2001 DODGE RAM transmission oil
[x] Cancel search: transmission oilPage 1157 of 2889

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐREAR SEAL AREA
LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs, oil galley pipe plugs, oil
filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurized the crank-
case as outlined in (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICA-
TION - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks or
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is specially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled. Refer to the service DiagnosisÐMechani-
cal, under the Oil Leak row, for components
inspections on possible causes and corrections.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT OIL
SEAL - REAR - REMOVAL), for proper replacement
procedures.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐCYLINDER BORE
HONING
Before honing, stuff plenty of clean shop towels
under the bores and over the crankshaft to keep
abrasive materials from entering the crankshaft
area.
(1) Used carefully, the Cylinder Bore Sizing Hone
C-823, equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best tool
for this job. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round, as well as removing light
scuffing, scoring and scratches. Usually, a few strokes
will clean up a bore and maintain the required lim-
its.
CAUTION: DO NOT use rigid type hones to remove
cylinder wall glaze.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done if
the cylinder bore is straight and round. Use a cylin-
der surfacing hone, Honing Tool C-3501, equipped
with 280 grit stones (C-3501-3810). about 20-60
strokes, depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Using honing
oil C-3501-3880, or a light honing oil, available from
major oil distributors.
CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits, or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.
The hone marks should INTERSECT at 50É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
1 - CROSSHATCH PATTERN
2 - INTERSECT ANGLE
9 - 10 ENGINE 3.9LBR/BE
ENGINE 3.9L (Continued)
Page 1158 of 2889

(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 50É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐHYDROSTATIC
LOCK
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the spark plugs.
(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(7) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(15) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐREPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐFORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS & SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN II
MopartEngine RTV GEN II is used to seal com-
ponents exposed to engine oil. This material is a spe-
cially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTV
MopartATF RTV is a specifically designed black
silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and seal-
ing properties to seal components exposed to auto-
matic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKER
MopartGasket Maker is an anaerobic type gasket
material. The material cures in the absence of air
when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The anaerobic
BR/BEENGINE 3.9L 9 - 11
ENGINE 3.9L (Continued)
Page 1159 of 2889

material is for use between two machined surfaces.
Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
MOPARtGASKET SEALANT
MopartGasket Sealant is a slow drying, perma-
nently soft sealer. This material is recommended for
sealing threaded fittings and gaskets against leakage
of oil and coolant. Can be used on threaded and
machined parts under all temperatures. This mate-
rial is used on engines with multi-layer steel (MLS)
cylinder head gaskets. This material also will pre-
vent corrosion. MopartGasket Sealant is available in
a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4oz./16 oz. can w/applicator.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET AND SEALER
APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier then using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
MopartEngine RTV GEN II or ATF RTV gasket
material should be applied in a continuous bead
approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in diameter. All
mounting holes must be circled. For corner sealing, a
3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop is placed in the
center of the gasket contact area. Uncured sealant
may be removed with a shop towel. Components
should be torqued in place while the sealant is still
wet to the touch (within 10 minutes). The usage of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing material off the location.
MopartGasket Sealant in an aerosol can should be
applied using a thin, even coat sprayed completely
over both surfaces to be joined, and both sides of a
gasket. Then proceed with assembly. Material in a
can w/applicator can be brushed on evenly over the
sealing surfaces. Material in an aerosol can should be
used on engines with multi-layer steel gaskets.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the upper crossmember and top core
support.
(4) Remove the transmission oil cooler (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/TRANSMISSION/TRANS COOLER -
REMOVAL).(5) Discharge the air conditioning system, if
equipped (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(6) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(7) Remove the A/C compressor with the lines
attached. Set aside.
(8) If equipped, remove the condenser (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
A/C CONDENSER - REMOVAL).
(9) Remove the washer bottle.
(10) Remove the fan and fan shroud (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
(11) Remove radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR - REMOVAL).
(12) Remove the generator with the wire connec-
tions (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARGING/GEN-
ERATOR - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove the air cleaner box.
(14) Disconnect the throttle linkage.
(15) Remove throttle body (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/THROTTLE BODY -
REMOVAL).
(16) Remove the intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL).
(17) Remove the distributor cap and wiring.
(18) Disconnect the heater hoses.
(19) Disconnect the power steering hoses, if
equipped.
(20) Perform the Fuel System Pressure release
procedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).Disconnect
the fuel supply line (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FITTING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(21) On Manual Transmission vehicles, remove the
shift lever.
(22) Raise and support the vehicle on a hoist.
(23) Remove the drain plug and drain the engine
oil.
(24) Remove engine front mount through-bolt nuts.
(25)Automatic TransmissionRemove the trans-
mission cooler line brackets from oil pan.
(26) Disconnect exhaust pipe at manifold.
(27) Remove starter motor (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL).
(28)Manual TransmissionRemove the transmis-
sion.(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
MANUAL - REMOVAL).
(29) Lower the vehicle.
CAUTION: DO NOT lift the engine by the intake
manifold.
(30) Install an engine lifting fixture.
9 - 12 ENGINE 3.9LBR/BE
ENGINE 3.9L (Continued)
Page 1160 of 2889

(31) Remove engine from vehicle and install
engine assembly on a repair stand.
INSTALLATION
(1) Remove engine from the repair stand and posi-
tion in the engine compartment. Position the
through-bolt into the support cushion brackets.
(2) Install an engine support fixture.
(3) Raise and support the vehicle on a hoist.
(4)Manual TransmissionInstall the transmis-
sion (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
MANUAL - INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the starter and connect the starter
wires (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING/
STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install exhaust pipe to manifold.
(7)Automatic TransmissionInstall the trans-
mission cooler line brackets on oil pan.
(8) Install engine front mount through-bolt nuts.
Tighten the nuts.
(9) Install the drain plug and tighten to 34 N´m
(25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) Lower the vehicle.
(11) Remove engine-lifting fixture.
(12) On Manual Transmission vehicles, install the
shift lever.
(13) Connect the fuel supply line (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/QUICK CON-
NECT FITTING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(14) Connect the power steering hoses, if equipped.
(15) Connect the heater hoses.
(16) Install the distributor cap and wiring.
(17) Install the intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION).(18) Using a new gasket, install throttle body
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
THROTTLE BODY - INSTALLATION).
(19) Connect the throttle linkage.
(20) Install the air cleaner box.
(21) Install the generator and wire connections
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING/STARTER
MOTOR - INSTALLATION).
(22) Install radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR - INSTALLATION).
(23) Install the fan and fan shroud (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
(24) Install the washer bottle.
(25) If equipped, install the condenser (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
A/C CONDENSER - INSTALLATION).
(26) Install the A/C compressor with the lines
attached.
(27) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(28) Evacuate and charge the air conditioning sys-
tem, if equipped (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
(29) Install the transmission oil cooler (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/TRANSMISSION/TRANS COOLER -
INSTALLATION).
(30) Install the upper crossmember and top core
support.
(31) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(32) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(33) Start engine and check for leaks.
BR/BEENGINE 3.9L 9 - 13
ENGINE 3.9L (Continued)
Page 1165 of 2889
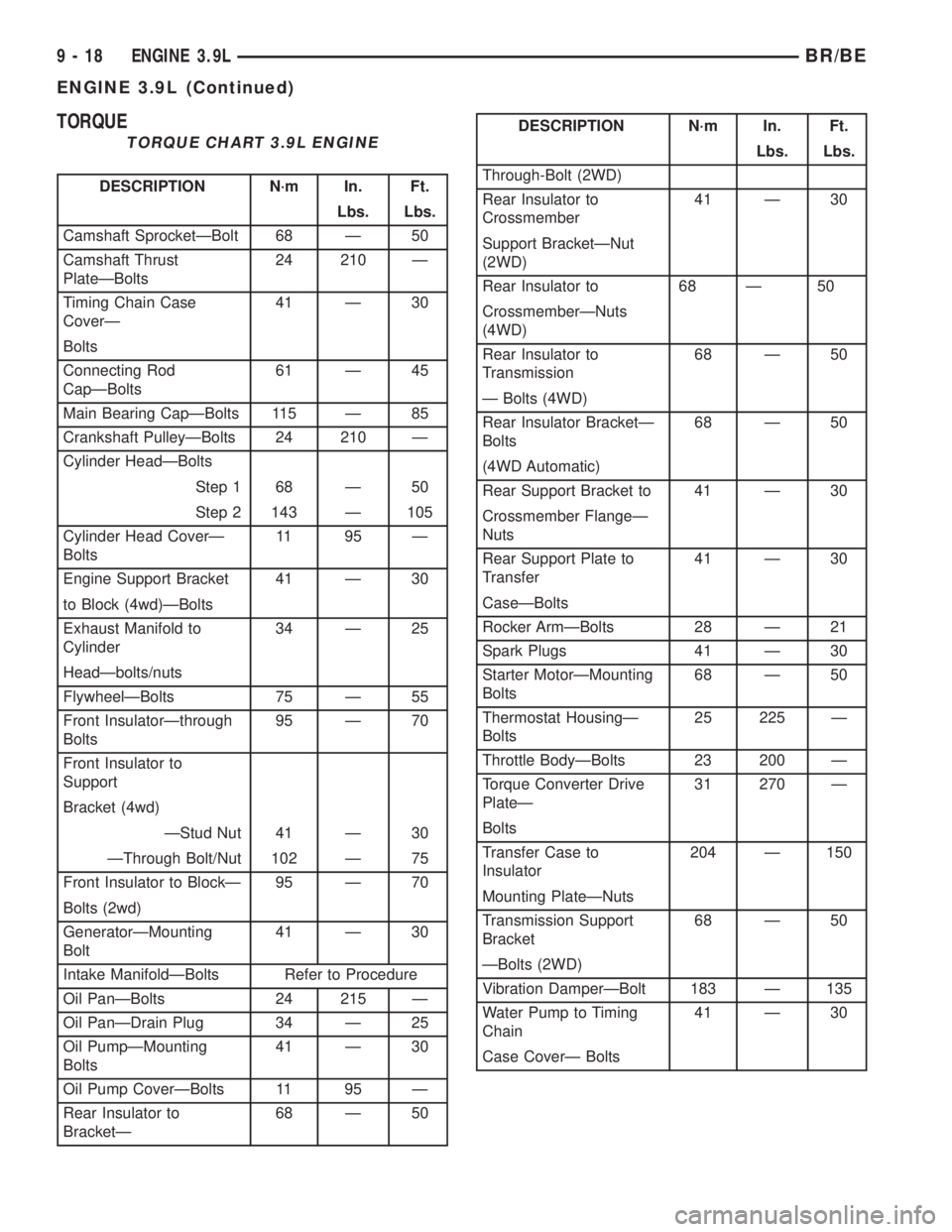
TORQUE
TORQUE CHART 3.9L ENGINE
DESCRIPTION N´m In. Ft.
Lbs. Lbs.
Camshaft SprocketÐBolt 68 Ð 50
Camshaft Thrust
PlateÐBolts24 210 Ð
Timing Chain Case
CoverÐ41 Ð 30
Bolts
Connecting Rod
CapÐBolts61 Ð 45
Main Bearing CapÐBolts 115 Ð 85
Crankshaft PulleyÐBolts 24 210 Ð
Cylinder HeadÐBolts
Step 1 68 Ð 50
Step 2 143 Ð 105
Cylinder Head CoverÐ
Bolts11 95 Ð
Engine Support Bracket 41 Ð 30
to Block (4wd)ÐBolts
Exhaust Manifold to
Cylinder34 Ð 25
HeadÐbolts/nuts
FlywheelÐBolts 75 Ð 55
Front InsulatorÐthrough
Bolts95 Ð 70
Front Insulator to
Support
Bracket (4wd)
ÐStud Nut 41 Ð 30
ÐThrough Bolt/Nut 102 Ð 75
Front Insulator to BlockÐ 95 Ð 70
Bolts (2wd)
GeneratorÐMounting
Bolt41 Ð 30
Intake ManifoldÐBolts Refer to Procedure
Oil PanÐBolts 24 215 Ð
Oil PanÐDrain Plug 34 Ð 25
Oil PumpÐMounting
Bolts41 Ð 30
Oil Pump CoverÐBolts 11 95 Ð
Rear Insulator to
BracketÐ68 Ð 50
DESCRIPTION N´m In. Ft.
Lbs. Lbs.
Through-Bolt (2WD)
Rear Insulator to
Crossmember41 Ð 30
Support BracketÐNut
(2WD)
Rear Insulator to 68 Ð 50
CrossmemberÐNuts
(4WD)
Rear Insulator to
Transmission68 Ð 50
Ð Bolts (4WD)
Rear Insulator BracketÐ
Bolts68 Ð 50
(4WD Automatic)
Rear Support Bracket to 41 Ð 30
Crossmember FlangeÐ
Nuts
Rear Support Plate to
Transfer41 Ð 30
CaseÐBolts
Rocker ArmÐBolts 28 Ð 21
Spark Plugs 41 Ð 30
Starter MotorÐMounting
Bolts68 Ð 50
Thermostat HousingÐ
Bolts25 225 Ð
Throttle BodyÐBolts 23 200 Ð
Torque Converter Drive
PlateÐ31 270 Ð
Bolts
Transfer Case to
Insulator204 Ð 150
Mounting PlateÐNuts
Transmission Support
Bracket68 Ð 50
ÐBolts (2WD)
Vibration DamperÐBolt 183 Ð 135
Water Pump to Timing
Chain41 Ð 30
Case CoverÐ Bolts
9 - 18 ENGINE 3.9LBR/BE
ENGINE 3.9L (Continued)
Page 1170 of 2889

COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
The alloy cast iron cylinder heads (Fig. 7) are held
in place by eight bolts. The spark plugs are located
at the peak of the wedge between the valves.
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable from the
battery.
(2) Drain cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the intake manifold-to-generator
bracket support rod. Remove the generator.
(4) Remove closed crankcase ventilation system.
(5) Disconnect the evaporation control system.
(6) Remove the air cleaner, air in-let hose and res-
onator.
(7) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Disconnect the fuel supply line from the fuel
rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/
QUICK CONNECT FITTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(9) Disconnect accelerator linkage and if so
equipped, the speed control and transmission kick-
down cables.
(10) Remove distributor cap and wires.
(11) Disconnect the coil wires.
(12) Disconnect coolant temperature sending unit
wire.
(13) Disconnect heater hoses and bypass hose.
(14) Disconnect the vacuum supply hoses from the
intake manifold.
(15) Disconnect the fuel injector harness and
secure out of the way.
(16) Remove cylinder head covers and gaskets
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLIN-
DER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).(17) Remove intake manifold and throttle body as
an assembly. Discard the flange side gaskets and the
front and rear cross-over gaskets.
(18) Remove exhaust manifolds (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL).
(19) Remove rocker arm assemblies and push rods.
Identify to ensure installation in original locations.
(20) Remove the head bolts from each cylinder
head and remove cylinder heads. Discard the cylin-
der head gasket.
(21) Remove spark plugs.
CLEANING
Clean all surfaces of cylinder block and cylinder
heads.
Clean cylinder block front and rear gasket surfaces
using a suitable solvent.
INSPECTION
Inspect all surfaces with a straightedge if there is
any reason to suspect leakage. If out-of-flatness
exceeds 0.00075mm (0.0001in.) times the span length
in any direction, either replace head or lightly
machine the head surface.
FOR EXAMPLE:ÐA 305 mm (12 in.) span is
0.102 mm (0.004 in.) out-of-flat. The allowable out-of-
flat is 305 x 0.00075 (12 x 0.00075) equals 0.23 mm
(0.009 in.). This amount of out-of-flat is acceptable.
The cylinder head surface finish should be
1.78-3.00 microns (70-125 microinches).
Inspect push rods. Replace worn or bent rods.
INSTALLATION
The alloy cast iron cylinder heads (Fig. 7) are held
in place by eight bolts. The spark plugs are located
at the peak of the wedge between the valves.
(1) Position the new cylinder head gaskets onto
the cylinder block.
(2) Position the cylinder heads onto head gaskets
and cylinder block.
(3) Starting at top center, tighten all cylinder head
bolts, in sequence, to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig.
7). Repeat procedure, tighten all cylinder head bolts
to 143 N´m (105 ft. lbs.) torque. Repeat procedure to
confirm that all bolts are at 143 N´m (105 ft. lbs.)
torque.
CAUTION: When tightening the rocker arm bolts, be
sure the piston in that cylinder is NOT at TDC. Con-
tact between the valves and piston could occur.
(4) Install push rods and rocker arm assemblies in
their original positions. Tighten the bolts to 28 N´m
(21 ft. lbs.) torque.
BR/BEENGINE 3.9L 9 - 23
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1171 of 2889

(5) Install the intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION) and throttle body assembly.
(6) Install exhaust manifolds (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION).
(7) Adjust spark plugs to specifications. Install the
plugs and tighten to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install coil wires.
(9) Connect coolant temperature sending unit wire.
(10) Connect the fuel injector harness.
(11) Connect the vacuum supply hoses to the
intake manifold.
(12) Connect the heater hoses and bypass hose.
(13) Install distributor cap and wires.
(14) Connect the accelerator linkage and, if so
equipped, the speed control and transmission kick-
down cables.
(15) Install the fuel supply line.
(16) Install the generator and accessory drive belt
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE
BELTS - INSTALLATION). Tighten generator
mounting bolt to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(17) Install the intake manifold-to-generator
bracket support rod. Tighten the bolts.
(18) Install cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(19) Install closed crankcase ventilation system.
(20) Connect the evaporation control system.
(21) Install the resonator assembly, air in-let hose
and air cleaner.
(22) Install the heat shields. Tighten the bolts to
41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(23) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(24) Connect the battery negative cable.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
REMOVAL
A steel-backed silicone gasket is used with the cyl-
inder head cover (Fig. 8). This gasket can be used
again.
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Disconnect closed ventilation system and evap-
oration control system from cylinder head cover.
(3) Remove cylinder head cover bolts, cover and
gasket. The gasket may be used again.
CLEANING
Clean cylinder head cover gasket surface.
Clean head rail, if necessary.
INSPECTION
Inspect cover for distortion and straighten, if nec-
essary.
Check the gasket for use in head cover installation.
If damaged, use a new gasket.
INSTALLATION
A steel-backed silicone gasket is used with the cyl-
inder head cover (Fig. 8). This gasket can be used
again.
(1) Position the cylinder head cover gasket onto
the head rail.
(2) Position the cylinder head cover onto the gas-
ket and install the bolts. Tighten the bolts to 11 N´m
(95 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install closed crankcase ventilation system and
evaporation control system.
(4) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(5) Start engine and check for leaks.
Fig. 7 Cylinder Head Bolt -Tightening Sequence
Fig. 8 Cylinder Head Cover Gasket
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER GASKET
9 - 24 ENGINE 3.9LBR/BE
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1192 of 2889

(3) Using the transmission jack, lower the trans-
mission and support cushion onto the crossmember
(Fig. 49).
(4) Install the support cushion bolts and tighten to
41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Remove the transmission jack.
(6) Lower the vehicle.
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION
A gear-type positive displacement pump (Fig. 50)is
mounted at the underside of the rear main bearing
cap. The pump uses a pick-up tube and screen
assembly to gather engine oil from the oil pan.
OPERATION
The pump draws oil through the screen and inlet
tube from the sump at the rear of the oil pan. The oil
is driven between the drive and idler gears and
pump body, then forced through the outlet to the
block. An oil gallery in the block channels the oil to
the inlet side of the full flow oil filter. After passing
through the filter element, the oil passes from the
center outlet of the filter through an oil gallery that
channels the oil up to the main gallery, which
extends the entire length on the right side of the
block. The oil then goes down to the No. 1 main bear-
ing, back up to the left side of the block, and into the
oil gallery on the left side of the engine.
Galleries extend downward from the main oil gal-
lery to the upper shell of each main bearing. The
crankshaft is drilled internally to pass oil from the
main bearing journals to the connecting rod journals.
Each connecting rod bearing has half a hole in it, oil
passes through the hole when the rods rotate and the
hole lines up, oil is then thrown off as the rod
rotates. This oil throwoff lubricates the camshaft
lobes, distributor drive gear, cylinder walls, and pis-
ton pins.The hydraulic valve tappets receive oil directly
from the main oil gallery. The camshaft bearings
receive oil from the main bearing galleries. The front
camshaft bearing journal passes oil through the cam-
shaft sprocket to the timing chain. Oil drains back to
the oil pan under the No. 1 main bearing cap.
The oil supply for the rocker arms and bridged
pivot assemblies is provided by the hydraulic valve
tappets, which pass oil through hollow push rods to a
hole in the corresponding rocker arm. Oil from the
rocker arm lubricates the valve train components.
The oil then passes down through the push rod guide
holes and the oil drain-back passages in the cylinder
head, past the valve tappet area, and then returns to
the oil pan (Fig. 51).
Fig. 50 Positive Displacement Oil PumpÐTypical
1 - INNER ROTOR AND SHAFT
2 - BODY
3 - DISTRIBUTOR DRIVESHAFT (REFERENCE)
4 - COTTER PIN
5 - RETAINER CAP
6 - SPRING
7 - RELIEF VALVE
8 - LARGE CHAMFERED EDGE
9 - BOLT
10 - COVER
11 - OUTER ROTOR
BR/BEENGINE 3.9L 9 - 45
REAR MOUNT (Continued)