Page 380 of 1943

CHASSIS ± BRAKES
Battery
Acceptance
Capacity
182CH58
Braking
Force
Regenerative
Braking ForceHydraulic
Braking Force
Vehicle SpeedRegenerative
Braking ForceHydraulic
Braking Force
Time
Changes in Regenerative Braking Force Changes in Braking Force Apportionment
Braking
Force
Driver's DemandDriver's Demand 11 8
2) Regenerative Brake Cooperative Control
a. General
The regenerative brake cooperative control uses the switching valves and linear solenoid valves to regu-
late the hydraulic pressure that is supplied to the wheel cylinders. It also operates cooperatively with
the regenerative braking force that is generated in the MG2 in accordance with the master cylinder pres-
sure.
b. Apportioning of the Brake Force
The apportioning of the brake force between the hydraulic brake and the regenerative brake varies by
the vehicle speed and time.
The apportioning of the brake force between the hydraulic brake and the regenerative brake is con-
trolled so that the total brake force of the hydraulic brake and the regenerative brake matches the brake
force that the driver requires.
� Imagery Drawing �
c. Operation
Regenerative brake cooperative control is executed when the vehicle is driven in the shift position ªDº
or ªBº.
The master cylinder pressure that is generated when the driver presses on the brake pedal is detected
by the pressure sensor, and the brake ECU calculates the brake force request factor. A portion of the
brake force request factor is transmitted to the HV ECU in the form of a regenerative brake activation
request factor. The HV ECU executes generative braking by commanding the electric motor to generate
negative torque.
The brake ECU controls the opening of the linear solenoid valves, which are used for increasing / de-
creasing the hydraulic pressure, to regulate the wheel cylinder hydraulic pressure in relation to the mas-
ter cylinder hydraulic pressure, thus compensating for the brake force that is not provided sufficiently
by the regenerative brake.
While the regenerative brake cooperative control is being prohibited due to an abnormality in the sys-
tem, or when the shift lever is in a position other than D or B, the regenerative braking force is not gener-
ated. At this time, only the hydraulic braking force is applied by turning ON (opening) the linear sole-
noid valve SLA and turning OFF (closing) the SLR.
Page 381 of 1943
CHASSIS ± BRAKES
182CH59
Reservoir TankAccumulator
Pump Motor
Pressure Switches
Relief
Valve
Master Cylinder
Pressure Sensor
Pressure Sensor
SLR SLA
Stroke
Simulator ON
ON ON
SS
Reservoir
Pressure
Sensor
SRrH
OFF
SRrR
OFF
P & B Valve
Rear Wheel CylindersFront Wheel Cylinders SFRH
OFF
SFRR
OFFPressure
Sensor
SFLH
OFF
SFLR
OFF
SMC1
ON ONSMC2
11 9
i) Regenerative Brake Cooperative Control
Page 382 of 1943
CHASSIS ± BRAKES
SMC2 SMC1
182CH60
AccumulatorReservoir Tank
Pump Motor
Pressure Switches
Relief
Valve
Master Cylinder
Pressure Sensor
Pressure
Sensor
SLRSLA
Stroke Simulator
OFF
SS
ON ON
Reservoir
Pressure
Sensor
Pressure
Sensor
P & B Valve
Rear Wheel Cylinders Front Wheel CylindersSRrH
OFF
SRrR
OFFSFRH
OFF
SFRR
OFFSFLH
OFF
SFLR
OFF
ON ON
120
ii) Without Regenerative Brake Cooperative Control (Hydraulic Brake Only)
Page 383 of 1943
CHASSIS ± BRAKES
182CH61
Reservoir Tank
Pump Motor
Pressure Switches
Relief
Valve
Master Cylinder
Pressure
SensorPressure Sensor
SLRSLA
OFF
Stroke Simulator
SS
OFF
Reservoir
Pressure
Sensor
Pressure
Sensor
SRrR
OFF
P & B Valve
Rear Wheel Cylinders Front Wheel CylindersOFF
SMC2 SMC1
SRrH
OFFSFRH
OFF
SFRR
OFFSFLH
OFF
SFLR
OFF
OFF OFF
Accumulator121
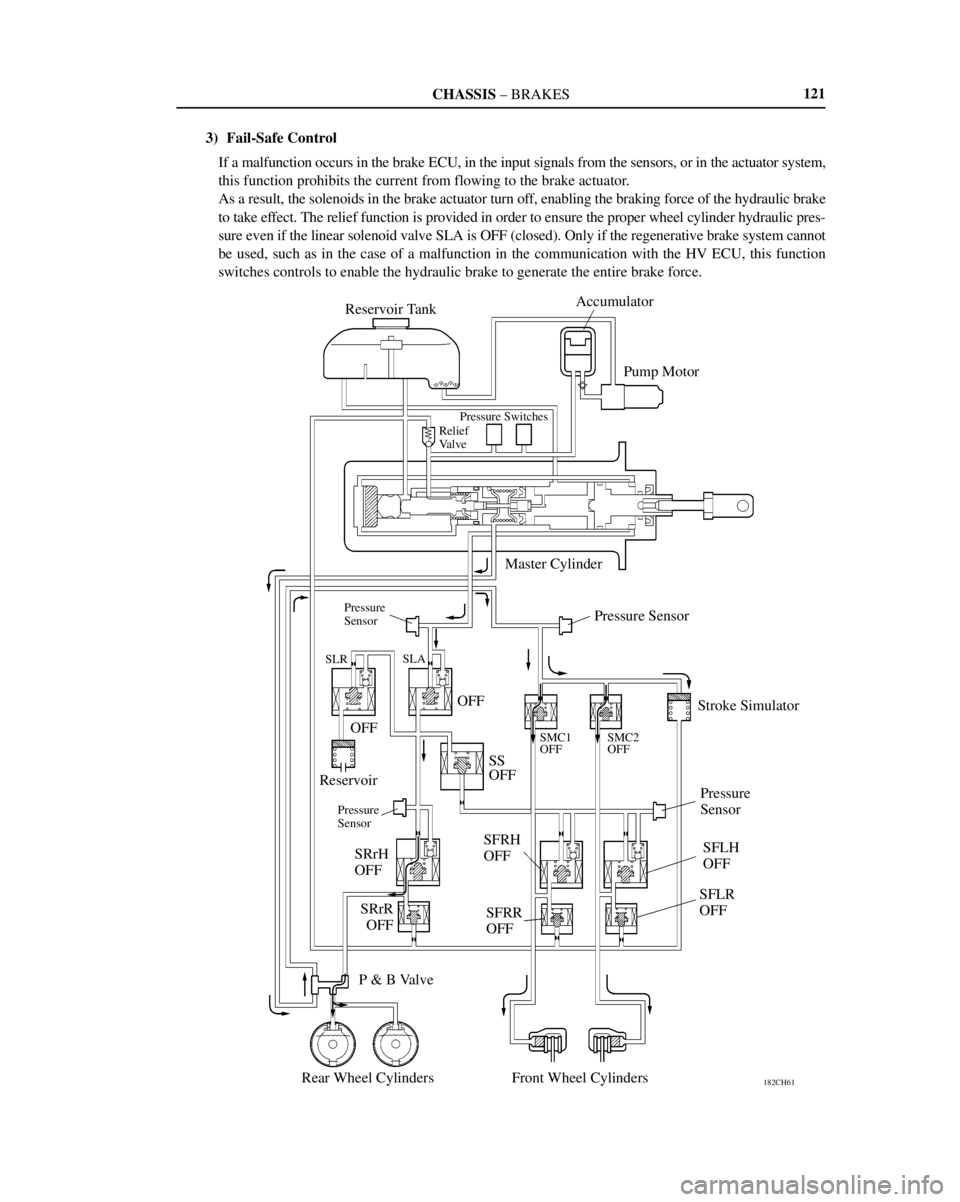
3) Fail-Safe Control
If a malfunction occurs in the brake ECU, in the input signals from the sensors, or in the actuator system,
this function prohibits the current from flowing to the brake actuator.
As a result, the solenoids in the brake actuator turn off, enabling the braking force of the hydraulic brake
to take effect. The relief function is provided in order to ensure the proper wheel cylinder hydraulic pres-
sure even if the linear solenoid valve SLA is OFF (closed). Only if the regenerative brake system cannot
be used, such as in the case of a malfunction in the communication with the HV ECU, this function
switches controls to enable the hydraulic brake to generate the entire brake force.
Page 385 of 1943
CHASSIS ± STEERING
182CH68
Rear Wheel
Speed SensorsBrake ECU
Torque Sensor Signal 1
Torque Sensor Signal 2
EMPS
ECUMeter ECU
Gateway ECUDLC3
Display ECU
Multi-information
Display
123
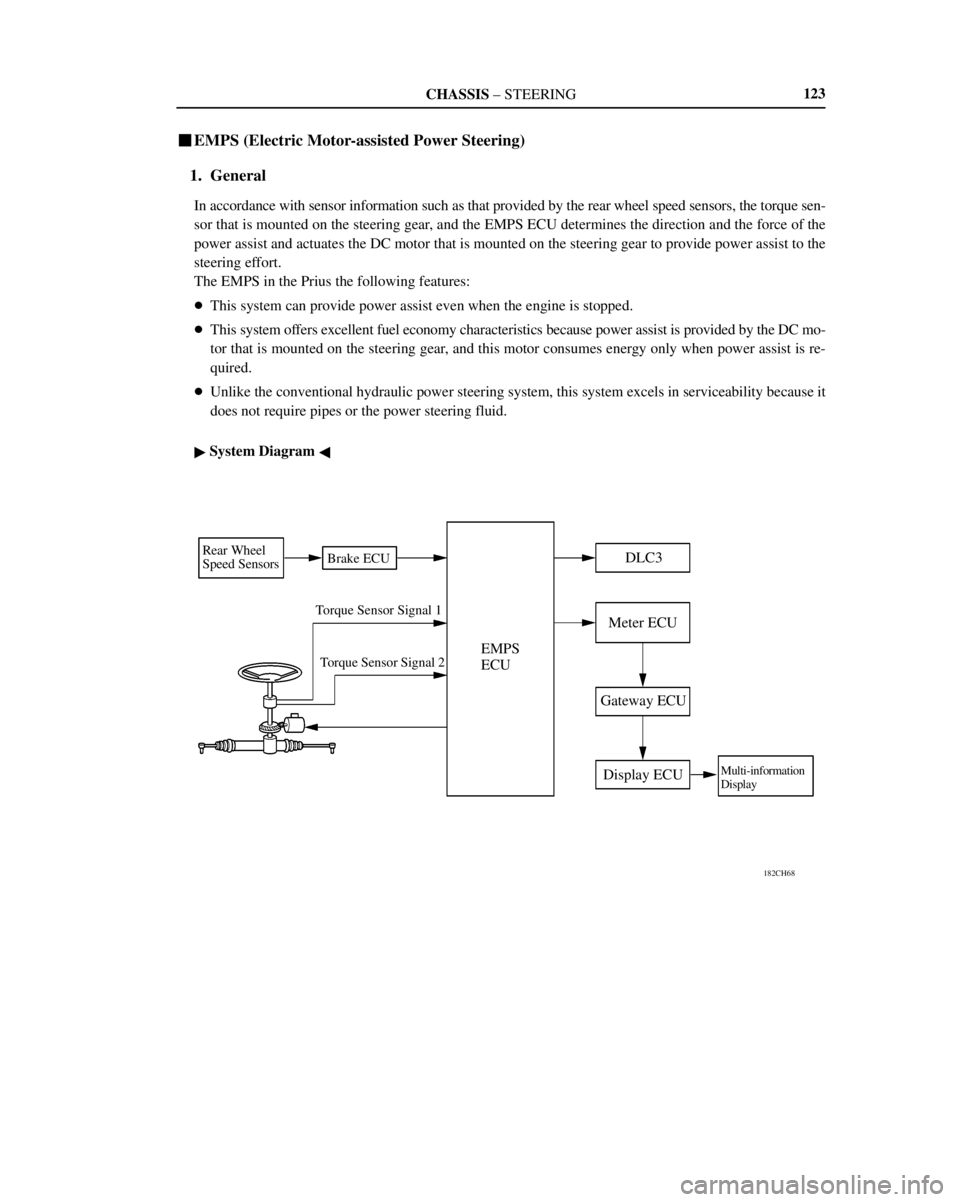
�EMPS (Electric Motor-assisted Power Steering)
1. General
In accordance with sensor information such as that provided by the rear wheel speed sensors, the torque sen-
sor that is mounted on the steering gear, and the EMPS ECU determines the direction and the force of the
power assist and actuates the DC motor that is mounted on the steering gear to provide power assist to the
steering effort.
The EMPS in the Prius the following features:
�This system can provide power assist even when the engine is stopped.
�This system offers excellent fuel economy characteristics because power assist is provided by the DC mo-
tor that is mounted on the steering gear, and this motor consumes energy only when power assist is re-
quired.
�Unlike the conventional hydraulic power steering system, this system excels in serviceability because it
does not require pipes or the power steering fluid.
� System Diagram �
Page 386 of 1943
CHASSIS ± STEERING
182CH69
Meter ECU
EMPS ECU
Relay
DC MotorRear Wheel Speed
Sensors and Rotors
Brake ECU Multi-information Display 124
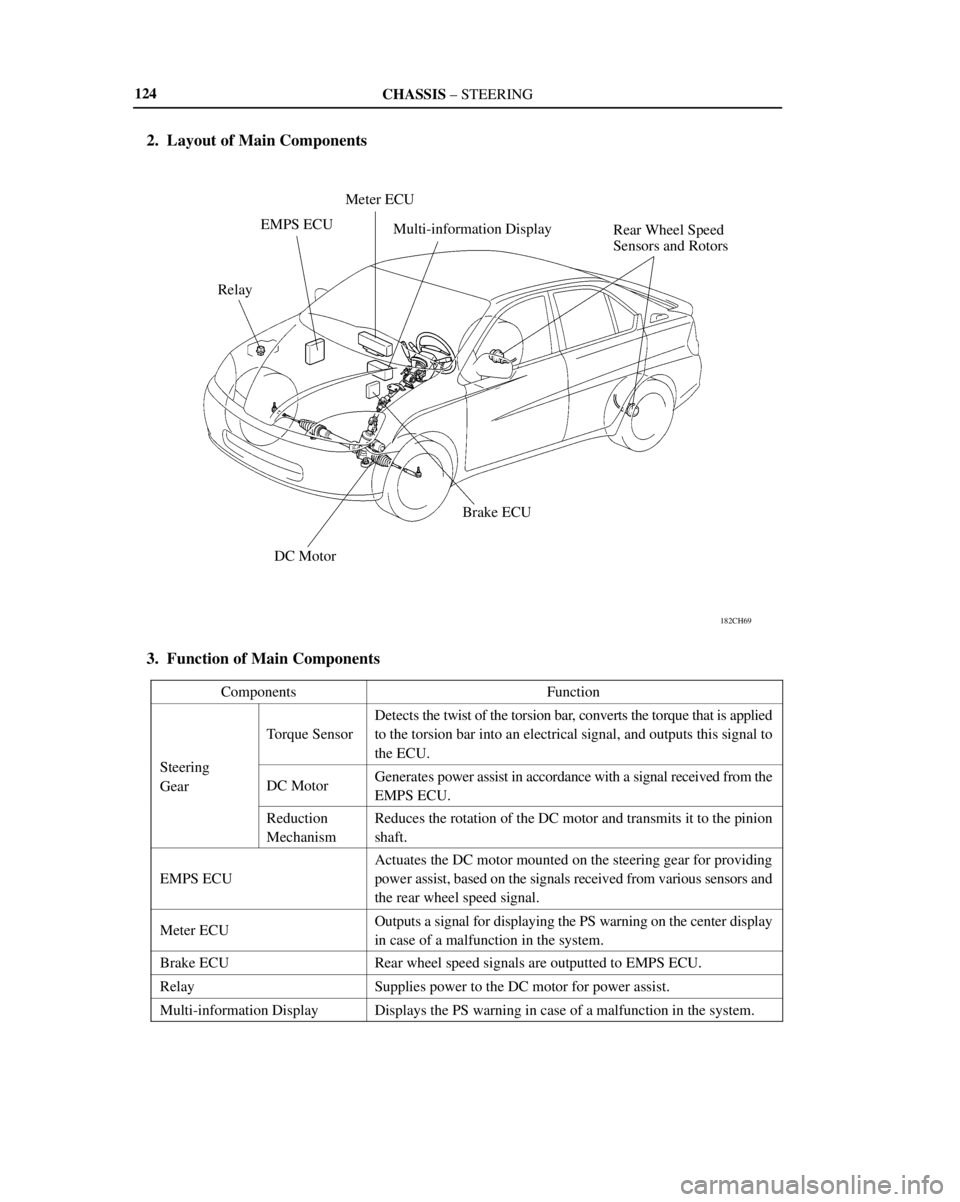
2. Layout of Main Components
3. Function of Main Components
ComponentsFunction
St i
Torque Sensor
Detects the twist of the torsion bar, converts the torque that is applied
to the torsion bar into an electrical signal, and outputs this signal to
the ECU.
Steering
Gear
DC MotorGenerates power assist in accordance with a signal received from the
EMPS ECU.
Reduction
MechanismReduces the rotation of the DC motor and transmits it to the pinion
shaft.
EMPS ECU
Actuates the DC motor mounted on the steering gear for providing
power assist, based on the signals received from various sensors and
the rear wheel speed signal.
Meter ECUOutputs a signal for displaying the PS warning on the center display
in case of a malfunction in the system.
Brake ECURear wheel speed signals are outputted to EMPS ECU.
RelaySupplies power to the DC motor for power assist.
Multi-information DisplayDisplays the PS warning in case of a malfunction in the system.
Page 451 of 1943

BODY ELECTRICAL ± ACCESSORIES
182BE46
Cruise Control Switch Signal
Brake Cancel Signal
(Stoplight Switch)
Accelerator Opening Angle Signal
(Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor)
Shift Position Signal
(Sift Position Sensor)
Brake ECUHV ECU
Cruise Control Area
� Switch Input Value
� Processing
� Required Vehicle Speed
� Calculation
Hybrid Control Area
� Required Torque
� Calculation
� Drive Force Distribution
� between Engine and � Electric Motor
Indicator Light
ECM
Inverter189
�CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM
1. General
The Prius has adopted a cruise control system that uses the hybrid system, and it is offered as an option. This
system, which is controlled by the HV ECU that is integrated with the cruise control ECU, operates the ve-
hicle through an optimal combination of the drive forces of the electric motor and the engine in accordance
with the setting on the cruise control switch.
2. Construction
The cruise control system mainly consists of an HV ECU, cruise control switches, indicator, stoplight switch,
accelerator pedal position sensor, and the shift position sensor.
The table below shows each of the functions.
Item
Function
HV ECUControls all the functions of the cruise control system in accordance with the
signals from the sensors.
Cruise Control Main
SwitchCruise control system's ON / OFF signal requirement.
Cruise Control Switch
A three-directional switch that provides the SET / COAST, RESUME /
ACCEL, and CANCEL functions. It requires the functions and settings in
accordance with its operations.
Indicator LightIt is provided in the combination meter to display whether the system is ON
or OFF.
Stop Light SwitchDetects that the driver has stepped on the brake pedal.
Accelerator Pedal
Position SensorDetects the accelerator pedal opening angle.
Shift Position SensorDetects the shift position.
Page 459 of 1943
IN0253
WRONG CORRECT
IN0252
WRONG CORRECT IN±6
± INTRODUCTIONREPAIR INSTRUCTIONS
6 Author�: Date�:
2001 PRIUS (RM778U)
(k) Care must be taken when jacking up and supporting the
vehicle. Be sure to lift and support the vehicle at the prop-
er locations (See page IN±8).
�Cancel the parking brake on the pedal place and
shift the transmission in N position.
�When jacking up the front wheels of the vehicle at
first place stoppers behind the rear wheels.
�When jacking up the rear wheels of the vehicle at
first place stoppers before the front wheels.
�When either the front or rear wheels only should be
jacked up, set rigid racks and place stoppers in front
and behind the other wheels on the ground.
�After the vehicle is jacked up, be sure to support it
on rigid racks . It is extremely dangerous to do any
work on a vehicle raised on a jack alone, even for
a small job that can be finished quickly.
(l) Observe the following precautions to avoid damage to the
following parts:
(1) Do not open the cover or case of the ECU unless
absolutely necessary. (If the IC terminals are
touched, the IC may be destroyed by static electric-
ity.)
(2) To disconnect vacuum hoses, pull off the end, not
the middle of the hose.
(3) To pull apart electrical connectors, pull on the con-
nector itself, not the wires.
(4) Be careful not to drop electrical components, such
as sensors or relays. If they are dropped on a hard
floor, they should be replaced and not reused.
(5) When steam cleaning an engine, protect the elec-
tronic components, air filter and emission±related
components from water.
(6) Never use an impact wrench to remove or install
temperature switches or temperature sensors.
(7) When checking continuity at the wire connector, in-
sert the tester probe carefully to prevent terminals
from bending.
(8) When using a vacuum gauge, never force the hose
onto a connector that is too large. Use a step±down
adapter for adjustment. Once the hose has been
stretched, it may leak air.