2003 DODGE RAM Oss
[x] Cancel search: OssPage 202 of 2895
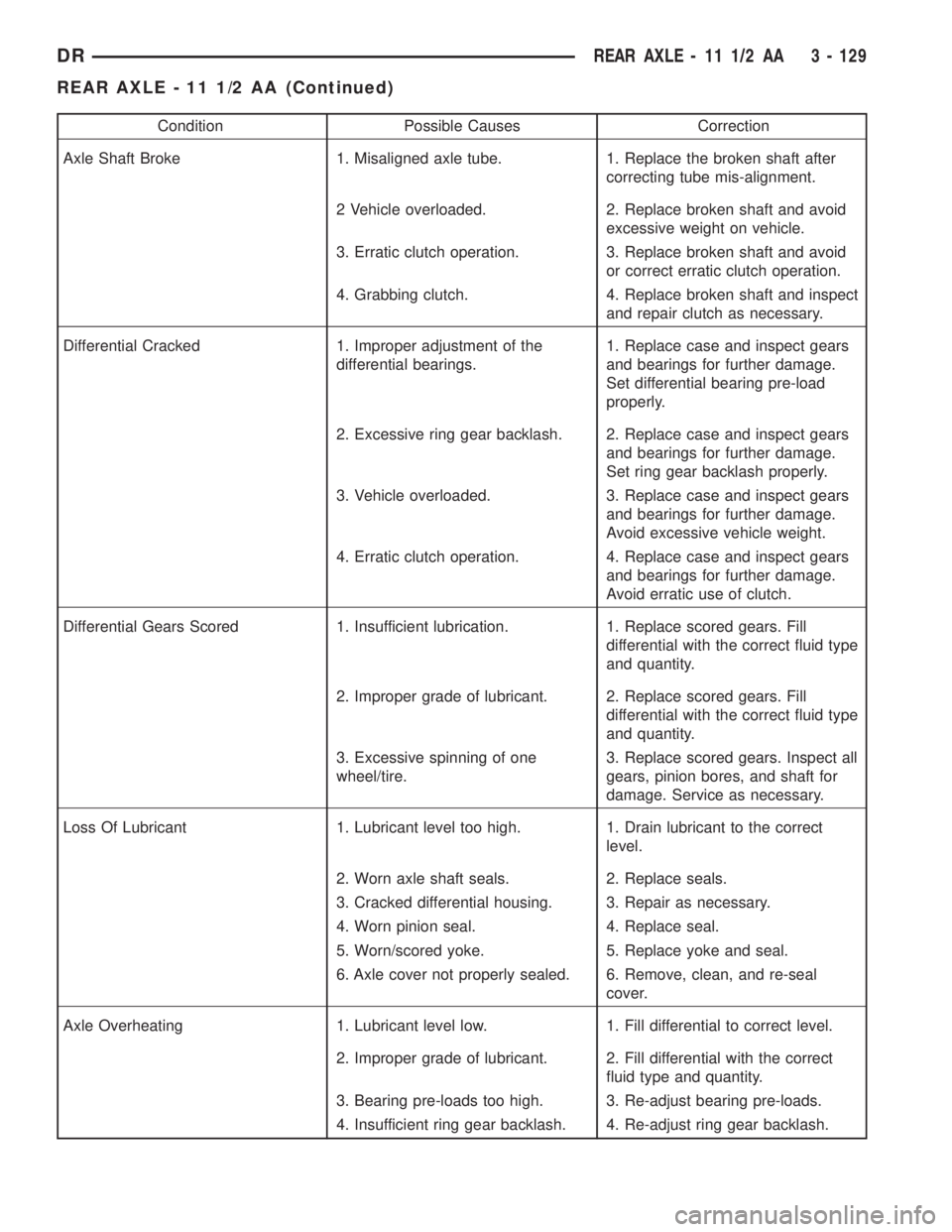
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal
cover.
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
DRREAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AA 3 - 129
REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 203 of 2895

Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern. Adjust backlash or
pinion depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a lifting device under the axle.
(3) Secure axle to device.
(4) Remove wheels and tires assemblies.
(5) Remove RWAL sensor from the differential
housing.
(6) Remove brake hose at the axle junction block
and axle vent hose.
(7) Disconnect parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(8) Remove brake calipers.
(9) Mark propeller shaft and companion flange for
installation alignment reference.
(10) Remove propeller shaft.
(11) Remove shock absorbers from axle.
(12) Remove U-bolets from axle.
(13) Separate the axle from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise axle with lifting device and align to the
leaf spring centering bolts.
(2) Install axle U-bolts and tighten to 149 N´m
(110 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install shock absorbers to axle and tighten to
specification.
(4) Install the RWAL sensor to the differential
housing.
(5) Connect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(6) Connect brake hose to the axle junction block
and axle vent hose.
(7) Align propeller shaft and pinion companion
flange reference marks and tighten companion flange
bolts to 115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install the wheels and tires.
(9) Fill differential to specifications.
3 - 130 REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AADR
REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 204 of 2895

(10) Remove lifting device from axle and lower the
vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim. The shim is located
between the rear pinion bearing and the pinion gear
head.
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 1).
(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 8897 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 1).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 2).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and install the
Cone-nut 6740 hand tight. Then check tool rotating
torque with an inch pound torque wrench. The rotat-
ing torque should be 1.7-2.26 N´m (15-20 in. lbs.).
(Fig. 1).(4) Place Arbor Discs 8289 on Arbor D-115-3 in
position in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 3).
(5) Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs
and snug the bearing cap bolts. Then cross tighten
cap bolts to 281 N´m (207 ft. lbs.).
NOTE: Arbor should rotate freely in the arbor discs.
(6) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(7) Position Scooter Block/Dial Indicator flush on
the pinion height block. Hold scooter block and zero
the dial indicator.
Fig. 1 PINION GEAR DEPTH GAUGE TOOLS
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 2 PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 3 GAUGE TOOLS IN HOUSING
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
DRREAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AA 3 - 131
REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 205 of 2895

(8) Slowly slide the scooter block across the pinion
height block over to the arbor (Fig. 4). Move the
scooter block till dial indicator crests the arbor, then
record the highest reading.
(9) Select a shim equal to the dial indicator read-
ing.
(10) Install the select shim between the rear pin-
ion bearing and the pinion gear head.
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARING PRELOAD AND
GEAR BACKLASH
Backlash is adjusted by moving the adjusters in
and out or both. By moving the adjusters the case/
ring gear will move closer or further away from the
pinion. In most cases this adjustment can be used to
achieve the correct gear tooth pattern and set the
case bearing preload.
(1) Remove adjuster lock bolts and adjuster locks
(Fig. 5).
(2) Loosen the differential bearing caps.
(3) Slide differential case toward the pinion gear
until the gears make contact/zero backlash. If zero
backlash cannot be obtained, turn the pinion side
adjuster until zero backlash is obtained.
(4) Holding the differential case toward the pinion
gear, turn bearing adjusters with Spanner Wrench
8883 (Fig. 6) until they make contact with the differ-
ential bearings/cups.
(5) Back off the ring gear side adjuster 4 holes, to
obtain initial ring gear backlash.
(6) Install ring gear side adjuster lock and bolt. Do
not tighten adjuster lock bolt at this time.
(7) Tighten pinion gear side adjuster firmly
against the differential case bearing cup.
(8) Rotate the pinion several times to seat the def-
erential bearings.(9) Loosen pinion gear side adjuster until it is no
longer in contact with the bearing cup, then tighten
it until it makes contact.
(10) Tighten pinion gear side adjuster an addi-
tional:
²New Bearings:6 Adjuster Holes
²Original Bearings:4 Adjuster Holes
(11) Install pinion gear side adjuster lock and bolt.
Do not tighten adjuster lock bolt at this time.
Fig. 4 PINION GEAR DEPTH MEASUREMENT
1 - ARBOR
2 - SCOOTER BLOCK
3 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 5 ADJUSTER LOCK BOLT
1 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
2 - ADJUSTER LOCK
3 - ADJUSTER LOCK BOLT
4 - BEARING CAP BOLT
Fig. 6 ADJUSTER SPANNER WRENCH
1 - WRENCH
2 - DIFFERENTIAL
3 - 132 REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AADR
REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 247 of 2895

cuit separation in the event of a front or rear brake
malfunction. The reservoir compartments will retain
enough fluid to operate the functioning hydraulic cir-
cuit.
Care must be exercised when removing/installing
the master cylinder connecting lines. The threads in
the cylinder fluid ports can be damaged if care is not
exercised. Start all brake line fittings by hand to
avoid cross threading.
The cylinder reservoir can be replaced when neces-
sary. However, the aluminum body section of the
master cylinder is not a repairable component.
NOTE: If diagnosis indicates that an internal mal-
function has occurred, the aluminum body section
must be replaced as an assembly.
OPERATION
The master cylinder bore contains a primary and
secondary piston. The primary piston supplies
hydraulic pressure to the front brakes. The secondary
piston supplies hydraulic pressure to the rear brakes.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MASTER
CYLINDER/POWER BOOSTER
(1) Start engine and check booster vacuum hose
connections. A hissing noise indicates vacuum leak.
Correct any vacuum leak before proceeding.
(2) Stop engine and shift transmission into Neu-
tral.
(3) Pump brake pedal until all vacuum reserve in
booster is depleted.
(4) Press and hold brake pedal under light foot
pressure. The pedal should hold firm, if the pedal
falls away master cylinder is faulty (internal leak-
age).
(5) Start engine and note pedal action. It should
fall away slightly under light foot pressure then hold
firm. If no pedal action is discernible, power booster,
vacuum supply, or vacuum check valve is faulty. Pro-
ceed to the POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST.
(6) If the POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST
passes, rebuild booster vacuum reserve as follows:
Release brake pedal. Increase engine speed to 1500
rpm, close the throttle and immediately turn off igni-
tion to stop engine.
(7) Wait a minimum of 90 seconds and try brake
action again. Booster should provide two or more vac-
uum assisted pedal applications. If vacuum assist is
not provided, booster is faulty.
POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST
(1) Connect vacuum gauge to booster check valve
with short length of hose and T-fitting (Fig. 36).(2) Start and run engine at curb idle speed for one
minute.
(3) Observe the vacuum supply. If vacuum supply
is not adequate, repair vacuum supply.
(4) Clamp hose shut between vacuum source and
check valve.
(5) Stop engine and observe vacuum gauge.
(6) If vacuum drops more than one inch HG (33
millibars) within 15 seconds, booster diaphragm or
check valve is faulty.
POWER BOOSTER CHECK VALVE TEST
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose from check valve.
(2) Remove check valve and valve seal from
booster.
(3) Use a hand operated vacuum pump for test.
(4) Apply 15-20 inches vacuum at large end of
check valve (Fig. 37).
(5) Vacuum should hold steady. If gauge on pump
indicates vacuum loss, check valve is faulty and
should be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MASTER CYLINDER
BLEEDING
A new master cylinder should be bled before instal-
lation on the vehicle. Required bleeding tools include
bleed tubes and a wood dowel to stroke the pistons.
Bleed tubes can be fabricated from brake line.
Fig. 36 Typical Booster Vacuum Test Connections
1 - TEE FITTING
2 - SHORT CONNECTING HOSE
3 - CHECK VALVE
4 - CHECK VALVE HOSE
5 - CLAMP TOOL
6 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
7 - VACUUM GAUGE
5 - 20 BRAKES - BASEDR
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 253 of 2895

HISSING
A hissing noise may be noticed when above normal
brake pedal pressure is applied, 40 lbs. or above. The
noise will be more noticeable if the vehicle is not
moving. The noise will increase with the brake pedal
pressure and an increase of system operating temper-
ature.
CLUNK-CHATTER-CLICKING
A clunk-chatter-clicking may be noticed when the
brake pedal is released quickly, after above normal
brake pedal pressure is applied 50-100 lbs..
BOOSTER FUNCTION TEST
With the engine off depress the brake pedal several
times to discharge the accumulator. Then depress the
brake pedal using 40 lbs. of force and start the
engine. The brake pedal should fall and then push
back against your foot. This indicates the booster is
operating properly.
ACCUMULATOR LEAKDOWN
(1) Start the engine, apply the brakes and turn the
steering wheel from lock to lock. This will ensure the
accumulator is charged. Turn off the engine and let
the vehicle sit for one hour. After one hour there
should be at least two power assisted brake applica-
tion with the engine off. If the system does not retain
a charge the booster must be replaced.
(2) With the engine off depress the brake pedal
several times to discharge the accumulator. Grasp
the accumulator and see if it wobbles or turns. If it
does the accumulator has lost a gas charge and the
booster must be replaced.
SEAL LEAKAGE
If the booster leaks from any of the seals the
booster assembly must be replaced (Fig. 48).²INPUT ROD SEAL:Fluid leakage from rear
end of the booster.
²PISTON SEAL:Fluid leakage from vent at
front of booster.
²HOUSING SEAL:Fluid leakage between hous-
ing and housing cover.
²SPOOL VALVE SEAL:Fluid leakage near
spool plug.
²RETURN PORT FITTING SEAL:Fluid leak-
age from port fitting.
HYDRAULIC BOOSTER DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Slow Brake Pedal Return 1. Excessive seal friction in booster. 1. Replace booster.
2. Faulty spool valve action. 2. Replace booster.
3. Restriction in booster return hose. 3. Replace hose.
4. Damaged input rod. 4. Replace booster.
Excessive Brake Pedal
Effort.1. Internal or external seal leakage. 1. Replace booster.
2. Faulty steering pump. 2. Replace pump.
Fig. 48 Hydraulic Booster Seals
1 - PUMP
2 - GEAR
3 - INPUT SEAL
4 - HOUSING SEAL
5 - ACCUMULATOR SEAL
6 - PISTON SEAL
7 - SPOOL PLUG SEAL
8 - RETURN
5 - 26 BRAKES - BASEDR
HYDRO-BOOST BRAKE BOOSTER (Continued)
Page 254 of 2895

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Brakes Self Apply 1. Dump valve faulty. 1. Replace booster.
2. Contamination in hydraulic
system.2. Flush hydraulic system and replace
booster.
3. Restriction in booster return hose. 3. Replace hose.
Booster Chatter, Pedal
Vibration1. Slipping pump belt. 1. Replace power steering belt.
2. Low pump fluid level. 2. Fill pump and check for leaks.
Grabbing Brakes 1. Low pump flow. 1. Test and repair/replace pump.
2. Faulty spool valve action. 2. Replace booster.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BLEEDING
The hydraulic booster is generally self-bleeding,
this procedure will normally bleed the air from the
booster. Normal driving and operation of the unit will
remove any remaining trapped air.
(1) Fill power steering pump reservoir.
(2) Disconnect fuel shutdown relay and crank the
engine for several seconds, Refer to Fuel System for
relay location and WARNING.
(3) Check fluid level and add if necessary.
(4) Connect fuel shutdown relay and start the
engine.
(5) Turn the steering wheel slowly from lock to
lock twice.
(6) Stop the engine and discharge the accumulator
by depressing the brake pedal 5 times.
(7) Start the engine and turn the steering wheel
slowly from lock to lock twice.
(8) Turn off the engine and check fluid level and
add if necessary.
NOTE: If fluid foaming occurs, wait for foam to dis-
sipate and repeat steps 7 and 8.
REMOVAL
NOTE: If the booster is being replaced because the
power steering fluid is contaminated, flush the
power steering system before replacing the booster.
(1) With engine off depress the brake pedal 5
times to discharge the accumulator.
(2) Remove brake lines from master cylinder.
(3) Remove mounting nuts from the master cylin-
der.
(4) Remove the bracket from the hydraulic booster
lines and master cylinder mounting studs.
(5) Remove the master cylinder.
(6) Remove the return hose and the two pressure
lines from the hydraulic booster (Fig. 49).(7) Remove the booster push rod clip, washer and
rod remove from the brake pedal.
(8) Remove the mounting nuts from the hydraulic
booster and remove the booster.INSTALLATION
(1) Install the hydraulic booster and tighten the
mounting nuts to 28 N´m (21 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install the booster push rod, washer and clip
onto the brake pedal.
(3) Install the master cylinder on the mounting
studs. and tighten the mounting nuts to 23 N´m (17
ft. lbs.).
(4) Install the brake lines to the master cylinder
and tighten to 19-200 N´m (170-200 in. lbs.).
(5) Install the hydraulic booster line bracket onto
the master cylinder mounting studs.
(6) Install the master cylinder mounting nuts and
tighten to 23 N´m (17 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 49 HYDRO-BOOST UNIT
1 - INLET HOSE
2 - HYDRO-BOOST UNIT
3 - MASTER CYLINDER UNIT
4 - RETURN HOSE
5 - OUTLET HOSE
DRBRAKES - BASE 5 - 27
HYDRO-BOOST BRAKE BOOSTER (Continued)
Page 260 of 2895

(6) Install the right cable to the front cable.
(7) Adjust the brake cable at the equalizer and
using the adjuster nut.
INSTALLATION - LEFT REAR CABLE
(1) Install the brake cable to the brake lever (Fig.
61).
(2) Install the brake cable to the frame bracket.
(3) Install the left brake cable to the equalizer.
(4) Adjust the brake cable at the equalizer and
adjuster nut.
SHOES
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Remove the disc brake caliper,(Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the disc brake rotor, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
REMOVAL).
(5) Lockout the parking brake cable (Fig. 63).
(6) Disengage the park brake cable from behind
the rotor assembly to allow easier disassembly of the
park brake shoes (Fig. 64).
(7) Remove the axleshaft (Fig. 65) (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/REAR AXLE - 9 1/4/
AXLE SHAFTS - REMOVAL).
(8) Disassemble the rear park brake shoes (Fig.
56).
CLEANING - REAR DRUM IN HAT BRAKE
Clean the individual brake components, including
the support plate exterior, with a water dampened
cloth or with brake cleaner. Do not use any other
cleaning agents. Remove light rust and scale from
the brake shoe contact pads on the support plate
with fine sandpaper.
INSPECTION - REAR DRUM IN HAT BRAKE
As a general rule, riveted brake shoes should be
replaced when worn to within 0.78 mm (1/32 in.) of
the rivet heads. Bonded lining should be replaced
when worn to a thickness of 1.6 mm (1/16 in.).
Examine the lining contact pattern to determine if
the shoes are bent or the drum is tapered. The lining
should exhibit contact across its entire width. Shoes
exhibiting contact only on one side should be
Fig. 62 PARKING BRAKE CABLE
1 - SUPPORT PLAT
2 - CABLE
3 - LEVER
Fig. 63 LOCK OUT PARKING CABLE
1 - LOCKING PLIERS
2 - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
Fig. 64 DISENGAGEMENT OF CABLE
1 - LEVER
2 - CABLE END
DRBRAKES - BASE 5 - 33
CABLES (Continued)