2002 DODGE RAM service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 1610 of 2255

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has two primary causes.
(1) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to reverse flush cooler and lines after
repair
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The transmission cooler and lines should be
reverse flushed whenever a malfunction generates
sludge and/or debris. The torque converter should
also be replaced at the same time.
Failure to flush the cooler and lines will result in
recontamination. Flushing applies to auxiliary coolers
as well. The torque converter should also be replaced
whenever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing procedures
will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
Fig. 88 Installing Overdrive Housing Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3995-A OR C-3972-A
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4471
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 157
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL (Continued)
Page 1611 of 2255

In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transmission recondition is
needed. Be sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick
closely. If there is any doubt about its condition,
drain out a sample for a double check.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in NEUTRAL and
the transmission fluid at normal operating tempera-
ture.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.
The transmission fluid level can be checked two
ways.
PROCEDURE ONE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operat-
ing temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive
vehicle if necessary to bring fluid temperature up to
normal hot operating temperature of 82ÉC (180ÉF).
(2) Position vehicle on level surface.
(3) Start and run engine at curb idle speed.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Shift transmission momentarily into all gear
ranges. Then shift transmission back to NEUTRAL.
(6) Clean top of filler tube and dipstick to keep
dirt from entering tube.
(7) Remove dipstick (Fig. 89) and check fluid level
as follows:
(a) Correct acceptable level is in crosshatch area.
(b) Correct maximum level is to MAX arrow
mark.
(c) Incorrect level is at or below MIN line.
(d)
If fluid is low, add only enough MopartATF +4,
type 9602, to restore correct level. Do not overfill.
PROCEDURE TWO
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approxi-
mately 2 seconds.
(3) Shift the transmission into REVERSE for
approximately 2 seconds.
(4) Shift the transmission into PARK.
(5) Hook up DRBtscan tool and select engine.(6) Select sensors.
(7) Read the transmission temperature value.
(8) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
figure. (Fig. 90)
(9) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
dipstick according to the figure.
NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission,
wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully
drain from the fill tube into the transmission before
rechecking the fluid level.
(10) Check transmission for leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
REPLACEMENT
For proper service intervals (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHED-
ULES - DESCRIPTION). The service fluid fill after a
filter change is approximately 3.8 liters (4.0 quarts).
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Place a large diameter shallow drain pan
beneath the transmission pan.
(3) Remove bolts holding front and sides of pan to
transmission (Fig. 91).
(4) Loosen bolts holding rear of pan to transmis-
sion.
(5) Slowly separate front of pan and gasket away
from transmission allowing the fluid to drain into
drain pan.
(6) Hold up pan and remove remaining bolt hold-
ing pan to transmission.
(7) While holding pan level, lower pan and gasket
away from transmission.
(8) Pour remaining fluid in pan into drain pan.
(9) Remove screws holding filter to valve body
(Fig. 92).
(10) Separate filter from valve body and pour fluid
in filter into drain pan.
(11) Dispose of used trans fluid and filter properly.
Fig. 89 Dipstick Fluid Level Marks - Typical
1 - DIPSTICK
2 - MAXIMUM CORRECT FLUID LEVEL
3 - ACCEPTABLE FLUID LEVEL
21 - 158 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1613 of 2255

INSTALLATION
(1) Position a new transmission oil filter onto the
valve body.
(2) Install the screws to hold the filter to the valve
body. Tighten the screws to 4 N´m (35 in.lbs.).
(3) Clean the gasket surfaces of the transmission
oil pan and transmission pan rail.
NOTE: The transmission pan oil gasket is reusable.
Inspect the sealing surfaces of the gasket. If the
sealing ribs on both surfaces appear to be in good
condition, clean the gasket of any foreign material
and reinstall.
(4) Position the oil pan gasket onto the oil pan.
(5) Position the oil pan and gasket onto the trans-
mission and install several bolts to hold the pan and
gasket to the transmission.
(6) Install the remainder of the oil pan bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 13.6 N´m (125 in.lbs.).
(7) Lower vehicle and fill transmission. (Refer to
21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC/
FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL
To avoid overfilling transmission after a fluid
change or overhaul, perform the following procedure:
(1) Remove dipstick and insert clean funnel in
transmission fill tube.
(2) Add following initial quantity of MopartAT F
+4, type 9602, to transmission:
(a) If only fluid and filter were changed, add3
pints (1-1/2 quarts)of ATF +4 to transmission.
(b) If transmission was completely overhauled,
torque converter was replaced or drained, and
cooler was flushed, add12 pints (6 quarts)of ATF
+4 to transmission.
(3) Apply parking brakes.
(4) Start and run engine at normal curb idle
speed.
(5) Apply service brakes, shift transmission
through all gear ranges then back to NEUTRAL, set
parking brake, and leave engine running at curb idle
speed.
(6) Remove funnel, insert dipstick and check fluid
level. If level is low,add fluid to bring level to
MIN mark on dipstick.Check to see if the oil level
is equal on both sides of the dipstick. If one side is
noticably higher than the other, the dipstick has
picked up some oil from the dipstick tube. Allow the
oil to drain down the dipstick tube and re-check.
(7) Drive vehicle until transmission fluid is at nor-
mal operating temperature.(8) With the engine running at curb idle speed, the
gear selector in NEUTRAL, and the parking brake
applied, check the transmission fluid level.
CAUTION: Do not overfill transmission, fluid foam-
ing and shifting problems can result.
(9) Add fluid to bring level up to MAX arrow
mark.
When fluid level is correct, shut engine off, release
park brake, remove funnel, and install dipstick in fill
tube.
FRONT CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The front clutch assembly (Fig. 93) is composed of
the front clutch retainer, pressure plate, clutch
plates, driving discs, piston, piston return spring,
return spring retainer, and snap-rings. The front
clutch is the forward-most component in the trans-
mission geartrain and is directly behind the oil pump
and is considered a driving component.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the clutch retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through the hub of the reaction shaft support.
With pressure applied between the clutch retainer
and piston, the piston moves away from the clutch
retainer and compresses the clutch pack. This action
applies the clutch pack, allowing torque to flow
through the input shaft into the driving discs, and
into the clutch plates and pressure plate that are
lugged to the clutch retainer. The waved snap-ring is
used to cushion the application of the clutch pack.
When pressure is released from the piston, the
spring returns the piston to its fully released position
and disengages the clutch. The release spring also
helps to cushion the application of the clutch assem-
bly. When the clutch is in the process of being
released by the release spring, fluid flows through a
vent and one-way ball-check-valve located in the
clutch retainer. The check-valve is needed to elimi-
nate the possibility of plate drag caused by centrifu-
gal force acting on the residual fluid trapped in the
clutch piston retainer.
21 - 160 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1626 of 2255

OVERDRIVE UNIT
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into PARK.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove transfer case, if equipped.
(4) Mark propeller shaft universal joint(s) and axle
pinion yoke, or the companion flange and flange
yoke, for alignment reference at installation, if necc-
esary.
(5) Disconnect and remove the rear propeller shaft,
if necessary. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIV-
ELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(6) Remove transmission oil pan, remove gasket,
drain oil and reinstall pan.
(7) If overdrive unit had malfunctioned, or if fluid
is contaminated, remove entire transmission. If diag-
nosis indicated overdrive problems only, remove just
the overdrive unit.
(8) Support transmission with transmission jack.
(9) Remove bolts attaching overdrive unit to trans-
mission (Fig. 119).
CAUTION: Support the overdrive unit with a jack
before moving it rearward. This is necessary to pre-
vent damaging the intermediate shaft. Do not allow
the shaft to support the entire weight of the over-
drive unit.
(10) Carefully work overdrive unit off intermediate
shaft. Do not tilt unit during removal. Keep it as
level as possible.(11) If overdrive unit does not require service,
immediately insert Alignment Tool 6227-2 in splines
of planetary gear and overrunning clutch to prevent
splines from rotating out of alignment. If misalign-
ment occurs, overdrive unit will have to be disassem-
bled in order to realign splines.
(12) Remove and retain overdrive piston thrust
bearing. Bearing may remain on piston or in clutch
hub during removal.
(13) Position drain pan on workbench.
(14) Place overdrive unit over drain pan. Tilt unit
to drain residual fluid from case.
(15) Examine fluid for clutch material or metal
fragments. If fluid contains these items, overhaul will
be necessary.
(16) If overdrive unit does not require any service,
leave alignment tool in position. Tool will prevent
accidental misalignment of planetary gear and over-
running clutch splines.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove transmission speed sensor and o-ring
seal from overdrive case (Fig. 120).
(2) Remove overdrive piston thrust bearing (Fig.
121).
Fig. 119 Overdrive Unit Bolts
1 - OVERDRIVE UNIT
2 - ATTACHING BOLTS (7)
Fig. 120 Transmission Speed Sensor
1 - SOCKET AND WRENCH
2 - SPEED SENSOR
3 - O-RING
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 173
Page 1633 of 2255

Do not use shop towels for wiping parts dry unless
the towels are made from a lint-free material. A suf-
ficient quantity of lint (from shop towels, cloths, rags,
etc.) could plug the transmission filter and fluid pas-
sages.
Discard the old case gasket and seals. Do not
attempt to salvage these parts. They are not reus-
able. Replace any of the overdrive unit snap-rings if
distorted or damaged.
Minor nicks or scratches on components can be
smoothed with crocus cloth. However, do not attempt
to reduce severe scoring on any components with
abrasive materials. Replace severely scored compo-
nents; do not try to salvage them.
INSPECTION
Check condition of the park lock components and
the overdrive case.
Check the bushings in the overdrive case. Replace
the bushings if severely scored or worn. Also replace
the case seal if loose, distorted, or damaged.
Examine the overdrive and direct clutch discs and
plates. Replace the discs if the facing is worn,
severely scored, or burned and flaking off. Replace
the clutch plates if worn, heavily scored, or cracked.
Check the lugs on the clutch plates for wear. The
plates should slide freely in the drum. Replace the
plates or drum if binding occurs.
Check condition of the annulus gear, direct clutch
hub, clutch drum and clutch spring. Replace the gear,
hub and drum if worn or damaged. Replace the
spring if collapsed, distorted, or cracked.
Be sure the splines and lugs on the gear, drum and
hub are in good condition. The clutch plates and
discs should slide freely in these components.
Inspect the thrust bearings and spring plate.
Replace the plate if worn or scored. Replace the bear-
ings if rough, noisy, brinnelled, or worn.
Inspect the planetary gear assembly and the sun
gear and bushings. If either the sun gear or the
bushings are damaged, replace the gear and bush-
ings as an assembly. The gear and bushings are not
serviced separately.
The planetary carrier and pinions must be in good
condition. Also be sure the pinion pins are secure and in
good condition. Replace the carrier if worn or damaged.
Inspect the overrunning clutch and race. The race
surface should be smooth and free of scores. Replace
the overrunning clutch assembly or the race if either
assembly is worn or damaged in any way.
Replace the shaft pilot bushing and inner bushing
if damaged. Replace either shaft bearing if rough or
noisy. Replace the bearing snap-rings if distorted or
cracked.
Check the machined surfaces on the output shaft.
These surfaces should clean and smooth. Very minor
nicks or scratches can be smoothed with crocus cloth.
Replace the shaft if worn, scored or damaged in any
way.
Inspect the output shaft bushings. The small bush-
ing is the intermediate shaft pilot bushing. The large
bushing is the overrunning clutch hub bushing.
Replace either bushing if scored, pitted, cracked, or
worn.
ASSEMBLY
GEARTRAIN AND DIRECT CLUTCH
(1) Soak direct clutch and overdrive clutch discs in
MopartATF +4, type 9602, transmission fluid. Allow
discs to soak for 10-20 minutes.
Fig. 146 Annulus Gear Snap-Ring Removal
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT
2 - ANNULUS GEAR
3 - SNAP-RING
Fig. 147 Annulus Gear Removal
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT
2 - ANNULUS GEAR
21 - 180 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1642 of 2255

OD THRUST PLATE SELECTION
(1) Place overdrive unit in vertical position. Mount
it on blocks, or in workbench with appropriate size
mounting hole cut into it. Be sure unit is facing
upward for access to direct clutch hub. Also be sure
output shaft is not loaded and internal components
are moved rearward for accurate measurement.
(2) Determine correct thickness overdrive piston
thrust plate as follows:
(a) Position Gauge Tool 6311 across face of over-
drive case. Then position Dial Caliper C-4962 over
gauge tool (Fig. 178).
(b) Measure distance to clutch hub thrust bear-
ing seat at four points 90É apart. Then average
measurements by adding them and dividing by 4.
(c) Select and install required thrust plate from
information in thrust plate chart (Fig. 179).
(3) Leave Alignment Tool 6227-2 in place. Tool will
keep planetary and clutch hub splines in alignment
until overdrive unit is ready for installation on trans-
mission.
(4) Transmission speed sensor can be installed at
this time if desired. However, it is recommended that
sensor not be installed until after overdrive unit is
secured to transmission.
OVERDRIVE PISTON
(1) Install new seals on overdrive piston.
(2) Stand transmission case upright on bellhous-
ing.
(3) Position Guide Ring 8114-1 on outer edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(4) Position Seal Guide 8114-3 on inner edge of
overdrive piston retainer.(5) Install overdrive piston in overdrive piston
retainer by:
(a) Aligning locating lugs on overdrive piston to
the two mating holes in retainer.
(b) Lubricate overdrive piston seals with Mopart
Door Ease, or equivalent.
(c) Install piston over Seal Guide 8114±3 and
inside Guide Ring 8114±1.
(d) Push overdrive piston into position in
retainer.
(e) Verify that the locating lugs entered the lug
bores in the retainer.
(6) Install intermediate shaft spacer on intermedi-
ate shaft.
(7) Install overdrive piston thrust plate on over-
drive piston.
(8) Install overdrive piston thrust bearing on over-
drive piston.
(9) Install transmission speed sensor and O-ring
seal in overdrive case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Be sure overdrive unit Alignment Tool 6227-2
is fully seated before moving unit. If tool is not
seated and gear splines rotate out of alignment, over-
drive unit will have to be disassembled in order to
realign splines.
(2) If overdrive piston retainer was not removed
during service and original case gasket is no longer
reusable, prepare new gasket by trimming it.
(3) Cut out old case gasket around piston retainer
with razor knife (Fig. 180).
(4) Use old gasket as template and trim new gas-
ket to fit.
(5) Position new gasket over piston retainer and
on transmission case. Use petroleum jelly to hold
gasket in place if necessary. Do not use any type of
sealer to secure gasket. Use petroleum jelly only.
Fig. 178 Overdrive Piston Thrust Plate Measurement
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6311
2 - DIRECT CLUTCH HUB THRUST BEARING SEAT
3 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4962
Fig. 179 Overdrive Piston Thrust Plate Selection
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 189
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1652 of 2255

INSPECTION
Inspect the planetary gear sets and annulus gears.
The planetary pinions, shafts, washers, and retaining
pins are serviceable. However, if a pinion carrier is
damaged, the entire planetary gear set must be
replaced as an assembly.
Replace the annulus gears if the teeth are chipped,
broken, or worn, or the gear is cracked. Replace the
planetary thrust plates and the tabbed thrust wash-
ers if cracked, scored or worn.
Inspect the machined surfaces of the intermediate
shaft. Be sure the oil passages are open and clear.
Replace the shaft if scored, pitted, or damaged.
Inspect the sun gear and driving shell. If either
component is worn or damaged, remove the sun gear
rear retaining ring and separate the sun gear andthrust plate from the driving shell. Then replace the
necessary component.
Replace the sun gear as an assembly if the gear
teeth are chipped or worn. Also replace the gear as
an assembly if the bushings are scored or worn. The
sun gear bushings are not serviceable. Replace the
thrust plate if worn, or severely scored. Replace the
driving shell if distorted, cracked, or damaged in any
way.
Replace all snap-rings during geartrain assembly.
Reusing snap-rings is not recommended.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Lubricate sun gear and planetary gears with
transmission fluid during assembly. Use petroleum
jelly to lubricate intermediate shaft bushing surfaces,
thrust washers and thrust plates and to hold these
parts in place during assembly.
Fig. 206 Sun Gear And Driving Shell Removal
1 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
2 - DRIVING SHELL
3 - SUN GEAR
Fig. 207 Rear Planetary Thrust Washer Removal
1 - SUN GEAR
2 - REAR PLANETARY THRUST WASHER
3 - DRIVING SHELL
Fig. 208 Rear Planetary And Annulus Gear Removal
1 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
2 - REAR ANNULUS GEAR
3 - REAR PLANETARY GEAR
Fig. 209 Rear Annulus Thrust Plate Removal
1 - REAR ANNULUS GEAR
2 - THRUST PLATE
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 199
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN/OUTPUT SHAFT (Continued)
Page 1665 of 2255
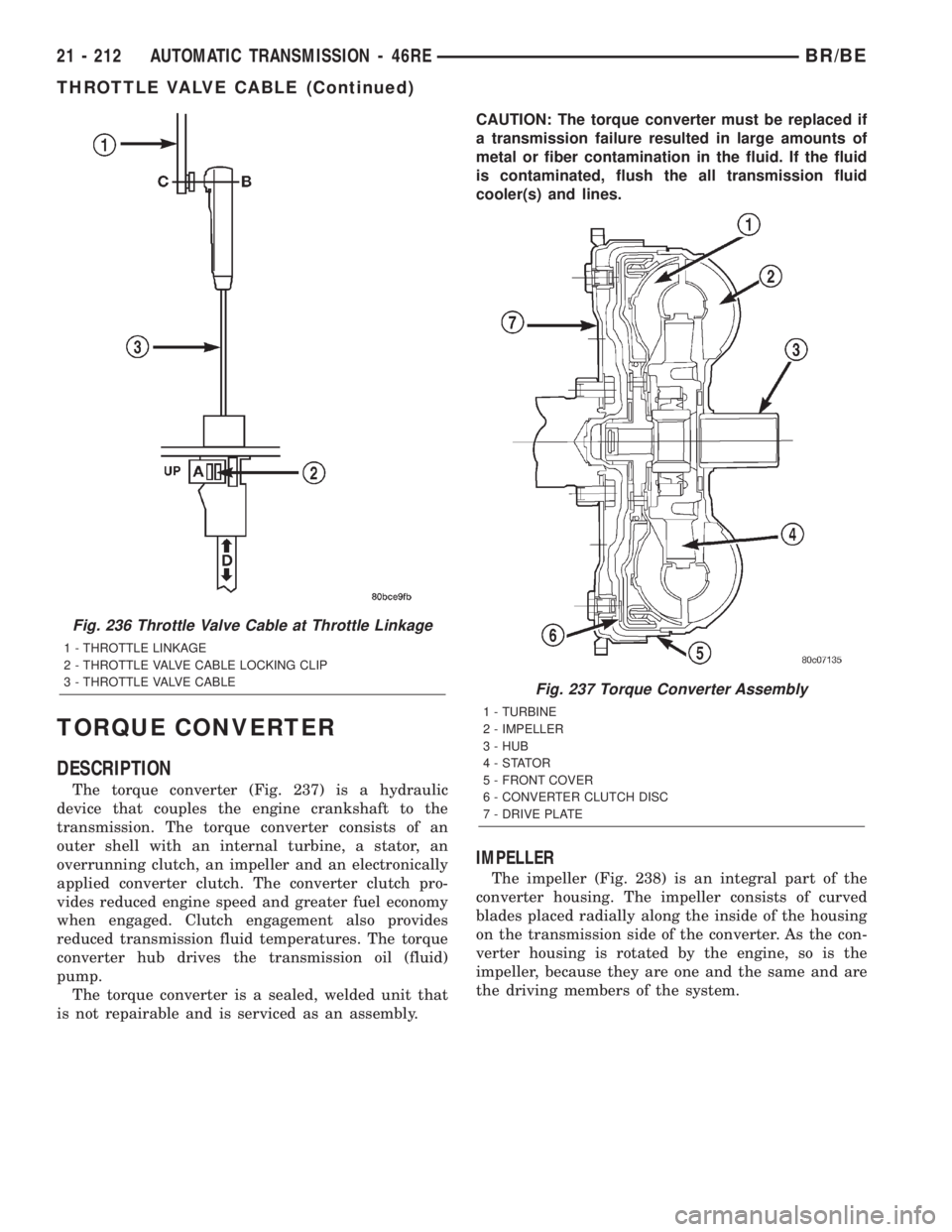
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 237) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The torque
converter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid)
pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid. If the fluid
is contaminated, flush the all transmission fluid
cooler(s) and lines.
IMPELLER
The impeller (Fig. 238) is an integral part of the
converter housing. The impeller consists of curved
blades placed radially along the inside of the housing
on the transmission side of the converter. As the con-
verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the
impeller, because they are one and the same and are
the driving members of the system.
Fig. 236 Throttle Valve Cable at Throttle Linkage
1 - THROTTLE LINKAGE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE LOCKING CLIP
3 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
Fig. 237 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - FRONT COVER
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
7 - DRIVE PLATE
21 - 212 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE (Continued)