2001 DODGE RAM height
[x] Cancel search: heightPage 1344 of 2889
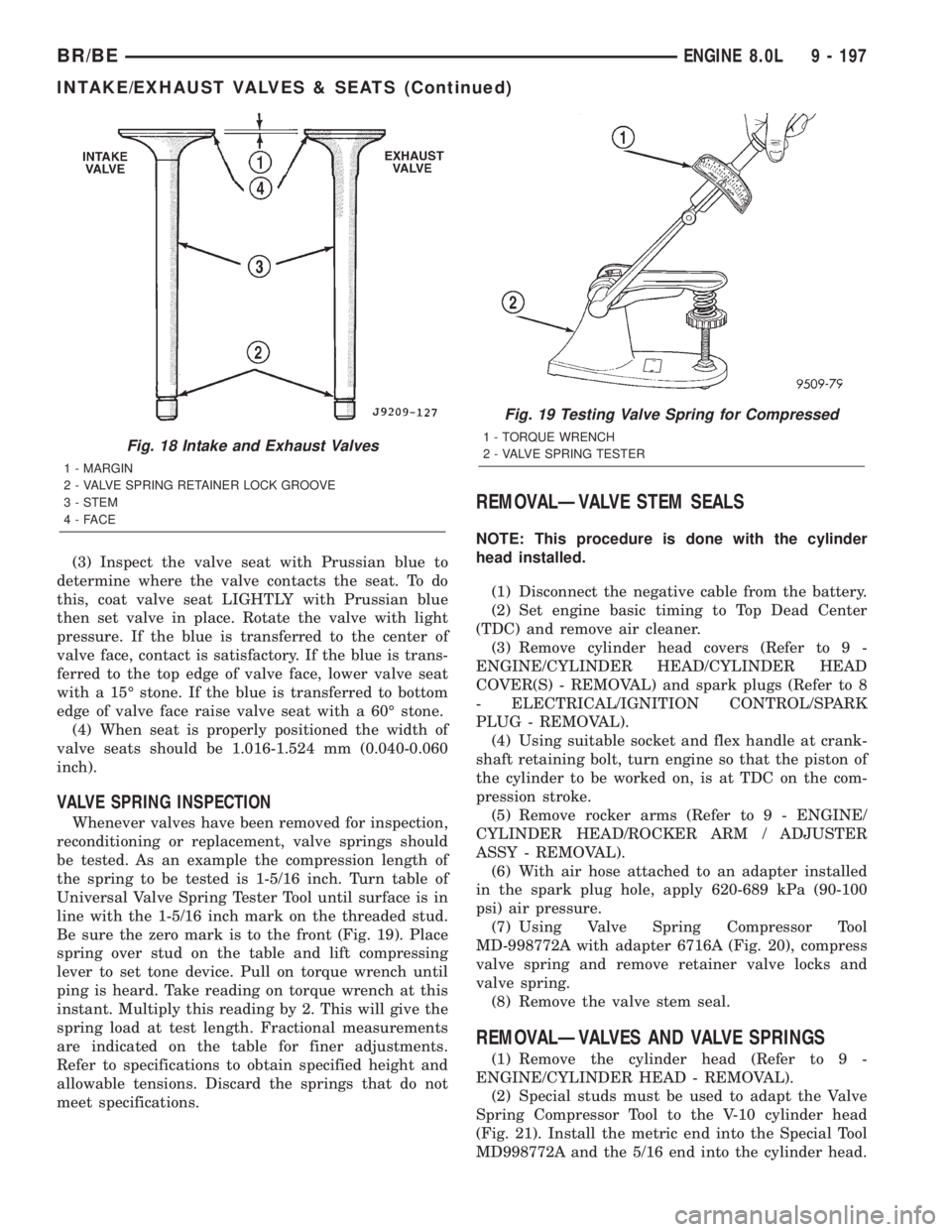
(3) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seat LIGHTLY with Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to the top edge of valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15É stone. If the blue is transferred to bottom
edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 60É stone.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
valve seats should be 1.016-1.524 mm (0.040-0.060
inch).
VALVE SPRING INSPECTION
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested. As an example the compression length of
the spring to be tested is 1-5/16 inch. Turn table of
Universal Valve Spring Tester Tool until surface is in
line with the 1-5/16 inch mark on the threaded stud.
Be sure the zero mark is to the front (Fig. 19). Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by 2. This will give the
spring load at test length. Fractional measurements
are indicated on the table for finer adjustments.
Refer to specifications to obtain specified height and
allowable tensions. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications.
REMOVALÐVALVE STEM SEALS
NOTE: This procedure is done with the cylinder
head installed.
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Set engine basic timing to Top Dead Center
(TDC) and remove air cleaner.
(3) Remove cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL) and spark plugs (Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK
PLUG - REMOVAL).
(4) Using suitable socket and flex handle at crank-
shaft retaining bolt, turn engine so that the piston of
the cylinder to be worked on, is at TDC on the com-
pression stroke.
(5) Remove rocker arms (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER
ASSY - REMOVAL).
(6) With air hose attached to an adapter installed
in the spark plug hole, apply 620-689 kPa (90-100
psi) air pressure.
(7) Using Valve Spring Compressor Tool
MD-998772A with adapter 6716A (Fig. 20), compress
valve spring and remove retainer valve locks and
valve spring.
(8) Remove the valve stem seal.
REMOVALÐVALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
(1) Remove the cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(2) Special studs must be used to adapt the Valve
Spring Compressor Tool to the V-10 cylinder head
(Fig. 21). Install the metric end into the Special Tool
MD998772A and the 5/16 end into the cylinder head.
Fig. 18 Intake and Exhaust Valves
1 - MARGIN
2 - VALVE SPRING RETAINER LOCK GROOVE
3 - STEM
4-FACE
Fig. 19 Testing Valve Spring for Compressed
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - VALVE SPRING TESTER
BR/BEENGINE 8.0L 9 - 197
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1345 of 2889

(3) Compress valve springs using Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD-998772A with Adapter 6716A
and Screw 6765 (Fig. 22). Tap the retainer using a
brass drift and ball peen hammer to loosen locks
away from retainer.
(4) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers and valve springs. Check for abnormal
wear, replace as required.
(5) Remove the valve stem seals.(6) Before removing valves, remove any burrs from
valve stem lock grooves to prevent damage to the
valve guides. Identify valves to ensure installation in
original location.
CLEANING
Clean valves thoroughly. Discard burned, warped,
or cracked valves.
Remove carbon and varnish deposits from inside of
valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
INSPECTION
Measure valve stems for wear. If wear exceeds
0.051 mm (0.002 in.), replace the valve.
Measure valve stem guide clearance as follows:
(1) Install Valve Guide Sleeve Tool C-3973 over
valve stem and install valve (Fig. 23). The special
sleeve places the valve at the correct height for
checking with a dial indicator.
(2) Attach dial indicator Tool C-3339 to cylinder
head and set it at right angles to valve stem being
measured (Fig. 24).
(3) Move valve to and from the indicator. The total
dial indicator reading should not exceed 0.432 mm
(0.017 in.). Ream the guides for valves with oversize
stems if dial indicator reading is excessive or if the
stems are scuffed or scored.
INSTALLATIONÐVALVE STEM SEAL
(1) Install new seal onto valve stem.
(2) Position valve spring onto valve stem.
(3) Position Valve Spring Compressor with Adapter
Studs onto cylinder head
Fig. 20 Valve Spring Compressor MD-998772A with
Adaptor 6716-A and Screw 6765
1 - SPECIAL TOOL MD 998772A
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6765
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6716A
4 - AIR HOSE
Fig. 21 Special Studs 6715 for V-10 Engine
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6715
Fig. 22 Valve Spring Compressor MD-998772A with
Adaptor 6716-A and Screw 6765
1 - SPECIAL TOOL MD 998772A
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6765
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6716A
4 - AIR HOSE
9 - 198 ENGINE 8.0LBR/BE
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1347 of 2889

install locks and release tool. Tap the retainer with a
brass or heavy plastic hammer to ensure locks have
been seated.
(8) If valves and/or seats were ground, measure
the installed height of springs. Make sure the mea-
surement is taken from bottom of spring seat in cyl-
inder head to the bottom surface of spring retainer. If
spacers are installed, measure from the top of spacer.
If height is greater than 42.86 mm (1-11/16 inches),
install a 1.587 mm (1/16 inch) spacer in head coun-
terbore. Ensure this brings spring height back to nor-
mal, 41.27 to 42.86 mm (1-5/8 to 1-11/16 inch).
(9) Install the cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER
ASSY
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect spark plug wires by pulling the boot
straight out in line with plug.
(2) Remove cylinder head cover and gasket (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER
HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the rocker arm bolts and the rocker
arm assembly (Fig. 26). Place rocker arm assemblies
on a bench in the same order as removed.
(4) Remove the push rods and place them on a
bench in the same order as removed.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: DO NOT rotate or crank the engine dur-
ing or immediately after rocker arm installation.
Allow the hydraulic roller tappets adequate time to
bleed down (about 5 minutes).
(1) Install the push rods in the same order as
removed.
(2) Install rocker arm assemblies in the same
order as removed. Tighten the rocker arm bolts to 28
N´m (21 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install cylinder head cover and gasket (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(4) Connect spark plug wires.
ENGINE BLOCK
CLEANING
Clean cylinder block thoroughly and check all core
hole plugs for evidence of leaking.
INSPECTION
Examine block for cracks or fractures.
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Cylinder Bore Indicator Tool,
Special tool 6879 or equivalent. The cylinder block
should be bored and honed with new pistons and
rings fitted if:
²The cylinder bores show more than 0.127 mm
(0.005 inch) out-of-round.
²The cylinder bores show a taper of more than
0.254 mm (0.010 inch).
²The cylinder walls are badly scuffed or scored.
Boring and honing operation should be closely coor-
dinated with the fitting of pistons and rings so spec-
ified clearances may be maintained.
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK)
REMOVALÐCAMSHAFT BEARINGS
This procedure requires that the engine is removed
from the vehicle.
(1) With engine completely disassembled, drive out
rear cam bearing core hole plug.
NOTE: It is not advisable to attempt to replace cam-
shaft bearings unless special removal and installa-
tion tools are available, such as recommended tool
8544 Camshaft Bushing Remover Installer.
Fig. 26 Rocker Arm
1 - ROCKER ARMS
2 - ROCKER ARM PEDESTALS
3 - RETAINER
9 - 200 ENGINE 8.0LBR/BE
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1419 of 2889

(29)Remove the camshaft (Fig. 91) and thrust plate.
INSPECTION
Camshaft
(1)Inspect the valve lobes and bearing journals for
cracks, pitting, scoring, or generally excessive wear.
Replace any camshaft that exceeds the allowable limits.
(2)Measure the bearing journals and lobes (Fig. 92).
CAUTION: If Camshaft lobes are worn, requiring
camshaft replacement, it is necessary to replace the
tappets also. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
SOLID LIFTERS - REMOVAL).
Camshaft Bushing/Bores
Camshaft bores No. 2±7do notuse a bushing.
(1) Inspect the camshaft bushing and bores for
signs of excessive wear.
(2) Measure the camshaft bushing and bores (Fig.
93) with a telescoping bore gauge and micrometer. If
out of specification, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE
BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) -
REMOVAL).
(3) Inspect the camshaft bushing oil hole for align-
ment with cylinder block (Fig. 94).
Fig. 92 Measuring
1 - VALVE LOBE
2 - CAMSHAFT JOURNAL
JOURNAL DIAMETER #1 54.028 mm (2.1270 in.) MIN.
JOURNAL DIAMETER #2 - 7 53.987 mm (2.1245 in.) MIN.
LOBE HEIGHT INTAKE 47.173 mm (1.857 in.) MIN.
LOBE HEIGHT EXHAUST 45.636 mm (1.796 in.) MIN.
Fig. 91 Camshaft Removal/Installation
Fig. 93 Measuring Camshaft Bushing and Bores
Fig. 94 Inspecting Oil Hole Alignment
1 - CAMSHAFT BUSHING
9 - 272 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) (Continued)
Page 1444 of 2889

CLEANING
Remove all gasket material from the oil pan and
cylinder block sealing surfaces. Extra effort may be
required around T-joint areas. Clean oil pan and
flush suction tube with a suitable solvent.
INSPECTION
Inspect the oil pan, suction tube, and tube braces
for cracks and damage. Replace any defective compo-
nent. Inspect the oil drain plug and drain hole
threads. Inspect the oil pan sealing surface for
straightness. Repair any minor imperfections with a
ball-peen hammer. Do not attempt to repair an oil
pan by welding.
INSTALLATION
(1) Fill the T-joint between the pan rail/gear hous-
ing and pan rail/rear seal retainer with sealant. Use
MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant or equiva-
lent.
(2) Place suction tube in oil pan and guide them
into place (Fig. 151). Using a new tube to oil pump
gasket, install and tighten the suction tube bolts by
hand. Starting with the oil pump inlet bolts, tighten
the bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the
remaining tube brace bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Starting in the center and working outward,
tighten the oil pan bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Install the flywheel housing assembly with the
starter motor attached and tighten bolts to 60 N´m
(44 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect starter motor cables.
(6) Install transmission and transfer case (if
equipped).
(7) Lower vehicle.
(8) Install battery negative cables.
(9) Fill the crankcase with new engine oil.
(10) Start engine and check for leaks. Stop engine,
check oil level, and adjust, if necessary.
OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Remove the threaded plug, spring and plunger
(Fig. 152). Insert a finger or a seal pick to lift the
plunger from the bore.
NOTE: If the plunger is stuck in the bore, it will be
necessary to remove the filter head.
CLEANING
(1) Clean the regulator spring and plunger with a
suitable solvent and blow dry with compressed air. If
the plunger bore requires cleaning, it is necessary to
remove the oil filter head to avoid getting debris into
the engine.
INSPECTION
Inspect the plunger and plunger bore for cracks
and excessive wear. Polished surfaces are acceptable.
Verify that the plunger moves freely in the bore.
Check the spring for height and load limitations
(Fig. 153). Replace the spring if out of limits shown
in the figure.
Fig. 152 Oil Pressure Regulator
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - PLUG
3 - GASKET
4 - SPRING
5 - VALVE
Fig. 153 Oil Pressure Regulator Spring Check
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 297
OIL PAN (Continued)
Page 1528 of 2889

(5) Install new plastic tie strap (Fig. 28) to secure
sensor pigtail harness to side of engine block. Thread
tie strap through casting hole on cylinder block.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The 5±pin, 12±volt, fuel pump relay is located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the
label on the PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) energizes
the electric fuel pump through the fuel pump relay.
The fuel pump relay is energized by first applying
battery voltage to it when the ignition key is turned
ON, and then applying a ground signal to the relay
from the PCM.
Whenever the ignition key is turned ON, the elec-
tric fuel pump will operate. But, the PCM will shut-
down the ground circuit to the fuel pump relay in
approximately 1±3 seconds unless the engine is oper-
ating or the starter motor is engaged.
REMOVAL
The fuel pump relay is located in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC) (Fig. 31). Refer to label on PDC
cover for relay location.
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
The fuel pump relay is located in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC) (Fig. 31). Refer to label on PDC
cover for relay location.
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The IAC stepper motor is mounted to the throttle
body, and regulates the amount of air bypassing the
control of the throttle plate. As engine loads and
ambient temperatures change, engine rpm changes.
A pintle on the IAC stepper motor protrudes into a
passage in the throttle body, controlling air flow
through the passage. The IAC is controlled by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to maintain the
target engine idle speed.
OPERATION
At idle, engine speed can be increased by retract-
ing the IAC motor pintle and allowing more air to
pass through the port, or it can be decreased by
restricting the passage with the pintle and diminish-
ing the amount of air bypassing the throttle plate.
The IAC is called a stepper motor because it is
moved (rotated) in steps, or increments. Opening the
IAC opens an air passage around the throttle blade
which increases RPM.
The PCM uses the IAC motor to control idle speed
(along with timing) and to reach a desired MAP dur-
ing decel (keep engine from stalling).
The IAC motor has 4 wires with 4 circuits. Two of
the wires are for 12 volts and ground to supply electri-
cal current to the motor windings to operate the step-
per motor in one direction. The other 2 wires are also
for 12 volts and ground to supply electrical current to
operate the stepper motor in the opposite direction.
To make the IAC go in the opposite direction, the
PCM just reverses polarity on both windings. If only
1 wire is open, the IAC can only be moved 1 step
(increment) in either direction. To keep the IAC
motor in position when no movement is needed, the
PCM will energize both windings at the same time.
This locks the IAC motor in place.
In the IAC motor system, the PCM will count
every step that the motor is moved. This allows the
PCM to determine the motor pintle position. If the
memory is cleared, the PCM no longer knows the
position of the pintle. So at the first key ON, the
PCM drives the IAC motor closed, regardless of
where it was before. This zeros the counter. From
this point the PCM will back out the IAC motor and
keep track of its position again.
Fig. 31 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
1 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 41
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1552 of 2889

CAUTION: Do not allow the ohmmeter to contact
terminals 85 or 86 during these tests. Damage to
ohmmeter may result.
(7) Attach the other jumper wire (12V +) to termi-
nal number 86. This will activate the relay. Continu-
ity should now be present between terminals number
87 and 30. Continuity should not be present between
terminals number 87A and 30.
(8) Disconnect jumper wires from relay and 12 Volt
power source.
(9) If continuity or resistance tests did not pass,
replace relay. If tests passed, refer to 8, Wiring Dia-
grams for (fuel system) relay wiring schematics and
for additional circuit information.
REMOVAL
The fuel heater relay is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) (Fig. 13). Refer to label under
PDC cover for relay location.
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
The fuel heater relay is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) (Fig. 13). Refer to label under
PDC cover for relay location.
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
FUEL INJECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTIONÐFUEL PUMP 245 H.P.
Although the fuel injection pump on the 245 horse-
power engine appears similar to other VP 44 injec-
tion pumps, there are internal differences that make
it unique. If pump replacement is necessary, be sure
to verify pump number. The pump number can be
found on the Fuel Injection Pump Data Plate (Fig.
14).
Fig. 13 Power Distribution Center (PDC) Location
1 - CLIP
2 - BATTERY
3 - TRAY
4 - NEGATIVE CABLE
5 - POSITIVE CABLE
6 - CLIP
7 - FENDER INNER SHIELD
8 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
Fig. 14 Fuel Injection Pump Data Plate Location
1 - PUMP DATA PLATE
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 65
FUEL HEATER RELAY (Continued)
Page 1643 of 2889
(9) Remove the reverse idler shaft support bolt
(front bolt) (Fig. 19).
(10) Loosen rear reverse idler shaft bolt (rear bolt)
(Fig. 19).
(11) Remove reverse idler shaft support segment
by sliding it straight out of housing.
(12) Support geartrain and rear housing on Fix-
ture 6747 as follows:
(a) Adjust height of reverse idler pedestal rod
until the reverse idle shaft bottoms in Cup 8115.
(b) Position Adapters 6747-1A and 6747-2B on
Fixture 6747.
(c) Slide fixture tool onto input shaft, counter-
shaft and idler gear (Fig. 20).
(d) Stand geartrain and rear housing upright on
fixture (Fig. 21). Have helper hold fixture tool in
place while housing and geartrain is being rotated
into upright position.
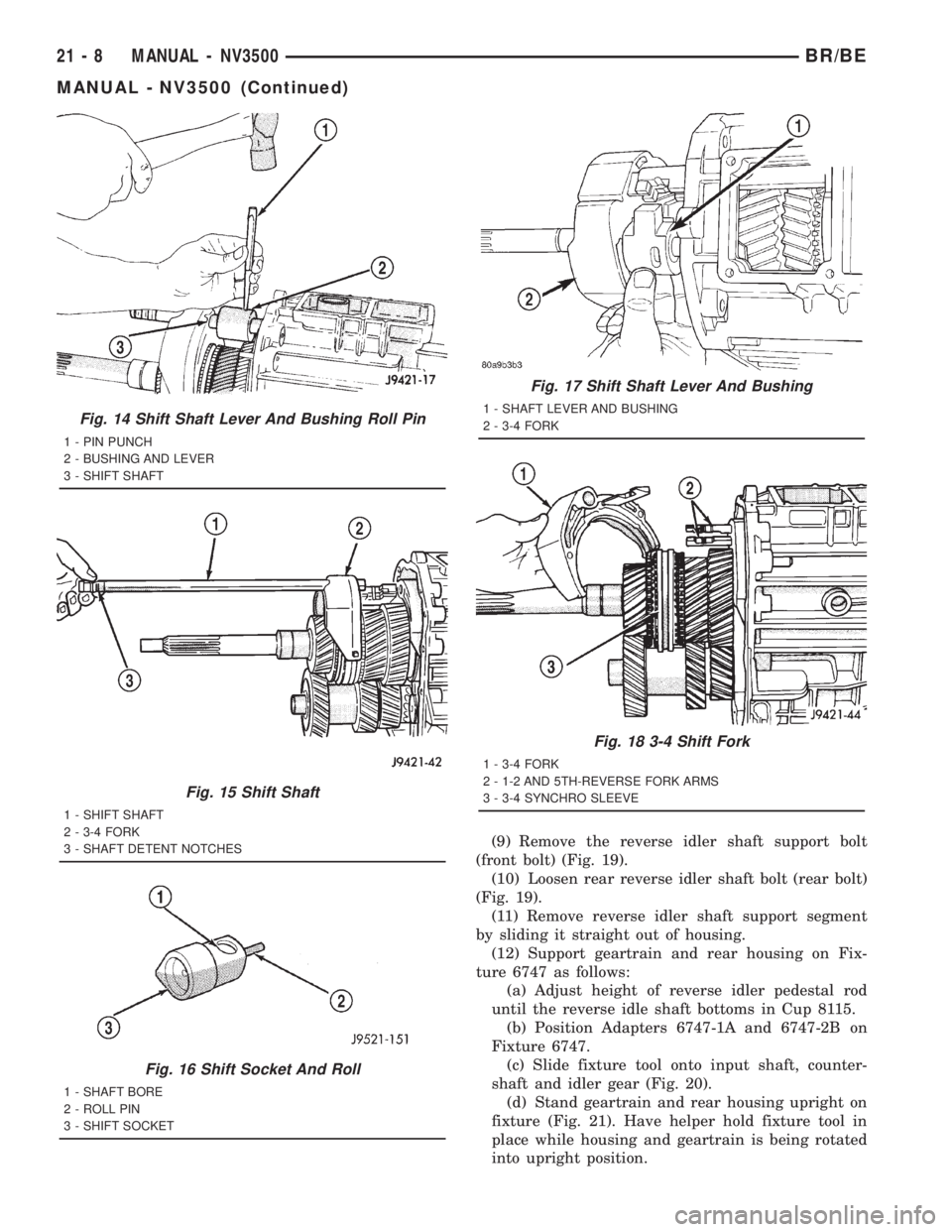
Fig. 14 Shift Shaft Lever And Bushing Roll Pin
1 - PIN PUNCH
2 - BUSHING AND LEVER
3 - SHIFT SHAFT
Fig. 15 Shift Shaft
1 - SHIFT SHAFT
2 - 3-4 FORK
3 - SHAFT DETENT NOTCHES
Fig. 16 Shift Socket And Roll
1 - SHAFT BORE
2 - ROLL PIN
3 - SHIFT SOCKET
Fig. 17 Shift Shaft Lever And Bushing
1 - SHAFT LEVER AND BUSHING
2 - 3-4 FORK
Fig. 18 3-4 Shift Fork
1 - 3-4 FORK
2 - 1-2 AND 5TH-REVERSE FORK ARMS
3 - 3-4 SYNCHRO SLEEVE
21 - 8 MANUAL - NV3500BR/BE
MANUAL - NV3500 (Continued)