2002 DODGE RAM engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 1331 of 2255

(29) Inspect transmission torque convertor housing
(automatic transmission) or clutch housing (manual
transmission) for damage to timing ring on drive
plate/flywheel.
(30) Verify that battery cable and solenoid feed
wire connections to the starter solenoid are tight and
clean. Inspect for chaffed wires or wires rubbing up
against other components.
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐ8.0L ENGINE
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected or incor-
rectly routed wires and hoses should be made. This
should be done before attempting to diagnose or ser-
vice the fuel injection system. A visual check will
help spot these faults and save unnecessary test and
diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will
include the following checks:
(1) Verify that the three 32±way electrical connec-
tors are fully inserted into the connector of the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) (Fig. 12).
(2) Inspect the battery cable connections. Be sure
that they are clean and tight.
(3) Inspect fuel pump relay and air conditioning
compressor clutch relay (if equipped). Inspect the
ASD relay connections. Inspect starter motor relay
connections. Inspect relays for signs of physical dam-
age and corrosion. The relays are located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) (Fig. 13). Refer to
label on PDC cover for relay location.
(4) Inspect ignition coil pack primary connections.
Verify that secondary cables are firmly connected to
coils (Fig. 14).
(5) Be sure that spark plug cables are firmly con-
nected and the spark plugs are in their correct firing
order. Be sure that camshaft position sensor wire
connector is firmly connected to harness connector.
Inspect spark plug condition. Refer to 8, Ignition.Connect vehicle to an oscilloscope and inspect spark
events for fouled or damaged spark plugs or cables.
(6) Verify that generator output wire, generator
connector and ground wire are firmly connected to
the generator.
(7) Inspect the system body grounds for loose or
dirty connections. Refer to 8, Wiring for ground loca-
tions.
(8) Verify crankcase ventilation (CCV) operation.
Refer to 25, Emission Control System for additional
information.
(9) Inspect fuel tube quick-connect fitting-to-fuel
rail connections.
(10) Verify that hose connections to all ports of
vacuum fittings on intake manifold are tight and not
leaking.
Fig. 11 Oxygen SensorsFig. 12 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
1 - PCM MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
3 - (3) 32±WAY CONNECTORS
Fig. 13 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
1 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
14 - 32 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE (Continued)
Page 1332 of 2255

(11) Inspect accelerator cable, transmission throt-
tle cable (if equipped) and cruise control cable con-
nections (if equipped). Check their connections to the
throttle arm of throttle body for any binding or
restrictions.
(12) If equipped with vacuum brake booster, verify
that vacuum booster hose is firmly connected to fit-
ting on intake manifold. Also check connection to
brake vacuum booster.
(13) Inspect the air cleaner inlet and air cleaner
element for dirt or restrictions.
(14) Inspect radiator grille area, radiator fins and
air conditioning condenser for restrictions.
(15) Verify that the intake manifold air tempera-
ture sensor wire connector is firmly connected to har-
ness connector (Fig. 15).(16) Verify that MAP sensor electrical connector is
firmly connected to MAP sensor (Fig. 16).
(17) Verify that fuel injector wire harness connec-
tors are firmly connected to injectors in the correct
order. Each harness connector is numerically tagged
with the injector number (INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.) of its
corresponding fuel injector and cylinder number.
(18) Verify harness connectors are firmly con-
nected to idle air control (IAC) motor and throttle
position sensor (TPS).
(19) Verify that wire harness connector is firmly
connected to the engine coolant temperature sensor
(Fig. 17).
Fig. 14 Ignition Coil PackÐ8.0L Engine
Fig. 15 Air Temperature SensorÐ8.0L Engine
1 - INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR TEMP. SENSOR
2 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
Fig. 16 Map Sensor Ð8.0L Engine
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - THROTTLE BODY
Fig. 17 Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐ8.0L
Engine
1 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMP. SENSOR
2 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
3 - GENERATOR
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 33
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE (Continued)
Page 1336 of 2255

INSTALLATION
(1) Position pedal/bracket assembly over pivot pin
(Fig. 22) .
(2) Install two new pivots/bushings. Using large
pliers, press both bushings together until they bot-
tom on sides of pedal/bracket assembly. Bushing
retaining ears will snap into position when properly
installed.
(3) From inside vehicle, hold up accelerator pedal.
Install throttle cable core wire and plastic cable
retainer into and through upper end of pedal arm
(the plastic retainer is snapped into pedal arm).
When installing plastic retainer to accelerator pedal
arm, note index tab on pedal arm (Fig. 21) . Align
index slot on plastic cable retainer to this index tab.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 5.9L
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is located
near the outer edge of the flywheel (starter ringear).
DESCRIPTION - 8.0L
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is located on
the right-lower side of the cylinder block, forward of
the right engine mount, just above the oil pan rail
(Fig. 23).
OPERATION
OPERATION - 5.9L
Engine speed and crankshaft position are provided
through the CKP sensor. The sensor generates pulses
that are the input sent to the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The PCM interprets the sensor input
to determine the crankshaft position. The PCM then
uses this position, along with other inputs, to deter-
mine injector sequence and ignition timing.
The sensor is a hall effect device combined with an
internal magnet. It is also sensitive to steel within a
certain distance from it.
On 5.9L V-8 engines, the flywheel/drive plate has 8
single notches, spaced every 45 degrees, at its outer
edge (Fig. 24).
The notches cause a pulse to be generated when
they pass under the sensor. The pulses are the input
to the PCM. For each engine revolution, there are 8
pulses generated on V-8 engines.
The engine will not operate if the PCM does not
receive a CKP sensor input.
Fig. 22 Accelerator PedalÐRemoval or Installation
1 - PEDAL MOUNTING BRACKET
2 - PIVOTS/BUSHINGS
3 - PEDAL/BRACKET
4 - PIVOT PIN
Fig. 23 CKP Sensor LocationÐ8.0L V-10 Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - HOLE
3 - OIL FILTER
4 - PLASTIC TIE STRAP
5 - PIGTAIL HARNESS
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 37
ACCELERATOR PEDAL (Continued)
Page 1338 of 2255

REMOVAL - 8.0L
The crankshaft position sensor is located on the
right-lower side of the cylinder block, forward of the
right engine mount, just above the oil pan rail (Fig.
27).
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Disconnect sensor pigtail harness from main
engine wiring harness.
(3) Remove sensor mounting bolt (Fig. 28).
(4) Cut plastic tie strap (Fig. 27) securing sensor
pigtail harness to side of engine block.
(5) Carefully pry sensor from cylinder block in a
rocking action with two small screwdrivers.
(6) Remove sensor from vehicle.
(7) Check condition of sensor o-ring (Fig. 29).
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 5.9L
(1) Position crankshaft position sensor to engine.
(2) Install mounting bolts and tighten to 8 N´m (70
in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect main harness electrical connector to
sensor.
(4) Install air cleaner tube.
INSTALLATION - 8.0L
The crankshaft position sensor is located on the
right-lower side of the cylinder block, forward of the
right engine mount, just above the oil pan rail (Fig.
27).
(1) Apply a small amount of engine oil to sensor
o-ring (Fig. 29).
(2) Install sensor into cylinder block with a slight
rocking action. Do not twist sensor into position as
damage to o-ring may result.
Fig. 27 Crankshaft Position Sensor LocationÐ8.0L
V-10 Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - HOLE
3 - OIL FILTER
4 - PLASTIC TIE STRAP
5 - PIGTAIL HARNESS
Fig. 28 Sensor Removal/InstallationÐ8.0L V-10
Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLT
3 - SENSOR POSITIONED FLUSH TO CYLINDER BLOCK
Fig. 29 Sensor O-RingÐ8.0L V-10 Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR O-RING
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - PIGTAIL HARNESS
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 39
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1344 of 2255

(2) Clean the area around the sensor before
removal.
(3) Remove the two sensor mounting bolts.
(4) Remove the sensor from the intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 5.9L
The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
throttle body (Fig. 35). An L-shaped rubber fitting is
used to connect the MAP sensor to throttle body (Fig.
36).
(1) Install rubber L-shaped fitting to MAP sensor.
(2) Position sensor to throttle body while guiding
rubber fitting over throttle body vacuum nipple.
(3) Install MAP sensor mounting bolts (screws).
Tighten screws to 3 N´m (25 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install air cleaner.
INSTALLATION - 8.0L
The MAP sensor is mounted into the right upper
side of the intake manifold (Fig. 37). A rubber gasket
is used to seal the sensor to the intake manifold. The
rubber gasket is part of the sensor and is not ser-
viced separately.
(1) Check the condition of the sensor seal. Clean
the sensor and lubricate the rubber gasket with clean
engine oil.
(2) Clean the sensor opening in the intake mani-
fold.
(3) Install the sensor into the intake manifold.
(4) Install sensor mounting bolts. Tighten bolts to
2 N´m (20 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install the electrical connector to sensor.
O2 SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Oxygen Sensors (O2S) are attached to, and
protrude into the vehicle exhaust system. Depending
on the emission package, the vehicle may use a total
of either 2 or 4 sensors.
Medium and Heavy Duty 8.0L V-10 Engine:
Four sensors are used (2 upstream, 1 pre-catalyst
and 1 post-catalyst). With this emission package, the
1/1 upstream sensor (left side) is located in the left
exhaust downpipe before both the pre-catalyst sensor
(1/2), and the main catalytic convertor. The 2/1
upstream sensor (right side) is located in the right
exhaust downpipe before both the pre-catalyst sensor
(1/2), and the main catalytic convertor. The pre-cata-
lyst sensor (1/2) is located after the 1/1 and 2/1 sen-
sors, and just before the main catalytic convertor.
The post-catalyst sensor (1/3) is located just after the
main catalytic convertor.
Heavy Duty 5.9L Engine:Two sensors are used.
They arebothreferred to as upstream sensors (left
side is referred to as 1/1 and right side is referred to
as 2/1). With this emission package, a sensor is
located in each of the exhaust downpipes before the
main catalytic convertor.
OPERATION
An O2 sensor is a galvanic battery that provides
the PCM with a voltage signal (0-1 volt) inversely
proportional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
In other words, if the oxygen content is low, the volt-
age output is high; if the oxygen content is high the
output voltage is low. The PCM uses this information
to adjust injector pulse-width to achieve the
14.7±to±1 air/fuel ratio necessary for proper engine
operation and to control emissions.
The O2 sensor must have a source of oxygen from
outside of the exhaust stream for comparison. Cur-
rent O2 sensors receive their fresh oxygen (outside
air) supply through the O2 sensor case housing.
Four wires (circuits) are used on each O2 sensor: a
12±volt feed circuit for the sensor heating element; a
ground circuit for the heater element; a low-noise
sensor return circuit to the PCM, and an input cir-
cuit from the sensor back to the PCM to detect sen-
sor operation.
Oxygen Sensor Heaters/Heater Relays:
Depending on the emissions package, the heating ele-
ments within the sensors will be supplied voltage
from either the ASD relay, or 2 separate oxygen sen-
sor relays. Refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams to determine
which relays are used.
The O2 sensor uses a Positive Thermal Co-efficient
(PTC) heater element. As temperature increases,
resistance increases. At ambient temperatures
Fig. 37 MAP Sensor LocationÐ8.0L V-10 EngineÐ
Typical
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - THROTTLE BODY
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 45
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1352 of 2255
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL INJECTOR
To perform a complete test of the fuel injectors and
their circuitry, use the DRB scan tool and refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the injector only, refer to the following:
Disconnect the fuel injector wire harness connector
from the injector. The injector is equipped with 2
electrical terminals (pins). Place an ohmmeter across
the terminals. Resistance reading should be approxi-
mately 12 ohms 1.2 ohms at 20ÉC (68ÉF).
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(2) Remove fuel injector rail assembly. Refer to
Fuel Injector Rail removal in this section.
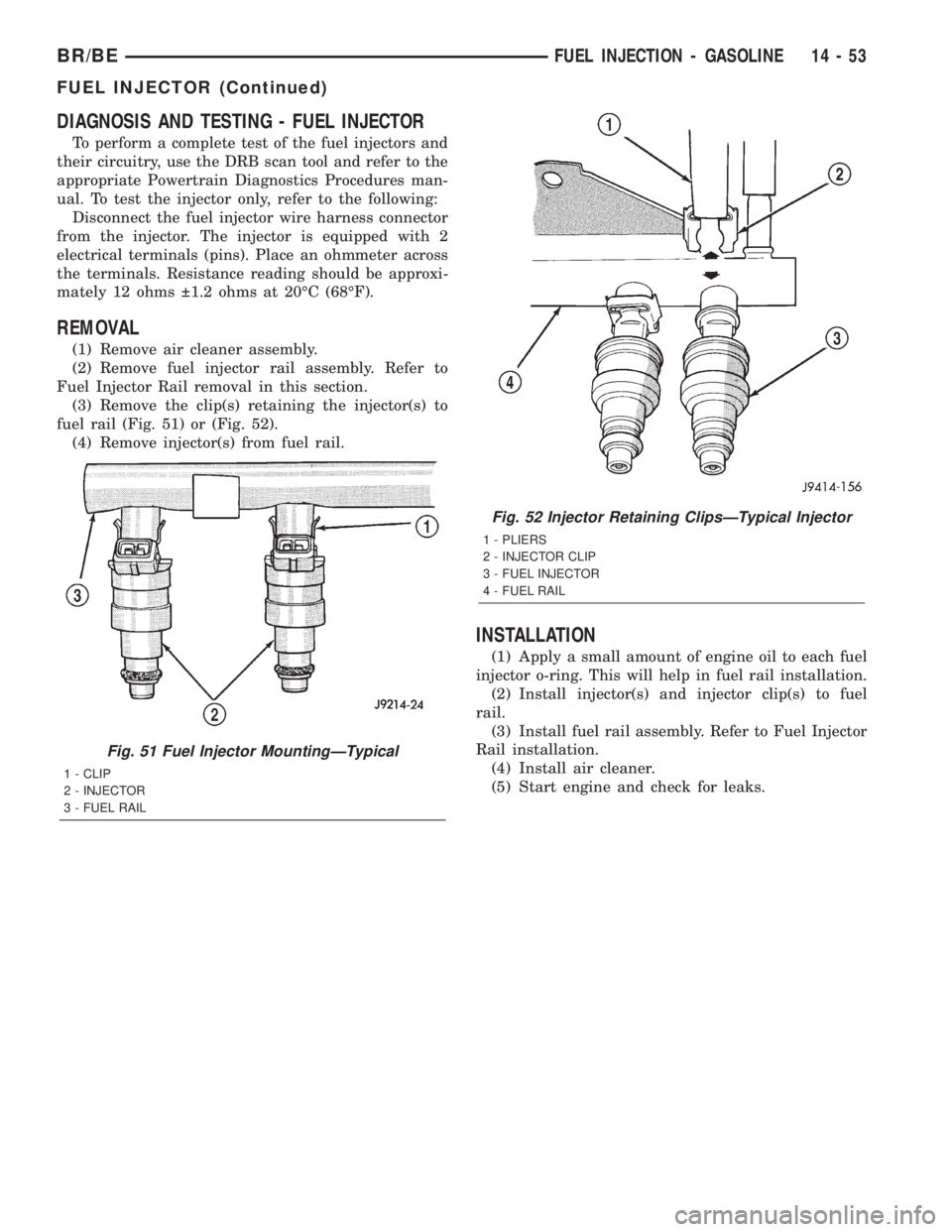
(3) Remove the clip(s) retaining the injector(s) to
fuel rail (Fig. 51) or (Fig. 52).
(4) Remove injector(s) from fuel rail.
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a small amount of engine oil to each fuel
injector o-ring. This will help in fuel rail installation.
(2) Install injector(s) and injector clip(s) to fuel
rail.
(3) Install fuel rail assembly. Refer to Fuel Injector
Rail installation.
(4) Install air cleaner.
(5) Start engine and check for leaks.
Fig. 51 Fuel Injector MountingÐTypical
1 - CLIP
2 - INJECTOR
3 - FUEL RAIL
Fig. 52 Injector Retaining ClipsÐTypical Injector
1 - PLIERS
2 - INJECTOR CLIP
3 - FUEL INJECTOR
4 - FUEL RAIL
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 53
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1355 of 2255

Fig. 1 FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS - DIESEL
1 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR 14 - FUEL SUPPLY LINE (LOW-PRESSURE, TO ENGINE)
2 - THROTTLE LEVER BELLCRANK AND APPS (ACCELERATOR
PEDAL POSITION SENSOR)15 - FUEL TRANSFER (LIFT) PUMP
3 - INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR HEATER/ELEMENTS 16 - OIL PRESSURE SENSOR
4 - HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES 17 - FUEL FILTER/WATER SEPARATOR
5 - FUEL HEATER 18 - DRAIN TUBE
6 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST PORT 19 - WATER-IN-FUEL (WIF) SENSOR
7 - MAP (BOOST) SENSOR 20 - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
8 - FUEL INJECTORS 21 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST PORT
9 - FUEL INJECTOR CONNECTOR 22 - CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (CMP)
10 - INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSOR 23 - OVERFLOW VALVE
11 - FUEL DRAIN MANIFOLD 24 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP
12 - DRAIN VALVE 25 - FUEL HEATER TEMPERATURE SENSOR (THERMOSTAT)
13 - FUEL RETURN LINE (TO FUEL TANK)
14 - 56 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1356 of 2255

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL SYSTEM AIR
LEAK VACUUM TEST
The proceeding test will determine if a fuel system
air leak exists at the engine. Air leaks will cause
hard starting and/or poor performance.
A hand-operated vacuum pump/gauge equipped
with a remote or built-on fluid container will be used.
A typical hand-operated pump is shown in (Fig. 2).
The use of a hand-operated pumpwitha fluid con-
tainer will prevent fuel oil from entering and possibly
damaging pump. Two rubber caps (one 5/16º and one
3/8º) will also be used to temporarily plug / seal fuel
system.
Vacuum Test Set-Up, Specifications and
Conditions
²Examine all engine fuel system components, fit-
tings, lines and hoses for visual evidence of fuel leak-
age. Repair as necessary before proceeding.
²Be sure gauge on your hand-operated pump is
accurate and pump does not leak. Perform a simple
test on pump. Add a 3 foot section (minimum) of
clear plastic hose to the pump.
²Apply maximum 15-20 inches of vacuum for
tests.
²System should hold 15-20 inches of vacuum for 5
continuous minutes. After 5 minutes, vacuum should
not drop more than 0.1 inch Hg for 1 minute.²Disconnect fuel supply and return lines (quick-
connects) at rear of engine (Fig. 3).
²Drain as much fuel as possible from engine fuel
lines. Also, completely drain fuel filter/water separa-
tor housing. Refer to Fuel Filter/Water Separator
Removal and Installation for fuel draining proce-
dures. This step must be done to prevent liquid fuel
from entering and possibly damaging your hand-op-
erated pump.
Testing All Engine Fuel System Components Together
This test will indicate an air leak is present some-
where on the engine.
(1) Be sure water drain valve is securely closed.
(2) Examine all engine fuel system components,
fittings, lines and hoses for visual evidence of fuel
leakage. Repair as necessary.
(3) Install 5/16º rubber cap to fuel return line on
engine (Fig. 4).
(4) Install hand-operated vacuum pump to fuel
supply line on engine (Fig. 4).
(5) Perform vacuum test. Be careful not to allow
liquid fuel to get into your hand-operated vacuum
pump.
(6) Vacuum holds ? End of test; no leaks found on
engine.
(7) Vacuum leak ? Proceed. The following tests will
isolate the component that is leaking.
Fig. 2 HAND-OPERATED VACUUM PUMP (TYPICAL)
1 - PUMP
2 - CONTAINER
Fig. 3 QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS LOCATION
1 - FUEL SUPPLY LINE
2 - SUPPORT BRACKET BOLT
3 - FUEL RETURN LINE
4 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS (2)
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 57