Page 445 of 1184
2C – 2 FRONT SUSPENSION
DAEWOO M-150 BL2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FRONT SUSPENSION
The front suspension for this vehicle is a combination
knuckle/strut and spring design.
The control arms pivot from the body. The lower control
arm pivots use rubber bushing. The upper end of the
strut is isolated by a rubber mount and contains a bear-
ing to allow the wheel to turn.
The lower end of the steering knuckle pivots on a ball
joint bolted to the control arm. The ball joint is fastened
to the steering knuckle with a bolt.When servicing the control arm-to-body attachment and
the stabilizer shaft-to-body insulators, make sure the at-
taching bolts are loose until the control arms are moved
to the trim height, which is curb height. Trim height is the
normal position to which the control arms move when
the vehicle is sitting on the ground. Refer to “General
Specifications” in this section.
Page 454 of 1184
FRONT SUSPENSION 2C–11
DAEWOO M-150 BL2
D16B515A
Installation Procedure
1. Install in the reverse order of removal.
Important: When installing the mountings, position the
opened mountings forward.
D16B516A
40–50 N�m2. Install the stabilizer shaft to the vehicle.
�Install the castellated nut.
Tighten
Tighten the stabilizer shaft–to–body castellated nut to
40–50 N�m (30–36 lb-ft).
�Install the cotter pin.
D16B517C
3. Install the front under longitudinal frame.
�Install the stabilizer shaft mounting bolts (1).
Tighten
Tighten the mounting bolts to 30–50 N�m (22–36 lb-
ft).
D16B518B
65 – 80 N�m
10 – 14 N�m�Install the front under longitudinal frame bolt (2).
Tighten
Tighten to bolt to 10–14 N�m (89–124 lb-in).
�Install the front under longitudinal frame nut (3).
Tighten
Tighten to nut to 65–80 N�m (48–59 lb-ft).
Page 492 of 1184
TIRES AND WHEELS 2E–9
DAEWOO M-150 BL2
Another method is to dismount the tire and rotate it
180 degrees on the rim. Do this only on the tire and
wheel assemblies which are known to be causing a
vibration because this method is just as likely to cause
good assemblies to vibrate.
TIRE AND WHEEL
MATCH-MOUNTING
The tires and wheels are match-mounted at the assem-
bly plant. Match-mounting aligns the radially stiffest part
of the tire, or high spot, to the smallest radius, or low
spot, of the wheel.
The high spot of the tire is originally marked by a red
paint mark or an adhesive label on the outboard side-
wall.
The low spot of the wheel will be at the location of the
valve stem.
Before dismounting a tire from its wheel, scribe a line on
the tire at the valve stem to assure that it is remounted in
the same position.
Replacement tires that are of original equipment quality
will have their high and low spot marked in the same
manner.
Page 508 of 1184
4A – 2 HYDRAULIC BRAKES
DAEWOO M-150 BL2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
WARNING LAMP OPERATION
This brake system uses a BRAKE warning lamp located
in the instrument panel cluster. When the ignition switch
is in the III position, the BRAKE warning lamp should il-
luminate. It should go off when the ignition switch return
to II position. The following conditions will activate the
BRAKE warning lamp.
�The lamp should be on whenever the parking brake
applied and the ignition switch is in the II position.
�A low fluid level in the master cylinder will turn the
BRAKE warning lamp on.
D17A007A
Page 511 of 1184

HYDRAULIC BRAKES 4A–5
DAEWOO M-150 BL2
WARNING LAMP OPERATION
This brake system uses a BRAKE warning lamp located
in the instrument panel cluster. When the ignition switch
is in the III position, the BRAKE warning lamp should
glow and then go OFF when the ignition switch returns
to the II position.The following conditions will activate the BRAKE lamp:
�Parking brake applied. The light should be on when-
ever the parking brake is applied and the ignition
switch is II.
�Low fluid level. A low fluid level in the master cylinder
will turn the BRAKE lamp ON.
BRAKE SYSTEM FAULT
���������� ����������Condition������������� �������������Probable cause�������������� ��������������Correction
Brake Warning Lamp ON�Brake fluid leaks.�Repair the leaks or add th fluid.
�Parking brake switch shorted to
ground.�Repair the short ground.
�Faulty the fluid level sensor.�Replace the sensor.
Stoplamp ON�Faulty the stoplamp switch.�Replace the stoplamp switch.
�Push rod length is short.�Adjust the push rod length of the
power booster.
�Stoplamp switch circuit shorted to
battery.�Repair or Replace the wiring harness.
Poor Braking�Brake fluid lacks or leaks.�Repair the leaks or add the fluid.
�Brake fluid contamination.�Replace the fluid.
�Air in the brake system.�Bleed the brake system.
�Damaged brake lines.�Replace the brake lines.
�Damaged vacuum hose or faulty
check valve.�Replace the vacuum hose or check
value.
Dragging Brake�No free play at the brake pedal.�Adjust the free play.
�Weakened the brake pedal return
spring.�Replace the return spring.
�Faulty master cylinder.�Replace the master cylinder.
�Air in the brake system.�Bleed the brake system.
Pedal Over Stroke�Brake fluid lacks or leaks.�Repair the leaks or add the fluid.
�Poor adjustment of the brake pedal
free play.�Adjust the push rod length of the
power booster.
Page 531 of 1184
4C – 2 POWER BOOSTER
DAEWOO M-150 BL2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
POWER BOOSTER
This booster is a single diaphragm, vacuum-suspended
unit. In a normal operating mode, with the service brakes
in the release position, a vacuum-suspended booster
operates with a vacuum on both sides of its diaphragm.
When the brakes are applied, air at atmospheric pres-
sure is admitted to one side of the diaphragm to pro-vide the power assist. When the brakes are released, at-
mospheric air is shut off from that side of the diaphragm.
The air is then drawn from the booster through the vacu-
um check valve by the vacuum source.
Important: If any hydraulic component is removed or
disconnected, it may be necessary to bleed all or part of
the brake system.
Page 532 of 1184
POWER BOOSTER 4C–3
DAEWOO M-150 BL2
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURES
POWER BOOSTER FUNCTIONAL
CHECK
1. With the engine stopped, eliminate the vacuum in the
booster by pumping the brake pedal several times.
2. Push the pedal down and hold it in this position.
3. Start the engine.
4. The booster is OK if the pedal drops further because
of extra force produced.
If the brake pedal does not drop, the vacuum system
(vacuum hoses, check valve, etc.) is probably defective
and should be checked.
If no defect is revealed by checking the vacuum system,
the defect is in the booster itself.
CHECK VALVE FUNCTIONAL CHECK
1. Remove the vacuum hose.
2. Suck the vacuum hose to power booster. And also,
suck the vacuum hose to engine.
3. If the air pass through the check valve or not, replace
the check valve. And if the vacuum hose to engine isonly sucked, the check valve OK.
D17A301B
Page 539 of 1184
4D – 2 FRONT DISC BRAKES
DAEWOO M-150 BL2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
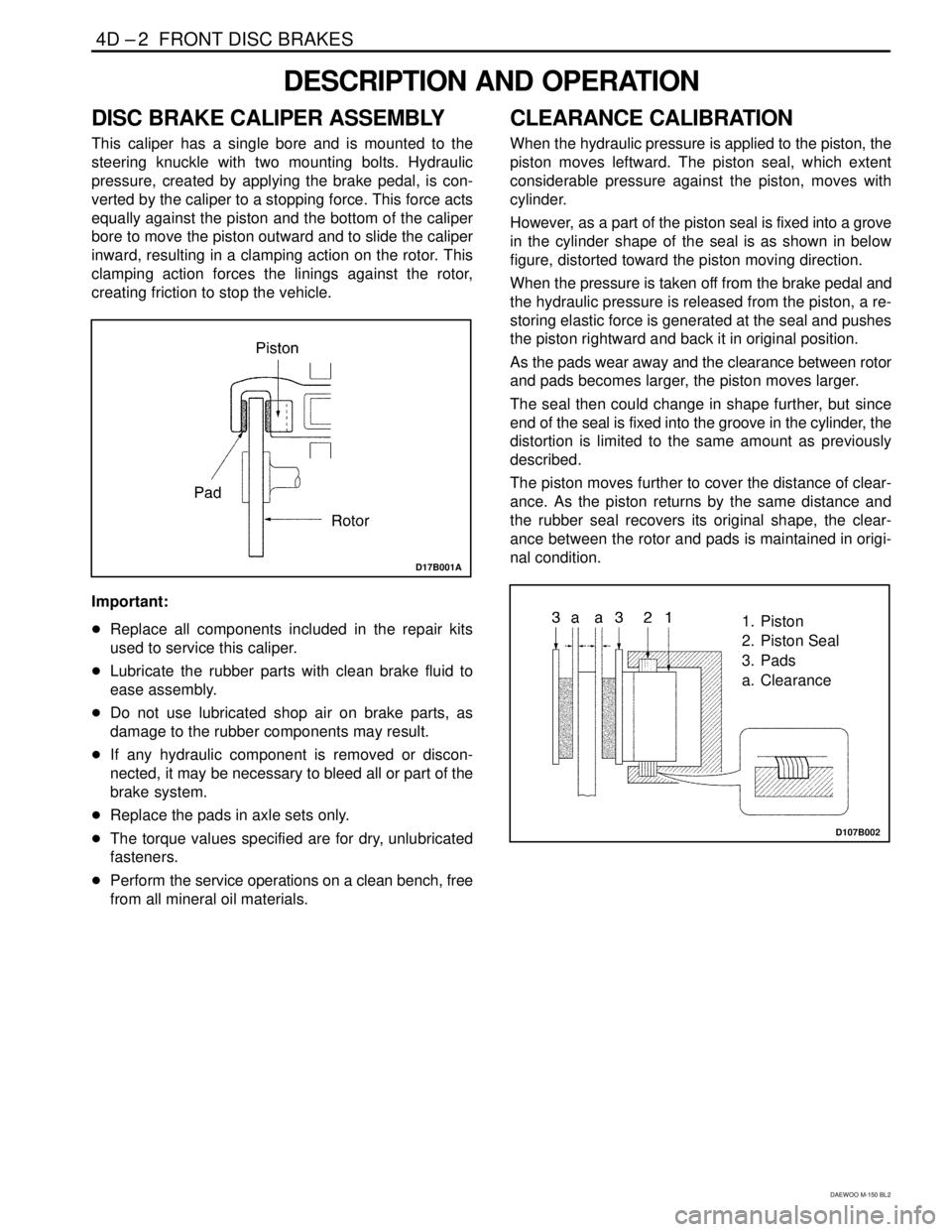
DISC BRAKE CALIPER ASSEMBLY
This caliper has a single bore and is mounted to the
steering knuckle with two mounting bolts. Hydraulic
pressure, created by applying the brake pedal, is con-
verted by the caliper to a stopping force. This force acts
equally against the piston and the bottom of the caliper
bore to move the piston outward and to slide the caliper
inward, resulting in a clamping action on the rotor. This
clamping action forces the linings against the rotor,
creating friction to stop the vehicle.
D17B001A
Important:
�Replace all components included in the repair kits
used to service this caliper.
�Lubricate the rubber parts with clean brake fluid to
ease assembly.
�Do not use lubricated shop air on brake parts, as
damage to the rubber components may result.
�If any hydraulic component is removed or discon-
nected, it may be necessary to bleed all or part of the
brake system.
�Replace the pads in axle sets only.
�The torque values specified are for dry, unlubricated
fasteners.
�Perform the service operations on a clean bench, free
from all mineral oil materials.
CLEARANCE CALIBRATION
When the hydraulic pressure is applied to the piston, the
piston moves leftward. The piston seal, which extent
considerable pressure against the piston, moves with
cylinder.
However, as a part of the piston seal is fixed into a grove
in the cylinder shape of the seal is as shown in below
figure, distorted toward the piston moving direction.
When the pressure is taken off from the brake pedal and
the hydraulic pressure is released from the piston, a re-
storing elastic force is generated at the seal and pushes
the piston rightward and back it in original position.
As the pads wear away and the clearance between rotor
and pads becomes larger, the piston moves larger.
The seal then could change in shape further, but since
end of the seal is fixed into the groove in the cylinder, the
distortion is limited to the same amount as previously
described.
The piston moves further to cover the distance of clear-
ance. As the piston returns by the same distance and
the rubber seal recovers its original shape, the clear-
ance between the rotor and pads is maintained in origi-
nal condition.
1. Piston
2. Piston Seal
3. Pads
a. Clearance
D107B002