR
Fig. 8 CORRECT CONTACT PATTERN
Fig. 9 INCORRECT BACKLASH
1 - COAST SIDE TOE
2 - DRIVE SIDE HEEL
Fig. 10 INCORRECT BACKLASH
1 - DRIVE SIDE TOE
2 - COAST SIDE HEEL
3 - 106 REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AADR
REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 181 of 2895
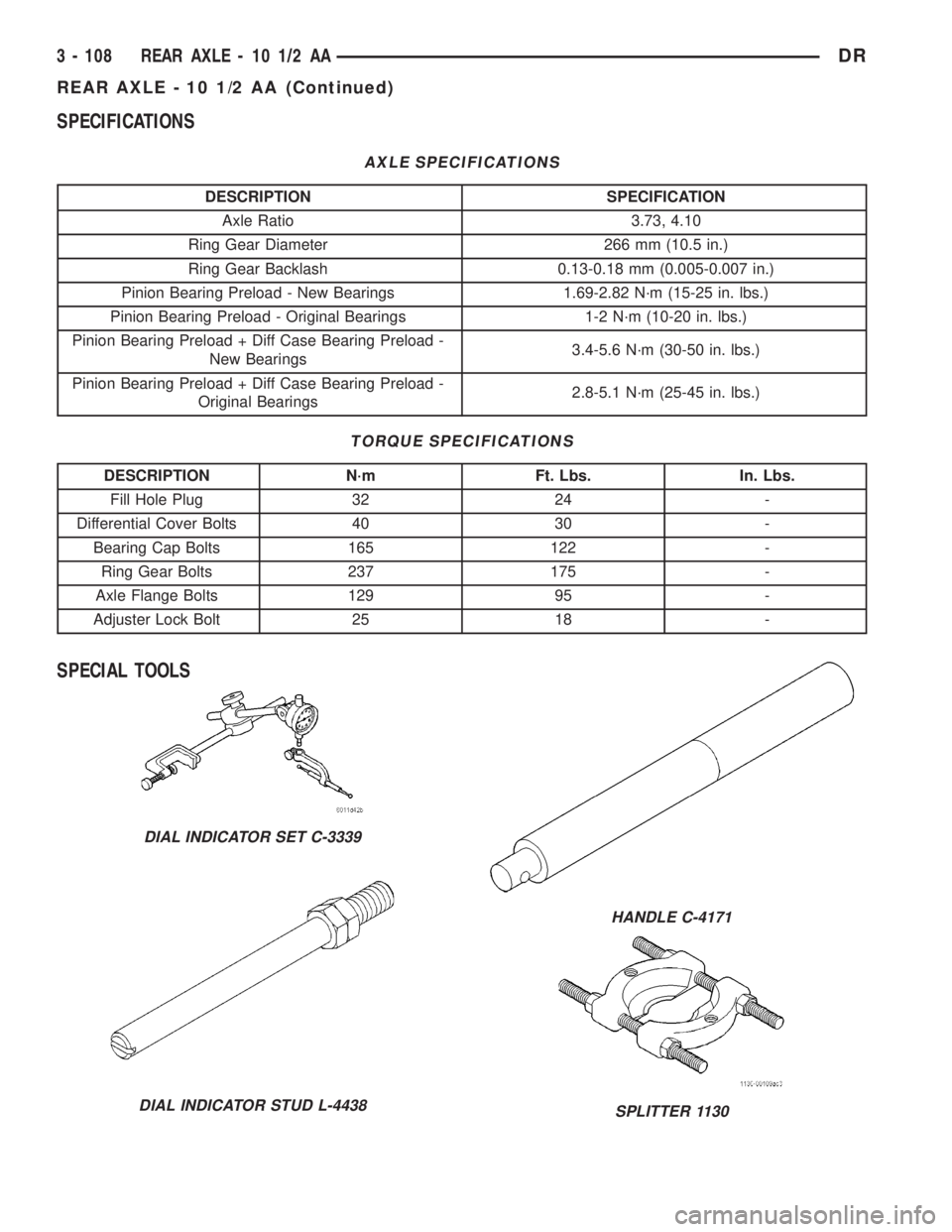
SPECIFICATIONS
AXLE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Axle Ratio 3.73, 4.10
Ring Gear Diameter 266 mm (10.5 in.)
Ring Gear Backlash 0.13-0.18 mm (0.005-0.007 in.)
Pinion Bearing Preload - New Bearings 1.69-2.82 N´m (15-25 in. lbs.)
Pinion Bearing Preload - Original Bearings 1-2 N´m (10-20 in. lbs.)
Pinion Bearing Preload + Diff Case Bearing Preload -
New Bearings3.4-5.6 N´m (30-50 in. lbs.)
Pinion Bearing Preload + Diff Case Bearing Preload -
Original Bearings2.8-5.1 N´m (25-45 in. lbs.)
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fill Hole Plug 32 24 -
Differential Cover Bolts 40 30 -
Bearing Cap Bolts 165 122 -
Ring Gear Bolts 237 175 -
Axle Flange Bolts 129 95 -
Adjuster Lock Bolt 25 18 -
SPECIAL TOOLS
DIAL INDICATOR SET C-3339
DIAL INDICATOR STUD L-4438
HANDLE C-4171
SPLITTER 1130
3 - 108 REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AADR
REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 186 of 2895

PINION SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove axle shafts.
(2) Mark propeller shaft and pinion flange for
installation reference and remove shaft.
(3) Rotate pinion gear three or four times.
(4) Measure and record the amount of torque nec-
essary to rotate the pinion gear with an inch pound
torque wrench (Fig. 20).
(5) Hold pinion flange with Flange Wrench 8979
(Fig. 21) and remove pinion flange nut and washer.(6) Remove pinion flange with Pinion Flange
Puller 8992 (Fig. 22).
(7) Remove pinion shaft seal with a pry tool or
slide hammer mounted screw.
INSTALLATION
(1) Installnewpinion seal with Installer 8896 and
Handle C-4171 (Fig. 23).
(2) Apply a light coat of teflon sealant to the pin-
ion flange splines.
(3) Lightly tap the pinion flange onto the pinion
until a few threads are showing.
(4) Install flange washer andnewpinion nut.
(5) Hold flange with Flange Wrench 8979 (Fig. 24)
and tighten pinion nut until pinion end play is taken
up.
Fig. 19 HUB NUT SOCKET
1 - SOCKET
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 20 PINION ROTATING TORQUE
1 - PINION FLANGE
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 21 FLANGE WRENCH
1 - PINION FLANGE
2 - FLANGE WRENCH
Fig. 22 PINION FLANGE PULLER
1 - PINION FLANGE
2 - PULLER
DRREAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA 3 - 113
AXLE BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 187 of 2895

(6) Rotate pinion several times to seat bearings.
(7) Measure pinion rotating torque with an inch
pound torque wrench and compare it to recorded
measurement.
(8) Tighten pinion nut in small increments, until
pinion rotating torque is 0.40-0.57 N´m (3-5 in. lbs.)
greater than recorded measurement.
(9) Rotate pinion several times then verify pinion
rotating torque again.
(10) Install axle shafts.
(11) Install propeller shaft with reference marks
aligned.
(12) Check and fill differential if necessary.
DIFFERENTIAL
DESCRIPTION
The differential case is a one-piece design. The dif-
ferential pinion shaft is retained with a snap ring.
Differential bearing preload and ring gear backlash
is adjusted by the use of adjusters. The adjuster are
between the differential bearings and the differential
housing. Pinion bearing preload is set and main-
tained by the use of a collapsible spacer. The
stamped steel cover provides a means for inspection
and servicing the differential.
OPERATION
During straight-ahead driving, the differential pin-
ion gears do not rotate on the pinion mate shaft. This
occurs because input torque applied to the gears is
divided and distributed equally between the two side
gears. As a result, the pinion gears revolve with the
pinion mate shaft but do not rotate around it (Fig.
25).
When turning corners, the outside wheel must
travel a greater distance than the inside wheel to
complete a turn. To accomplish this, the differential
allows the axle shafts to turn at unequal speeds (Fig.
26). In this instance, the input torque applied to the
pinion gears is not divided equally. The pinion gears
now rotate around the pinion mate shaft in opposite
directions. This allows the side gear and axle shaft
attached to the outside wheel to rotate at a faster
speed.
Fig. 23 PINION SEAL INSTALLER
1 - HANDLE
2 - INSTALLER
Fig. 24 FLANGE WRENCH
1 - FLANGE WRENCH
2 - PINION FLANGE
Fig. 25 DIFFERENTIAL-STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING
1 - IN STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING EACH WHEEL ROTATES AT
100% OF CASE SPEED
2 - PINION GEAR
3 - SIDE GEAR
4 - PINION GEARS ROTATE WITH CASE
3 - 114 REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AADR
PINION SEAL (Continued)