Page 336 of 1943
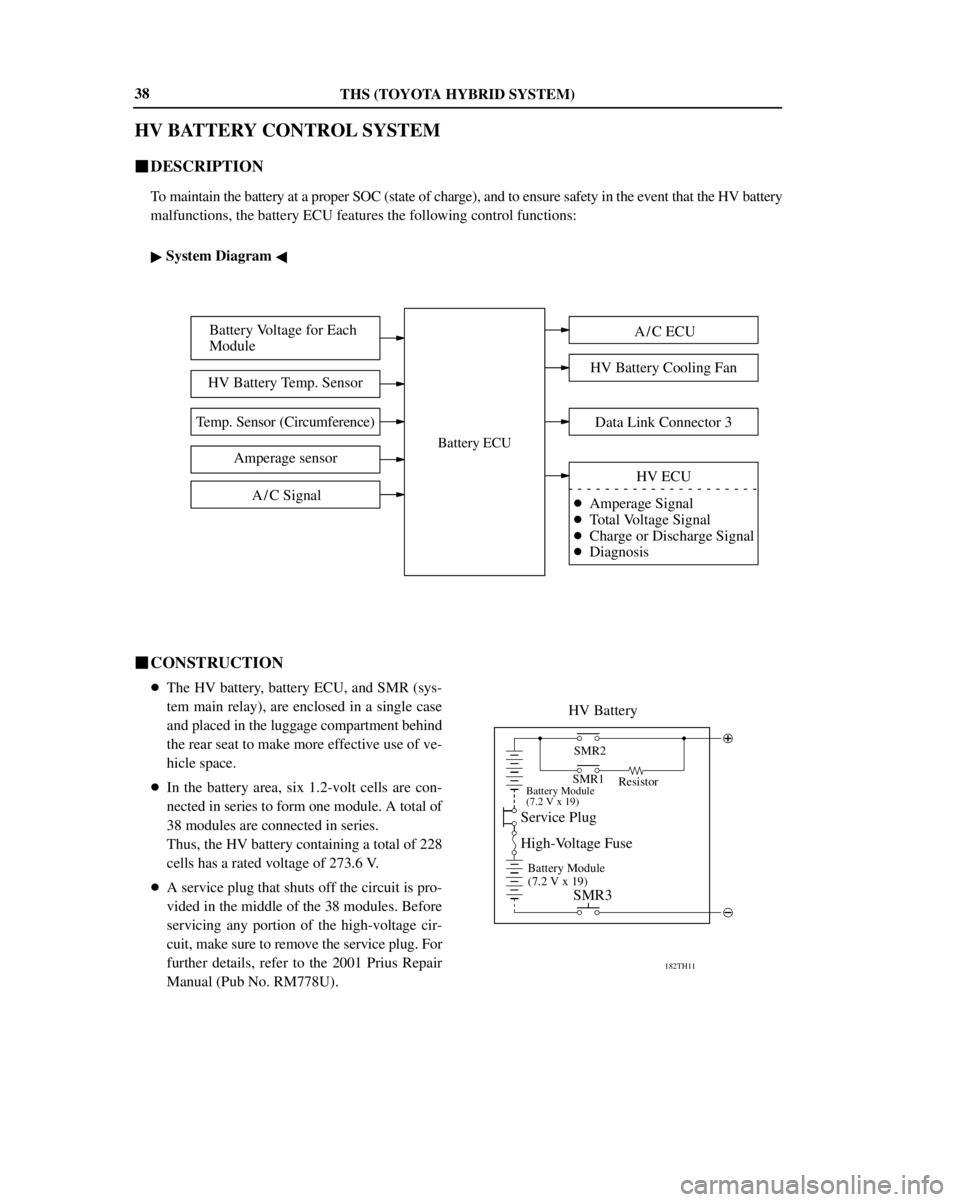
THS (TOYOTA HYBRID SYSTEM)
Battery Voltage for Each
Module
HV Battery Temp. Sensor
Temp. Sensor (Circumference)
Amperage sensor
A / C Signal
Battery ECU
A / C ECU
HV Battery Cooling Fan
HV ECU
�Amperage Signal
�Total Voltage Signal
�Charge or Discharge Signal
�DiagnosisData Link Connector 3
182TH11
HV Battery
SMR2
Battery Module
(7.2 V x 19)
Service Plug
High-Voltage Fuse
Battery Module
(7.2 V x 19)
SMR3
Resistor SMR1
38
HV BATTERY CONTROL SYSTEM
�DESCRIPTION
To maintain the battery at a proper SOC (state of charge), and to ensure safety in the event that the HV battery
malfunctions, the battery ECU features the following control functions:
� System Diagram �
�CONSTRUCTION
�The HV battery, battery ECU, and SMR (sys-
tem main relay), are enclosed in a single case
and placed in the luggage compartment behind
the rear seat to make more effective use of ve-
hicle space.
�In the battery area, six 1.2-volt cells are con-
nected in series to form one module. A total of
38 modules are connected in series.
Thus, the HV battery containing a total of 228
cells has a rated voltage of 273.6 V.
�A service plug that shuts off the circuit is pro-
vided in the middle of the 38 modules. Before
servicing any portion of the high-voltage cir-
cuit, make sure to remove the service plug. For
further details, refer to the 2001 Prius Repair
Manual (Pub No. RM778U).
Page 350 of 1943

CHASSIS ± P111 HYBRID TRANSAXLE
182CH25
182CH26Shift Position
Sensor
Shift
Position
SensorMain
Sub
HV
ECU
Serial Data
LinkEngine
ECUCombination
Meter
Voltage
: Defined
: Region
Voltage
Signal
Stroke B
D
N
R
P
PRNDBSwitch
Signal
Service Tip
Because it is extremely difficult to precisely assemble the shift position sensors, do not disassemble the
shift lever. 88
�SHIFT CONTROL
1. Shift Lever
A column-type shift lever with 5 positions has been adopted. The shift lever is operated by moving it in the
vehicle's longitudinal direction to ensure excellent ease of use. The shift lever is integrated with the shift posi-
tion sensor.
2. Shift Control
For shift control, a shift-by-wire system has been
adopted. This system uses electrical signals that
are output by the shift position sensor to determine
the shift position. For operating the parking lock
pawl in the transaxle, however, a shift cable is used
for attaining P position.
The shift position sensor outputs two systems of
signals: the main switch signals, and the sub
switch signals containing high and low voltages.
When these signals match, the HV ECU deter-
mines the respective shift position.
Page 361 of 1943
CHASSIS ± SUSPENSION AND AXLES
182CH36
12-point Nut
Double-Row Angular
Ball Bearing
182CH37
ABS Speed Sensor
Double-Row
Angular Ball
Bearing99
�AXLES
1. Front Axle
�The front axle use a double-row angular ball bearing which offers low rolling resistance.
�A lock nut (12-point) has been adopted and staked for tightening the axle hub in order to ensure the tighten-
ing performance. This nut cannot be reused.
2. Rear Axle
�The rear axle use a double-row angular ball
bearing which offers low rolling resistance.
�ABS speed sensor and rotor are built in the axle
bearing.
Page 366 of 1943
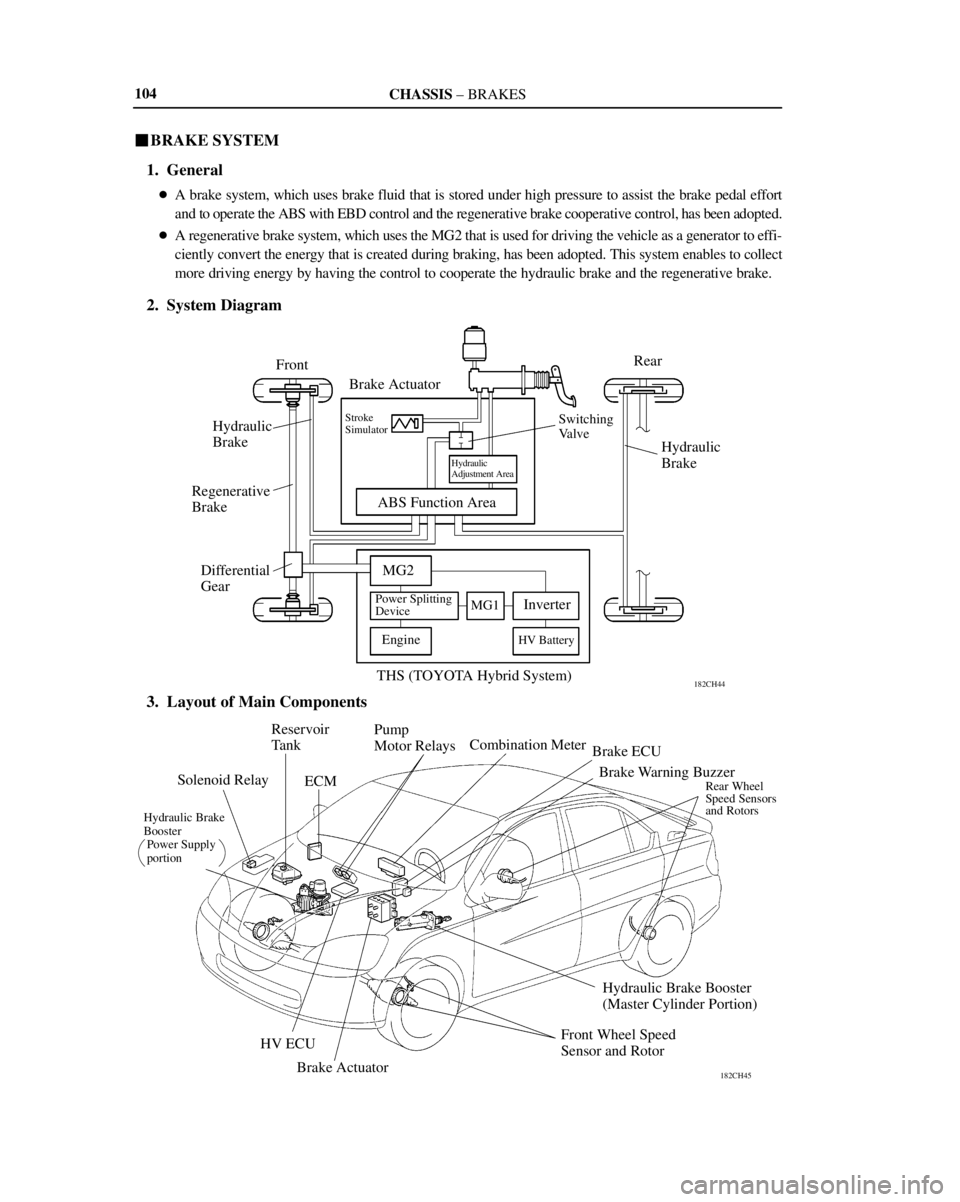
CHASSIS ± BRAKES
182CH44
Front
Brake ActuatorRear
Hydraulic
Brake
Differential
Gear
Stroke
Simulator
Hydraulic
Adjustment Area
ABS Function AreaHydraulic
Brake
MG2
MG1Inverter
EngineHV Battery
THS (TOYOTA Hybrid System) Regenerative
Brake
Switching
Valve
Power Splitting
Device
182CH45
Combination Meter
Brake ECU
Brake Warning Buzzer
Rear Wheel
Speed Sensors
and Rotors
Hydraulic Brake Booster
(Master Cylinder Portion)
Front Wheel Speed
Sensor and Rotor
Brake Actuator HV ECU
Hydraulic Brake
Booster
Power Supply
portion
Solenoid RelayReservoir
Tank
ECMPump
Motor Relays 104
�BRAKE SYSTEM
1. General
�A brake system, which uses brake fluid that is stored under high pressure to assist the brake pedal effort
and to operate the ABS with EBD control and the regenerative brake cooperative control, has been adopted.
�A regenerative brake system, which uses the MG2 that is used for driving the vehicle as a generator to effi-
ciently convert the energy that is created during braking, has been adopted. This system enables to collect
more driving energy by having the control to cooperate the hydraulic brake and the regenerative brake.
2. System Diagram
3. Layout of Main Components
Page 367 of 1943
CHASSIS ± BRAKES105
4. Function of Main Components
ComponentsFunction
ABS Warning
LightLights up to alert the driver when the brake ECU detects the
malfunction in the ABS.
Combination
Meter
Brake System
�Lights up together with the ABS warning light to alert the driver
when the brake ECU detects the malfunction not only in the ABS
but also in the EBD controlBrake System
Warning Lightbut also in the EBD control.
�Lights up to alert the driver when the malfunction occurs in the
brake system.
Stop Light SwitchDetects the brake depressing signal.
Brake Warning BuzzerEmits a continuous sound to inform the driver that the ABS ECU
detects the malfunction in the hydraulic brake booster.
Speed SensorsDetect the wheel speed of each of the four wheels.
Brake ECU
�Processes various sensor signals, regenerative brake signals, to
execute control of the ABS control, EBD control, regenerative
coordination control and hydraulic brake booster.
�Communicates control data with the HV ECU.
HV ECUMaintains serial communication with the brake ECU to exchange
regenerative coordination control signals.
Hydraulic Brake Booster�Assists with the pedal effort applied to the brake pedal.
�Supplies hydraulic pressure.
Brake ActuatorControls the brake fluid pressure to each brake wheel cylinder by
signals from the brake ECU.
Solenoid RelaySupplies power to the ABS's solenoid valve's in the brake actuator.
Pump Motor RelaysControl the pump motor operation in the hydraulic brake booster.
Page 368 of 1943
CHASSIS ± BRAKES
182CH46
SMC1
SMC2
SS
SLA
SLRSFRH
SFRR
SFLH
SFLR
SRrH
SRrRABS Solenoid Valves Switching Solenoid Valves
Linear Solenoid Valves
Hydraulic Brake BoosterAccumulator
Pump and
Pump
Motor
Pressure Switch PH
Pressure Switch PL
Master Cylinder and
Brake Booster
Brake Actuator
Pressure
Sensor
SLR
SLA
Reservoir
Pressure
Sensor
P & B Valve
Rear Wheel CylindersSRrH
SRrRSS
SMC1 SMC2
Pressure
Sensor
Front Wheel CylindersPressure
Sensor
Stroke
Simulator
SFRH
SFRR
SFLRSFLH 106
5. Hydraulic Circuit
Page 369 of 1943
CHASSIS ± BRAKES107
6. Construction and Operation
The brake system of Prius consists of the following components:
Components
Function
Pump and Pump Motor
Draws up the brake fluid from the reservoir tank
and provides high hydraulic pressure to the
accumulator.
Accumulator
Stores the hydraulic pressure that was generated
by the pump. The accumulator is filled with
highpressure nitrogen gas.
Power
Supply
PortionPressure Switches
Monitors the hydraulic pressure of the
accumulator and outputs control signals for the
pump motor.
There are two types: the pressure switch PH for
controlling the pump, and the pressure switch PL
for giving a warning when the pressure is low.
Hydraulic
Brake
Booster
Relief Valve
Returns the brake fluid to the reservoir tank to
prevent excessive pressure if the pump operates
continuously due to a malfunction of the pressure
switch.
Reservoir TankStores the brake fluid.
Brake Fluid Level
Warning SwitchDetects the low brake fluid level.
Master
Master Cylinder
Generates the hydraulic pressure in accordance
with the pedal effort that is applied to the brake
pedal.
Master
Cylinder
Portion
Brake Booster
Regulates the accumulator pressure in accordance
with the pedal effort that is applied to the brake
pedal and introduces this pressure to the boosterBrake Boosterpedal and introduces this pressure to the booster
chamber in order to provide a power assist to the
brakes.
Pressure SensorsDetects the pressure of the master cylinder,
regulator, and front and rear wheel cylinders.
Switching
Solenoid ValvesSwitches the hydraulic path between normal
braking and braking under control.
Brake
Actuator
ABS Control Solenoid
Valves
Pressure Holding
Valves
Pressure Reduction
Valves
Controls the hydraulic pressure that is applied to
the wheel cylinders during ABS control or EBD
control.
Actuator
Linear Solenoid Valve
Regulates the hydraulic pressure to the wheel
cylinders during braking in accordance with the
fluctuations in the regenerative brake force.
Reservoir
Temporarily stores the brake fluid when
regulating the hydraulic pressure to the wheel
cylinders in accordance with the fluctuations in
the regenerative brake force.
Stroke SimulatorGenerates a pedal stroke during braking in
accordance with the driver's pedal effort.
Page 376 of 1943
CHASSIS ± BRAKES
182CH52
Spring
for 1st
Stage
Spring
for 2nd
StageTo
ReservoirStroke
Simulator
Full Stroke
Pedal Stroke 2nd Stage
Spring
Characteristics
1st Stage +
2nd Stage
Spring
Characteristics
Master Cylinder Hydraulic Pressure From
Master
Cylinder
182CH53
From wheel Cylinder (SLR)
182CH54
11 4
4) Stroke Simulator
The stroke simulator generates a pedal stroke in accordance with the driver's pedal effort during braking.
Containing 2 types of coil springs with different spring constants, the stroke simulator provides pedal
stroke characteristics in 2 stages in relation to the master cylinder pressure.
5) Reservoir
Temporarily stores the brake fluid to absorb
the pressure when regulating the wheel cylin-
der pressure.
6) Pressure Sensors
Mounted on the brake actuator, the pressure
sensor linearly detects the pressure that is gen-
erated in the master cylinder, regulator, and
the front and rear wheel cylinders and outputs
them to brake ECU.