2002 DODGE RAM oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 1770 of 2255
Studs, Oil Pump Pilot - C-3288-B
Gauge, Pressure - C-3292
Gauge, Pressure - C-3293SP
Set, Dial Indicator - C-3339
Compressor, Spring - C-3422-B
Puller, Slide Hammer - C-3752
Gauge, Throttle Setting - C-3763
Installer, Seal - C-3860-A
Remover, Seal - C-3985-B
Installer, Overdrive Piston Seal - 8114
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 317
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE (Continued)
Page 1771 of 2255
Installer, Seal - C-3995-A
Handle, Universal - C-4171
Remover/Installer, Bushing - C-4470
Dial Caliper - C-4962
Set, Bushing Remover/Installer - C-3887-J
Nut, Bushing Remover - SP-1191, From kit C-3887-J
Remover, Front Clutch Bushing - SP-3629, From kit
C-3887-J
Cup, Bushing Remover - SP-3633, From kit C-3887-J
Installer, Oil Pump Bushing - SP-5118, From kit
C-3887-J
21 - 318 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE (Continued)
Page 1773 of 2255

OPERATION
Both the accumulator and the 3-4 accumulator
function the same. Line pressure is directed to the
small end of the piston when the transmission is
placed into a DRIVE position (Fig. 62), bottoming it
against the accumulator plate. When the 1-2 upshift
occurs (Fig. 63), line pressure is directed to the large
end of the piston and then to the kickdown servo. As
the line pressure reaches the accumulator, the com-
bination of spring pressure and line pressure forces
the piston away from the accumulator plate. This
causes a balanced pressure situation, which results
in a cushioned band application. After the kickdown
servo has become immovable, line pressure will fin-
ish pushing the accumulator up into its bore. When
the large end of the accumulator piston is seated in
its bore, the band or clutch is fully applied.
NOTE: The accumulator is shown in the inverted
position for illustrative purposes.
INSPECTION
Inspect the accumulator piston and seal rings (Fig.
64). Replace the seal rings if worn or cut. Replace the
piston if chipped or cracked.
Check condition of the accumulator inner and
outer springs (Fig. 64). Replace the springs if the
coils are cracked, distorted or collapsed.
BANDS
DESCRIPTION
KICKDOWN (FRONT) BAND
The kickdown, or ªfrontº, band (Fig. 65) holds the
common sun gear of the planetary gear sets. The
front (kickdown) band is made of steel, and faced on
its inner circumference with a friction-type lining.
One end of the band is anchored to the transmission
Fig. 62 Accumulator in DRIVE - FIRST Gear Position
1 - LINE PRESSURE
Fig. 63 Accumulator in SECOND Gear Position
1 - BOTTOM OF BORE
2 - LINE PRESSURE
3 - SHUTTLE VALVE
Fig. 64 Accumulator Components
1 - INNER SPRING
2 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
3 - OUTER SPRING
4 - SEAL RINGS
21 - 320 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
ACCUMULATOR (Continued)
Page 1775 of 2255
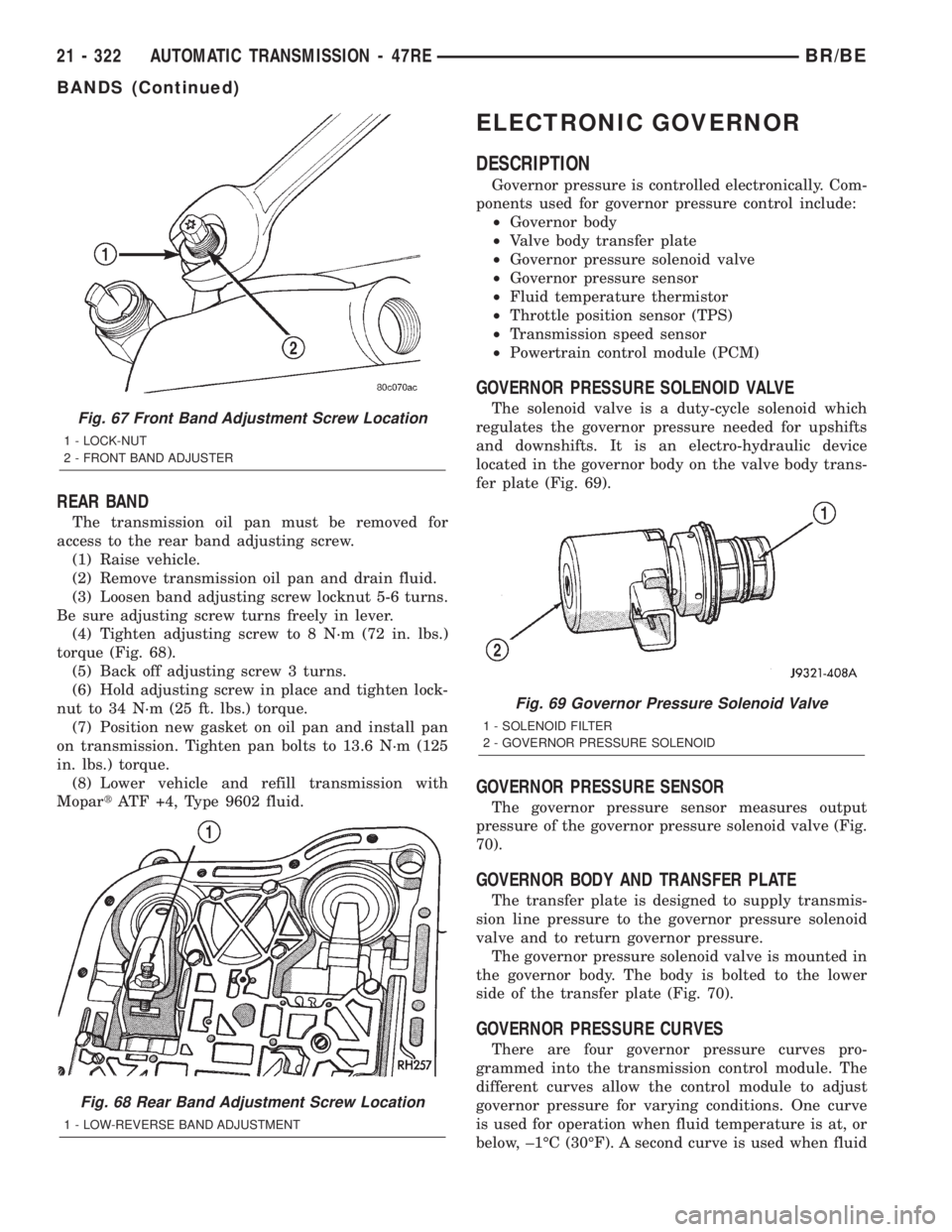
REAR BAND
The transmission oil pan must be removed for
access to the rear band adjusting screw.
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Remove transmission oil pan and drain fluid.
(3) Loosen band adjusting screw locknut 5-6 turns.
Be sure adjusting screw turns freely in lever.
(4) Tighten adjusting screw to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.)
torque (Fig. 68).
(5) Back off adjusting screw 3 turns.
(6) Hold adjusting screw in place and tighten lock-
nut to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Position new gasket on oil pan and install pan
on transmission. Tighten pan bolts to 13.6 N´m (125
in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Lower vehicle and refill transmission with
MopartATF +4, Type 9602 fluid.
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR
DESCRIPTION
Governor pressure is controlled electronically. Com-
ponents used for governor pressure control include:
²Governor body
²Valve body transfer plate
²Governor pressure solenoid valve
²Governor pressure sensor
²Fluid temperature thermistor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Transmission speed sensor
²Powertrain control module (PCM)
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The solenoid valve is a duty-cycle solenoid which
regulates the governor pressure needed for upshifts
and downshifts. It is an electro-hydraulic device
located in the governor body on the valve body trans-
fer plate (Fig. 69).
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The governor pressure sensor measures output
pressure of the governor pressure solenoid valve (Fig.
70).
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate is designed to supply transmis-
sion line pressure to the governor pressure solenoid
valve and to return governor pressure.
The governor pressure solenoid valve is mounted in
the governor body. The body is bolted to the lower
side of the transfer plate (Fig. 70).
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
There are four governor pressure curves pro-
grammed into the transmission control module. The
different curves allow the control module to adjust
governor pressure for varying conditions. One curve
is used for operation when fluid temperature is at, or
below, ±1ÉC (30ÉF). A second curve is used when fluid
Fig. 67 Front Band Adjustment Screw Location
1 - LOCK-NUT
2 - FRONT BAND ADJUSTER
Fig. 68 Rear Band Adjustment Screw Location
1 - LOW-REVERSE BAND ADJUSTMENT
Fig. 69 Governor Pressure Solenoid Valve
1 - SOLENOID FILTER
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID
21 - 322 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
BANDS (Continued)
Page 1776 of 2255

temperature is at, or above, 10ÉC (50ÉF) during nor-
mal city or highway driving. A third curve is used
during wide-open throttle operation. The fourth curve
is used when driving with the transfer case in low
range.
OPERATION
Compensation is required for performance varia-
tions of two of the input devices. Though the slope of
the transfer functions is tightly controlled, offset may
vary due to various environmental factors or manu-
facturing tolerances.
The pressure transducer is affected by barometric
pressure as well as temperature. Calibration of the
zero pressure offset is required to compensate for
shifting output due to these factors.
Normal calibration will be performed when sump
temperature is above 50 degrees F, or in the absence
of sump temperature data, after the first 10 minutes
of vehicle operation. Calibration of the pressure
transducer offset occurs each time the output shaft
speed falls below 200 RPM. Calibration shall be
repeated each 3 seconds the output shaft speed is
below 200 RPM. A 0.5 second pulse of 95% duty cycle
is applied to the governor pressure solenoid valve
and the transducer output is read during this pulse.
Averaging of the transducer signal is necessary to
reject electrical noise.
Under cold conditions (below 50 degrees F sump),
the governor pressure solenoid valve response may
be too slow to guarantee 0 psi during the 0.5 second
calibration pulse. Calibration pulses are continued
during this period, however the transducer output
valves are discarded. Transducer offset must be read
at key-on, under conditions which promote a stable
reading. This value is retained and becomes the off-
set during the9cold9period of operation.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The inlet side of the solenoid valve is exposed to
normal transmission line pressure. The outlet side of
the valve leads to the valve body governor circuit.
The solenoid valve regulates line pressure to pro-
duce governor pressure. The average current sup-
plied to the solenoid controls governor pressure. One
amp current produces zero kPa/psi governor pres-
sure. Zero amps sets the maximum governor pres-
sure.
The powertrain control module (PCM) turns on the
trans control relay which supplies electrical power to
the solenoid valve. Operating voltage is 12 volts
(DC). The PCM controls the ground side of the sole-
noid using the governor pressure solenoid control cir-
cuit.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The sensor output signal provides the necessary
feedback to the PCM. This feedback is needed to ade-
quately control governor pressure.
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate channels line pressure to the
solenoid valve through the governor body. It also
channels governor pressure from the solenoid valve
to the governor circuit. It is the solenoid valve that
develops the necessary governor pressure.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
LOW TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE
When the transmission fluid is cold the conven-
tional governor can delay shifts, resulting in higher
than normal shift speeds and harsh shifts. The elec-
tronically controlled low temperature governor pres-
sure curve is higher than normal to make the
transmission shift at normal speeds and sooner. The
PCM uses a temperature sensor in the transmission
oil sump to determine when low temperature gover-
nor pressure is needed.
NORMAL OPERATION
Normal operation is refined through the increased
computing power of the PCM and through access to
data on engine operating conditions provided by the
PCM that were not available with the previous
stand-alone electronic module. This facilitated the
development of a load adaptive shift strategy - the
ability to alter the shift schedule in response to vehi-
cle load condition. One manifestation of this capabil-
ity is grade9hunting9prevention - the ability of the
transmission logic to delay an upshift on a grade if
the engine does not have sufficient power to main-
tain speed in the higher gear. The 3-2 downshift and
the potential for hunting between gears occurs with a
Fig. 70 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 323
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1779 of 2255
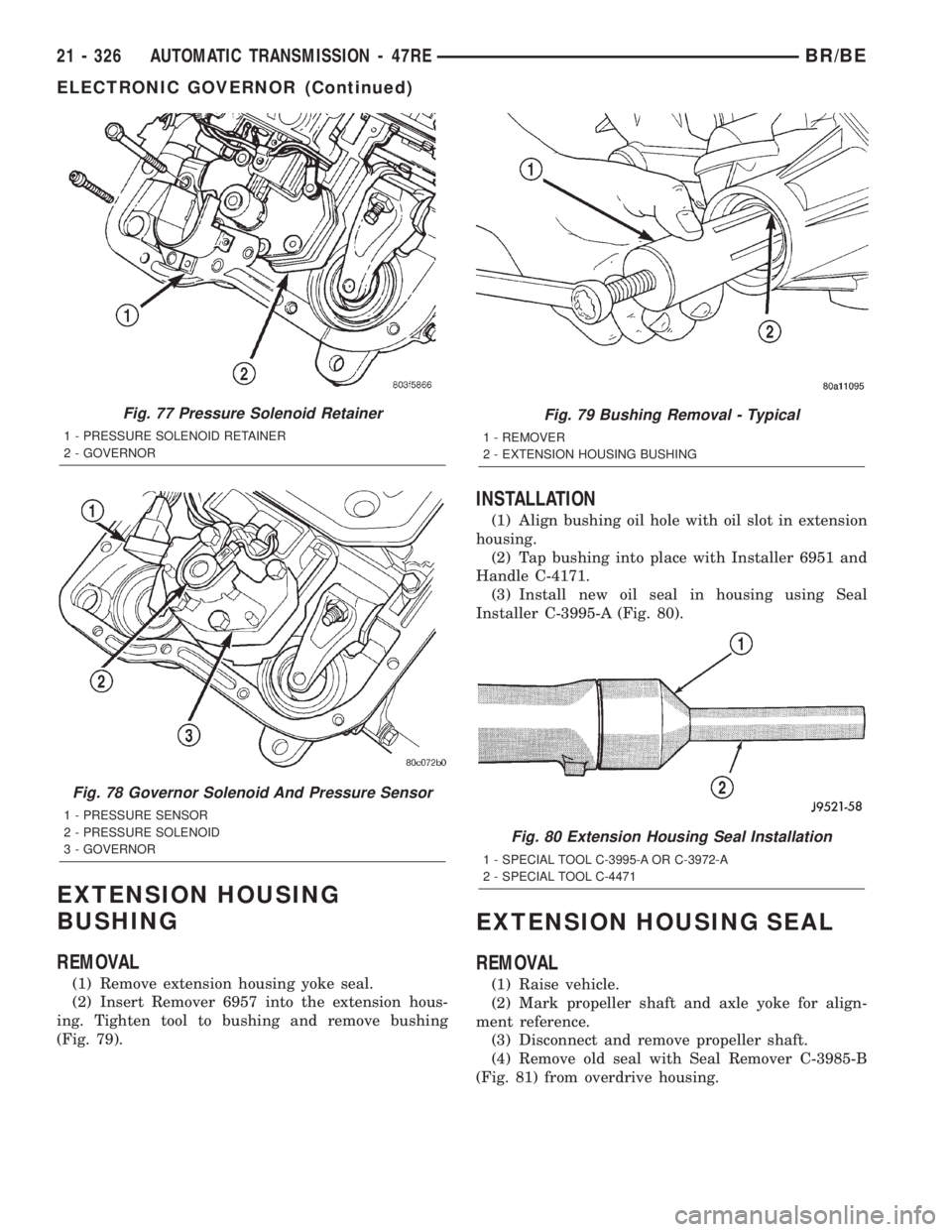
EXTENSION HOUSING
BUSHING
REMOVAL
(1) Remove extension housing yoke seal.
(2) Insert Remover 6957 into the extension hous-
ing. Tighten tool to bushing and remove bushing
(Fig. 79).
INSTALLATION
(1) Align bushing oil hole with oil slot in extension
housing.
(2) Tap bushing into place with Installer 6951 and
Handle C-4171.
(3) Install new oil seal in housing using Seal
Installer C-3995-A (Fig. 80).
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Mark propeller shaft and axle yoke for align-
ment reference.
(3) Disconnect and remove propeller shaft.
(4) Remove old seal with Seal Remover C-3985-B
(Fig. 81) from overdrive housing.
Fig. 77 Pressure Solenoid Retainer
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID RETAINER
2 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 78 Governor Solenoid And Pressure Sensor
1 - PRESSURE SENSOR
2 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
3 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 79 Bushing Removal - Typical
1 - REMOVER
2 - EXTENSION HOUSING BUSHING
Fig. 80 Extension Housing Seal Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3995-A OR C-3972-A
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4471
21 - 326 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1781 of 2255

sludge and/or debris. The torque converter should
also be replaced at the same time.
Failure to flush the cooler and lines will result in
recontamination. Flushing applies to auxiliary cool-
ers as well. The torque converter should also be
replaced whenever a failure generates sludge and
debris. This is necessary because normal converter
flushing procedures will not remove all contami-
nants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transmission recondition is
needed. Be sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick
closely. If there is any doubt about its condition,
drain out a sample for a double check.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in NEUTRAL and
the transmission fluid at normal operating tempera-
ture.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.
The transmission fluid level can be checked two
ways.
PROCEDURE ONE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operat-
ing temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive
vehicle if necessary to bring fluid temperature up to
normal hot operating temperature of 82ÉC (180ÉF).(2) Position vehicle on level surface.
(3) Start and run engine at curb idle speed.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Shift transmission momentarily into all gear
ranges. Then shift transmission back to NEUTRAL.
(6) Clean top of filler tube and dipstick to keep
dirt from entering tube.
(7) Remove dipstick (Fig. 83) and check fluid level
as follows:
(a) Correct acceptable level is in crosshatch area.
(b) Correct maximum level is to MAX arrow
mark.
(c) Incorrect level is at or below MIN line.
(d) If fluid is low, add only enough MopartAT F
+4, type 9602, to restore correct level. Do not over-
fill.
PROCEDURE TWO
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approxi-
mately 2 seconds.
(3) Shift the transmission into REVERSE for
approximately 2 seconds.
(4) Shift the transmission into PARK.
(5) Hook up DRBtscan tool and select engine.
(6) Select sensors.
(7) Read the transmission temperature value.
(8) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
chart.
(9) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
dipstick according to the chart (Fig. 84).
NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission,
wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully
drain from the fill tube into the transmission before
rechecking the fluid level.
(10) Check transmission for leaks.
Fig. 83 Dipstick Fluid Level MarksÐTypical
1 - DIPSTICK
2 - MAXIMUM CORRECT FLUID LEVEL
3 - ACCEPTABLE FLUID LEVEL
21 - 328 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1783 of 2255

INSTALLATION
(1) Position a new transmission oil filter onto the
valve body.
(2) Install the screws to hold the filter to the valve
body. Tighten the screws to 4 N´m (35 in.lbs.).
(3) Clean the gasket surfaces of the transmission
oil pan and transmission pan rail.
NOTE: The transmission pan oil gasket is reusable.
Inspect the sealing surfaces of the gasket. If the
sealing ribs on both surfaces appear to be in good
condition, clean the gasket of any foreign material
and reinstall.
(4) Position the oil pan gasket onto the oil pan.
(5) Position the oil pan and gasket onto the trans-
mission and install several bolts to hold the pan and
gasket to the transmission.
(6) Install the remainder of the oil pan bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 13.6 N´m (125 in.lbs.).
(7) Lower vehicle and fill transmission. (Refer to
21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC/
FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL
To avoid overfilling transmission after a fluid
change or overhaul, perform the following procedure:
(1) Remove dipstick and insert clean funnel in
transmission fill tube.
(2) Add following initial quantity of MopartAT F
+4, type 9602, to transmission:
(a) If only fluid and filter were changed, add3
pints (1-1/2 quarts)of ATF +4 to transmission.
(b) If transmission was completely overhauled,
torque converter was replaced or drained, andcooler was flushed, add12 pints (6 quarts)of ATF
+4 to transmission.
(3) Apply parking brakes.
(4)
Start and run engine at normal curb idle speed.
(5)Apply service brakes, shift transmission through
all gear ranges then back to NEUTRAL, set parking
brake, and leave engine running at curb idle speed.
(6) Remove funnel, insert dipstick and check fluid
level. If level is low,add fluid to bring level to
MIN mark on dipstick.Check to see if the oil level
is equal on both sides of the dipstick. If one side is
noticably higher than the other, the dipstick has
picked up some oil from the dipstick tube. Allow the
oil to drain down the dipstick tube and re-check.
(7) Drive vehicle until transmission fluid is at nor-
mal operating temperature.
(8) With the engine running at curb idle speed, the
gear selector in NEUTRAL, and the parking brake
applied, check the transmission fluid level.
CAUTION: Do not overfill transmission, fluid foam-
ing and shifting problems can result.
(9)
Add fluid to bring level up to MAX arrow mark.
When fluid level is correct, shut engine off, release
park brake, remove funnel, and install dipstick in fill
tube.
FRONT CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The front clutch assembly (Fig. 87) is composed of
the front clutch retainer, pressure plate, clutch
plates, driving discs, piston, piston return spring,
return spring retainer, and snap-rings. The front
clutch is the forward-most component in the trans-
mission geartrain and is directly behind the oil pump
and is considered a driving component.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between the
clutch retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is pro-
vided by the oil pump, transferred through the control
valves and passageways, and enters the clutch through
the hub of the reaction shaft support. With pressure
applied between the clutch retainer and piston, the pis-
ton moves away from the clutch retainer and com-
presses the clutch pack. This action applies the clutch
pack, allowing torque to flow through the input shaft
into the driving discs, and into the clutch plates and
pressure plate that are lugged to the clutch retainer.
The waved snap-ring is used to cushion the application
of the clutch pack.
Fig. 86 Transmission Filter
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - FILTER
21 - 330 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)