2002 DODGE RAM engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 1406 of 2255

REMOVAL - DIESEL
The IAT sensor is located in the left/rear side of
the intake manifold (Fig. 32).
The IAT sensor is located in the left/rear side of
the intake manifold (Fig. 32).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from IAT sensor
(Fig. 32).
(2) Remove IAT sensor from intake manifold (Fig.
33).
(3) Discard sensor o-ring (Fig. 33).
INSTALLATION - DIESEL
The IAT sensor is located in the left/rear side of
the intake manifold (Fig. 32).
(1) Clean sensor mounting hole (Fig. 33) of rust or
contaminants.
(2) Install new o-ring to sensor. Apply clean engine
oil to sensor o-ring and sensor threads.
(3) Install IAT sensor into intake manifold.
Tighten to 14 N´m (10 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect sensor electrical connector.
Fig. 31 Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
Location
1 - MANIFOLD AIR PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR
2 - REAR OF CYLINDER HEAD
3 - IAT SENSOR
4 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
Fig. 32 IAT Sensor
1 - SENSOR MOUNTING HOLES
2 - O-RING
3 - IAT SENSOR
4 - MAP SENSOR
5 - O-RING
Fig. 33 Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
Location
1 - MANIFOLD AIR PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR
2 - REAR OF CYLINDER HEAD
3 - IAT SENSOR
4 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 107
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1407 of 2255

MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL
The MAP sensor is installed into the rear of the
intake manifold (Fig. 31).
OPERATION - DIESEL
The MAP sensor reacts to air pressure changes in
the intake manifold. It provides an input voltage to
the Engine Control Module (ECM). As pressure
changes, MAP sensor voltage will change. The
change in MAP sensor voltage results in a different
input voltage to the ECM. The ECM uses this input,
along with inputs from other sensors to provide fuel
timing, fuel control and engine protection. Engine
protection is used to derate (drop power off) the
engine if turbocharger pressure becomes to high.
REMOVAL - DIESEL
The MAP sensor is located in the left/rear side of
the intake manifold (Fig. 34).
The MAP sensor is located in the left/rear side of
the intake manifold (Fig. 34).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from MAP sen-
sor (Fig. 34).
(2) Remove MAP sensor from intake manifold (Fig.
35).
(3) Discard sensor o-ring (Fig. 35).
INSTALLATION
The MAP sensor is located in the left/rear side of
the intake manifold (Fig. 34).
(1) Clean sensor mounting hole (Fig. 35) of rust or
contaminants.
(2) Install new o-ring to sensor. Apply clean engine
oil to sensor o-ring and sensor threads.
(3) Install MAP sensor into intake manifold.
Tighten to 14 N´m (10 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect sensor electrical connector.
PTO SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
OPERATION
This Engine Control Module (ECM) input is used
only on models equipped with aftermarket Power
Take Off (PTO) units.
The input is used to tell the ECM that the PTO
has been engaged. When engaged, the ECM will dis-
able certain OBD II functions until the PTO has been
turned off.
Fig. 34 MAP Sensor Location
1 - MANIFOLD AIR PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR
2 - REAR OF CYLINDER HEAD
3 - IAT SENSOR
4 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
Fig. 35 MAP Sensor Removal/Installation
1 - SENSOR MOUNTING HOLES
2 - O-RING
3 - IAT SENSOR
4 - MAP SENSOR
5 - O-RING
14 - 108 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELBR/BE
Page 1442 of 2255

PUMP
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................33
OPERATION...........................33
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PUMP LEAKAGE . 33
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER
STEERING PUMP - INITIAL OPERATION....33
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUSHING
POWER STEERING SYSTEM............34
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - GASOLINE ENGINE..........35
REMOVAL - DIESEL ENGINE............36
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - GASOLINE ENGINE......37INSTALLATION - DIESEL ENGINE.........37
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING PUMP..............38
PULLEY
REMOVAL.............................38
INSTALLATION.........................39
HOSES - PRESSURE
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................39
HOSES - RETURN
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................39
PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The P-Series pump is used on these vehicles (Fig.
1). The pump shaft has a pressed-on pulley that is
belt driven by the crankshaft pulley on gasoline
engines. The pump is driven off the back of the vac-
uum pump on the diesel engine.
Trailer tow option vehicles are equipped with a
power steering pump oil cooler. The oil cooler is
mounted to the front crossmember.
NOTE: Power steering pumps are not interchange-
able with pumps installed on other vehicles.
OPERATION
Hydraulic pressure is provided by the pump for the
power steering gear. The power steering pump is a
constant flow rate and displacement, vane-type
pump. The pump is connected to the steering gear
via the pressure hose and the return hose. On vehi-
cles equipped with a hydraulic booster, the pump
supplies the hydraulic pressure for the booster.
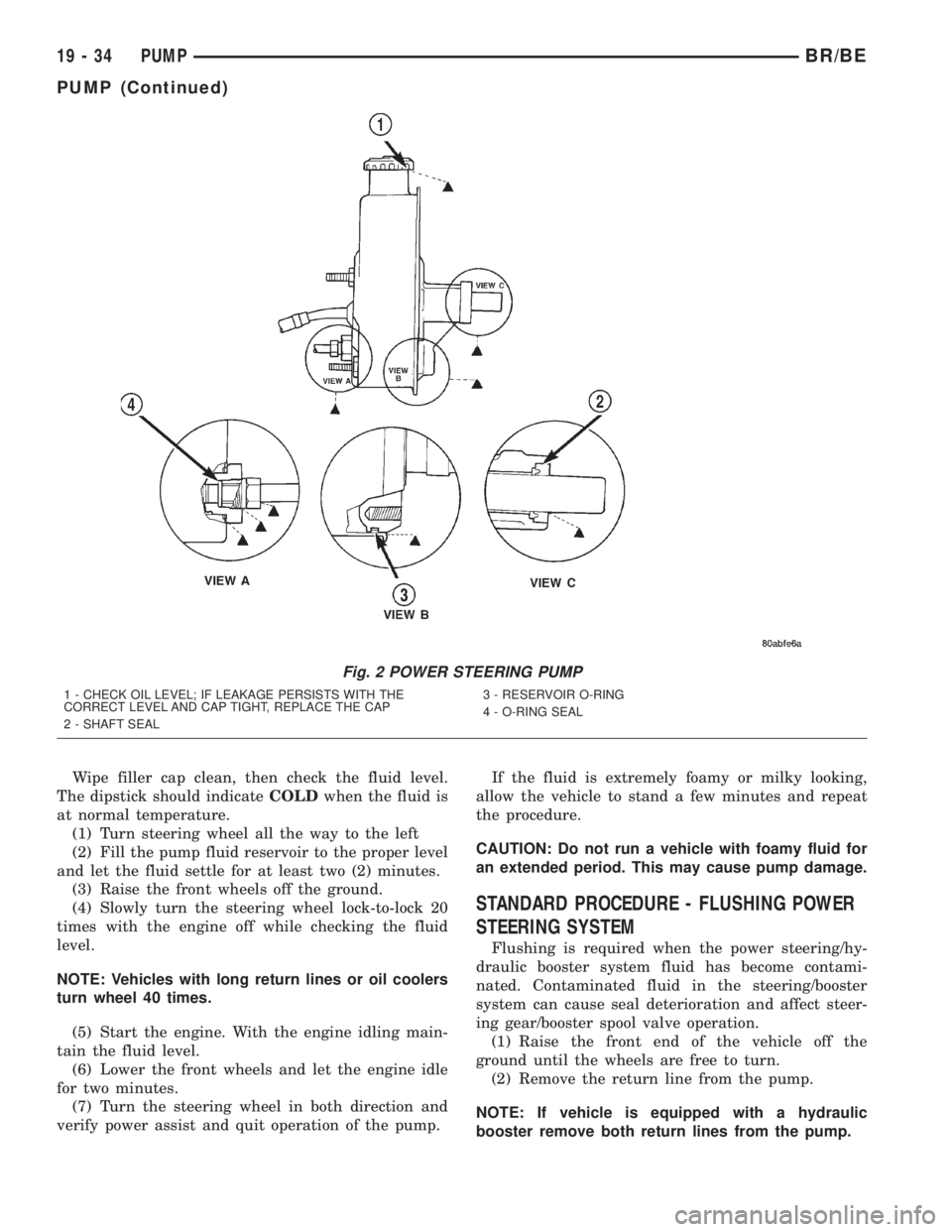
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PUMP LEAKAGE
(1) Possible pump leakage areas. (Fig. 2).
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER STEERING
PUMP - INITIAL OPERATION
WARNING: THE FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE
CHECKED WITH ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT INJURY
FROM MOVING COMPONENTS.
CAUTION: Use MOPAR Power Steering Fluid or
equivalent. Do not use automatic transmission fluid
and do not overfill.
Fig. 1 P-SeriesÐPump
1 - RESERVOIR CAP AND DIPSTICK
2 - RESERVOIR
BR/BEPUMP 19 - 33
Page 1443 of 2255
Wipe filler cap clean, then check the fluid level.
The dipstick should indicateCOLDwhen the fluid is
at normal temperature.
(1) Turn steering wheel all the way to the left
(2) Fill the pump fluid reservoir to the proper level
and let the fluid settle for at least two (2) minutes.
(3) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(4) Slowly turn the steering wheel lock-to-lock 20
times with the engine off while checking the fluid
level.
NOTE: Vehicles with long return lines or oil coolers
turn wheel 40 times.
(5) Start the engine. With the engine idling main-
tain the fluid level.
(6) Lower the front wheels and let the engine idle
for two minutes.
(7) Turn the steering wheel in both direction and
verify power assist and quit operation of the pump.If the fluid is extremely foamy or milky looking,
allow the vehicle to stand a few minutes and repeat
the procedure.
CAUTION: Do not run a vehicle with foamy fluid for
an extended period. This may cause pump damage.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUSHING POWER
STEERING SYSTEM
Flushing is required when the power steering/hy-
draulic booster system fluid has become contami-
nated. Contaminated fluid in the steering/booster
system can cause seal deterioration and affect steer-
ing gear/booster spool valve operation.
(1) Raise the front end of the vehicle off the
ground until the wheels are free to turn.
(2) Remove the return line from the pump.
NOTE: If vehicle is equipped with a hydraulic
booster remove both return lines from the pump.
Fig. 2 POWER STEERING PUMP
1 - CHECK OIL LEVEL; IF LEAKAGE PERSISTS WITH THE
CORRECT LEVEL AND CAP TIGHT, REPLACE THE CAP
2 - SHAFT SEAL3 - RESERVOIR O-RING
4 - O-RING SEAL
19 - 34 PUMPBR/BE
PUMP (Continued)
Page 1445 of 2255

REMOVAL - DIESEL ENGINE
(1) Remove and cap steering pump hoses and vac-
uum pump vacuum line.
(2) Remove the sender unit from engine block and
plug hole in block (Fig. 5).
(3) Remove the serpentine belt, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove and cap the oil feed line from the bot-
tom of the vacuum pump (Fig. 6).
(5) Remove the lower bolt that attaches the vacu-
um/steering pump assembly to the engine block.
Remove the nut from the steering pump attaching
bracket (Fig. 6).
(6) Remove upper bolt from the pump assembly
(Fig. 7) and remove the assembly.
(7) Remove the mounting gasket.
(8) Remove the steering pump to vacuum pump
bracket attaching nuts (Fig. 8).
(9) Slide the steering pump from the bracket. Use
care not to damage the internal oil seal in the vac-
uum pump (Fig. 9).
(10) Remove the two pump body spacers.
Fig. 5 Oil Pressure Sending Unit
1 - OIL PRESSURE SENDER UNIT
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - ENGINE BLOCK
4 - STEERING PUMP
Fig. 6 Oil
1 - ENGINE BLOCK
2 - LOWER PUMP ASSEMBLY BOLT
3 - STEERING PUMP BRACKET ATTACHING NUT
4 - BATTERY GROUND CABLE
5 - OIL FEED LINE
Fig. 7 Pump Assembly Upper Bolt
1 - PUMP UPPER BOLT
2 - DRIVE COVER
19 - 36 PUMPBR/BE
PUMP (Continued)
Page 1446 of 2255

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - GASOLINE ENGINE
(1) Install the front pump bracket and tighten
bolts to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.). On 8.0L engine install
rear pump bracket and tighten nut to 47 N´m (35 ft.
lbs.), tighten bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install the pump pulley with Installer
C-4063±B, (Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP/PULLEY
- INSTALLATION).
(3) Install steering pump assembly on the engine
block. Install the upper stud and bolt in bracket.
(4) Pivot the pump down past the coolant tube and
install the lower bolts in bracket.
(5) Tighten the bolts and nut to 41 N´m (30 ft.
lbs.).
(6) Connect the hoses to the pump.
(7) Install the serpentine drive belt, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION), (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCES-
SORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLATION).
(8) Fill the reservoir with power steering fluid,
(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
INSTALLATION - DIESEL ENGINE
(1) Install the two pump body spacers.
(2) Rotate the drive gear until the steering pump
and vacuum pump drive dogs align. Install the steer-
ing pump onto the vacuum pump bracket. Use care
to avoid damaging the oil seal in the vacuum pump
during installation.The steering pump housing
and spacers must mate completely with the
vacuum pump bracket.
(3) Install the vacuum pump bracket to steering
pump nuts and tighten to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(4) Position new gasket on vacuum pump assem-
bly. Use sealer if necessary to retain the gasket.
(5) Align and install the pump assembly on the
engine. Ensure the steering pump stud is inserted
into the block bracket. Tighten the pump- to-engine
block attaching bolts to 77 N´m (57 ft. lbs.).
(6) Install the steering pump to attaching bracket
nut and tighten to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(7) Remove plug and install the oil pressure send-
ing unit and electrical connector.
(8) Install the oil feed line to the vacuum pump.
Tighten the oil line connection to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs./ 5
ft. lbs.).
Fig. 8 Bracket Mounting Nuts
1 - VACUUM PUMP
2 - ATTACHING NUTS
3 - STEERING PUMP
4 - PUMP SPACERS
5 - OIL FEED FITTING
Fig. 9 Steering Pump & Vacuum Pump
1 - PUMP SHAFT
2 - VACUUM FITTING
3 - VACUUM PUMP DRIVE
4 - OIL SEAL
5 - MOUNTING BRACKET
6 - DRIVE DOG
7 - PUMP SPACERS
BR/BEPUMP 19 - 37
PUMP (Continued)
Page 1456 of 2255

GEAR RATIOS
GEAR RATIO
FIRST 5.61:1
SECOND 3.04:1
THIRD 1.67:1
FOURTH 1.00:1
FIFTH 0.75:1
REVERSE 5.04:1
IDENTIFICATION
The transmission identification tag is attached to
the driver side PTO cover (Fig. 3).
The tag provides the transmission model number,
build date and part number. Be sure to reinstall the
I.D. tag if removed during service. The information
on the tag is essential to correct parts ordering.
OPERATION
The manual transmission receives power through
the clutch assembly from the engine. The clutch disc
is splined to the transmission input shaft and is
turned at engine speed at all times that the clutch is
engaged. The input shaft is connected to the trans-
mission countershaft through the mesh of fourth
speed gear on the input shaft and the fourth counter-
shaft gear. At this point all the transmission gears
are spinning.The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. This move-
ment moves the internal transmission shift compo-
nents to begin the shift sequence. As the shift lever
moves the selected shift rail, the shift fork attached
to that rail begins to move. The fork is positioned in
a groove in the outer circumference of the synchro-
nizer sleeve. As the shift fork moves the synchronizer
sleeve, the synchronizer begins to speed-up or slow
down the selected gear (depending on whether we are
up-shifting or down-shifting). The synchronizer does
this by having the synchronizer hub splined to the
mainshaft, or the countershaft in some cases, and
moving the blocker ring into contact with the gear's
friction cone. As the blocker ring and friction cone
come together, the gear speed is brought up or down
to the speed of the synchronizer. As the two speeds
match, the splines on the inside of the synchronizer
sleeve become aligned with the teeth on the blocker
ring and the friction cone and eventually will slide
over the teeth, locking the gear to the mainshaft, or
countershaft, through the synchronizer.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check. A correct lubricant level
check can only be made when the vehicle is level.
Also allow the lubricant to settle for a minute or so
before checking. These recommendations will ensure
an accurate check and avoid an underfill or overfill
condition. Always check the lubricant level after any
addition of fluid to avoid an incorrect lubricant level
condition.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, adaptor or extension housing, or from the front/
rear seals. A suspected leak could also be the result
of an overfill condition. Leaks at the rear of the
extension or adapter housing will be from the hous-
ing oil seals. Leaks at component mating surfaces
will probably be the result of inadequate sealer, gaps
in the sealer, incorrect bolt tightening or use of a
non-recommended sealer. A leak at the front of the
transmission will be from either the front bearing
retainer or retainer seal. Lubricant may be seen drip-
ping from the clutch housing after extended opera-
tion. If the leak is severe, it may also contaminate
the clutch disc causing the disc to slip, grab and or
chatter.
Fig. 3 Identification Tag Location
1 - PTO COVER
2 - I.D. TAG
BR/BEMANUAL - NV4500 21 - 3
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1542 of 2255

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
46RE
DESCRIPTION
The 46RE (Fig. 1) is a four speed fully automatic
transmissions with an electronic governor. The 46RE
is equipped with a lock-up clutch in the torque con-
verter. First through third gear ranges are provided
by the clutches, bands, overrunning clutch, and plan-
etary gear sets in the transmission. Fourth gear
range is provided by the overdrive unit that contains
an overdrive clutch, direct clutch, planetary gear set,
and overrunning clutch.The transmission contains a front, rear, and direct
clutch which function as the input driving compo-
nents. It also contains the kickdown (front) and the
low/reverse (rear) bands which, along with the over-
running clutch and overdrive clutch, serve as the
holding components. The driving and holding compo-
nents combine to select the necessary planetary gear
components, in the front, rear, or overdrive planetary
gear set, transfer the engine power from the input
shaft through to the output shaft.
The valve body is mounted to the lower side of the
transmission and contains the valves to control pres-
sure regulation, fluid flow control, and clutch/band
application. The oil pump is mounted at the front of
the transmission and is driven by the torque con-
verter hub. The pump supplies the oil pressure nec-
essary for clutch/band actuation and transmission
lubrication.
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 89