2002 DODGE RAM oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 1456 of 2255

GEAR RATIOS
GEAR RATIO
FIRST 5.61:1
SECOND 3.04:1
THIRD 1.67:1
FOURTH 1.00:1
FIFTH 0.75:1
REVERSE 5.04:1
IDENTIFICATION
The transmission identification tag is attached to
the driver side PTO cover (Fig. 3).
The tag provides the transmission model number,
build date and part number. Be sure to reinstall the
I.D. tag if removed during service. The information
on the tag is essential to correct parts ordering.
OPERATION
The manual transmission receives power through
the clutch assembly from the engine. The clutch disc
is splined to the transmission input shaft and is
turned at engine speed at all times that the clutch is
engaged. The input shaft is connected to the trans-
mission countershaft through the mesh of fourth
speed gear on the input shaft and the fourth counter-
shaft gear. At this point all the transmission gears
are spinning.The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. This move-
ment moves the internal transmission shift compo-
nents to begin the shift sequence. As the shift lever
moves the selected shift rail, the shift fork attached
to that rail begins to move. The fork is positioned in
a groove in the outer circumference of the synchro-
nizer sleeve. As the shift fork moves the synchronizer
sleeve, the synchronizer begins to speed-up or slow
down the selected gear (depending on whether we are
up-shifting or down-shifting). The synchronizer does
this by having the synchronizer hub splined to the
mainshaft, or the countershaft in some cases, and
moving the blocker ring into contact with the gear's
friction cone. As the blocker ring and friction cone
come together, the gear speed is brought up or down
to the speed of the synchronizer. As the two speeds
match, the splines on the inside of the synchronizer
sleeve become aligned with the teeth on the blocker
ring and the friction cone and eventually will slide
over the teeth, locking the gear to the mainshaft, or
countershaft, through the synchronizer.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check. A correct lubricant level
check can only be made when the vehicle is level.
Also allow the lubricant to settle for a minute or so
before checking. These recommendations will ensure
an accurate check and avoid an underfill or overfill
condition. Always check the lubricant level after any
addition of fluid to avoid an incorrect lubricant level
condition.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, adaptor or extension housing, or from the front/
rear seals. A suspected leak could also be the result
of an overfill condition. Leaks at the rear of the
extension or adapter housing will be from the hous-
ing oil seals. Leaks at component mating surfaces
will probably be the result of inadequate sealer, gaps
in the sealer, incorrect bolt tightening or use of a
non-recommended sealer. A leak at the front of the
transmission will be from either the front bearing
retainer or retainer seal. Lubricant may be seen drip-
ping from the clutch housing after extended opera-
tion. If the leak is severe, it may also contaminate
the clutch disc causing the disc to slip, grab and or
chatter.
Fig. 3 Identification Tag Location
1 - PTO COVER
2 - I.D. TAG
BR/BEMANUAL - NV4500 21 - 3
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1485 of 2255

DRIVE GEAR AND RETAINER
(1) Install bearing on drive gear with Installer
6448 (Fig. 109).
(2) Lubricate pilot bearing with petroleum jelly
and install it in drive gear bore.
(3) Install drive gear on mainshaft. Work gear
rearward until mainshaft hub is seated in pilot bear-
ing.
(4) Install bearing cup in front retainer with Han-
dle C-4171 and Installer C-4308 (Fig. 110).
(5) Install new oil seal in front bearing retainer
with Installer 6052 (Fig. 111). Use one or two wood
blocks to support retainer as shown. Lubricate seal
lip with petroleum jelly after installation.
(6) Clean contact surfaces of gear case and front
bearing retainer with a wax and grease remover.
(7) Apply Mopar Silicone Sealer or equivalent to
flange surface of front bearing retainer (Fig. 112).(8) Install front bearing retainer over drive gear
and start it into case.
(9) Start front bearing retainer in gear case. Verify
retainer lube channel is at the top-center(12
O'clock)position (Fig. 112).
(10) Align front bearing retainer bolt holes and tap
retainer into place with plastic mallet. Installnew
retainer bolts and tighten to 30 N´m (22 ft. lbs.) (Fig.
113).
NOTE: Never reuse the old bolts.
Fig. 108 Drive Gear Thrust Bearing
1 - MAINSHAFT
2 - DRIVE GEAR THRUST BEARING
Fig. 109 Front Bearing On Drive Gear
1 - INSTALLER 6448
2 - BEARING
3 - DRIVE GEAR
Fig. 110 Front Bearing Cup In Retainer
1 - INSTALLER C-4308
2 - HANDLE C-4171
3 - WOOD BLOCKS
4 - RETAINER
Fig. 111 Bearing Retainer Oil Seal
1 - INSTALLER 6052
2 - RETAINER
3 - WOOD BLOCK
21 - 32 MANUAL - NV4500BR/BE
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1486 of 2255
MAINSHAFT END PLAY
(1) Install mainshaft rear bearing cup in case and
over bearing. Tap bearing cup into place with plastic
mallet.
(2) Install rear bearing plate to hold mainshaft
and rear bearing in position (Fig. 114).
NOTE: Do not install any end play shims at this
time.
(3) Tighten rear bearing plate bolts securely.
(4) Place gear case in upright position on bench.
Either cut hole in bench to accept drive gear and
front retainer or use C-clamps to secure transmission
on bench.
NOTE: Do not leave transmission unsupported.
(5) Install Extension Rod 8161 into a suitable
threaded hole in rear of case.(6) Mount dial indicator on extension rod and posi-
tion indicator plunger against end of mainshaft.
(7) Move mainshaft forward to remove all play
then zero dial indicator.
(8) Move mainshaft upward and record dial indica-
tor reading. Move mainshaft with pry tool positioned
between drive gear and case.
(9) End play should be 0.051-0.15 mm (0.002-0.006
in.). Select fit shims are available to adjust end play.
If end play adjustment is required, remove bearing
plate and install necessary shim.
(10) Reinstall rear bearing plate with oil hole in
bearing plate at the top (Fig. 114).
(11) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or equivalent to
bearing plate bolt threads. Install and tighten bolts
to 23 N´m (200 in. lbs.).
(12) Install mainshaft fifth gear with Installer
6446 (Fig. 115). Gear is seated when it contacts rear
bearing.
COUNTERSHAFT FIFTH GEAR SYNCHRO
(1) Install thrust washer pin in countershaft (Fig.
116).
(2) Install thrust washer on countershaft. Turn
washer until pin engages in washer notch (Fig. 117).
NOTE: The flat side of washer faces the rear and
cone side faces the front.
(3) Lubricate and install fifth gear bearing on
countershaft (Fig. 118).
(4) Install synchro sleeve on hub of countershaft
fifth gear with tapered side of sleeve facing front and
the flat side facing rear (Fig. 119).
(5) Install shift fork in synchro sleeve (Fig. 120).
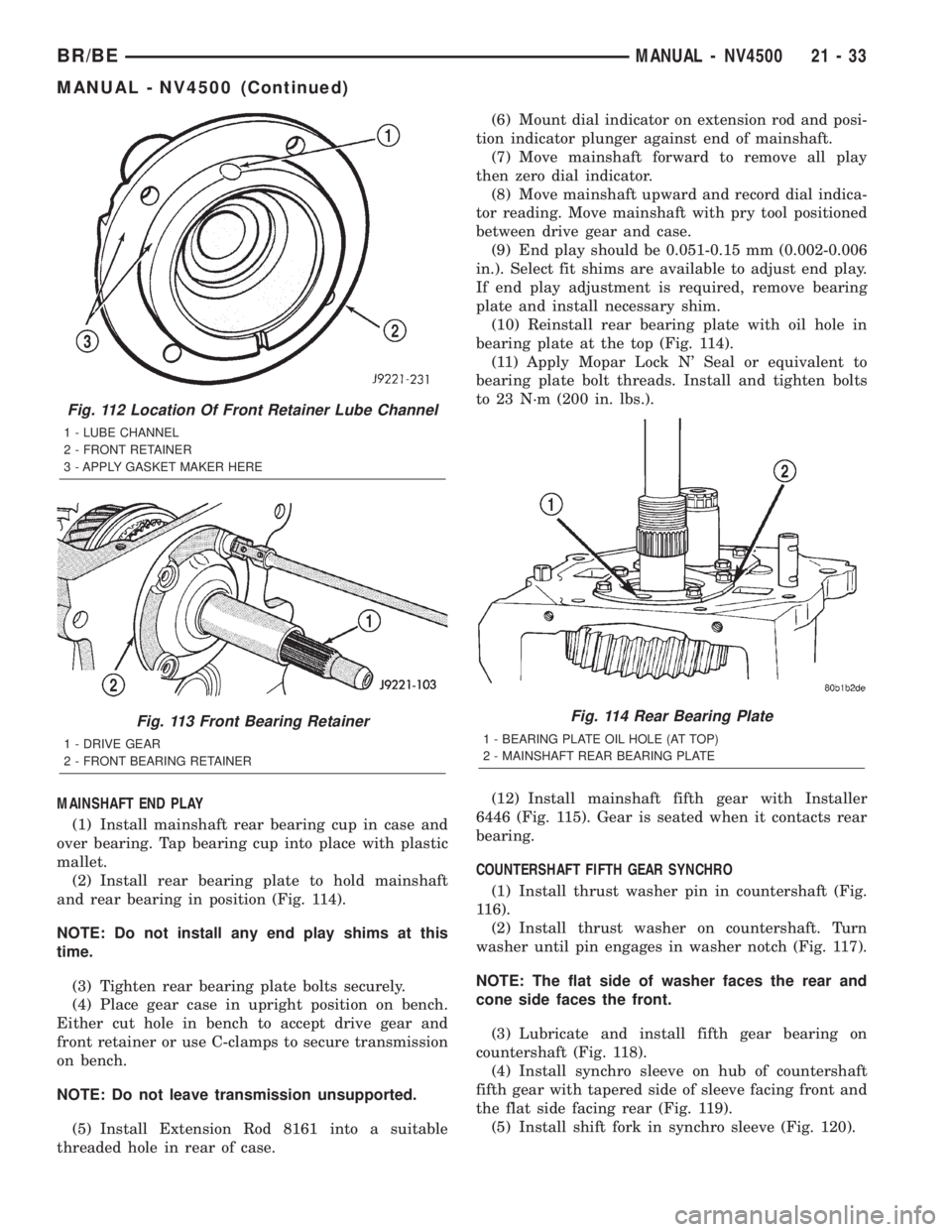
Fig. 112 Location Of Front Retainer Lube Channel
1 - LUBE CHANNEL
2 - FRONT RETAINER
3 - APPLY GASKET MAKER HERE
Fig. 113 Front Bearing Retainer
1 - DRIVE GEAR
2 - FRONT BEARING RETAINER
Fig. 114 Rear Bearing Plate
1 - BEARING PLATE OIL HOLE (AT TOP)
2 - MAINSHAFT REAR BEARING PLATE
BR/BEMANUAL - NV4500 21 - 33
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1501 of 2255

OPERATION
The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. As the shift
lever moves the selected shift rail, the shift fork
attached to that rail begins to move. The fork is posi-
tioned in a groove in the outer circumference of the
synchronizer sleeve. As the shift fork moves the syn-
chronizer sleeve, the synchronizer begins to speed-up
or slow down the selected gear (depending on
whether we are up-shifting or down-shifting). The
synchronizer does this by having the synchronizer
hub splined to the mainshaft or the countershaft in
some cases, and moving the blocker ring into contact
with the gear's friction cone. As the blocker ring and
friction cone come together, the gear speed is brought
up or down to the speed of the synchronizer. As the
two speeds match, the splines on the inside of the
synchronizer sleeve become aligned with the teeth on
the blocker ring and friction cone and eventually willslide over the teeth, locking the gear to the main-
shaft or countershaft through the synchronizer.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check. A correct lubricant level
check can only be made when the vehicle is level.
Also allow the lubricant to settle for a minute or so
before checking. These recommendations will ensure
an accurate check and avoid an underfill or overfill
condition. Always check the lubricant level after any
addition of fluid to avoid an incorrect lubricant level
condition.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, adaptor or extension housing, or from the front/
rear seals. A suspected leak could also be the result
of an overfill condition. Leaks at the rear of the
extension or adapter housing will be from the hous-
ing oil seals. Leaks at component mating surfaces
will probably be the result of inadequate sealer, gaps
in the sealer, incorrect bolt tightening or use of a
non-recommended sealer. A leak at the front of the
transmission will be from either the front bearing
retainer or retainer seal. Lubricant may be seen drip-
ping from the clutch housing after extended opera-
tion. If the leak is severe, it may also contaminate
the clutch disc causing the disc to slip, grab and or
chatter.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants. The con-
sequence of using non-recommended lubricants is
noise, excessive wear, internal bind and hard shift-
ing. Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear,
shift rail, synchro, and bearing damage. If a leak
goes undetected for an extended period, the first indi-
cations of component damage are usually hard shift-
ing and noise.
Component damage, incorrect clutch adjustment or
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc are additional
probable causes of increased shift effort. Incorrect
adjustment or a worn/damaged pressure plate or disc
can cause incorrect release. If clutch problem is
advanced, gear clash during shifts can result. Worn
or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash when
shifting into any forward gear. In some new or
rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
Fig. 2 Shift Pattern
Fig. 3 Identification Tag Location
1 - IDENTIFICATION TAGS
21 - 48 MANUAL - NV5600BR/BE
MANUAL - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1511 of 2255

INPUT SHAFT
(1) Remove fifth gear blocker ring from the input
shaft (Fig. 36).(2) Remove fifth gear friction cone from the input
shaft (Fig. 37).
(3) Remove output shaft pocket bearing race from
the input shaft with Puller L-4518 (Fig. 38).
(4) Remove input shaft bearing and oil guide from
the input shaft with Sleeve 6444-8, Adapters 8243,
Puller Rods 6444-6 and the remainder of Puller 6444
(Fig. 39).
OUTPUT SHAFT
NOTE: Some gear and synchro components can be
installed backwards. Mark the gears, clutch gears,
synchro hubs, and sleeves for installation reference
during teardown. Use paint or a scriber for marking
purposes. Then stack the geartrain parts in order of
removal.
Fig. 35 OUTPUT SHAFT POCKET BEARING
1 - PULLER
2 - ADAPTERS
Fig. 36 FIFTH GEAR BLOCKER RING
1 - FIFTH GEAR BLOCKER RING
2 - INPUT SHAFT
Fig. 37 FIFTH GEAR FRICTION CONE
1 - FIFTH GEAR FRICTION CONE
2 - INPUT SHAFT
21 - 58 MANUAL - NV5600BR/BE
MANUAL - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1514 of 2255
(6) Remove countershaft from the press and Fix-
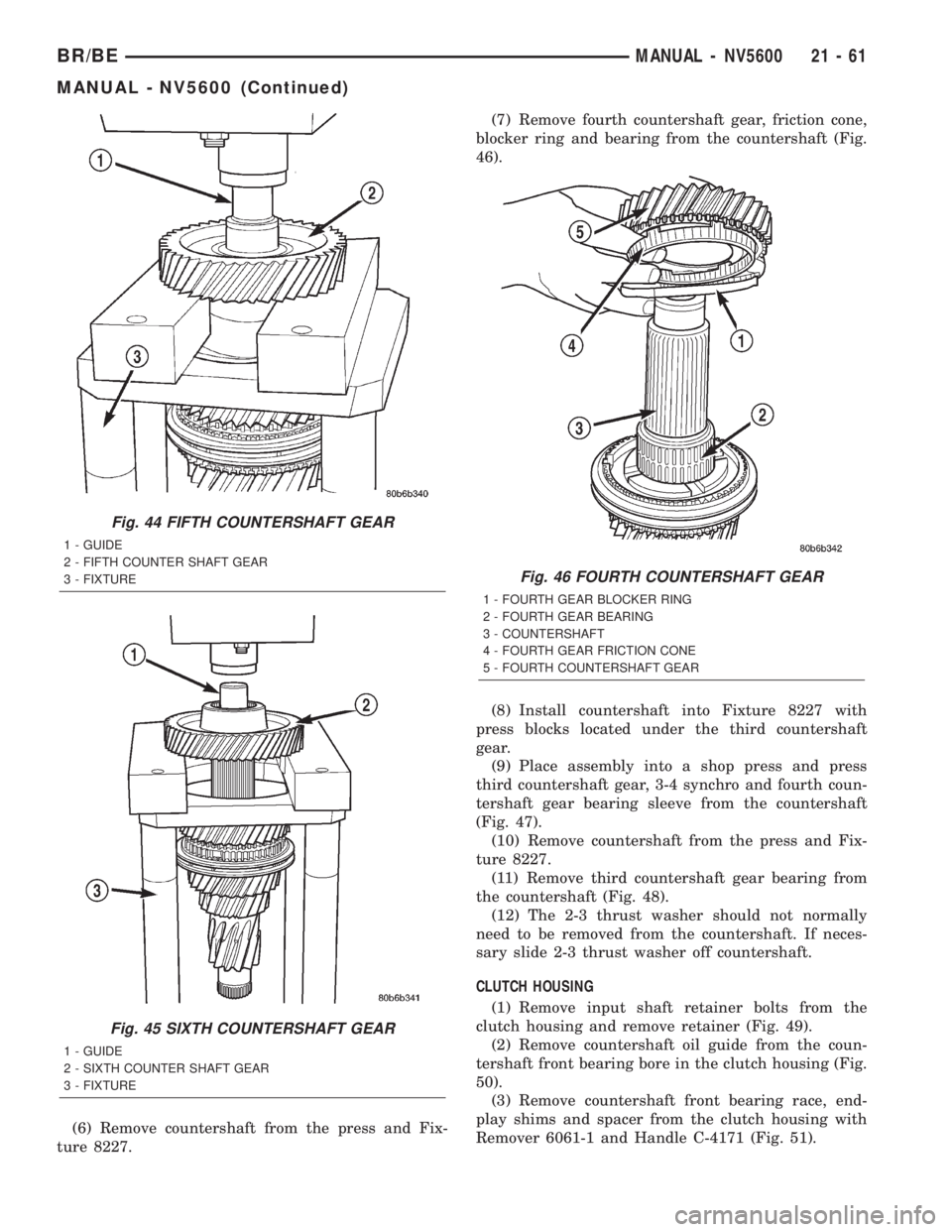
ture 8227.(7) Remove fourth countershaft gear, friction cone,
blocker ring and bearing from the countershaft (Fig.
46).
(8) Install countershaft into Fixture 8227 with
press blocks located under the third countershaft
gear.
(9) Place assembly into a shop press and press
third countershaft gear, 3-4 synchro and fourth coun-
tershaft gear bearing sleeve from the countershaft
(Fig. 47).
(10) Remove countershaft from the press and Fix-
ture 8227.
(11) Remove third countershaft gear bearing from
the countershaft (Fig. 48).
(12) The 2-3 thrust washer should not normally
need to be removed from the countershaft. If neces-
sary slide 2-3 thrust washer off countershaft.
CLUTCH HOUSING
(1) Remove input shaft retainer bolts from the
clutch housing and remove retainer (Fig. 49).
(2) Remove countershaft oil guide from the coun-
tershaft front bearing bore in the clutch housing (Fig.
50).
(3) Remove countershaft front bearing race, end-
play shims and spacer from the clutch housing with
Remover 6061-1 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 51).
Fig. 44 FIFTH COUNTERSHAFT GEAR
1 - GUIDE
2 - FIFTH COUNTER SHAFT GEAR
3 - FIXTURE
Fig. 45 SIXTH COUNTERSHAFT GEAR
1 - GUIDE
2 - SIXTH COUNTER SHAFT GEAR
3 - FIXTURE
Fig. 46 FOURTH COUNTERSHAFT GEAR
1 - FOURTH GEAR BLOCKER RING
2 - FOURTH GEAR BEARING
3 - COUNTERSHAFT
4 - FOURTH GEAR FRICTION CONE
5 - FOURTH COUNTERSHAFT GEAR
BR/BEMANUAL - NV5600 21 - 61
MANUAL - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1515 of 2255
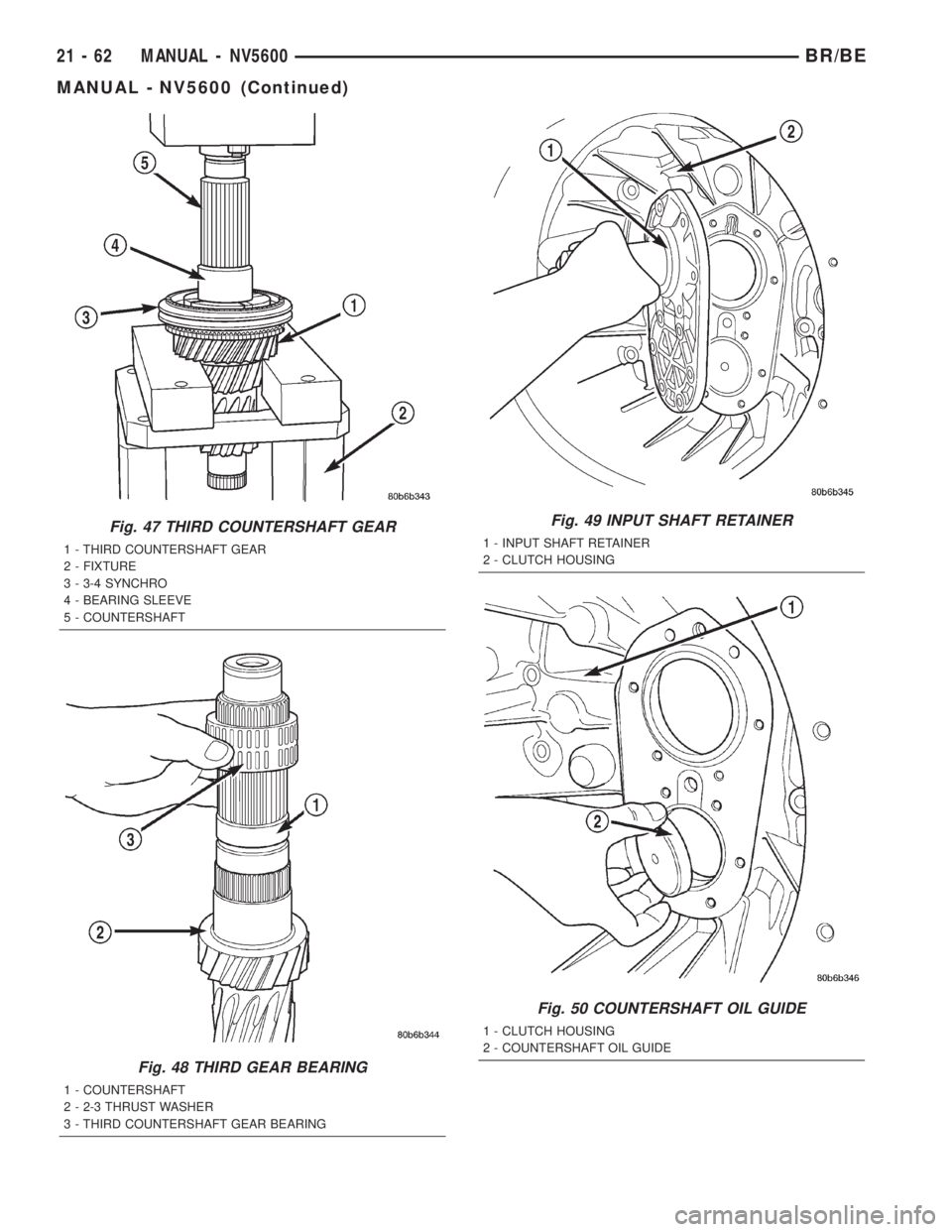
Fig. 47 THIRD COUNTERSHAFT GEAR
1 - THIRD COUNTERSHAFT GEAR
2 - FIXTURE
3 - 3-4 SYNCHRO
4 - BEARING SLEEVE
5 - COUNTERSHAFT
Fig. 48 THIRD GEAR BEARING
1 - COUNTERSHAFT
2 - 2-3 THRUST WASHER
3 - THIRD COUNTERSHAFT GEAR BEARING
Fig. 49 INPUT SHAFT RETAINER
1 - INPUT SHAFT RETAINER
2 - CLUTCH HOUSING
Fig. 50 COUNTERSHAFT OIL GUIDE
1 - CLUTCH HOUSING
2 - COUNTERSHAFT OIL GUIDE
21 - 62 MANUAL - NV5600BR/BE
MANUAL - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1516 of 2255

(4) Remove input shaft bearing race with Remover/
Installer 8237 and Handle C-4171.
(5) Remove input shaft oil guide and retainer seal
(Fig. 52).
CLEANING
Clean the gears, bearings shafts, extension/adapter
housing and gear case with solvent. Dry all parts
except the bearings with compressed air. Allow the
bearings to either air dry or wipe them dry with
clean shop towels.
INSPECTION
NOTE: Minor corrosion, nicks, or pitting can be
smoothed with 400 grit emery and polished out with
crocus cloth.
Inspect the reverse idler gear, bearings, shaft and
thrust washers. Replace the bearings if the rollers
are worn, chipped, cracked, flat-spotted or brinnelled.
Replace the gear if the teeth are chipped, cracked or
worn thin.
Inspect the front bearing retainer and bearing cup.
Replace the bearing cup if scored, cracked, brinnelled
or rough. Check the release bearing slide surface of
the retainer carefully. Replace the retainer if worn or
damaged in any way.
Inspect mainshaft bearing surfaces, splines, snap
ring grooves and threads. Replace the shaft if any
surfaces exhibit considerable wear or damage.
Inspect the countershaft and bearings. Replace the
shaft if any surfaces exhibit considerable wear or
damage.
Inspect shift forks for wear and distortion. Check
fit of the sleeve in the fork to be sure the two parts
fit and work smoothly. Replace the fork if the roll pin
holes are worn oversize or damaged. Do not attempt
to salvage a worn fork. Replace shift fork roll pins if
necessary or if doubt exists about their condition.
The all bearings for wear, roughness, flat spots,
pitting or other damage. Replace the bearings if nec-
essary.
Inspect the blocker rings and fiction cones. replace
either part if worn or damaged in any way. Replace if
the friction material is burned, flaking off or worn.
Inspect synchro components wear or damage.
Replace parts if worn, cracked or distorted.
Inspect all of the thrust washers and locating pins.
Replace the pins if bent or worn. Replace the wash-
ers if worn or the locating pin notches are distorted.
Inspect the case and housing/adapter sealing and
mating surfaces are free of burrs and nicks. Inspcet
the alignment dowels in the case top surface and in
the housing/adapter are tight and in good condition.
Replace the gear case or housing/adapter if cracked
or broken.
Fig. 51 FRONT COUNTERSHAFT BEARING
1 - CLUTCH HOUSING
2 - HANDLE
3 - REMOVER
Fig. 52 OIL GUIDE AND SEAL
1 - INPUT SHAFT OIL GUIDE
2 - INPUT SHAFT OIL SEAL
BR/BEMANUAL - NV5600 21 - 63
MANUAL - NV5600 (Continued)