Page 335 of 1943
THS (TOYOTA HYBRID SYSTEM)
182TH34
Battery Pack Upper Case
Service Plug
SMR
(System Main Relay)Battery ECU
HV Battery Module37
HV BATTERY
�DESCRIPTION
The sealed nickel metal hydride (Ni-MH) battery technology has been further evolved in the newly devel-
oped HV battery that offers features such as high power density, lightweight, and longevity, that are specifi-
cally designed to match the characteristics of the THS. Because the THS effects charge / discharge control
to maintain a constant level of SOC (state of charge) while the vehicle is operating normally, it does not rely
on the use of external rechargers.
In the battery area, six 1.2-volt cells are connected in series to form one module. A total of 38 modules are
divided into two holders and connected in series. Thus, the HV battery containing a total of 228 cells has a
rated voltage of 273.6 V.
The electrode plates in the HV battery are made of materials such as porous nickel and metal hydride alloy.
Page 336 of 1943
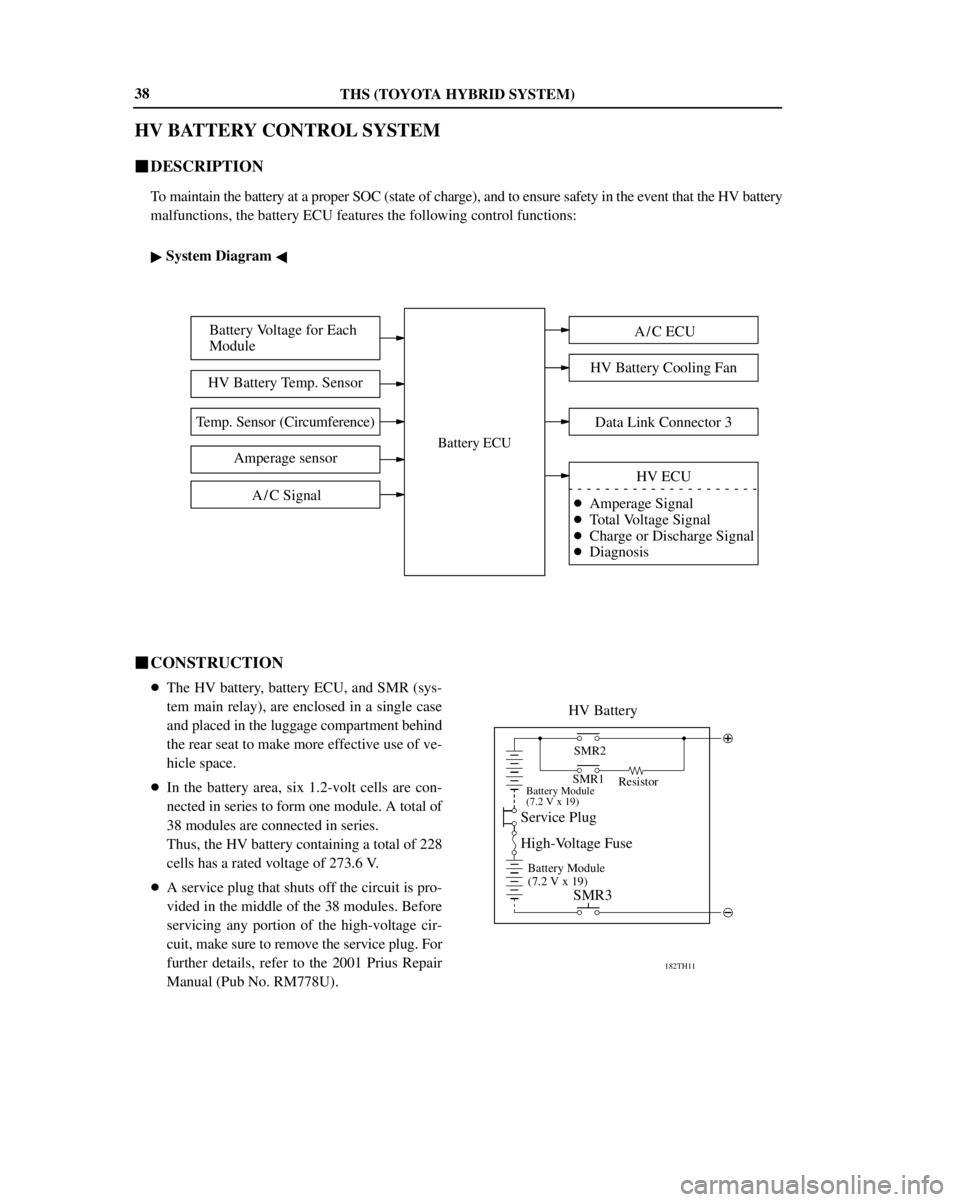
THS (TOYOTA HYBRID SYSTEM)
Battery Voltage for Each
Module
HV Battery Temp. Sensor
Temp. Sensor (Circumference)
Amperage sensor
A / C Signal
Battery ECU
A / C ECU
HV Battery Cooling Fan
HV ECU
�Amperage Signal
�Total Voltage Signal
�Charge or Discharge Signal
�DiagnosisData Link Connector 3
182TH11
HV Battery
SMR2
Battery Module
(7.2 V x 19)
Service Plug
High-Voltage Fuse
Battery Module
(7.2 V x 19)
SMR3
Resistor SMR1
38
HV BATTERY CONTROL SYSTEM
�DESCRIPTION
To maintain the battery at a proper SOC (state of charge), and to ensure safety in the event that the HV battery
malfunctions, the battery ECU features the following control functions:
� System Diagram �
�CONSTRUCTION
�The HV battery, battery ECU, and SMR (sys-
tem main relay), are enclosed in a single case
and placed in the luggage compartment behind
the rear seat to make more effective use of ve-
hicle space.
�In the battery area, six 1.2-volt cells are con-
nected in series to form one module. A total of
38 modules are connected in series.
Thus, the HV battery containing a total of 228
cells has a rated voltage of 273.6 V.
�A service plug that shuts off the circuit is pro-
vided in the middle of the 38 modules. Before
servicing any portion of the high-voltage cir-
cuit, make sure to remove the service plug. For
further details, refer to the 2001 Prius Repair
Manual (Pub No. RM778U).
Page 337 of 1943

THS (TOYOTA HYBRID SYSTEM)
182TH12
SOCExample of change in SOC
Upper SOC control limit
Control regionTarget SOC
control
Lower SOC control limit
Time
Overcharged region
Overcharged region
39
1. Battery ECU
The battery ECU provides the following functions.
SOC (state of charge) Control
While the vehicle is in motion, the HV battery
undergoes repetitive charging / discharging
cycles, as it becomes discharged by the MG2
during acceleration and charged by the regenera-
tive brake during deceleration. The battery ECU
outputs charge / discharge requests to the HV
ECU so that the SOC can be constantly main-
tained at a center level, by estimating the charg-
ing / discharging amperage.
Cooling Fan Control
To ensure the HV battery's performance considering the heat that is generated in the HV battery during
charging and discharging, the battery ECU controls the operation of the cooling fan.
HV Battery Malfunction Monitoring
This function includes the monitoring of the temperature and the voltage of the battery via the battery ECU.
If a malfunction is detected, the battery ECU protects the HV battery by restricting or stopping the charging
and discharging of the HV battery. In addition, this function illuminates the warning light, outputs DTCs
(Diagnostic Trouble Codes), and stores them in memory. For further details on the DTCs, refer to the 2001
Prius Repair Manual (Pub No. RM778U).
Page 338 of 1943
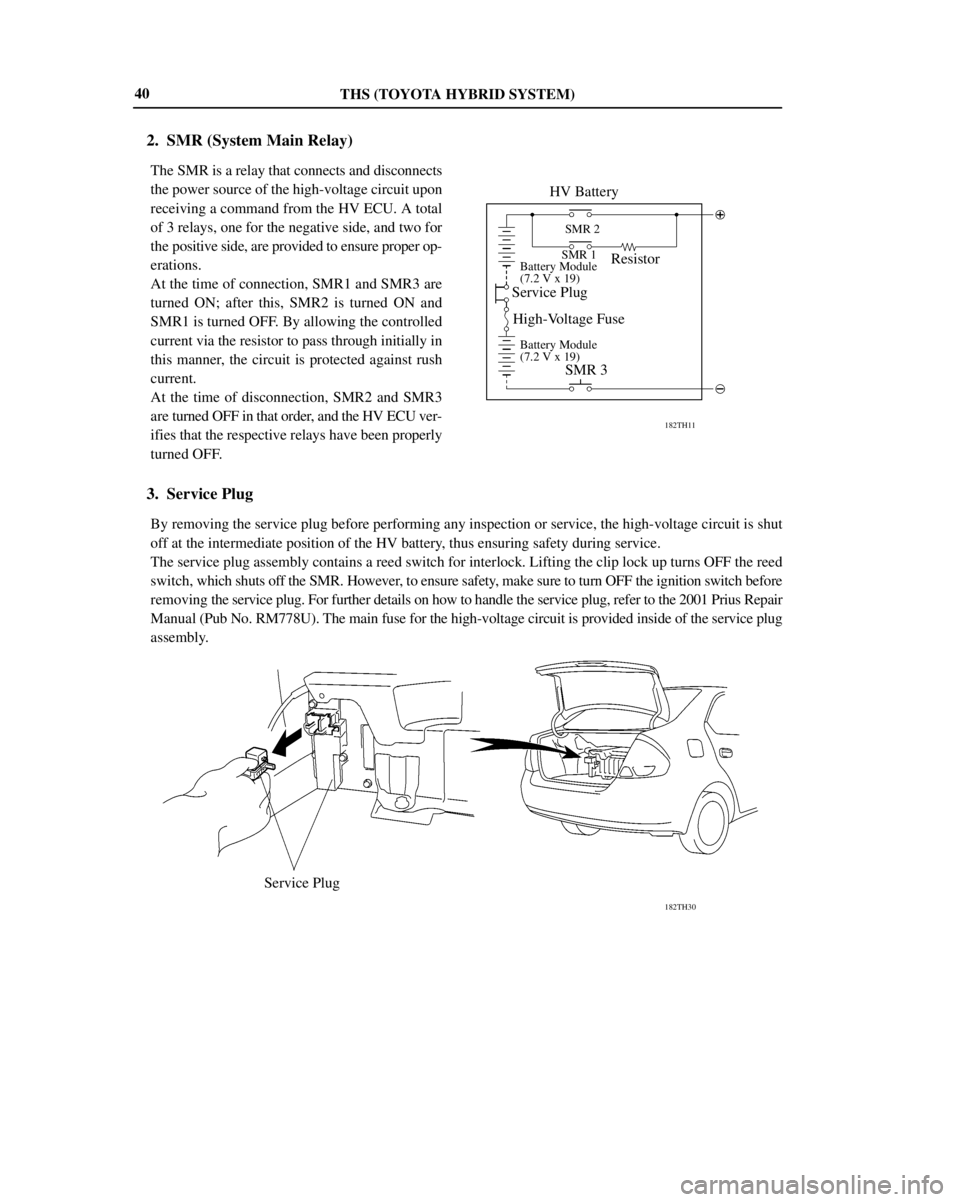
THS (TOYOTA HYBRID SYSTEM)
182TH11
HV Battery
SMR 2
SMR 1
Battery Module
(7.2 V x 19)
Resistor
Service Plug
High-Voltage Fuse
Battery Module
(7.2 V x 19)
SMR 3
182TH30
Service Plug 40
2. SMR (System Main Relay)
The SMR is a relay that connects and disconnects
the power source of the high-voltage circuit upon
receiving a command from the HV ECU. A total
of 3 relays, one for the negative side, and two for
the positive side, are provided to ensure proper op-
erations.
At the time of connection, SMR1 and SMR3 are
turned ON; after this, SMR2 is turned ON and
SMR1 is turned OFF. By allowing the controlled
current via the resistor to pass through initially in
this manner, the circuit is protected against rush
current.
At the time of disconnection, SMR2 and SMR3
are turned OFF in that order, and the HV ECU ver-
ifies that the respective relays have been properly
turned OFF.
3. Service Plug
By removing the service plug before performing any inspection or service, the high-voltage circuit is shut
off at the intermediate position of the HV battery, thus ensuring safety during service.
The service plug assembly contains a reed switch for interlock. Lifting the clip lock up turns OFF the reed
switch, which shuts off the SMR. However, to ensure safety, make sure to turn OFF the ignition switch before
removing the service plug. For further details on how to handle the service plug, refer to the 2001 Prius Repair
Manual (Pub No. RM778U). The main fuse for the high-voltage circuit is provided inside of the service plug
assembly.
Page 339 of 1943
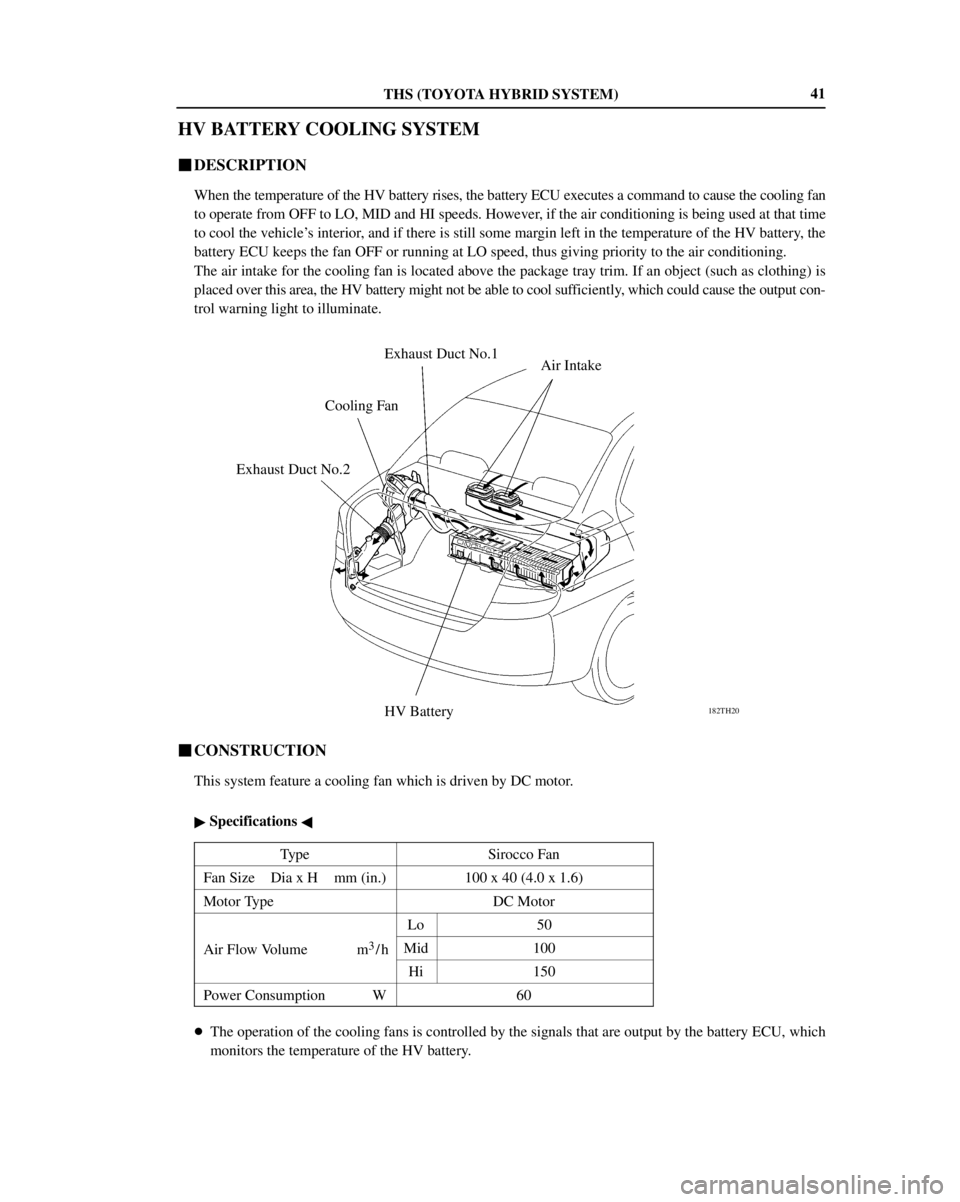
THS (TOYOTA HYBRID SYSTEM)
182TH20
Cooling FanAir Intake
HV Battery Exhaust Duct No.2Exhaust Duct No.141
HV BATTERY COOLING SYSTEM
�DESCRIPTION
When the temperature of the HV battery rises, the battery ECU executes a command to cause the cooling fan
to operate from OFF to LO, MID and HI speeds. However, if the air conditioning is being used at that time
to cool the vehicle's interior, and if there is still some margin left in the temperature of the HV battery, the
battery ECU keeps the fan OFF or running at LO speed, thus giving priority to the air conditioning.
The air intake for the cooling fan is located above the package tray trim. If an object (such as clothing) is
placed over this area, the HV battery might not be able to cool sufficiently, which could cause the output con-
trol warning light to illuminate.
�CONSTRUCTION
This system feature a cooling fan which is driven by DC motor.
� Specifications �
TypeSirocco Fan
Fan Size Dia x H mm (in.)100 x 40 (4.0 x 1.6)
Motor TypeDC Motor
Lo50
Air Flow Volume m3/hMid100
Hi150
Power Consumption W60
�The operation of the cooling fans is controlled by the signals that are output by the battery ECU, which
monitors the temperature of the HV battery.
Page 340 of 1943
THS (TOYOTA HYBRID SYSTEM)
182TH21
Lead-calcium Alloy 42
AUXILIARY BATTERY
�DESCRIPTION
The shielded, maintenance-free 12V battery (S34B20L) for the Prius is used.
Battery fluid is filtered into separators in order to reduce hydrogen gas released which occurs when the battery
is charged.
Therefore, battery fluid does not need to be replaced, as long as the specified battery is used.
HV IMMOBILISER SYSTEM
The HV immobiliser system has been designed to prevent the vehicle from being stolen. This system uses a
ECM that stores the ID code of the authorized ignition key. If an attempt is made to start the HV system using
an unauthorized key, the ECM prohibit fuel delivery and ignition, effectively disabling the engine.
Page 344 of 1943
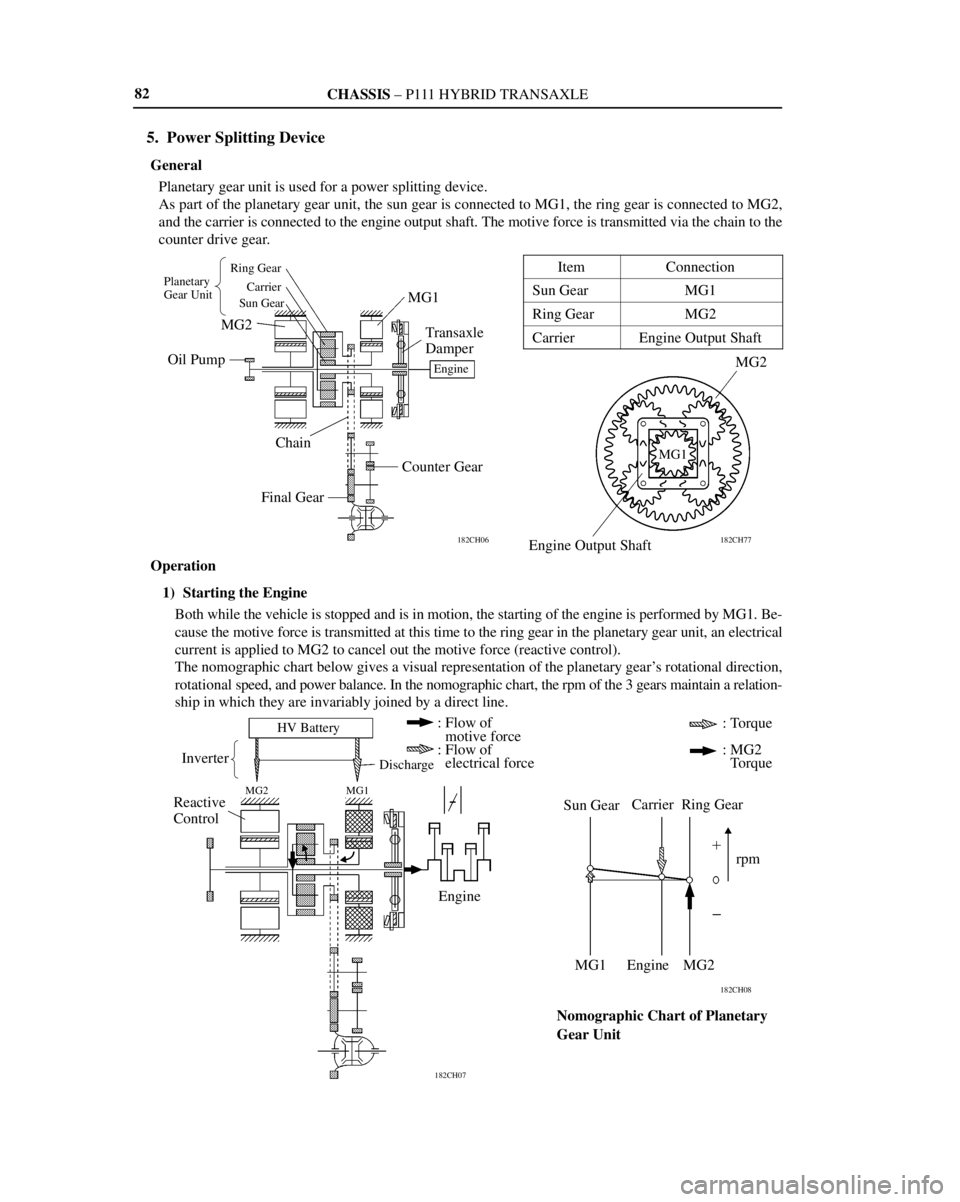
CHASSIS ± P111 HYBRID TRANSAXLE
182CH77 182CH06
Planetary
Gear UnitRing Gear
Carrier
Sun Gear
MG2
Oil PumpMG1
Transaxle
Damper
Engine
Chain
Counter Gear
Final Gear
MG2
Engine Output Shaft
MG1
182CH08
182CH07
HV Battery
Inverter
MG2 MG1
Engine : Flow of
: motive force
: Flow of
: electrical force
Discharge
Reactive
Control: Torque
: MG2
: Torque
Sun GearCarrier Ring Gear
rpm
MG1 Engine MG2
Nomographic Chart of Planetary
Gear Unit
82
5. Power Splitting Device
General
Planetary gear unit is used for a power splitting device.
As part of the planetary gear unit, the sun gear is connected to MG1, the ring gear is connected to MG2,
and the carrier is connected to the engine output shaft. The motive force is transmitted via the chain to the
counter drive gear.
Item
Connection
Sun GearMG1
Ring GearMG2
CarrierEngine Output Shaft
Operation
1) Starting the Engine
Both while the vehicle is stopped and is in motion, the starting of the engine is performed by MG1. Be-
cause the motive force is transmitted at this time to the ring gear in the planetary gear unit, an electrical
current is applied to MG2 to cancel out the motive force (reactive control).
The nomographic chart below gives a visual representation of the planetary gear's rotational direction,
rotational speed, and power balance. In the nomographic chart, the rpm of the 3 gears maintain a relation-
ship in which they are invariably joined by a direct line.
Page 345 of 1943
CHASSIS ± P111 HYBRID TRANSAXLE
182CH10
182CH09
: Flow of
: motive force
: Flow of
: electrical force
RechargingInverterHV Battery
Reactive
Control
MG2MG1Generate
EngineSun Gear Carrier Ring Gear
rpm
MG1 Engine MG2
: Torque
: MG2
: Torque
Nomographic Chart of Planetary
Gear Unit
Discharge
182CH12
182CH11
Inverter
HV Battery
Discharge
Drive
MG2
MG1
Engine : Flow of
: motive force
: Flow of
: electrical force
Sun Gear Carrier Ring Gear
rpm
MG1Engine
MG2
Nomographic Chart of Planetary
Gear Unit
: Driving
: Load
: MG2
: Torque
83
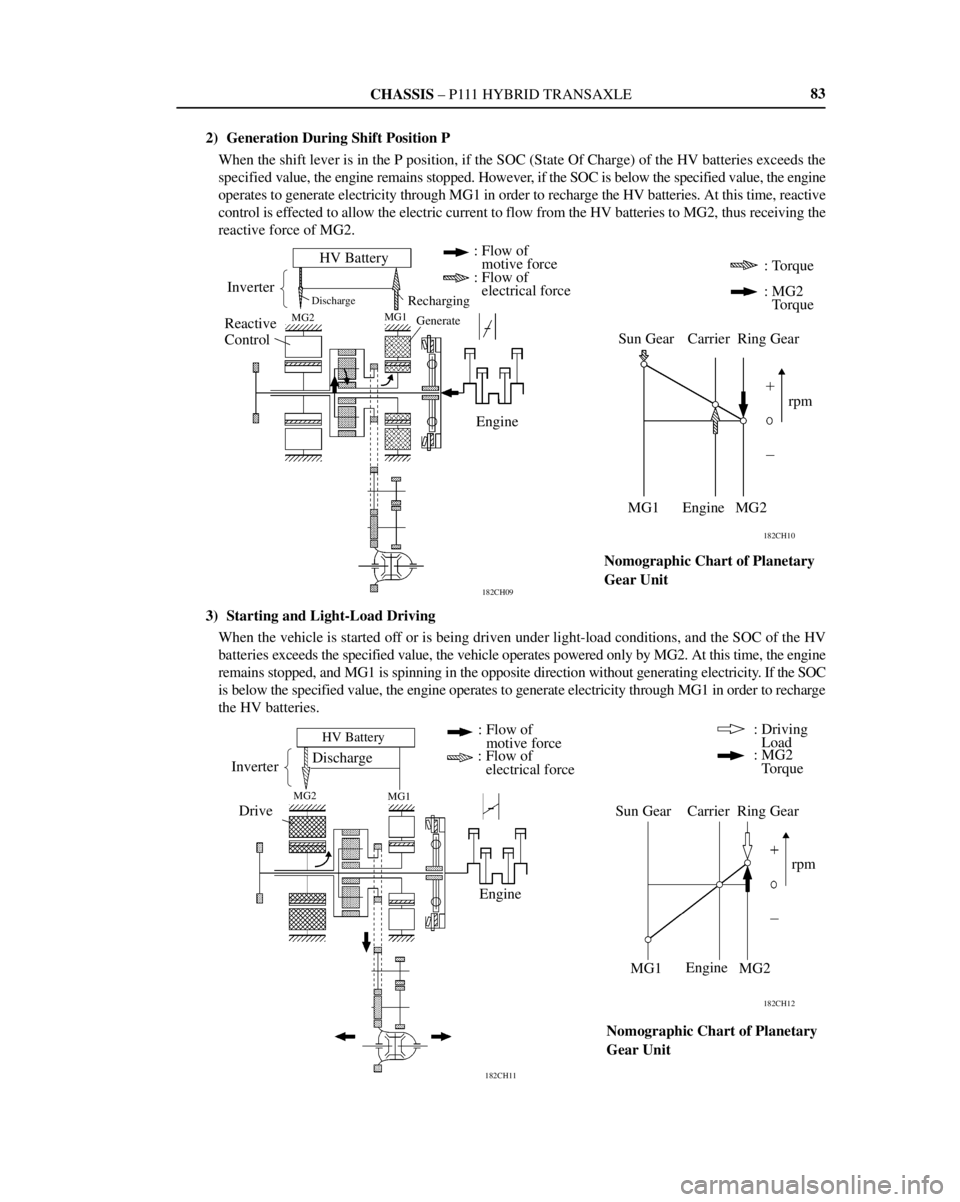
2) Generation During Shift Position P
When the shift lever is in the P position, if the SOC (State Of Charge) of the HV batteries exceeds the
specified value, the engine remains stopped. However, if the SOC is below the specified value, the engine
operates to generate electricity through MG1 in order to recharge the HV batteries. At this time, reactive
control is effected to allow the electric current to flow from the HV batteries to MG2, thus receiving the
reactive force of MG2.
3) Starting and Light-Load Driving
When the vehicle is started off or is being driven under light-load conditions, and the SOC of the HV
batteries exceeds the specified value, the vehicle operates powered only by MG2. At this time, the engine
remains stopped, and MG1 is spinning in the opposite direction without generating electricity. If the SOC
is below the specified value, the engine operates to generate electricity through MG1 in order to recharge
the HV batteries.