Page 256 of 1943

2001 PRIUS (EWD414U)
M OVERALL ELECTRICAL WIRING DIAGRAM
9
1011 12
19 PRIUS (
Cont' d)
9A 5A 1A
10 A 22 A 23 A 12 A12A8A4A
16 C 25 C 24 C 15 C11A7A3A
9C 28C 27C 18C10A6A2A
5D 13D 20D 19D 3B 10B 4B 1B
To Data Link
Connector 3
<2±5><2±6> Fr om Stop Light SW
<3±4>
24 B 16 B 14 B 22 B15 B 23 B
To Hybr id
Vehicle
Contr ol ECU
< 1±19> < 1±20> To EMPS ECU
< 20±4>
B16A15A 14A13A 19B20B 11B12B24 A21 B
1IB1 2IB1 5IB1
ABS
J10
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR
W±BB10 B11,
BRAKE ECUAB B13, D C , B12B 3 , C B 1 B 2,
BRAKE ACTUATORAB
B WRB WRB WRB WRP±B W± L GR± GG± W
LGVG RR G BRP
W±B L PL
PL Y BR
BR±BB W
(
Shielded) (
Shielded)
(
Shielded) (
Shielded) (
Shielded) (
Shielded)
(
Shielded) (
Shielded)(
Shielded) (
Shielded)
HVI + HVI ± HV O+ HVO± FL+ FL± FSS FR+ FR± RL+ RL ± RS S RR+ RR± RRO RLO VCM PMC E2 SG1 VREG PREG EREG SG2 VFR PFR EFR SG3 VRR PRR ERR SG4 TC D/ G TS STP
(
Shielded)
AA
A
221112
A 4
ABS SPEED
SENSOR FRONT LHA 5
ABS SPEED
SENSOR FRONT RHA23
ABS SPEED
SENSOR REAR L H12
A2 4
ABS SPEED
SENSOR REAR RH (
Shielded) A
W±B B± Y
W± B20 C
BZ6B
IG1
G
13 IA2
G1 2B±Y
DA
EB EB
B±Y
B±Y
J14 J15,
J UNCTI ON
CONNECTORAB
B14
BRAKE
WARNING BUZZERBUZZER
Page 258 of 1943
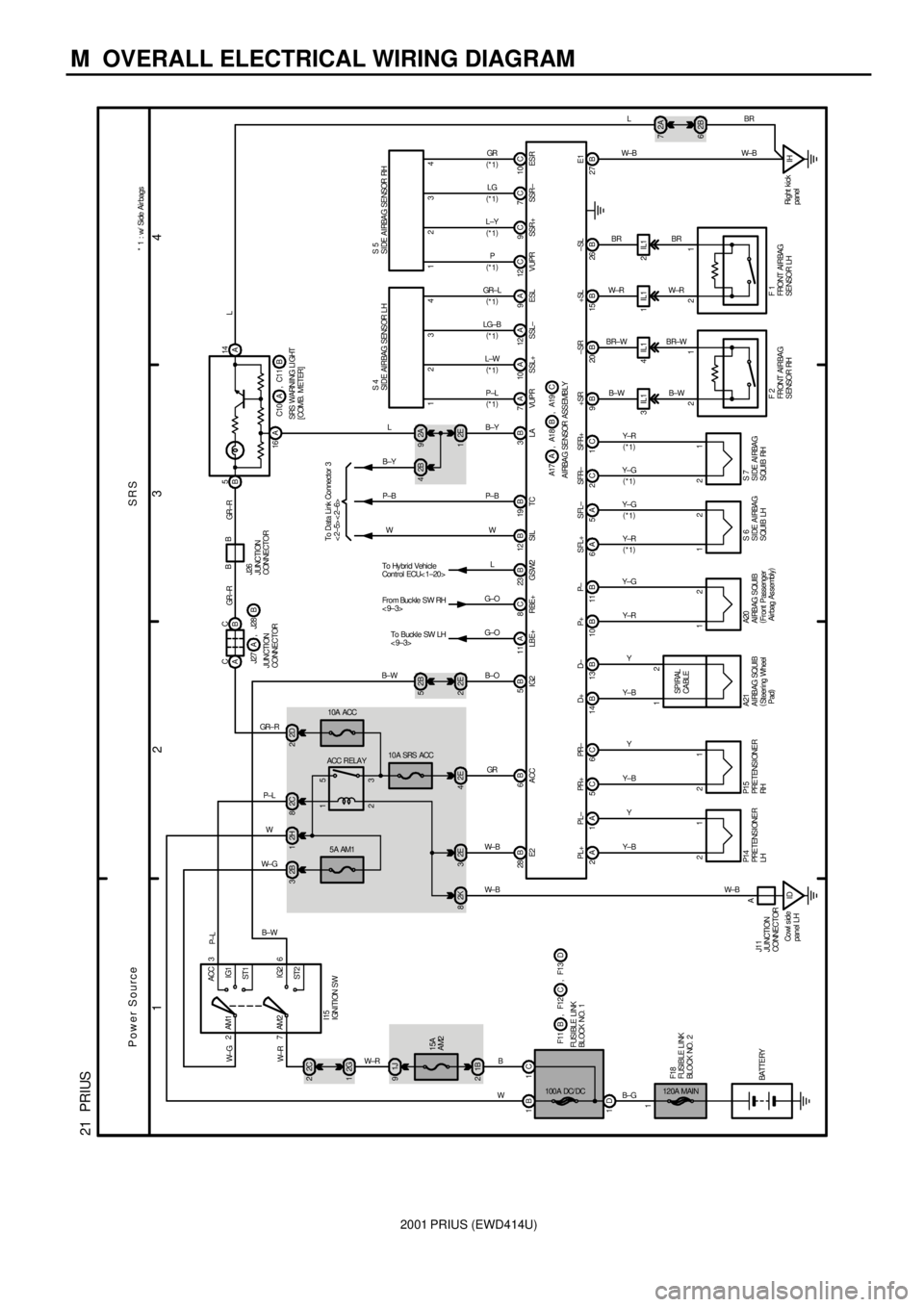
2001 PRIUS (EWD414U)
M OVERALL ELECTRICAL WIRING DIAGRAM
1
234
21 PRIUS
2ACC
IG1
ST1
IG2
ST2 AM1
7AM2
1
120A MAIN
1B 1C
1D2H 1
5A AM1
2B 3
ID Co wl s id e
panel LH2K 8
1B 215A
AM2 1J 92C 2
2G 1
A
W±B W± B W± GW
W±R B
WB±G
W±R W± G
I15
IGNITION SW
100 A DC/ DCBATTERYF18
FUSI BLE L I NK
BLOCK NO. 2F11 F12,
FUSIBLE LINK
BL OCK NO. 1BCF13, DSI L TC 5B 12B 19B 6B12C9C7C10C
12
SPI RAL
CA BLE
21
2 1 14 B 13 B 10 B 11 B 9 B 20 B
21 15 B 26 B
B± W
IG2
Y±R
Y
Y± B
A17 A1 8,
AI RBAG SENSOR ASSEMBLYAB
Y± G B± W BR±WW±RBR
F 2
FRONT AIRBAG
S ENSOR RH A21
AI RBAG SQUI B
(
Steering Wheel
Pad)A20
AI RBAG SQUI B
(
Front Passenger
Airbag As sembly)
F 1
FRONT AI RBAG
SENSOR LH±SL +SL ±SR +SR P± P+ D± D+
GR
LG
L±Y
PESR SSR± SSR+ VUPR ACC
3IL1 4IL1 1IL1 2IL1
BR±WW±RBR
GR W P±B
A19 , C
B±O
To Data Link Connector 3
<2±5><2±6>
2 1 6A 5AY±R Y± GS 6
SIDE AIRBAG
SQUIB LHSFL± SFL+
C 2C 1
21
Y± GY±RS 7
S I DE AI RBA G
SQUIB RHSFR+ SFR± 2E 3
C 5C 6
21
Y± BYP15
PRETENSIONER
RHPR± PR+
W± BPL+ PL±
P14
PRETENSIONER
LH
Y
Y± BA
1 21 2A4 3 2 1 123
7A 10A 12A 9A4
GR± L
LG±B
L±W
P±LESL SSL± SSL+ VUPR 3B
LA
B±Y2E 12A 9 2B 4
B±YL
W P± B
2B 5
2E 2B± W
10A ACC
2D 2
2 1
3 5 2C 8
10 A SRS ACC
2E 4
GR± R
P±L
6
B± W
3
P±L
ACC RELAY
S 4
SI DE AI RBAG SENSOR L HS 5
S I DE A I RBA G SE NSOR RH
SRS Power Source
C
B C
A5
B14
A
16 A
LBE+8To Buckle SW LH
< 9±3>
RBE+23 B
LGSW2To Hy brid Vehicle
Con t r ol ECU< 1 ±20 >
11
From Buckle SW RH
<9±3>
G±O
AC
G±O
GR± R BB
GR ±R
J26
JUNCTI ON
CONNECTOR
C10 C1 1,
SRS WARNI NG LI GHT
[COMB. METER]AB J27 J28,
JUNCTION
CONNECTORAB* 1 : w/ Side Air bags
(
*1) (
*1) (
*1) (
*1) (
*1) (
*1) (
*1) (
*1)
(
*1) (
*1) (
*1) (
*1)
28 B
E2
J11
JUNCTI ON
CONNECTOR
Right kick
panel
W±BIHB 27E1W±B
2A 7
2B 6 LLBR
Page 260 of 1943
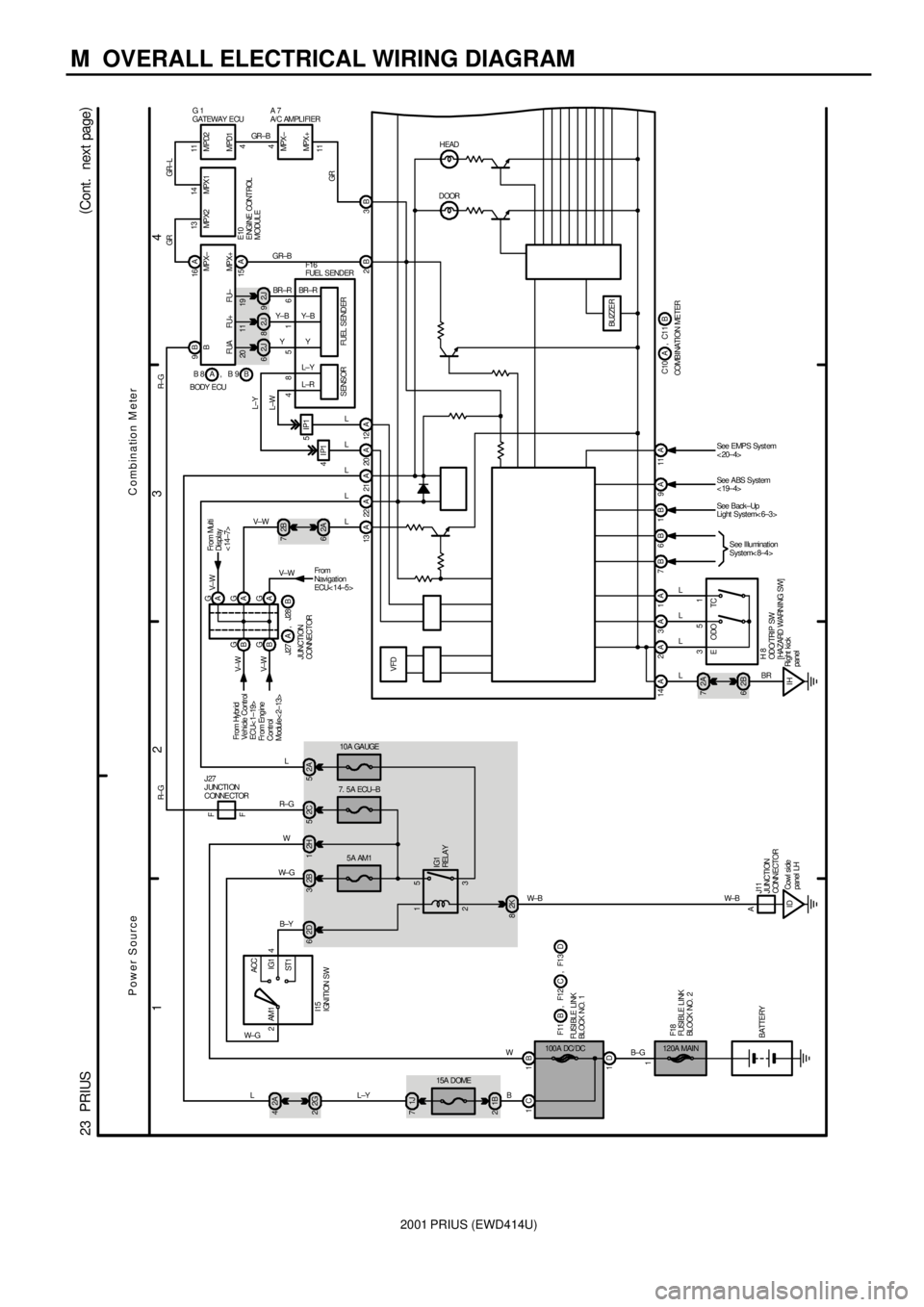
2001 PRIUS (EWD414U)
M OVERALL ELECTRICAL WIRING DIAGRAM
1
234
23 PRIUS(
Cont. next page)
5
3 1
2
5A AM1
A12H
D 1 C 1B1
120A MAIN1I15
IGNITION SW100 A DC/ DC
4 AM1
ST1IG1 ACC
2
2B 3 2D 6
IDCowl si de
panel LH 2K 8 1B 2
W±B W±B
B±Y W± GW
B WB±GJ11
JUNCTI ON
CONNECTOR BATTERYF18
FUSI BLE L I NK
BLOCK NO. 2IG1
RELA Y
F11 F12,
FUSI BLE LI NK
BL OCK NO. 1BCF13, D
10A GAUGE
2A 5
W±G
15A DOME
1J 722 A 21 A 13 A 20 A 12 A
14A 2A3A1A 7B6B1B9A 11ABUZZER2B 3B
D OORHEAD
Combination M eter Power Source
2A 4
2B 7
2G 2
2A 6 G
A
G
A G
B
G
B
2A 7
2B 6
IHRight kick
panel51
See Illumination
System< 8±4>
LL±YSee Back±Up
Light System< 6±3> See ABS System
< 19±4> See EMPS Syst em
< 20±4>
15 A
2J 62J82J916 A 9B
7. 5A ECU±B
2C 5
BR L L L L
R± GL V± W LL
L
L
L Y Y± B BR±R GR±B GR ±B
From
Navigation
ECU< 1 4±5 >
R± G R± G
GR GR± L
GR V±W
V±W
V± W
J27 J28,
JUNCTION
CONNECTORAB Fr om Engine
Control
Module< 2±13>From Hybr id
Vehicle Control
ECU< 1±19> F
F
J27
J UNCTI ON
CONNE CTOR BODY ECUB A B 8 B 9, F16
FUEL SENDER
E10
E NGI NE CONT ROL
MODUL E
G 1
GATEWAY ECUA 7
A/ C AMPL I FI ER
13 14 11
4 4
11MPX + MPD1 MP X2 MPX 1 MPD2
MPX ±
C10 C11,
COMBINATION METERAB 4IP15IP1L±WL±Y
48516
3
H 8
OD O/ TRI P SW
[ HA ZARD WARNI NG SW] VFD
TC ODO EA G
From Mul ti
Di spl ay
< 14±7> V± W
MP X+ MP X± B
FU± FU+ FUA
19 11 20
BR±R
Y± B
Y
L±Y
L±R
FUEL SENDER SENSOR
Page 263 of 1943

2001 PRIUS (EWD414U)
M
78
6 5
(
Cont. next page)
24 PRIUS (
Cont' d)
9B 18B
4IE1 5IE1
4IK1 5IK1 A
B
C
EA
B
C
2F 615 A 16 A
11 A 4 A 5 B4B13 D 14 D 23 C
3D 22D 18BIA25
1 2
F2B 6C 5C17 C 15 C 16 C 14 C 13 C
6 II1 8 II1 7 II1 9 II1 10 II1
M 20 C C18 19 C 22 C 21 C
M DD
Air Conditioning
B A
A/ C AMPLI FI ER, A 8 A 7 A 9, C4C 1B 3C 1C 2C2 1
1 2 18
34
1 211
1422
12345 12345 B±R
G±W
G
R±L
L±O
B± LGR± LW±G
BRW±G
BR± WB± R
G±W
G
R±L
GR± B GRGR± BLG P±G R±WW
W W W
W± L BR±W
W± L BR±W
W±L BR± W V± YW W W W
W
W
W W W
W
W
W
W± R BR±YY±RL BR±R
B 8
BODY ECUA
E 8 E 9,
ENGI NE CONTROL MODULEBC
A10
A/ C ROOM
TEMP. SENSOR A12
A/ C THERMI STOR
Fr om FAN NO. 1 and
FA N NO. 2 Rel ay< 22± 4>
LOCK SGLOCK CF S5TS TS SGTPI S5 TPI TPI AI F AI R S5 TP SGTP TP AMC AMHMP X+ MP2 + NE A CTRF TR SGTR TE SGTE
A 2
A/C MAGNETIC
CLUTCH AND
L OCK SENSORMP X+ MPD2 MPX 1 MPX 2 TA M
MP X± MPD1 NEO A CT E 2
GR
, DE10 A 6
AMBI ENT
TEMP.
SENSOR
A11
A/C SOLAR
SENSOR C11
COMBINATION
METE RG 1
GATE WAY
ECU
IK12
Fr om FAN NO. 3 Rel ay
< 22±4>
A1 5
AI R MI X CONTROL SE RVO MOTOR A1 4
AI R I NLE T CONTROL S ERVO MOTOR IDH
Y
10 A
Fr om Conv erter
< 1±13>
MP X+ MPX ± HRLY
Page 271 of 1943

NEW MODEL OUTLINE
MAIN MECHANISM
12
Low-emission & high-fuel efficiency.
TOYOTA hybrid system leading the way into the next
generation.
Tackling the challenge for high fuel efficiency and
low emissions
Prius - the mass-production gasoline hybrid vehicle - already meets all of the various strict emission levels
being proposed throughout the world, well ahead of the competition. What's more, through the use of the
hybrid system, surpassing fuel efficiency and a massive reduction in CO
2 has become a reality. The Prius
can truly be acclaimed as ªthe clean and environmentally friendly vehicle.º
Emission Reduction Features
1. Precision Emission Control
Through full utilization of the two Oxygen sensors, precision emission control is made possible even when
the engine is frequently stopped and re±started. Furthermore, excellent purification of exhaust gas is ensured
through the catalytic converter, resulting in reduced emissions.
2. Vapor Reducing Fuel Tank System
We have developed a new fuel tank system that can dramatically reduce the amount of fuel vapor generated
in the tank both when the vehicle is moving as well as when it is at a standstill. This system is the first one
in the world to be used.
3. TOYOTA HC Adsorber and Catalyst System
A new system has been adopted which adsorbs the HC that is emmitted between the time the engine is cold-
started and the catalytic converter is still cool and not yet activated, until the time the catalytic converter be-
comes active.
After the catalytic converter has been activated, the HC disassociates little by little and is then purified.
4. Adoption of a Thin-walled High-density Cell Catalytic Converter
In order to reduce the amount of time taken until the catalytic converter is activated, we developed a catalytic
chamber with a super thin ceramic wall. Also, high-density cells have been utilized as a measure to improve
strength and increase contact area with exhaust gas. Through these measures we have been able to achieve
a balance of reliability and purification efficiency.
Page 289 of 1943
ENGINE ± 1NZ-FXE ENGINE
171EG07
182EG07
Crankshaft Position
Sensor RotorOil HolePin
No.5 Journal
Balance Weight
No.1 Journal 48
4. Connecting Rod
�The connecting rods are made of high-strength
material for weight reduction.
�The connecting rod cap is held by bolts tight-
ened to plastic region.
5. Crankshaft
�The crankshaft has 5 journals and 4 balance weights.
�A crankshaft position sensor rotor has been pressed into the crankshaft to realize an integrated configura-
tion.
�The surface roughness of the pins and journals have been improved for low-friction operation.
�The bearing width has been reduced for low-friction operation.
Page 290 of 1943
ENGINE ± 1NZ-FXE ENGINE
171EG09
VVT-i ControllerTiming ChainExhaust Camshaft
Intake Camshaft
Chain Guide Chain Tension ArmChain Tensioner
171EG10
Exhaust Camshaft
Timing Rotor
Intake Camshaft
VVT-i Controller49
�VALVE MECHANISM
1. General
�Each cylinder has 2 intake valves and 2 exhaust valves.
�The valves are directly opened and closed by 2 camshafts.
�The intake and exhaust camshafts are driven by a roller timing chain.
�The VVT-i system is used to improve fuel economy, engine performance and reduce exhaust emission.
2. Camshafts
�In conjunction with the adoption of the VVT-i system, an oil passage is provided in the intake camshaft
in order to supply engine oil to the VVT-i system.
�A VVT-i controller has been installed on the front of the intake camshaft to vary the timing of the intake
valves.
�The timing rotor is provided behind the intake camshaft to trigger the camshaft position sensor.
Page 296 of 1943
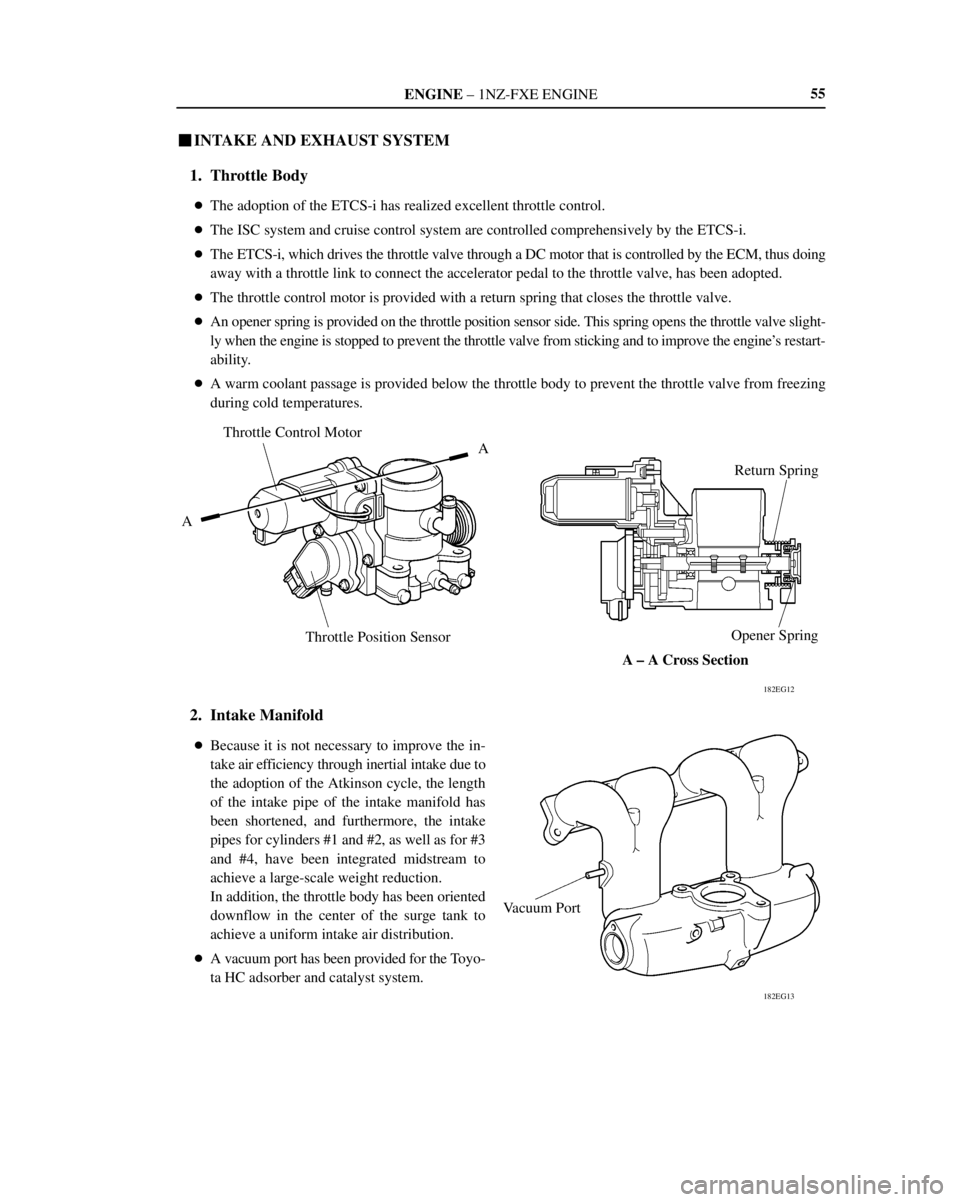
ENGINE ± 1NZ-FXE ENGINE
182EG12
A ± A Cross Section Throttle Control Motor
AA
Throttle Position SensorReturn Spring
Opener Spring
182EG13
Vacuum Port55
�INTAKE AND EXHAUST SYSTEM
1. Throttle Body
�The adoption of the ETCS-i has realized excellent throttle control.
�The ISC system and cruise control system are controlled comprehensively by the ETCS-i.
�The ETCS-i, which drives the throttle valve through a DC motor that is controlled by the ECM, thus doing
away with a throttle link to connect the accelerator pedal to the throttle valve, has been adopted.
�The throttle control motor is provided with a return spring that closes the throttle valve.
�An opener spring is provided on the throttle position sensor side. This spring opens the throttle valve slight-
ly when the engine is stopped to prevent the throttle valve from sticking and to improve the engine's restart-
ability.
�A warm coolant passage is provided below the throttle body to prevent the throttle valve from freezing
during cold temperatures.
2. Intake Manifold
�Because it is not necessary to improve the in-
take air efficiency through inertial intake due to
the adoption of the Atkinson cycle, the length
of the intake pipe of the intake manifold has
been shortened, and furthermore, the intake
pipes for cylinders #1 and #2, as well as for #3
and #4, have been integrated midstream to
achieve a large-scale weight reduction.
In addition, the throttle body has been oriented
downflow in the center of the surge tank to
achieve a uniform intake air distribution.
�A vacuum port has been provided for the Toyo-
ta HC adsorber and catalyst system.