2002 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY ECU
[x] Cancel search: ECUPage 961 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
60-22 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Failure modes
Failures where the vehicle can still be driven safely are indicated by the ACE warning lamp illuminating continuously
with an amber colour. The amber warning lamp will remain illuminated until the ignition is turned off. For all faults the
warning lamp will only illuminate again if the fault is still present. Failures which require the driver to stop the vehicle
immediately are indicated by the ACE warning lamp flashing with a red colour and an audible warning. All faults are
recorded by the ACE ECU and can be retrieved with diagnostic equipment.
The following tables show the type of system failures and their effects on the system operation. Torsion bar 'floppy'
means that fluid is allowed to circulate freely through the system. With no pressure in the actuators the torsion bar will
have no effect on vehicle roll. 'Locked bars' means that all pump flow is directed through the valve block and returns
to the reservoir. Both DCV's close and fluid is trapped in the actuators but can flow from one actuator to the other via
the valve block. In this condition the torsion bar will perform similar to a conventional anti-roll bar, resisting roll but still
allowing the axles to articulate.
Acceleration sensors
Pressure transducer
14 Reverse switch Input
15 Accelerometer - lower (signal) Input
16 Pressure transducer (signal) Input
17 Accelerometer - upper (signal) Input
18 Accelerometer - upper (supply) Output
19 Engine speed Input
20 Main earth 1 -
21 Pressure transducer (earth) Input
22 DCV 2 (earth) Input
23 DCV 1 (earth) Input
24 DCV 1 & 2 (supply) Output
25 Pressure control valve (earth) Input
26 Not used -
27 Pressure control valve (supply) Output
28 Main supply (+ V Batt) Input
29 to 31 Not used -
32 Main earth 2 -
33 Accelerometer - lower (signal) Input
34 Accelerometer - upper (signal) Input
35 Not used -
36 Warning lamp Output
Failure Effect
Valve stuck closed No ACE control
Short circuit - Ground No ACE control
Short circuit - VBatt No ACE control
Loose sensor Erractic ACE activity when driving in straight line
Failure Effect
Short circuit - VBatt Large sensor dead band - possible random movementsPin No. Description Input/Output
Page 962 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-23
Road speed signal
Engine speed signal
Reverse gear signal
Ignition ON signal
Pressure control valve failure
Failure Effect
Open circuit No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - Ground No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - VBatt No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Failure Effect
Open circuit No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - Ground No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - VBatt No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Failure Effect
Open circuit No reverse signal to ECU. ACE active in reverse, may give
abnormal handling when reversing
Short circuit - Ground No reverse signal to ECU. ACE active in reverse, may give
abnormal handling when reversing
Short circuit - VBatt Permanent reverse signal to ECU. Permanent 'Locked
bars' condition
Failure Effect
Open circuit ECU does not receive ignition ON signal. No ARC control,
'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - Ground ECU does not receive ignition ON signal. No ARC control,
'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - VBatt Permanent ignition ON signal to ECU. Possibility of flat
battery
Failure Effect
Open circuit No ACE control
Short circuit - Ground No ACE control
Short circuit - VBatt No ACE control
Valve stuck open No ACE control
Valve stuck closed Maximum system pressure - no proportional control.
Pressure relief valve operating at 185 bar (2683 lbf.in
2)
Page 964 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-25
Operation
Hydraulic circuit diagram
1Pressure transducer
2Directional control valve 2
3Front torsion bar assembly
4Actuator
5Actuator
6Rear torsion bar assembly
7Directional control valve 18Valve block
9Pressure control valve
10Reservoir
11Filter
12High pressure filter
13Hydraulic pump
14Attenuator hose
Vehicle not moving
When the engine is running and the vehicle is not moving, both DCV's are closed, locking fluid in each side of the
actuator pistons. The hydraulic pump draws fluid from the reservoir and passes it at very low pressure to the valve
block. Because both DCV's are closed, after the fluid passes through the high pressure filter, it is directed through the
pressure control valve to the reservoir. The pressure control valve is open fully to allow the full flow to pass to the
reservoir. The DCV's will remain closed until the ECU detects a need to operate.
Page 965 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
60-26 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Vehicle moving and turning left
When the vehicle is turning left, the accelerometers detect the cornering forces applied and transmit signals to the
ECU. The ECU determines that an opposing force must be applied to the torsion bars to counter the cornering forces.
The ECU supplies a current to the solenoid of the DCV2. Simultaneously, a current is sent from the ECU to the
pressure control valve which operates to restrict the flow of fluid returning to the reservoir.
The restriction causes the hydraulic pressure in the system to rise and the pressure is sensed by the pressure
transducer which sends a signal to the ECU. The ECU determines from the inputs it receives what pressure is required
and adjusts the pressure control valve accordingly.
The pressure in the system is applied to the annulus of each actuator, applying an opposing force to the torsion bar
and minimising the cornering effect on the vehicle and maintaining the vehicle attitude. The fluid displaced from the
full area of the actuator is returned to the reservoir via the valve block.
As the cornering force is removed when the vehicle straightens up, the ECU opens the pressure control valve to
reduce the pressure in the system. The fluid bleeds from the actuator back into the system as the cornering force is
reduced, removing the force from the torsion bar. When the vehicle is moving in a straight line DCV 2 closes.
Vehicle moving and turning right
When the vehicle is turning right, the accelerometers detect the cornering forces applied and transmit signals to the
ECU. The ECU determines that an opposing force must be applied to the torsion bars to counter the cornering forces.
The ECU supplies a current to the solenoid of the DCV1. Simultaneously, a current is sent from the ECU to the
pressure control valve which operates to restrict the flow of fluid through the by-pass gallery.
The restriction causes the hydraulic pressure in the system to rise and the pressure is sensed by the pressure
transducer which sends a signal corresponding to the pressure to the ECU. The ECU determines from the inputs it
receives what pressure is required and adjusts the pressure control valve accordingly.
The pressure in the system is applied to the full area of each actuator, applying an opposing force to the torsion bar
and minimising the cornering effect on the vehicle and maintaining the vehicle attitude. The fluid displaced from the
annulus of the actuator is returned to the reservoir via the valve block.
As the cornering force is removed when the vehicle straightens up, the ECU opens the pressure control valve to
reduce the pressure in the system. The fluid bleeds from the actuator back into the system as the cornering force is
reduced, removing the force from the torsion bar. When the vehicle is moving in a straight line the DCV 1 closes.
Vehicle moving in a straight line
The ECU is constantly monitoring the signals received from the accelerometers and operates the DCV's and pressure
control valve to maintain the vehicle attitude when the vehicle is moving.
Off-road driving
Off-road detection is achieved by the ECU by monitoring the signals from the upper and lower accelerometers for
varying degrees of body movement. Off-road driving generates differing signals to the accelerometers which in turn
produce differing outputs due to their vertical separation and the location of the roll centre of the vehicle. The two
signals are passed through a filter to remove any offset caused by the vehicle leaning or the terrain. The ECU then
uses this signal to calculate the percentage of road roughness.
Below 25 mph (40 km/h) the percentage of road roughness calculated is used by the ECU to limit the operation of the
ACE system. The system is completely inoperative at speeds below 2 mph (3 km/h). At speeds above 25 mph (40
km/h) the system disables the percentage road roughness signal and full ACE system assistance is restored.
Side slope detection
The ECU uses side slope detection when the upper and lower accelerometers detect an average acceleration of more
than
± 0.2 g and a road speed of less than 25 mph (40 km/h).
When side slope is detected both DCV's close to provide a 'locked bars' condition. This condition increases stability
and gives a consistent vehicle response. As the road speed increases up to 25 mph (40 km/h), the level of average
lateral acceleration must also increase and be maintained for the system to recognise that the vehicle is on a side
slope. If the side slope angle is steep and the road speed is low, the ECU will detect the side slope in a short time.
Page 968 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
REPAIRS 60-29
REPAIRS
Bushes - Panhard rod
$% 60.10.07
Remove
1.Raise front of vehicle.
WARNING: Do not work on or under a
vehicle supported only by a jack. Always
support the vehicle on safety stands.
2.Remove 2 nuts and bolts securing Panhard rod
to axle and chassis.
3.Remove Panhard rod from vehicle.
4.Use tool LRT-60-013 fitted with LRT-60-013/1
and LRT-60-013/3 to press out bushes from
Panhard rod. Refit
1.Clean bush locations in Panhard rod.
2.Use tool LRT-60-013 fitted with LRT-60-013/1
and LRT-60–013/2 to press new bushes into
Panhard rod. Ensure pressure is applied to
the outer edge of the bush, not the rubber
inner.
3.Position Panhard rod to axle and chassis.
4.Fit bolts securing Panhard rod but do not
tighten at this stage.
5.Remove stand(s) and lower vehicle.
6.Tighten bolts securing Panhard rod to 230 Nm
(170 lbf.ft).
CAUTION: Nuts and bolts must be tightened
with weight of vehicle on suspension.
Page 969 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
60-30 REPAIRS
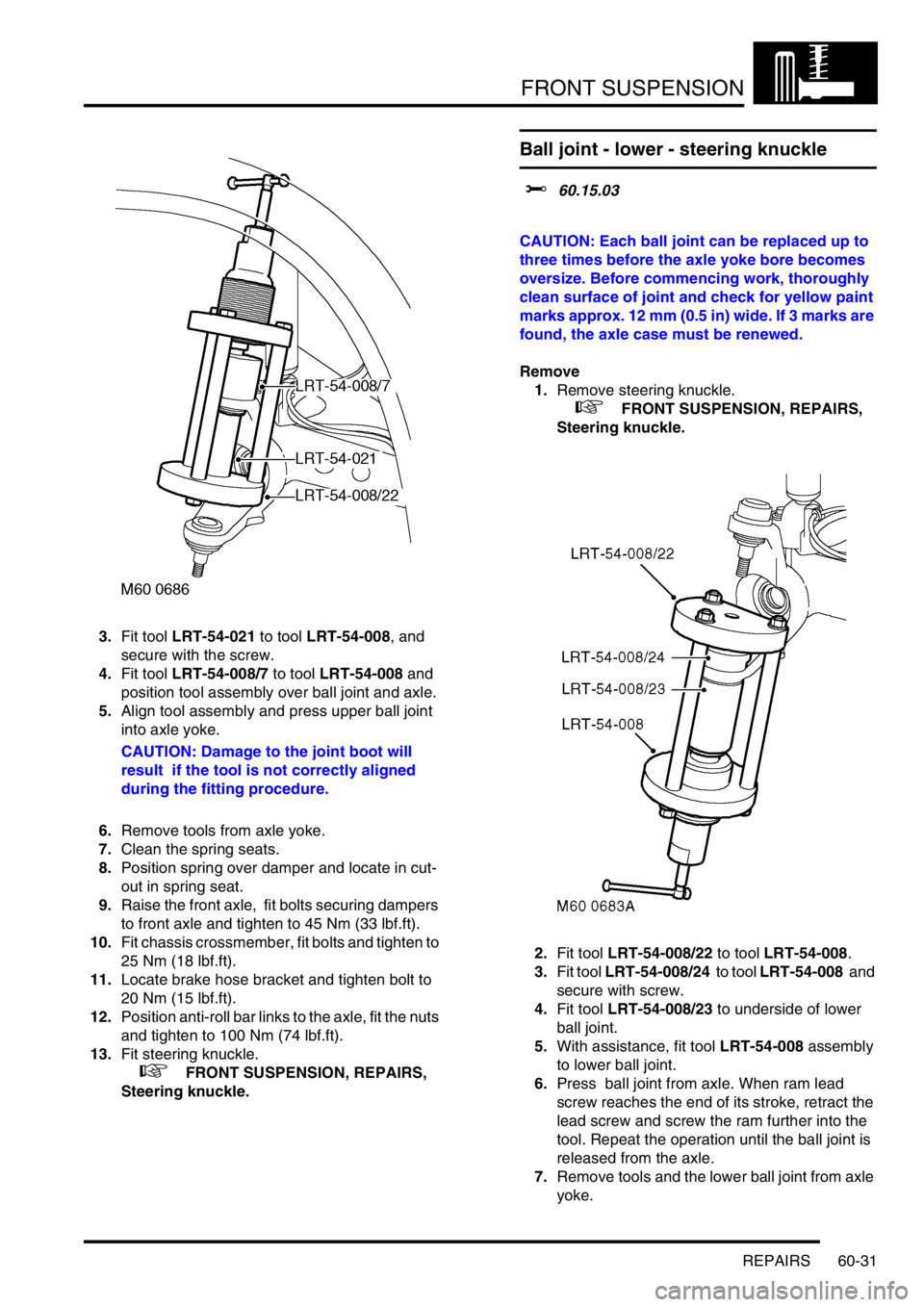
Ball joint - upper - steering knuckle
$% 60.15.02
CAUTION: Each ball joint can be replaced up to
three times before the axle yoke bore becomes
oversize. Before commencing work, thoroughly
clean surface of joint and check for yellow paint
marks approx. 12 mm (0.5 in) wide. If 3 marks are
found, the axle case must be renewed.
Remove
1.Remove steering knuckle.
+ FRONT SUSPENSION, REPAIRS,
Steering knuckle.
2.Support the chassis on stands.
3.Support the front axle on stands.
4.Remove 2 nuts securing anti-roll bar lower links
to front axle, use a 16 mm spanner to prevent
link joint from turning.
5.Remove 2 bolts securing each front damper to
axle.
6.Remove 8 bolts securing chassis crossmember
and remove crossmember.
7.Remove bolt securing brake hose and ABS
sensor harness bracket to axle.
8.Lower the front axle, release front spring from
damper and remove front spring.9.Fit tool LRT-54-008/22 to tool LRT-54-008.
10.Fit tool LRT-54-008/4 to tool LRT-54-008, and
secure with screw.
11.Fit tool LRT-54-008 with all attachments to
upper ball joint..
12.Fit tool LRT-54-008/5 to the top of the ball
joint.
13.Press upper ball joint from axle. When ram lead
screw reaches the end of its stroke, retract the
lead screw and screw the ram further into the
tool. Repeat the operation until the ball joint is
released from the axle.
14.Dismantle the tools.
Refit
1.Clean upper ball joint location and surrounding
area of axle yoke.
2.Apply a 12 mm (0.5 in) wide yellow paint stripe
on axle yoke, adjacent to upper ball joint
location.
Page 970 of 1672
FRONT SUSPENSION
REPAIRS 60-31
3.Fit tool LRT-54-021 to tool LRT-54-008, and
secure with the screw.
4.Fit tool LRT-54-008/7 to tool LRT-54-008 and
position tool assembly over ball joint and axle.
5.Align tool assembly and press upper ball joint
into axle yoke.
CAUTION: Damage to the joint boot will
result if the tool is not correctly aligned
during the fitting procedure.
6.Remove tools from axle yoke.
7.Clean the spring seats.
8.Position spring over damper and locate in cut-
out in spring seat.
9.Raise the front axle, fit bolts securing dampers
to front axle and tighten to 45 Nm (33 lbf.ft).
10.Fit chassis crossmember, fit bolts and tighten to
25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
11.Locate brake hose bracket and tighten bolt to
20 Nm (15 lbf.ft).
12.Position anti-roll bar links to the axle, fit the nuts
and tighten to 100 Nm (74 lbf.ft).
13.Fit steering knuckle.
+ FRONT SUSPENSION, REPAIRS,
Steering knuckle.
Ball joint - lower - steering knuckle
$% 60.15.03
CAUTION: Each ball joint can be replaced up to
three times before the axle yoke bore becomes
oversize. Before commencing work, thoroughly
clean surface of joint and check for yellow paint
marks approx. 12 mm (0.5 in) wide. If 3 marks are
found, the axle case must be renewed.
Remove
1.Remove steering knuckle.
+ FRONT SUSPENSION, REPAIRS,
Steering knuckle.
2.Fit tool LRT-54-008/22 to tool LRT-54-008.
3.Fit tool LRT-54-008/24 to tool LRT-54-008 and
secure with screw.
4.Fit tool LRT-54-008/23 to underside of lower
ball joint.
5.With assistance, fit tool LRT-54-008 assembly
to lower ball joint.
6.Press ball joint from axle. When ram lead
screw reaches the end of its stroke, retract the
lead screw and screw the ram further into the
tool. Repeat the operation until the ball joint is
released from the axle.
7.Remove tools and the lower ball joint from axle
yoke.
Page 971 of 1672
FRONT SUSPENSION
60-32 REPAIRS
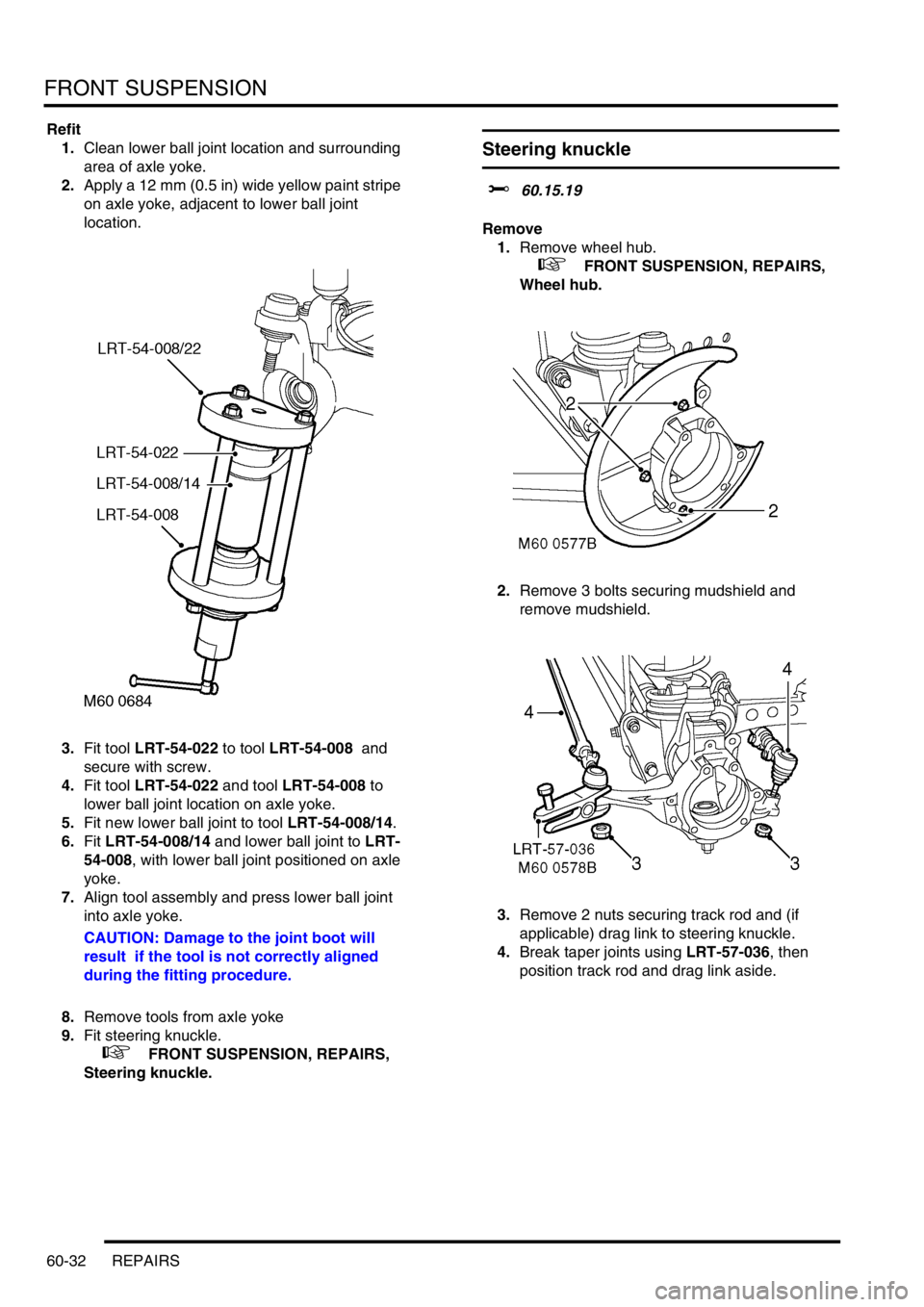
Refit
1.Clean lower ball joint location and surrounding
area of axle yoke.
2.Apply a 12 mm (0.5 in) wide yellow paint stripe
on axle yoke, adjacent to lower ball joint
location.
3.Fit tool LRT-54-022 to tool LRT-54-008 and
secure with screw.
4.Fit tool LRT-54-022 and tool LRT-54-008 to
lower ball joint location on axle yoke.
5.Fit new lower ball joint to tool LRT-54-008/14.
6.Fit LRT-54-008/14 and lower ball joint to LRT-
54-008, with lower ball joint positioned on axle
yoke.
7.Align tool assembly and press lower ball joint
into axle yoke.
CAUTION: Damage to the joint boot will
result if the tool is not correctly aligned
during the fitting procedure.
8.Remove tools from axle yoke
9.Fit steering knuckle.
+ FRONT SUSPENSION, REPAIRS,
Steering knuckle.
Steering knuckle
$% 60.15.19
Remove
1.Remove wheel hub.
+ FRONT SUSPENSION, REPAIRS,
Wheel hub.
2.Remove 3 bolts securing mudshield and
remove mudshield.
3.Remove 2 nuts securing track rod and (if
applicable) drag link to steering knuckle.
4.Break taper joints using LRT-57-036, then
position track rod and drag link aside.