2002 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 942 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-3
1Damper 2 off
2Bolt 2 off
3Turret 2 off
4Nut 8 off
5Nut
6Bolt 4 off
7Nut
8Washer
9Anti-roll bar link RH
10Torsion/Anti-roll bar assembly
11Anti-roll bar link LH
12Washer
13Nut
14Nut
15Mounting rubber 2 off
16Clamp plate 2 off
17Bolt 2 off
18Lower spring seat LH
19Front axle20Nut
21Bush
22Panhard rod
23Bolt
24Radius arm LH
25Bolt
26Bush
27Nut
28Nut
29Bush
30Bolt
31Radius arm RH
32Bolt
33Bush
34Nut
35Lower spring seat RH
36Coil spring 2 off
37Upper spring seat 2 off
Page 943 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
60-4 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
The front suspension comprises two dampers and coil springs, two radius arms, a Panhard rod and an anti-roll bar.
The front axle provides the location points for the dampers, springs, radius arms and the Panhard rod.
The anti-roll bar assembly is an essential part of the front suspension. On vehicles without Active Cornering
Enhancement (ACE) a conventional 'passive' anti-roll bar is fitted. On vehicles fitted with the ACE system, a thicker
diameter anti-roll bar, known as a torsion bar, is used with an actuator at one end.
+ FRONT SUSPENSION, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - ACE.
The hydraulic dampers and coil springs provide springing for each front wheel. The long travel dampers, springs and
radius arms provide maximum axle articulation and wheel travel for off-road driving. The front axle is controlled
longitudinally by two forged steel radius arms and transversely by a Panhard rod.
Radius arms
Each radius arm is manufactured from forged steel. Two bushes are pressed into the forward end of the radius arm.
The forward end of the radius arm is located in a fabricated bracket on the axle and secured through the bushes with
two bolts and nuts. A bush is pressed into the rear of the radius arm which is also located in a fabricated bracket on
each chassis longitudinal and secured through the bush with a bolt and nut.
The radius arms prevent longitudinal movement of the front axle and because of their length allow maximum axle
articulation. The stiffness of the bushes in each radius arm also contributes to the vehicle roll stiffness.
Each radius arm has a notch on its lower edge which provides location for the vehicle jack.
Dampers
Two conventional telescopic dampers are used to control body/axle movement. A turret is located on a bracket welded
to the chassis. The upper spring seat has four studs which pass through holes in the bracket and align with
corresponding holes in the turret. Four nuts are screwed onto the studs and secure the turret and upper spring seat
to the chassis.
A fabricated platform is welded to the axle. The platform has two captive nuts which provide for the attachment of the
damper. A lower spring seat is located on the platform. Each spring seat is handed and has a bracket which secures
the ABS sensor harness and the front brake hose.
Each damper is fitted with a bush at its upper end. The bush locates in the top of the turret and is secured with a cross
bolt. The lower attachment point for the damper is also fitted with a bush. This bush has a spindle through its centre
with a hole at each end. The spindle is seated on the lower spring seat and the axle platform and secured with two
bolts. The coil spring is fitted in a compressed state between the upper and lower spring seats and assists the damper
in controlling the body/axle movement. The upper and lower bushes are replaceable items.
Rubber bump stops are fitted to the chassis above each end of the axle. The bump stops are progressive in their
compression and prevent the axle from contacting the chassis in the event of maximum suspension travel being
reached. The bump stops revert to their original shape once the compression load has been removed from them.
The damper functions by restricting the flow of a hydraulic fluid through internal galleries within the damper body. A
chromium plated rod moves axially within the damper. As the rod moves, its movement is limited by the flow of fluid
through the galleries thus providing damping of undulations in the terrain. The damper rod is sealed at its exit point
from the body to maintain fluid within the unit and prevent the ingress of dirt and moisture. The seal also acts as a
wiper to keep the rod outer diameter clean. A plastic shroud protects the rod and slides over the body as the damper
moves. The coil spring aids the damper to extend after being compressed and also aids the damping process.
Page 944 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-5
Coil springs
Coil springs are fitted to the front axle of the vehicle. The front springs differ between petrol and Diesel variants. Each
spring is retained at its base by the lower spring seat. The top of each spring is located in the upper spring seat
isolator. The upper spring seat is manufactured from natural rubber , with a bonded metal plate and four bonded studs
which provide for the attachment of the damper turret. The rubber isolator reduces noise transmitted to the chassis
and body from the suspension.
The coil springs must be installed correctly. The bottom coil of the spring locates in a recess in the lower spring seat.
The top coil of the spring is ground flat to locate the upper spring seat isolator.
Coil Spring Specifications – Models up to 03 Model Year
The front springs on petrol variants are manufactured from carbon chrome 13.9 mm (0.55 in) diameter bar. The spring
has 7.6 coils and a free length of 377 mm (14.8 in). The petrol front spring is identified by a pink and orange stripe
painted on a number of coils.
The front springs on Diesel variants are manufactured from carbon chrome 13.9 mm (0.55 in) diameter bar. The spring
has 7.6 coils and a free length of 383 mm (15.0 in). The Diesel front spring is identified by a white and purple stripe
painted on a number of coils.
Coil Spring Specifications – Models from 03 Model Year
The introduction of the 03MY vehicle introduced a range of additional spring fitments. These were introduced to cover
the introduction of the 4.6l V8 engine, the fitment of a front mounted winch and to optimise the vehicle trim heights.
The coil springs are manufactured from silicon manganese 13.8 mm or 13.9 mm (0.54 in or 0.55 in) diameter bar. The
following spring data table shows the colour codes, number of coils and spring free length.
Page 945 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
60-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Spring Data
The following table shows spring fitment applicablity.
Spring Fitment Applicability
The following table shows standard springs and uprated springs required when a front winch is fitted.
Winch Fitment Spring Applicability
Panhard rod
A Panhard rod is used to ensure that the axle remains centrally located. The Panhard rod has bushes pressed into
housings at each end which provide for the attachment to the axle and chassis. One end of the Panhard rod locates
in a fabricated bracket on the axle and is secured with a bolt and locknut. The opposite end is attached to a fabricated
bracket on the chassis and is also secured with a bolt and a locknut. The Panhard rod is shaped at one end to allow
clearance for the axle casing.
The attachment bolts for the Panhard rod are coated with a clear, dry wax which reduces friction on the bolt and allows
the correct torque to be applied to the clamping of the bushes. The bolts can be re-used, but if bolt replacement is
necessary the correct bolt with the wax coating must be used.
On models from 03 Model Year, the Panhard rod is shortened by 30 mm (1.18 in). This modification was introduced
to enhance the suspension bump steer characteristics in line with other suspension improvements introduced
simultaneously. The change to the Panhard rod also required the relocation of the attachment brackets on the axle
casing and the chassis.
Colour Code Total No. of Coils Free Length
Red/Purple 7.4 371 mm (14.6 in)
Yellow/Purple 7.4 378.4 mm (14.9 in)
Blue/Purple 7.4 365 mm (14.4 in)
Grey/Purple 7.4 387 mm (15.2 in)
Purple/Purple 7.4 373.8 mm (14.7 in)
Yellow/Orange 7.4 394.6 mm (15.5 in)
Green/Orange 7.4 382.6 mm (15 in)
Pink/Brown 7.6 405.6 mm (15.9 in)
Left Hand Drive Right Hand Drive
RH side LH side RH side LH side
Red/Purple Red/Purple Yellow/Purple Blue/Purple
Yellow/Purple Yellow/Purple Grey/Purple Purple/Purple
Grey/Purple Grey/Purple Yellow/Orange Green/Orange
Standard Spring Winch Fitted Spring
RH Side LH Side Both Sides
Red/Purple Red/Purple Grey/Purple
Yellow/Purple Blue/Purple Yellow/Orange
Yellow/Purple Yellow/Purple Yellow/Orange
Grey/Purple Purple/Purple Green/Orange
Grey/Purple Grey/Purple Green/Orange
Yellow/Orange Green/Orange Pink/Brown
Page 950 of 1672
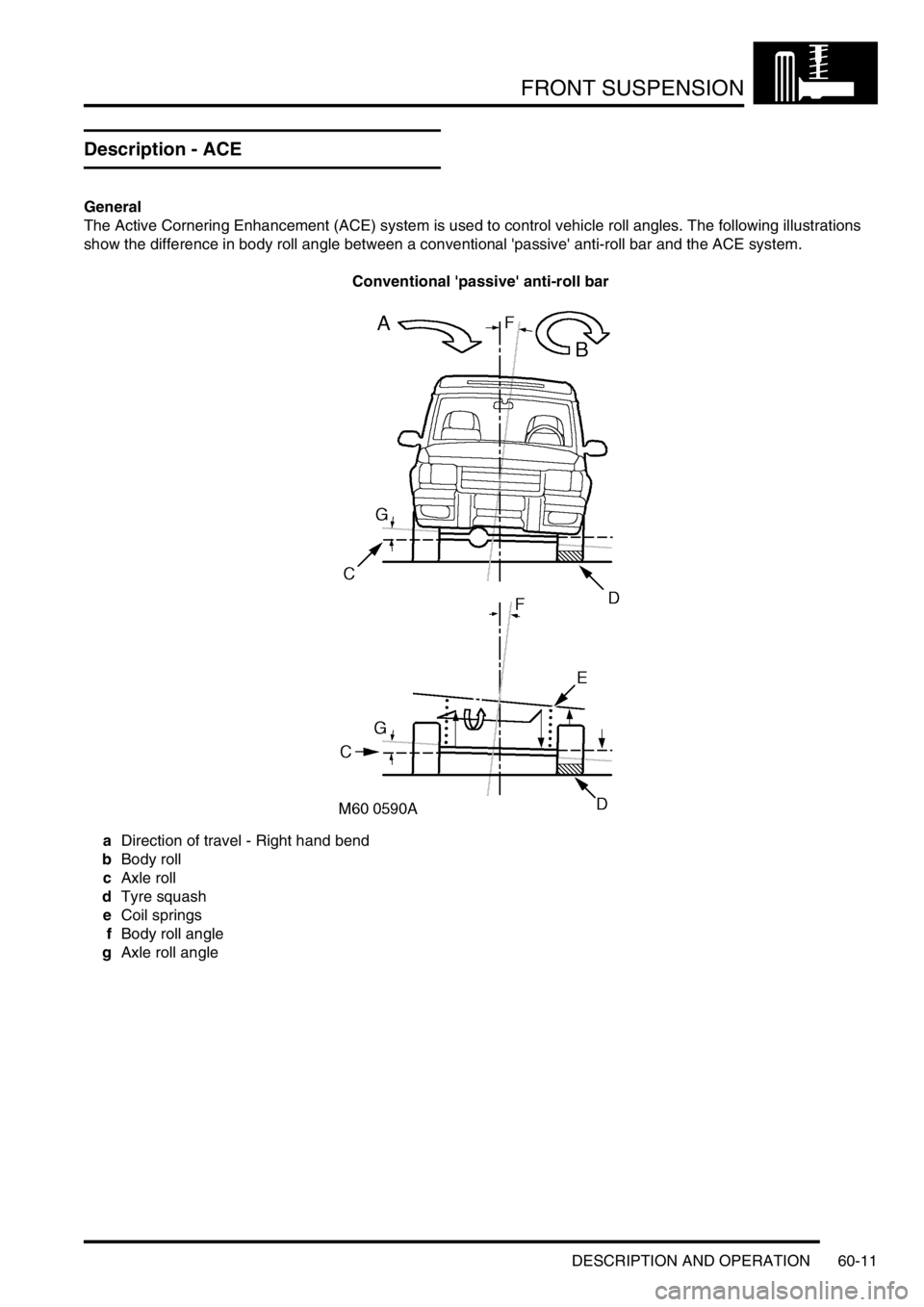
FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-11
Description - ACE
General
The Active Cornering Enhancement (ACE) system is used to control vehicle roll angles. The following illustrations
show the difference in body roll angle between a conventional 'passive' anti-roll bar and the ACE system.
Conventional 'passive' anti-roll bar
aDirection of travel - Right hand bend
bBody roll
cAxle roll
dTyre squash
eCoil springs
fBody roll angle
gAxle roll angle
Page 951 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
60-12 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ACE system
aDirection of travel - Right hand bend
bBody roll
cAxle roll
dTyre squash
eTorsion/Anti-roll bar
fDirection of torsion/anti-roll bar twist
gCoil springs
hBody roll angle
iAxle roll angle
jReduced body roll angle with ACE system
The system is electrically and hydraulically operated with all operations controlled by an ACE ECU located behind the
glovebox in the passenger side footwell. The ACE system comprises front and rear torsion bars and actuators, two
accelerometers, ECU, hydraulic pump, valve block and a fluid reservoir.
The ACE system gives improved vehicle handling and suspension characteristics and is active for both on and off-
road driving. This is achieved by hydraulic actuators applying torque to the front and rear torsion bars in response to
lateral forces sensed by accelerometers. The ACE system prevents body roll with cornering forces of up to 0.4 g. From
0.4 g there is a progressive increase in body roll but significantly lower than a passive system. A passive system will
have a progressive increase in roll angle as soon as cornering forces are applied and will have a higher roll angle than
the ACE system for the same cornering force.
The ACE system can also detect if the vehicle is driven off-road. If off-road conditions are detected the ACE system
operation will be reduced or completely disabled at a speed of 25 mph (40 km/h) or less.
Page 955 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
60-16 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Valve block
1Cap
2'O' ring
3Coil
4'O' ring
5Directional control valve 1 (extend)
6Pressure transducer
7Mounting bush 3 off
8Valve block
9'O' ring
10High pressure filter
11'O' ring
12Cap13Stud 4 off
14Pipe connections
15Cap
16'O' ring
17Coil
18'O' ring
19Pressure control valve
20Directional control valve 2 (retract)
21'O' ring
22Coil
23'O' ring
24Cap
Page 956 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-17
The valve block directs hydraulic pressure to the actuators via solenoid operated directional control valves. A solenoid
operated pressure control valve regulates the required pressure to the actuators. The three valve solenoids are
controlled by signals received from the ACE ECU. A pressure transducer monitors the pressure delivered by the
pump. A replacable high pressure filter is installed into the lower face of the valve block and filters fluid before it
reaches the valves.
The valve block is located on the outside of the right hand chassis longitudinal. The valve block is secured to the
chassis with three bolts and rubber bushes. The rubber bushes isolate the valve block from the chassis, preventing
hydraulic noise from the valve block transmitting through the chassis and body.
The two solenoid operated directional control valves (DCV's) are fitted to ports in the top face of the valve block. The
DCV's are screwed into the valve block and sealed with O ring seals. Each DCV has a solenoid for electrical operation
of the valve. The solenoid is sealed to the DCV with two O ring and secured with a cap. The cap, coil and O rings are
serviceable items. The DCV's are non-serviceable and failure of a DCV requires the replacement of the valve block
assembly.
The pressure control valve is fitted to a port in the rear face of the valve block. The pressure control valve is screwed
into the valve block and sealed with O rings. The pressure control valve has a coil for electrical operation. The coil is
sealed to the pressure control valve with two O rings and secured with a cap. The cap, coil and O rings are serviceable
items. The pressure control valve is non-serviceable and failure requires replacement of the valve block assembly.
The pressure transducer is fitted to a port in the forward face of the valve block. The pressure transducer is screwed
into the valve block and sealed with an O ring seal. The pressure transducer is a serviceable item.
The high pressure filter locates in a port on the lower face of the valve block. The gauze and fibre filter is sealed in
the port with O ring seals. A threaded cap secures the filter in the valve block and is also sealed with an O ring seal.
A threaded hole on the lower face of the filter allows a bolt to be fitted to remove the filter from the port. If a system
component is replaced, the filter must be changed.
Four ports are located on the forward face of the valve block and two ports on the rear. Each port is fitted with a seal
pack which contains two O ring seals and backing rings. The ACE pipes locate and seal in the seal packs and are
secured to the valve block with the studs and nuts located on the forward and rear faces.
Actuators
Two actuators are used for the ACE system and are attached to the front and rear torsion bars. The actuators apply
hydraulically generated force to the torsion bar to oppose lateral forces caused by the vehicle cornering.
Each actuator is a conventional double-acting cylinder. A piston is attached to a rod and moves within the cylinder
when hydraulic pressure is applied. The rod is sealed at the point where it exits the cylinder. The outer end of the rod
is threaded and locates in a bush in the ACE long arm and secured with a nut. A rubber gaiter covers the rod and
prevents dirt and moisture from damaging the rod surface and cylinder seals. The cylinder has a forked attachment
which locates on the short arm bush and secured with a bolt and nut.
Two banjo connections provide for the attachment of the hydraulic hoses from the ACE valve block. The connections
provide hydraulic flow to each side of the piston to extend or retract the rod.