2002 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY CD changer
[x] Cancel search: CD changerPage 27 of 1672

CONTENTS
24 CONTENTS
Electric windows block diagram ...................................................................................................... 86-5-1
Electric windows component layout ................................................................................................ 86-5-2
Description ...................................................................................................................................... 86-5-4
Operation ....................................................................................................................................... 86-5-11
REPAIRS
Switch - rear door ......................................................................................................................... 86-5-13
Switch - console ............................................................................................................................ 86-5-13
Switch - heated rear screen ............................................................................................................ 86-5-14
IN CAR ENTERTAINMENT....................................................................... 86-6-1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ICE System Component layout....................................................................................................... 86-6-1
Base and mid line ICE system control diagram .............................................................................. 86-6-2
High line ICE system control diagram............................................................................................. 86-6-3
Description ...................................................................................................................................... 86-6-4
REPAIRS
Radio cassette player ..................................................................................................................... 86-6-13
Speaker - low/full range - front door ............................................................................................. 86-6-14
Speaker - low range - rear door ..................................................................................................... 86-6-14
Switches - remote control - ICE .................................................................................................... 86-6-15
Amplifier - aerial .............................................................................................................................. 86-6-15
Speaker - mid range - front door ................................................................................................... 86-6-16
Speaker - high range - rear door .................................................................................................. 86-6-16
Amplifier - power ........................................................................................................................... 86-6-17
Speaker - tail door ........................................................................................................................ 86-6-18
CD autochanger ............................................................................................................................ 86-6-18
HARNESSES ............................................................................................ 86-7-1
REPAIRS
Harness - injectors - diesel ............................................................................................................ 86-7-1
Harness - body ............................................................................................................................. 86-7-1
Harness - engine - V8 ..................................................................................................................... 86-7-8
Harness - engine - diesel ................................................................................................................ 86-7-13
Harness - main ............................................................................................................................. 86-7-16
DRIVING AIDS .......................................................................................... 86-8-1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Park Distance Control – Component Location................................................................................ 86-8-1
Park Distance Control – Control Diagram....................................................................................... 86-8-2
Description ...................................................................................................................................... 86-8-4
Operation ........................................................................................................................................ 86-8-10
REPAIRS
Control unit (ECU) - parking aid...................................................................................................... 86-8-13
Sounder - parking aid rear ............................................................................................................. 86-8-14
Sensor - parking aid - rear - inner ................................................................................................... 86-8-15
Sensor - parking aid - rear - outer .................................................................................................. 86-8-16
Page 154 of 1672

ENGINE - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 12-1-15
Oil cooler
1Front oil gallery – full-flow filter to oil cooler
matrix
2Full-flow filter adaptor outlet port to oil cooler
(open at >74
° C)
3Full-flow filter inlet port
4Oil cooler housing
5Full-flow filter outlet port to cylinder block
6Coolant inlet port
7Oil cooler banjo bolt seals (2 off)
8Banjo bolts (2 off)
9Banjo bolt oil holes – to oil cooler matrix
10Rear oil gallery – full-flow filter/oil cooler outlet
to cylinder block11Centre oil gallery – from pump to full-flow filter
12Inlet port to centrifuge filter
13Sealing ring – centrifuge filter housing to oil
cooler housing
14Port – oil cooler matrix
15Oil cooler matrix
16Inlet port from pump via cylinder block to oil
cooler housing
17Outlet port from oil cooler housing to cylinder
block
18Rear view of oil cooler housing
The engine oil cooler assembly is located on the left hand side of the engine block behind the oil centrifuge and oil
filter. The housing is bolted to the engine block by seven bolts. A matrix is included in the oil cooler housing which
acts as a heat exchanger. Coolant flow circulates through the oil cooler housing under pressure from the coolant pump
and distributes the flow evenly around the matrix fins and then along the block into three core holes for cylinder
cooling. Coolant enters the oil cooler through a pipe with a rubber hose extension at the rear side of the engine. The
coolant hose is attached to the stub pipe of the oil cooler by a spring clip.
Oil drawn from the sump by the oil pump passes through the oil cooler via the cylinder block. The flow of coolant
around the exterior surface of the oil cooler matrix cools a proportion of the engine oil flow as it passes through the
oil cooler matrix.
The oil cooler is sealed to the cylinder block by a gasket which must be replaced every time the oil cooler housing is
removed.
Page 426 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-33
The turbocharger is exposed to extremely high operating temperatures (up to 1,000 °C (1832 °F)) because of the hot
exhaust gases and the high speed revolution of the turbine (up to 150,000 rev/min). In order to resist wear of the
turbine bearings a flow of lubrication oil is supplied from the engine lubrication system to keep the bearings cool. Oil
is supplied from a tapping at the front of the full-flow filter adaptor housing via a metal pipe with banjo connections.
Oil is returned to the sump via a metal pipe which connects to the cylinder block at a port below the turbocharger
assembly.
A heatshield is attached to the left hand side of the engine to protect adjacent components from the heat generated
at the turbocharger. The heatshield is attached to the engine by two bolts an additional bolt attaches the heatshield
to the turbocharger casting.
The engine control module controls the amount of boost pressure the engine receives by way of the turbocharger.
When full boost is reached a control signal is sent to the wastegate modulator, and a vacuum is applied to the
wastegate valve. The wastegate valve opens, bypassing some of the exhaust gas away from the turbine to be output
to the exhaust system.
The engine should be allowed to idle for 15 seconds following engine start up and before the engine is switched off
to protect the turbocharger by maintaining oil supply to the turbine bearings.
Intercooler
The intercooler is an air-to-air heat exchanger which lowers the intake air temperature to obtain a higher air density
for better combustion efficiency. The intercooler receives compressed air from the turbocharger via a metal pipe; it
cools the intake air via the intercooler matrix and delivers it to the intake manifold by means of a rubber hose which
connects between the intercooler outlet and the intake manifold outlet. The rubber hose is connected to ports at each
end by metal band clips.
+ COOLING SYSTEM - Td5, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
The intercooler is located at the front of the engine bay, forward of the radiator.
Page 590 of 1672

COOLING SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 26-1-7
Pipes and hoses
The coolant circuit comprises flexible hoses and metal formed pipes which direct the coolant into and out of the
engine, radiator and heater matrix. Plastic pipes are used for the bleed and overflow pipes to the expansion tank.
A bleed screw is installed in the radiator top hose and is used to bleed air during system filling. A drain plug to drain
the heater and cylinder block circuit of coolant is located on the underside of the coolant pump feed pipe.
Oil cooler
The oil cooler is located on the left hand side of the engine block behind the oil centrifuge and oil filter. Oil from the oil
pump is passed through a heat exchanger which is surrounded by coolant in a housing on the side of the engine.
Full water pump flow is directed along the cooler housing which also distributes the flow evenly along the block into
three core holes for cylinder cooling. This cools the engine oil before it is passed into the engine. A small percentage
of the coolant from the oil cooler passes into a metal pipe behind the engine. It then flows into the lower radiator via
a hose.
Fuel cooler
The fuel cooler is located on the right hand side of the engine and is attached to the inlet manifold. The cooler is
cylindrical in design and has a coolant feed connection at its forward end. A 'T' connection at the rear of the cooler
provides a connection for the coolant return from the heater matrix and coolant return from the fuel cooler.
The 'T' connection houses a thermostat which opens at approximately 82
°C. This prevents the cooler operating in
cold climates.
Two quick release couplings on the cooler allow for the connection of the fuel feed from the pressure regulator and
return to the fuel tank. A counter flow system is used within the cooler.
Fuel flows around a coolant jacket within the cooler and flows from the back to the front of the cooler. As the hot fuel
cools travelling slowly forwards it meets progressively colder coolant travelling in the opposite direction maintaining a
differential cooling effect.
EGR Cooler
The EGR Cooler is mounted on the front of the cylinder head. Coolant from the oil cooler flows around the EGR cooler,
cooling the exhaust gas, to improve exhaust emissions, before being returned to the expansion tank.
Coolant pump
1Drive lugs (hidden)
2Housing
3'O' rings4Cover
5Feed hose connection
6Impeller
Page 593 of 1672

COOLING SYSTEM - TD5
26-1-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Operation
Coolant flow - Engine warm up
Refer to illustration.
+ COOLING SYSTEM - Td5, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Cooling system coolant flow.
During warm up the coolant pump moves fluid through the cylinder block and it emerges from the outlet housing. From
the outlet housing, the warm coolant flow is prevented from flowing through the upper and lower radiators because
both thermostats are closed. The coolant is directed into the heater circuit.
Some coolant from the by-pass pipe can pass through small sensing holes in the flow valve. The warm coolant enters
a tube in the thermostat housing and surrounds 90% of the thermostat sensitive area. Cold coolant returning from the
radiator bottom hose conducts through 10% of the thermostat sensitive area. In cold ambient temperatures the engine
temperature can be raised by up to 10
°C (50°F) to compensate for the heat loss of the 10% exposure to the cold
coolant return from the radiator bottom hose.
At engine speeds below 1500 rev/min, the by-pass valve is closed only allowing the small flow through the sensing
holes. As the engine speed increases above 1500 rev/min, the greater flow and pressure from pump overcomes the
light spring and opens the by-pass flow valve. The flow valve opens to meet the engine's cooling needs at higher
engine speeds and prevents excess pressure in the cooling system. With both thermostats closed, maximum flow is
directed through the heater circuit.
The heater matrix acts as a heat exchanger reducing the coolant temperature as it passes through the matrix. Coolant
emerges from the heater matrix and flows to the fuel cooler 'T' connection via the heater return hose. From the fuel
cooler the coolant is directed into the coolant pump feed pipe and recirculated around the heater circuit. In this
condition the cooling system is operating at maximum heater performance.
Coolant flow - Engine hot
As the coolant temperature increases the main thermostat opens. This allows some coolant from the outlet housing
to flow through the top hose and into the radiator to be cooled. The hot coolant flows from the left tank in the radiator,
along the tubes to the right tank. The air flowing through the fins between the tubes cools the coolant as it passes
through the radiator.
A controlled flow of the lower temperature coolant is drawn by the pump and blended with hot coolant from the by-
pass and the heater return pipes in the pump feed pipe. The pump then passes this coolant, via the cylinder block, to
the oil cooler housing, cooling the engine oil before entering the block to cool the cylinders.
When the fuel temperature increases, the heat from the fuel conducts through the fuel cooler 'T' connection and
causes the fuel thermostat to open.
Pre EU3 models: Coolant from the cylinder block flows through the oil cooler and via a pipe and hose enters the
lower radiator. The coolant in the lower radiator is subjected to an additional two passes through the lower radiator to
further reduce the coolant temperature. From the lower radiator the coolant flows , via a hose, to the fuel cooler.
As the hot fuel cools, travelling slowly forwards through the cooler, it meets the progressively colder coolant travelling
in the opposite direction from the lower radiator.
EU3 models: Coolant from the cylinder block flows through the oil cooler to the EGR cooler and then back to the
expansion tank. and via a pipe and hose enters the lower radiator. The lower temperature coolant from the oil cooler
housing is subjected to an additional two passes through the lower radiator to further reduce the coolant temperature.
From the lower radiator the coolant flows , via a hose, to the fuel cooler.
As the hot fuel cools, travelling slowly forwards through the cooler, it meets the progressively colder coolant travelling
in the opposite direction from the lower radiator.
Page 611 of 1672

COOLING SYSTEM - V8
26-2-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Operation
Coolant flow - Engine warm up
Refer to illustration.
+ COOLING SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Cooling system coolant flow.
During warm-up the coolant pump moves fluid through the cylinder block and it emerges from the inlet manifold outlet
pipe. From the outlet pipe, the warm coolant flow is prevented from flowing through the radiator because the
thermostat is closed. The coolant is directed into the heater circuit.
Some coolant from the by-pass pipe can pass through small sensing holes in the flow valve. The warm coolant enters
a tube in the thermostat housing and surrounds 90% of the thermostat sensitive area. Cold coolant returning from the
radiator bottom hose conducts through 10% of the thermostat sensitive area. In cold ambient temperatures the engine
temperature can be raised by up to 10
°C (50°F) to compensate for the heat loss of the 10% exposure to the cold
coolant returning from the radiator bottom hose.
At engine idle speed, the by-pass valve is closed only allowing the small flow through the sensing holes. As the engine
speed increases above idle, the greater flow and pressure from the pump overcomes the light spring and opens the
by-pass flow valve. The flow valve opens to meet the engines cooling needs at higher engine speeds and prevents
excess pressure in the system. With the thermostat closed, maximum flow is directed through the heater circuit.
The heater matrix acts as a heat exchanger reducing coolant temperature as it passes through the matrix. Coolant
emerges from the matrix and flows into the coolant pump feed pipe and recirculated around the heater circuit. In this
condition the cooling system is operating at maximum heater performance.
Coolant flow - Engine hot
As the coolant temperature increases the thermostat opens. This allows some coolant from the outlet housing to flow
through the top hose and into the radiator to be cooled. The hot coolant flows from the left tank in the radiator, along
the tubes to the right tank. The air flowing through the fins between the tubes cools the coolant as it passes through
the radiator.
A controlled flow of the lower temperature coolant is drawn by the pump and blended with hot coolant from the by-
pass and the heater return pipes in the pump feed pipe. The pump then passes this coolant into the cylinder block to
cool the cylinders.
Page 1170 of 1672
INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS
REPAIRS 76-3-17
9.Fit drinks tray.
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Drink tray assembly - centre
fascia.
10.Fit and secure radio DIN socket.
11.Fit screw cover to radio aperture.
12.Fit radio cassette player.
+ IN CAR ENTERTAINMENT,
REPAIRS, Radio cassette player.
Carpet - front
$% 76.49.02
Remove
1. Models with premium ICE: Remove power
amplifier.
+ IN CAR ENTERTAINMENT,
REPAIRS, Amplifier - power.
2. Models with premium ICE: Remove CD
autochanger.
+ IN CAR ENTERTAINMENT,
REPAIRS, CD autochanger.
3.Remove centre console.
lFor models with manual gearbox:
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Console - centre - manual
models.
lFor models with automatic gearbox:
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Console - centre - automatic
models.
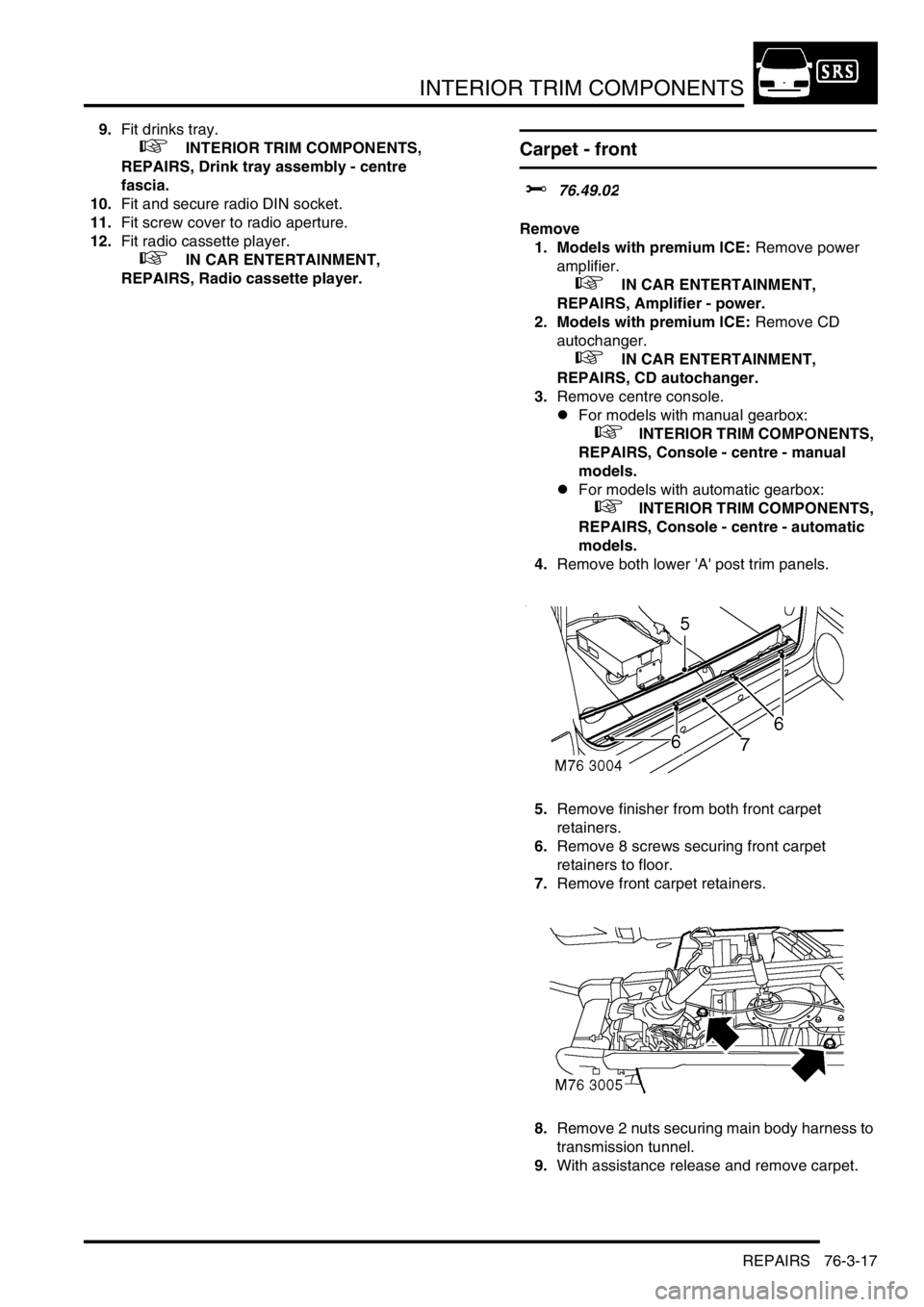
4.Remove both lower 'A' post trim panels.
5.Remove finisher from both front carpet
retainers.
6.Remove 8 screws securing front carpet
retainers to floor.
7.Remove front carpet retainers.
8.Remove 2 nuts securing main body harness to
transmission tunnel.
9.With assistance release and remove carpet.
Page 1171 of 1672
INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS
76-3-18 REPAIRS
Refit
1.With assistance position carpet.
2.Secure main body harness to transmission
tunnel with nuts.
3.Position front carpet retainers and secure to
floor with screws.
4.Fit finishers to front carpet retainers
5.Fit both lower 'A' post trim panels.
6.Fit centre console.
lFor models with manual gearbox:
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Console - centre - manual
models.
lFor models with automatic gearbox:
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Console - centre - automatic
models.
7. Models with premium ICE: Fit CD
autochanger.
+ IN CAR ENTERTAINMENT,
REPAIRS, CD autochanger.
8. Models with premium ICE: Fit power
amplifier.
+ IN CAR ENTERTAINMENT,
REPAIRS, Amplifier - power.
Carpet - rear
$% 76.49.03
Remove
1. Models with premium ICE: Remove power
amplifier.
+ IN CAR ENTERTAINMENT,
REPAIRS, Amplifier - power.
2.Remove RH front seat.
+ SEATS, REPAIRS, Seat - front.
3.Remove both 'B' post lower trim panels.
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Trim casing - lower - 'B' post.
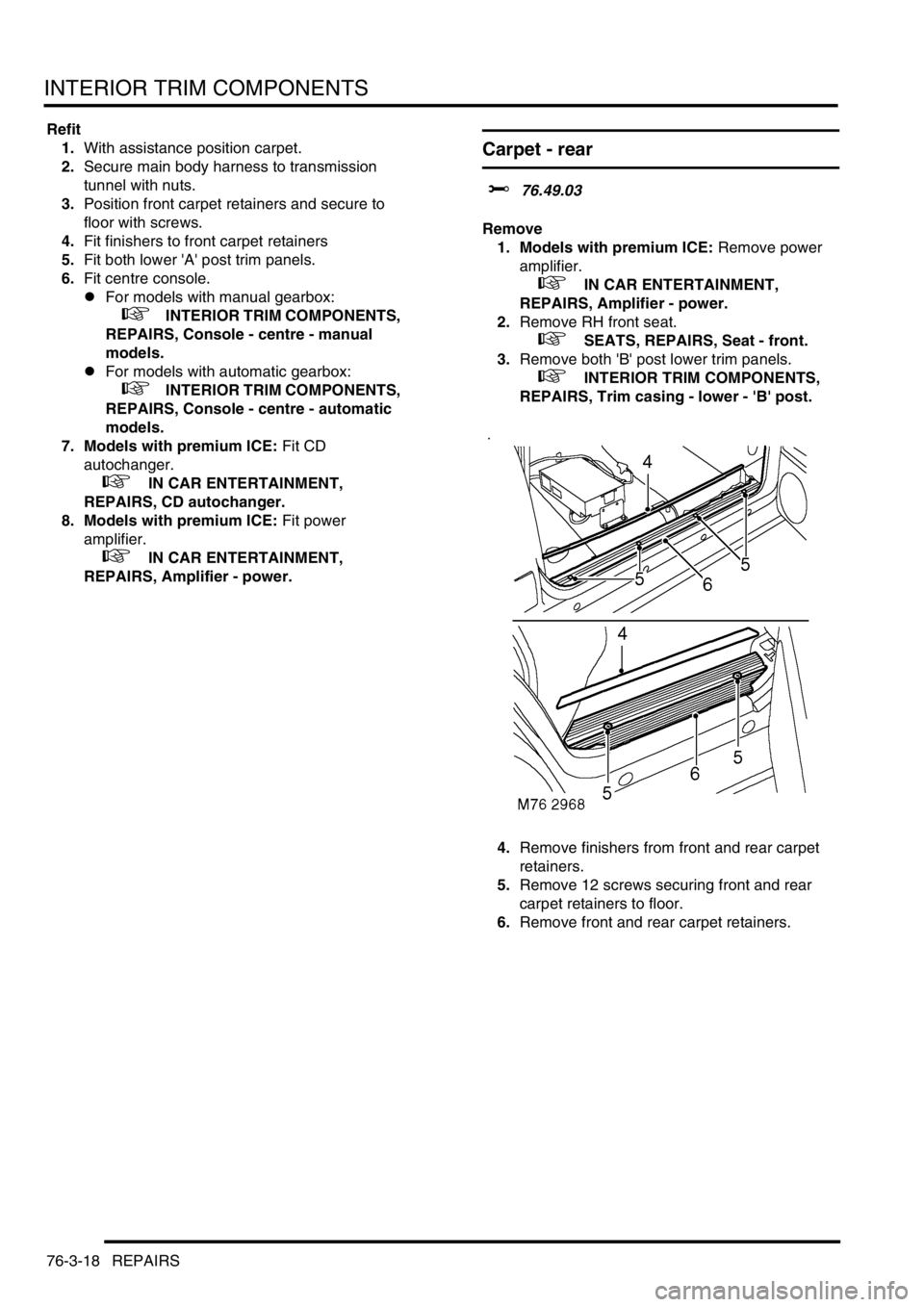
4.Remove finishers from front and rear carpet
retainers.
5.Remove 12 screws securing front and rear
carpet retainers to floor.
6.Remove front and rear carpet retainers.