2001 INFINITI QX4 fuse
[x] Cancel search: fusePage 1742 of 2395

Terminal ArrangementNBEL0148
MEL069M
FUSE BLOCK Ð JUNCTION BOX (J/B)
Terminal Arrangement
Page 1743 of 2395
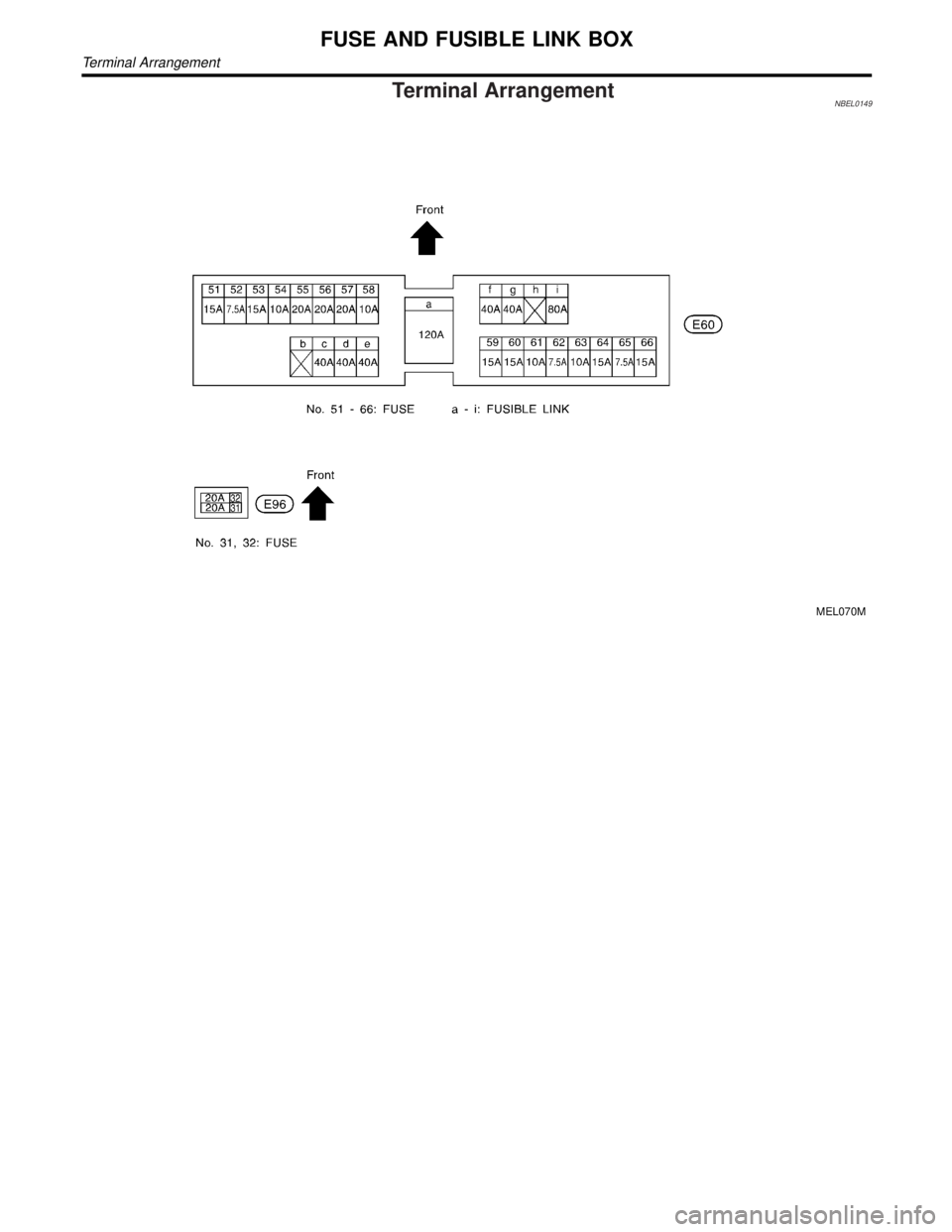
Terminal ArrangementNBEL0149
MEL070M
FUSE AND FUSIBLE LINK BOX
Terminal Arrangement
Page 1758 of 2395

Description=NBGI0003S02
Number Item Description
1 Power conditionIThis shows the condition when the system receives battery positive voltage (can be oper-
ated).
2 Fusible linkIThe double line shows that this is a fusible link.
IThe open circle shows current flow in, and the shaded circle shows current flow out.
3Fusible link/fuse loca-
tionIThis shows the location of the fusible link or fuse in the fusible link or fuse box. For
arrangement, refer to EL-10, ªPOWER SUPPLY ROUTINGº.
4 FuseIThe single line shows that this is a fuse.
IThe open circle shows current flow in, and the shaded circle shows current flow out.
5 Current ratingIThis shows the current rating of the fusible link or fuse.
6 ConnectorsIThis shows that connector E3 is female and connector M1 is male.
IThe G/R wire is located in the 1A terminal of both connectors.
ITerminal number with an alphabet (1A, 5B, etc.) indicates that the connector is SMJ con-
nector. Refer to GI-19.
7 Optional spliceIThe open circle shows that the splice is optional depending on vehicle application.
8 SpliceIThe shaded circle shows that the splice is always on the vehicle.
9 Page crossingIThis arrow shows that the circuit continues to an adjacent page.
IThe A will match with the A on the preceding or next page.
10 Common connectorIThe dotted lines between terminals show that these terminals are part of the same con-
nector.
11 Option abbreviationIThis shows that the circuit is optional depending on vehicle application.
12 RelayIThis shows an internal representation of the relay. For details, refer to EL-7, ªSTANDARD-
IZED RELAYº.
13 ConnectorsIThis shows that the connector is connected to the body or a terminal with bolt or nut.
14 Wire colorIThis shows a code for the color of the wire.
B = Black
W = White
R = Red
G = Green
L = Blue
Y = Yellow
LG = Light GreenBR = Brown
OR = Orange
P = Pink
PU = Purple
GY = Gray
SB = Sky Blue
CH = Dark Brown
DG = Dark Green
When the wire color is striped, the base color is given first, followed by the stripe color as
shown below:
Example: L/W = Blue with White Stripe
15 Option descriptionIThis shows a description of the option abbreviation used on the page.
16 SwitchIThis shows that continuity exists between terminals 1 and 2 when the switch is in the A
position. Continuity exists between terminals 1 and 3 when the switch is in the B position.
17 Assembly partsIConnector terminal in component shows that it is a harness incorporated assembly.
18 Cell codeIThis identifies each page of the wiring diagram by section, system and wiring diagram
page number.
19 Current flow arrowIArrow indicates electric current flow, especially where the direction of standard flow (verti-
cally downward or horizontally from left to right) is difficult to follow.
IA double arrow ª
º shows that current can flow in either direction depending on cir-
cuit operation.
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AT
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS
Description
GI-13
Page 1759 of 2395
Number Item Description
20 System branchIThis shows that the system branches to another system identified by cell code (section
and system).
21 Page crossingIThis arrow shows that the circuit continues to another page identified by cell code.
IThe C will match with the C on another page within the system other than the next or pre-
ceding pages.
22 Shielded lineIThe line enclosed by broken line circle shows shield wire.
23Component box in
wave lineIThis shows that another part of the component is also shown on another page (indicated
by wave line) within the system.
24 Component nameIThis shows the name of a component.
25 Connector numberIThis shows the connector number.
IThe letter shows which harness the connector is located in.
IExample:M: main harness. For detail and to locate the connector, refer to EL-442, ªMain
Harnessº. A coordinate grid is included for complex harnesses to aid in locating connec-
tors.
26 Ground (GND)IThe line spliced and grounded under wire color shows that ground line is spliced at the
grounded connector.
27 Ground (GND)IThis shows the ground connection.
28 Connector viewsIThis area shows the connector faces of the components in the wiring diagram on the
page.
29 Common componentIConnectors enclosed in broken line show that these connectors belong to the same com-
ponent.
30 Connector colorIThis shows a code for the color of the connector. For code meaning, refer to wire color
codes, Number 14 of this chart.
31Fusible link and fuse
boxIThis shows the arrangement of fusible link(s) and fuse(s), used for connector views of
ªPOWER SUPPLY ROUTINGº in EL section.
The open square shows current flow in, and the shaded square shows current flow out.
32 Reference areaIThis shows that more information on the Super Multiple Junction (SMJ), Electrical Units
etc., exists at the end of the manual. Refer to GI-19 for details.
HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS
Description (Cont'd)
GI-14
Page 1765 of 2395

manual.
Fuse block Ð Junction box (J/B)
Fuse block Ð Junction box (J/B) connector number is shown in the
Reference Area of the wiring diagram. For connector terminal and
fuse arrangement, refer to the ªFUSE BLOCK Ð Junction Box
(J/B)º electrical reference page at the end of the manual.
Fuse and fusible link box
For fuse arrangement in the fuse and fusible link box, refer to the
ªFUSE AND FUSIBLE LINK BOXº electrical reference page at the
end of the manual.
Electrical units
Electrical unit connector symbols are shown in the Connector Area
of the wiring diagram.
However, when there is not enough space to show the connector
terminal arrangement in the Connector Area of the wiring diagram,
the electrical unit connector number is shown in the Reference
Area of the wiring diagram. For electrical unit connector terminal
arrangement, refer to the ªELECTRICAL UNITSº electrical refer-
ence page at the end of the manual. Most of the electrical unit
connectors on this page are shown from the harness side of the
connector.
Joint connector
Joint connector symbols are shown in the connector area of the
wiring diagram. For connector internal wiring layout and joint con-
nector terminal arrangement, refer to the ªJOINT CONNECTOR
(J/C)º electrical reference page at the end of the manual.
HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS
Description (Cont'd)
GI-20
Page 1773 of 2395

NOTE:
Refer to ªHOW TO CHECK TERMINALº in GI-21 to probe or
check terminal.
TESTING FOR ªOPENSº IN THE CIRCUITNBGI0004S0303Before you begin to diagnose and test the system, you should
rough sketch a schematic of the system. This will help you to logi-
cally walk through the diagnosis process. Drawing the sketch will
also reinforce your working knowledge of the system.
SGI846
Continuity Check Method
The continuity check is used to find an open in the circuit. The
Digital Multimeter (DMM) set on the resistance function will indicate
an open circuit as over limit (no beep tone or no ohms symbol).
Make sure to always start with the DMM at the highest resistance
level.
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits please refer
to the schematic above.
1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2) Start at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other
end. (At the fuse block in this example)
3) Connect one probe of the DMM to the fuse block terminal on
the load side.
4) Connect the other probe to the fuse block (power) side of SW1.
Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the circuit has
good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM
would indicate an over limit or infinite resistance condition.
(point A)
5) Connect the probes between SW1 and the relay. Little or no
resistance will indicate that portion of the circuit has good con-
tinuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would
indicate an over limit or infinite resistance condition. (point B)
6) Connect the probes between the relay and the solenoid. Little
or no resistance will indicate that portion of the circuit has good
continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would
indicate an over limit or infinite resistance condition. (point C)
Any circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the above
example.
Voltage Check Method
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits please refer
to the previous schematic.
In any powered circuit, an open can be found by methodically
checking the system for the presence of voltage. This is done by
switching the DMM to the voltage function.
1) Connect one probe of the DMM to a known good ground.
2) Begin probing at one end of the circuit and work your way to
the other end.
3) With SW1 open, probe at SW1 to check for voltage.
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-28
Page 1774 of 2395
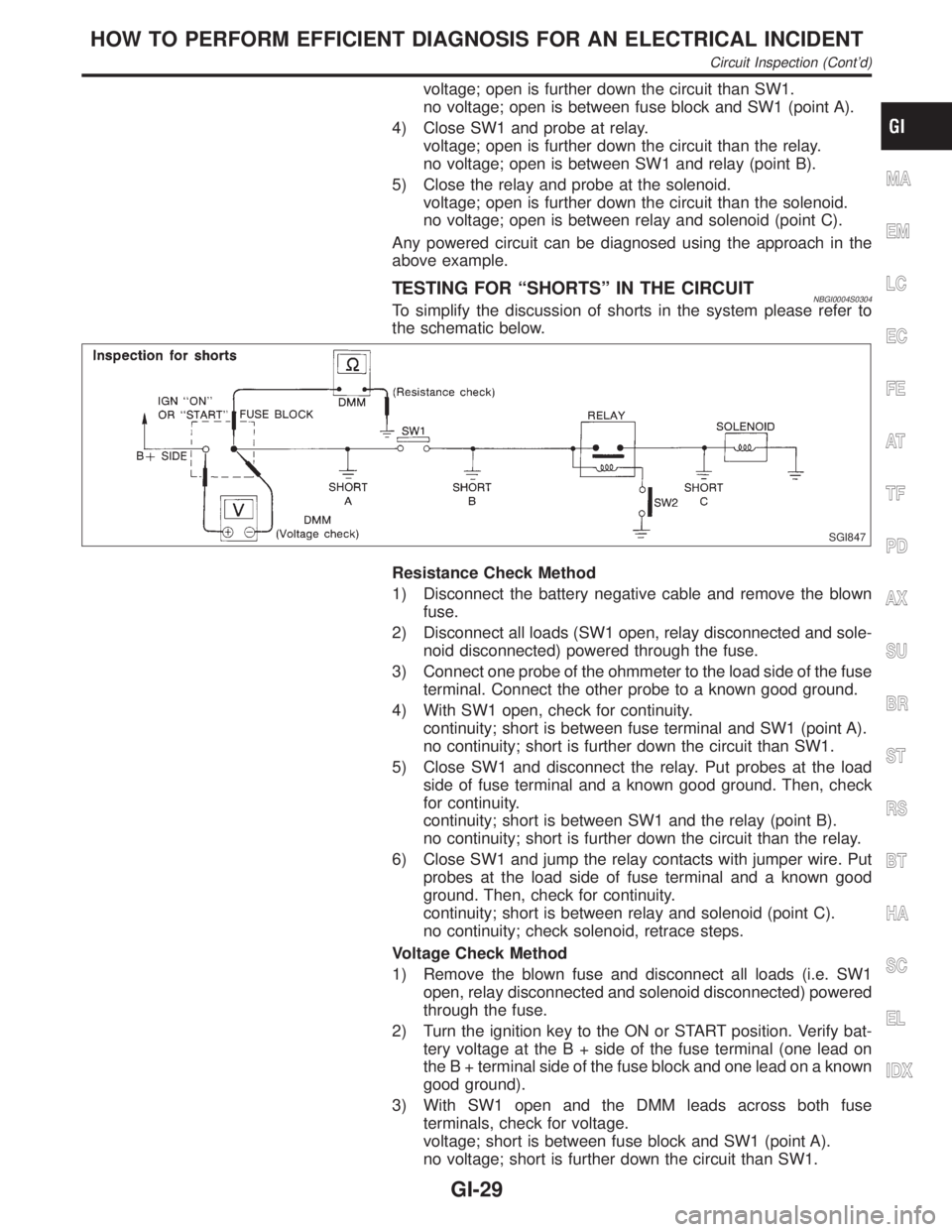
voltage; open is further down the circuit than SW1.
no voltage; open is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
4) Close SW1 and probe at relay.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the relay.
no voltage; open is between SW1 and relay (point B).
5) Close the relay and probe at the solenoid.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the
above example.
TESTING FOR ªSHORTSº IN THE CIRCUITNBGI0004S0304To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system please refer to
the schematic below.
SGI847
Resistance Check Method
1) Disconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown
fuse.
2) Disconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and sole-
noid disconnected) powered through the fuse.
3) Connect one probe of the ohmmeter to the load side of the fuse
terminal. Connect the other probe to a known good ground.
4) With SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
5) Close SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load
side of fuse terminal and a known good ground. Then, check
for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
6) Close SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wire. Put
probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good
ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
Voltage Check Method
1) Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i.e. SW1
open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered
through the fuse.
2) Turn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Verify bat-
tery voltage at the B + side of the fuse terminal (one lead on
the B + terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known
good ground).
3) With SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse
terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AT
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-29
Page 1775 of 2395

4) With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the
DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
5) With SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper
wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the
relay and the disconnected solenoid (point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
GROUND INSPECTIONNBGI0004S0305Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of
electrical and electronic circuits. Ground connections are often
exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corro-
sion (rust) can become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted
resistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper
grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drastically affect an
electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can eas-
ily affect the circuit. Even when the ground connection looks clean,
there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
1) Remove the ground bolt or screw.
2) Inspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
3) Clean as required to assure good contact.
4) Reinstall bolt or screw securely.
5) Inspect for ªadd-onº accessories which may be interfering with
the ground circuit.
6) If several wires are crimped into one ground eyelet terminal,
check for proper crimps. Make sure all of the wires are clean,
securely fastened and providing a good ground path. If multiple
wires are cased in one eyelet make sure no ground wires have
excess wire insulation.
SGI853
VOLTAGE DROP TESTSNBGI0004S0306Voltage drop tests are often used to find components or circuits
which have excessive resistance. A voltage drop in a circuit is
caused by a resistancewhen the circuit is in operation.
Check the wire in the illustration. When measuring resistance with
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-30