2002 DODGE RAM check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 1109 of 2255

LOWER SEAL
(1) Remove the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the oil pump (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the rear main bearing cap and discard
the old lower seal.
INSTALLATION
The service seal is a two piece, Viton seal. The
upper seal half can be installed with crankshaft
removed from engine or with crankshaft installed.
When a new upper seal is installed, install a new
lower seal. The lower seal half can be installed only
with the rear main bearing cap removed.
UPPER SEAL ÐCRANKSHAFT REMOVED
(1) Clean the cylinder block rear cap mating sur-
face. Be sure the seal groove is free of debris. Check
for burrs at the oil hole on the cylinder block mating
surface to rear cap.
(2) Lightly oil the new upper seal lips with engine
oil.
(3) Install the new upper rear bearing oil seal with
the white paint facing toward the rear of the engine.
(4) Position the crankshaft into the cylinder block.
(5) Lightly oil the new lower seal lips with engine
oil.
(6) Install the new lower rear bearing oil seal into
the bearing cap with the white paint facing towards
the rear of the engine.
(7) Apply 5 mm (0.20 in.) drop of MopartGasket
Maker, or equivalent, on each side of the rear main
bearing cap (Fig. 31). DO NOT over-apply sealant or
allow the sealant to contact the rubber seal. Assem-
ble bearing cap to cylinder block immediately after
sealant application.
(8) To align the bearing cap, use cap slot, align-
ment dowel, and cap bolts. DO NOT remove excess
material after assembly. DO NOT strike rear cap
more than two times for proper engagement.
(9) Clean and oil all cap bolts. Install all main
bearing caps. Install all cap bolts and alternately
tighten to 115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) Install oil pump (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PUMP - INSTALLATION).
(11) Apply MopartGEN II Silicone Rubber Adhe-
sive Sealant, or equivalent, at bearing cap-to-block
joint to provide cap to block and oil pan sealing (Fig.
32). Apply enough sealant so that a small amount is
squeezed out. Withdraw nozzle and wipe excess seal-
ant off the oil pan seal groove.
(12) Install new front crankshaft oil seal (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT OIL
SEAL - FRONT - INSTALLATION).(13) Immediately install the oil pan (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
UPPER SEALÐCRANKSHAFT INSTALLED
(1) Clean the cylinder block mating surfaces before
oil seal installation. Check for burrs at the oil hole on
the cylinder block mating surface to rear cap.
(2) Lightly oil the new upper seal lips with engine
oil. To allow ease of installation of the seal, loosen at
least the two main bearing caps forward of the rear
bearing cap.
Fig. 31 Sealant Application to Bearing Cap
1 - MOPAR SILICONE RUBBER ADHESIVE SEALANT SLOTS
2 - MOPARTGASKET MAKER (OR EQUIVALENT)
3 - CAP ALIGNMENT SLOT
4 - REAR MAIN BEARING CAP
Fig. 32 Apply Sealant to Bearing Cap-to-Block Joint
1 - MOPAR SILICONE RUBBER ADHESIVE SEALANT NOZZLE
TIP
2 - SEALANT APPLIED
3 - CYLINDER BLOCK
4 - REAR MAIN BEARING CAP
9 - 34 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR (Continued)
Page 1111 of 2255

CAUTION: This procedure MUST be followed when
installing a new bushing or seizure to shaft may
occur.
(4) Install the intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the distributor (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/DISTRIBUTOR -
INSTALLATION).
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐHYDRAULIC
TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, check the oil pressure. If vehicle
has no oil pressure gauge, install a reliable gauge at
the pressure sending-unit. The pressure should be
between 207-552 kPa (30-80 psi) at 3,000 RPM.
Check the oil level after the engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize
oil level, check dipstick. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the FULL mark or below the
ADD OIL mark on dipstick. Either of these two con-
ditions could be responsible for noisy tappets.
OIL LEVEL
HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark, it is possible
for the connecting rods to dip into the oil. With the
engine running, this condition could create foam in
the oil pan. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the
hydraulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to
lose length and allow valves to seat noisily.
LOW
Low oil level may allow oil pump to take in air.
When air is fed to the tappets, they lose length,
which allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on
intake side of oil pump through which air can be
drawn will create the same tappet action. Check the
lubrication system from the intake strainer to the
pump cover, including the relief valve retainer cap.
When tappet noise is due to aeration, it may be
intermittent or constant, and usually more than one
tappet will be noisy. When oil level and leaks have
been corrected, operate the engine at fast idle. Run
engine for a sufficient time to allow all of the air
inside the tappets to be bled out.
TAPPET NOISE DIAGNOSIS
(1) To determine source of tappet noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed.
(2) Feel each valve spring or rocker arm to detect
noisy tappet. The noisy tappet will cause the affected
spring and/or rocker arm to vibrate or feel rough in
operation.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is
the case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
(3)
Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger, or by the
plunger partially sticking in the tappet body cylinder.
The tappet should be replaced. A heavy click is caused
by a tappet check valve not seating, or by foreign par-
ticles wedged between the plunger and the tappet
body. This will cause the plunger to stick in the down
position. This heavy click will be accompanied by
excessive clearance between the valve stem and rocker
arm as valve closes. In either case, tappet assembly
should be removed for inspection and cleaning.
(4) The valve train generates a noise very much
like a light tappet noise during normal operation.
Care must be taken to ensure that tappets are mak-
Fig. 34 Distributor Driveshaft Bushing Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3053
2 - BUSHING
Fig. 35 Burnishing Distributor Driveshaft Bushing
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3053
2 - BUSHING
9 - 36 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
DISTRIBUTOR BUSHING (Continued)
Page 1113 of 2255

(8) Start and operate engine. Warm up to normal
operating temperature.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to valve mechanism,
engine must not be run above fast idle until all
hydraulic tappets have filled with oil and have
become quiet.
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The pistons are made of aluminum and have three
ring grooves, the top two grooves are for the compres-
sion rings and the bottom groove is for the oil control
ring. The connecting rods are forged steel and are
coined prior to heat treat. The piston pins are press
fit.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON FITTING
Piston and cylinder wall must be clean and dry.
Specified clearance between the piston and the cylin-
der wall is 0.013-0.038 mm (0.0005-0.0015 inch) at
21ÉC (70ÉF).
Piston diameter should be measured at the top of
skirt, 90É to piston pin axis. Cylinder bores should be
measured halfway down the cylinder bore and trans-
verse to the engine crankshaft center line.
Pistons and cylinder bores should be measured at
normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
Check the pistons for taper and elliptical shape
before they are fitted into the cylinder bore (Fig. 37).
PISTON MEASUREMENT CHART
PISTON A DIA = PISTON BORE
SIZE DIAMETER DIAMETER
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX.
mm
(in.)mm
(in.)mm
(in.)mm (in.)
AÐÐÐ Ð
B101.580 101.592 101.605 101.618
(3.9992) (3.9997) (4.0002) (4.0007)
C101.592 101.605 101.618 101.630
(3.9997) (4.0002) (4.0007) (4.0012)
D101.605 101.618 101.630 101.643
(4.0002) (4.0007) (4.0012) (4.0017)
EÐÐÐ Ð
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
PISTON PIN BORE 25.007 - 25.015 mm
(.9845 - .9848 in.)
RING GROOVE
HEIGHT
OIL RAIL 4.033 - 4.058 mm
(.1588 - .1598 in.)
COMPRESSION
RAIL1.529 - 1.554 mm
(.0602 - .0612 in.)
TOTAL FINISHED 470.8 2 grams
WEIGHT (16.607 .0706 ounces)
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the engine from the vehicle (Refer to 9
- ENGINE - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove top ridge of cylinder bores with a reli-
able ridge reamer before removing pistons from cyl-
inder block. Be sure to keep tops of pistons covered
during this operation.
(5) Be sure each connecting rod and connecting rod
cap is identified with the cylinder number. Remove
connecting rod cap. Install connecting rod bolt guide
set on connecting rod bolts.
Fig. 37 Piston Measurements
1 - 49.53 mm
(1.95 IN.)
9 - 38 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (Continued)
Page 1114 of 2255

(6) Pistons and connecting rods must be removed
from top of cylinder block. When removing the
assemblies from the engine, rotate crankshaft so that
the connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore and at
BDC.Be careful not to nick crankshaft journals.
(7) After removal, install bearing cap on the mat-
ing rod.
CLEANING
Clean the piston and connecting rod assembly
using a suitable solvent.
INSPECTION
Check the connecting rod journal for excessive
wear, taper and scoring (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the connecting rod for signs of twist or bend-
ing.
Check the piston for taper and elliptical shape
before it is fitted into the cylinder bore (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON & CONNECT-
ING ROD - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the piston for scoring, or scraping marks in
the piston skirts. Check the ring lands for cracks
and/or deterioration.
INSTALLATION
(1) Be sure that compression ring gaps are stag-
gered so that neither is in line with oil ring rail gap.
(2) Before installing the ring compressor, be sure
the oil ring expander ends are butted and the rail
gaps located properly (Fig. 38).(3) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil. Slide Piston Ring Compressor Tool C-385
over the piston and tighten with the special wrench
(part of Tool C-385).Be sure position of rings
does not change during this operation.
(4) Install connecting rod bolt protectors on rod
bolts. The long protector should be installed on the
numbered side of the connecting rod.
(5) Rotate crankshaft so that the connecting rod
journal is on the center of the cylinder bore. Be sure
connecting rod and cylinder bore number are the
same. Insert rod and piston into cylinder bore and
guide rod over the crankshaft journal.
(6) Tap the piston down in cylinder bore, using a
hammer handle. At the same time, guide connecting
rod into position on crankshaft journal.
(7) The notch, or groove, on top of piston must be
pointing toward front of engine. The larger chamfer
of the connecting rod bore must be installed toward
crankshaft journal fillet.
(8) Install rod caps. Be sure connecting rod, con-
necting rod cap, and cylinder bore number are the
same. Install nuts on cleaned and oiled rod bolts and
tighten nuts to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(10) Install the cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
(11) Install the engine into the vehicle (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - INSTALLATION).
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING
(1) Measurement of end gaps:
(a) Measure piston ring gap 2 in. from bottom of
cylinder bore. An inverted piston can be used to
push the rings down to ensure positioning rings
squarely in the cylinder bore before measuring.
(b) Insert feeler gauge in the gap. The top com-
pression ring gap should be between 0.254-0.508
mm (0.010-0.020 in.). The second compression ring
gap should be between 0.508-0.762 mm
(0.020-0.030 in.). The oil ring gap should be 0.254-
1.270 mm (0.010-0.050 in.).
(c) Rings with insufficient end gap may be prop-
erly filed to the correct dimension. Rings with
excess gaps should not be used.
(2) Install rings, and confirm ring side clearance:
(a) Install oil rings being careful not to nick or
scratch the piston. Install the oil control rings
according to instructions in the package. It is not
necessary to use a tool to install the upper and
Fig. 38 Proper Ring Installation
1 - OIL RING SPACER GAP
2 - SECOND COMPRESSION RING GAP OIL RING RAIL GAP
(TOP)
3 - OIL RING RAIL GAP (BOTTOM)
4 - TOP COMPRESSION RING GAP
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 39
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1118 of 2255

tappets, which pass oil through hollow push rods to a
hole in the corresponding rocker arm. Oil from the
rocker arm lubricates the valve train components.The oil then passes down through the push rod guide
holes and the oil drain-back passages in the cylinder
head, past the valve tappet area, and then returns to
the oil pan (Fig. 49).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
LEAKS
Begin with a through visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil-soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
be sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light source.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
Fig. 47 Engine Rear Support Cushion Assemblies
Fig. 48 Positive Displacement Oil PumpÐTypical
1 - INNER ROTOR AND SHAFT
2 - BODY
3 - DISTRIBUTOR DRIVESHAFT (REFERENCE)
4 - COTTER PIN
5 - RETAINER CAP
6 - SPRING
7 - RELIEF VALVE
8 - LARGE CHAMFERED EDGE
9 - BOLT
10 - COVER
11 - OUTER ROTOR
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 43
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1123 of 2255
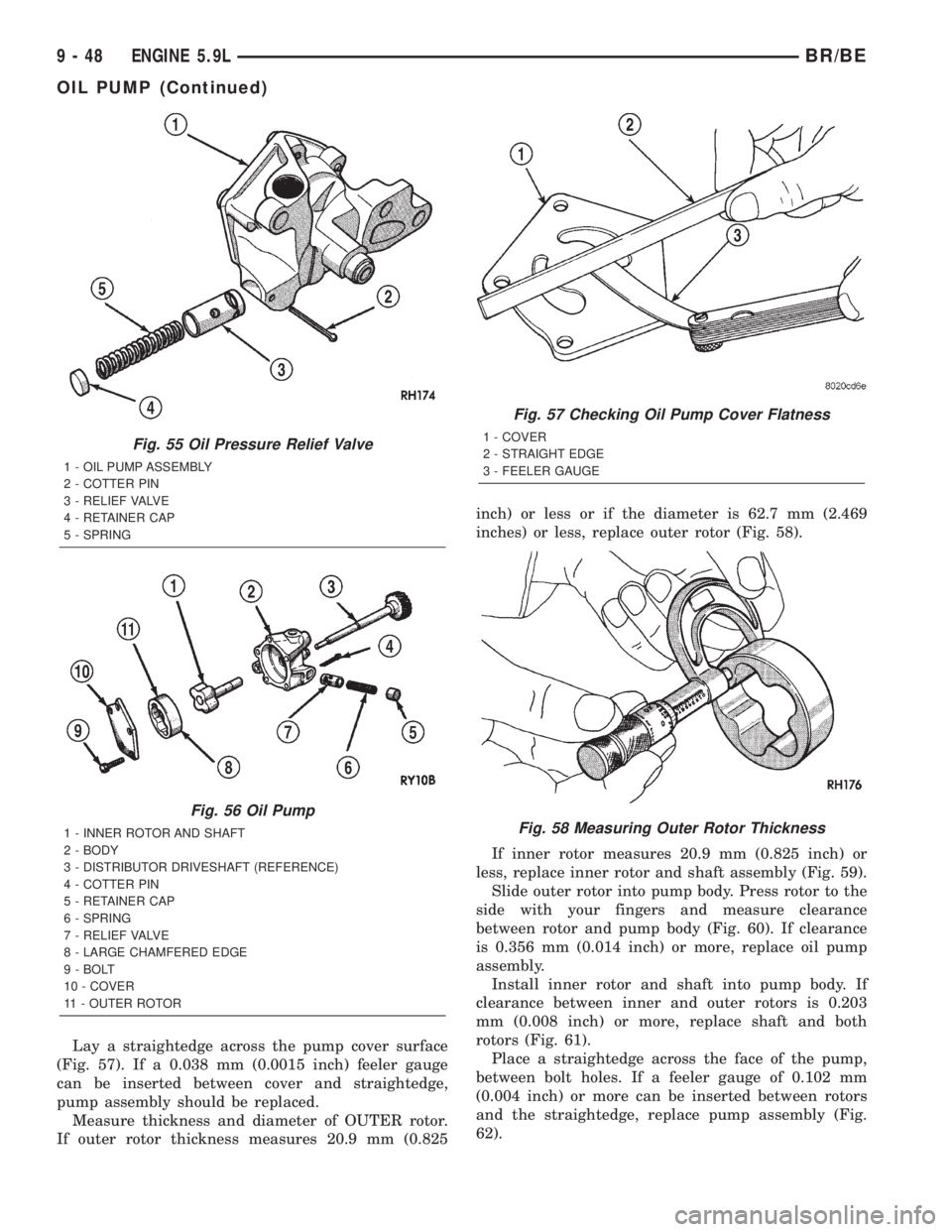
Lay a straightedge across the pump cover surface
(Fig. 57). If a 0.038 mm (0.0015 inch) feeler gauge
can be inserted between cover and straightedge,
pump assembly should be replaced.
Measure thickness and diameter of OUTER rotor.
If outer rotor thickness measures 20.9 mm (0.825inch) or less or if the diameter is 62.7 mm (2.469
inches) or less, replace outer rotor (Fig. 58).
If inner rotor measures 20.9 mm (0.825 inch) or
less, replace inner rotor and shaft assembly (Fig. 59).
Slide outer rotor into pump body. Press rotor to the
side with your fingers and measure clearance
between rotor and pump body (Fig. 60). If clearance
is 0.356 mm (0.014 inch) or more, replace oil pump
assembly.
Install inner rotor and shaft into pump body. If
clearance between inner and outer rotors is 0.203
mm (0.008 inch) or more, replace shaft and both
rotors (Fig. 61).
Place a straightedge across the face of the pump,
between bolt holes. If a feeler gauge of 0.102 mm
(0.004 inch) or more can be inserted between rotors
and the straightedge, replace pump assembly (Fig.
62).
Fig. 55 Oil Pressure Relief Valve
1 - OIL PUMP ASSEMBLY
2 - COTTER PIN
3 - RELIEF VALVE
4 - RETAINER CAP
5 - SPRING
Fig. 56 Oil Pump
1 - INNER ROTOR AND SHAFT
2 - BODY
3 - DISTRIBUTOR DRIVESHAFT (REFERENCE)
4 - COTTER PIN
5 - RETAINER CAP
6 - SPRING
7 - RELIEF VALVE
8 - LARGE CHAMFERED EDGE
9 - BOLT
10 - COVER
11 - OUTER ROTOR
Fig. 57 Checking Oil Pump Cover Flatness
1 - COVER
2 - STRAIGHT EDGE
3 - FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 58 Measuring Outer Rotor Thickness
9 - 48 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1126 of 2255

(13) Disconnect the heater hoses and bypass hose.
(14) Remove the closed crankcase ventilation and
evaporation control systems.
(15) Remove intake manifold bolts.
(16) Lift the intake manifold and throttle body out
of the engine compartment as an assembly.
(17) Remove and discard the flange side gaskets
and the front and rear end seals.
(18) Remove the throttle body bolts and lift the
throttle body off the intake manifold (Fig. 65). Dis-
card the gasket.
(19) If required, remove the plenum pan and gas-
ket. Discard gasket.
CLEANING
Clean manifold in solvent and blow dry with com-
pressed air.
Clean cylinder block front and rear gasket surfaces
using a suitable solvent.
The plenum pan rail must be clean and dry (free of
all foreign material).
INSPECTION
Inspect manifold for cracks.
Inspect mating surfaces of manifold for flatness
with a straightedge.
INSTALLATION
(1) If removed, position new plenum gasket and
install plenum pan (Fig. 66).
(2) Tighten plenum pan mounting bolts as follows:²Step 1. Tighten bolts to 5.4 N´m (48 in. lbs.)
²Step 2. Tighten bolts to 9.5 N´m (84 in. lbs.)
²Step 3. Check all bolts are at 9.5 N´m (84 in.
lbs.)
(3) Install the flange gaskets. Ensure that the ver-
tical port alignment tab is resting on the deck face of
the block. Also the horizontal alignment tabs must be
in position with the mating cylinder head gasket tabs
(Fig. 68). The words MANIFOLD SIDE should be vis-
ible on the center of each flange gasket.
(4) Apply MopartGEN II Silicone Rubber Adhe-
sive Sealant, or equivalent, to the four corner joints.
An excessive amount of sealant is not required to
ensure a leak proof seal. However, an excessive
amount of sealant may reduce the effectiveness of
the flange gasket. The sealant should be approxi-
mately 5 mm (0.2 in) in diameter and 15 mm (0.6 in.)
long.
(5) Install the front and rear end seals (Fig. 67)
Make sure the molded dowel pins on the end seals
fully enter the corresponding holes in the cylinder
block.
(6) Carefully lower intake manifold into position
on the cylinder block and cylinder heads. After intake
manifold is in place, inspect to make sure seals are
in place.
(7) Using a new gasket, install the throttle body
onto the intake manifold. Tighten the bolts to 23 N´m
(200 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install the intake manifold bolts and tighten as
follows (Fig. 69):
Fig. 65 Throttle Body Assembly
1 - FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY
2 - FUEL RAIL MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - FUEL RAIL CONNECTING HOSES
Fig. 66 Plenum Pan Bolt Tightening Sequence
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 51
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1127 of 2255
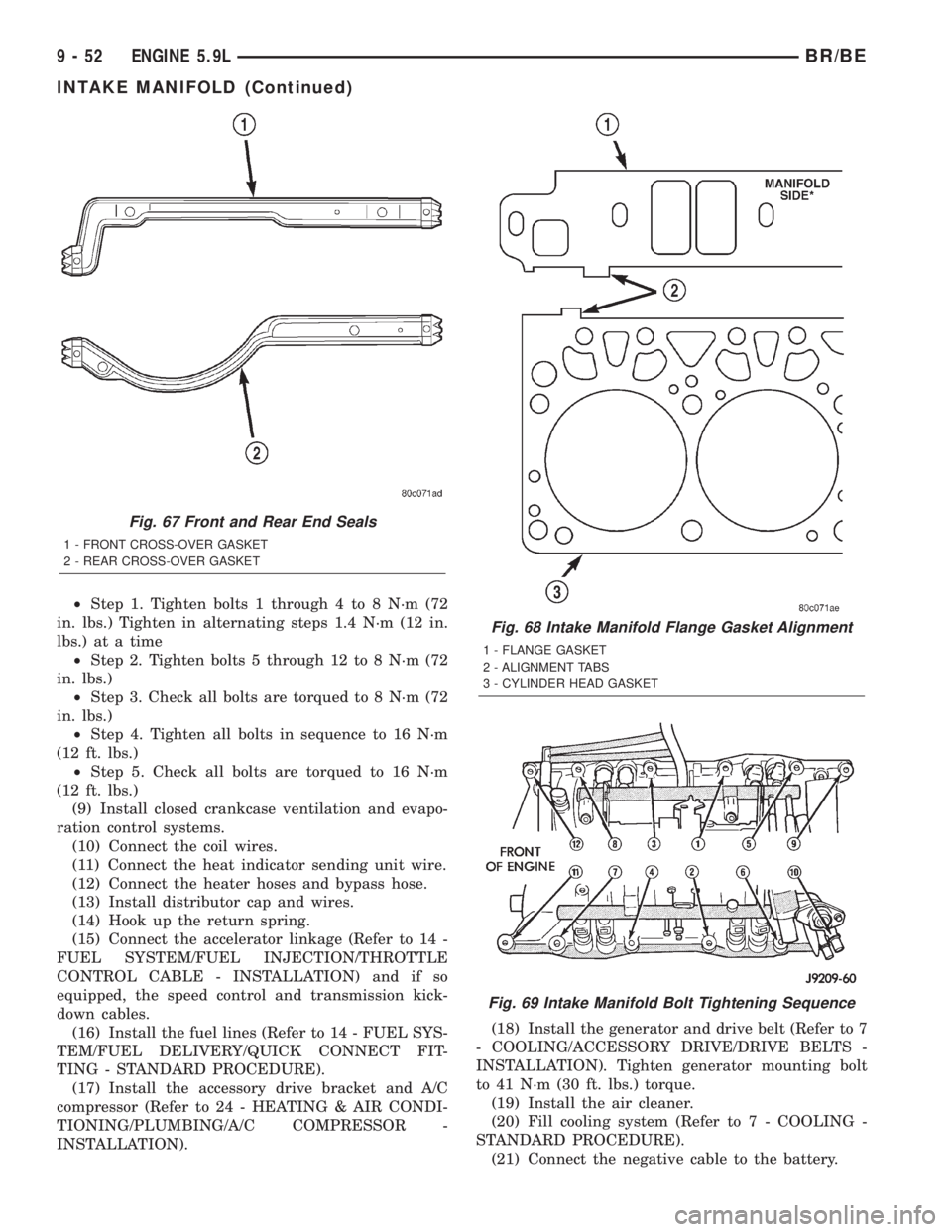
²Step 1. Tighten bolts 1 through 4 to 8 N´m (72
in. lbs.) Tighten in alternating steps 1.4 N´m (12 in.
lbs.) at a time
²Step 2. Tighten bolts 5 through 12 to 8 N´m (72
in. lbs.)
²Step 3. Check all bolts are torqued to 8 N´m (72
in. lbs.)
²Step 4. Tighten all bolts in sequence to 16 N´m
(12 ft. lbs.)
²Step 5. Check all bolts are torqued to 16 N´m
(12 ft. lbs.)
(9) Install closed crankcase ventilation and evapo-
ration control systems.
(10) Connect the coil wires.
(11) Connect the heat indicator sending unit wire.
(12) Connect the heater hoses and bypass hose.
(13) Install distributor cap and wires.
(14) Hook up the return spring.
(15) Connect the accelerator linkage (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/THROTTLE
CONTROL CABLE - INSTALLATION) and if so
equipped, the speed control and transmission kick-
down cables.
(16) Install the fuel lines (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FIT-
TING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(17) Install the accessory drive bracket and A/C
compressor (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COMPRESSOR -
INSTALLATION).(18) Install the generator and drive belt (Refer to 7
- COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION). Tighten generator mounting bolt
to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(19) Install the air cleaner.
(20) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(21) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
Fig. 67 Front and Rear End Seals
1 - FRONT CROSS-OVER GASKET
2 - REAR CROSS-OVER GASKET
Fig. 68 Intake Manifold Flange Gasket Alignment
1 - FLANGE GASKET
2 - ALIGNMENT TABS
3 - CYLINDER HEAD GASKET
Fig. 69 Intake Manifold Bolt Tightening Sequence
9 - 52 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)