2001 DODGE RAM oil type
[x] Cancel search: oil typePage 421 of 2889

WARNING: WEAR PROTECTIVE EYEWEAR THAT
MEETS THE REQUIREMENTS OF OSHA AND ANSI
Z87.1±1968. WEAR STANDARD INDUSTRIAL RUB-
BER GLOVES.
KEEP LIGHTED CIGARETTES, SPARKS, FLAMES,
AND OTHER IGNITION SOURCES AWAY FROM THE
AREA TO PREVENT THE IGNITION OF COMBUSTI-
BLE LIQUIDS AND GASES. KEEP A CLASS (B) FIRE
EXTINGUISHER IN THE AREA WHERE THE
FLUSHER WILL BE USED.
KEEP THE AREA WELL VENTILATED.
DO NOT LET FLUSHING SOLVENT COME IN CON-
TACT WITH YOUR EYES OR SKIN: IF EYE CONTAM-
INATION OCCURS, FLUSH EYES WITH WATER FOR
15 TO 20 SECONDS. REMOVE CONTAMINATED
CLOTHING AND WASH AFFECTED SKIN WITH
SOAP AND WATER. SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION.
(1) Remove cover plate filler plug on Tool 6906-B.
Fill reservoir 1/2 to 3/4 full of fresh flushing solution.
Flushing solvents are petroleum based solutions gen-
erally used to clean automatic transmission compo-
nents.DO NOTuse solvents containing acids, water,
gasoline, or any other corrosive liquids.
(2) Reinstall filler plug on Tool 6906-B.
(3) Verify pump power switch is turned OFF. Con-
nect red alligator clip to positive (+) battery post.
Connect black (-) alligator clip to a good ground.
(4) Disconnect the cooler lines at the transmission.
NOTE: When flushing transmission cooler and
lines, ALWAYS reverse flush.
NOTE: The converter drainback valve must be
removed and an appropriate replacement hose
installed to bridge the space between the transmis-
sion cooler line and the cooler fitting. Failure to
remove the drainback valve will prevent reverse
flushing the system. A suitable replacement hose
can be found in the adapter kit supplied with the
flushing tool.
(5) Connect the BLUE pressure line to the OUT-
LET (From) cooler line.
(6) Connect the CLEAR return line to the INLET
(To) cooler line
(7) Turn pump ON for two to three minutes to
flush cooler(s) and lines.
(8) Turn pump OFF.
(9) Disconnect CLEAR suction line from reservoir
at cover plate. Disconnect CLEAR return line at
cover plate, and place it in a drain pan.
(10) Turn pump ON for 30 seconds to purge flush-
ing solution from cooler and lines. Turn pump OFF.(11) Place CLEAR suction line into a one quart
container of MopartATF +4, type 9602, Automatic
Transmission Fluid.
(12) Turn pump ON until all transmission fluid is
removed from the one quart container and lines. This
purges any residual cleaning solvent from the trans-
mission cooler and lines. Turn pump OFF.
(13) Disconnect alligator clips from battery. Recon-
nect flusher lines to cover plate, and remove flushing
adapters from cooler lines.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUSHING COOLER
AND TUBES - WITHOUT RADIATOR IN-TANK
TRANSMISSION OIL COOLER
When a transmission failure has contaminated the
fluid, the oil cooler(s) must be flushed. The torque
converter must also be replaced. This will insure that
metal particles or sludged oil are not later trans-
ferred back into the reconditioned (or replaced) trans-
mission.
(1) Remove cover plate filler plug on Tool 6906B.
Fill reservoir 1/2 to 3/4 full of fresh flushing solution.
Flushing solvents are petroleum based solutions gen-
erally used to clean automatic transmission compo-
nents.DO NOTuse solvents containing acids, water,
gasoline, or any other corrosive liquids.
(2) Reinstall filler plug on Tool 6906B.
(3) Verify pump power switch is turned OFF. Con-
nect red alligator clip to positive (+) battery post.
Connect black (-) alligator clip to a good ground.
(4) Disconnect the cooler lines at the transmission.
NOTE: When flushing transmission cooler and
lines, ALWAYS reverse flush.
NOTE: The converter drainback valve must be
removed and an appropriate replacement hose
installed to bridge the space between the transmis-
sion cooler line and the cooler fitting. Failure to
remove the drainback valve will prevent reverse
flushing the system. A suitable replacement hose
can be found in the adapter kit supplied with the
flushing tool.
(5) Connect the BLUE pressure line to the OUT-
LET (From) cooler line.
(6) Connect the CLEAR return line to the INLET
(To) cooler line
(7) Remove the transmission oil cooler from the
vehicle. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/TRANSMISSION/
TRANS COOLER - REMOVAL)
(8) Remove the transmission oil cooler thermostat.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/TRANSMISSION/TRANS
COOLER - DISASSEMBLY)
7 - 86 TRANSMISSIONBR/BE
TRANS COOLER - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 422 of 2889

(9) Re-install the thermostat cover onto the oil
cooler and install the snap-ring.
(10) Re-connect the oil cooler to the transmission
cooler lines.
(11) Turn pump ON for two to three minutes to
flush cooler(s) and lines.
NOTE: This flushes the bypass circuit of the cooler
only.
(12) Turn pump OFF.
(13) Remove the thermostat cover from the oil
cooler.
(14) Install Special Tool Cooler Plug 8414 into the
transmission oil cooler.
(15) Re-install the thermostat cover onto the oil
cooler and install the snap-ring.
(16) Turn pump ON for two to three minutes to
flush cooler(s) and lines.
NOTE: This flushes the main oil cooler core pas-
sages only.
(17) Turn pump OFF.
(18) Remove the thermostat cover from the oil
cooler.
(19) Remove Special Tool Cooler Plug 8414 from
the transmission oil cooler.
(20) Install a new thermostat spring, thermostat,
cover, and snap-ring into the transmission oil cooler.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/TRANSMISSION/TRANS
COOLER - ASSEMBLY)
(21) Install the transmission oil cooler onto the
vehicle. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/TRANSMISSION/
TRANS COOLER - INSTALLATION)
(22) Disconnect CLEAR suction line from reservoir
at cover plate. Disconnect CLEAR return line at
cover plate, and place it in a drain pan.
(23) Turn pump ON for 30 seconds to purge flush-
ing solution from cooler and lines. Turn pump OFF.
(24) Place CLEAR suction line into a one quart
container of MopartATF +4, type 9602, Automatic
Transmission fluid.
(25) Turn pump ON until all transmission fluid is
removed from the one quart container and lines. This
purges any residual cleaning solvent from the trans-
mission cooler and lines. Turn pump OFF.
(26) Disconnect alligator clips from battery. Recon-
nect flusher lines to cover plate, and remove flushing
adapters from cooler lines.
REMOVALÐAIR TO OIL COOLER
(1) Remove front bumper.
(2) Place a drain pan under the oil cooler.
(3) Raise the vehicle.
(4) Disconnect the oil cooler quick-connect fittings
from the transmission lines.(5) Remove the charge air cooler-to-oil cooler bolt
(Fig. 8).
(6) Remove two mounting nuts.
(7) Remove the oil cooler and line assembly
towards the front of vehicle. Cooler must be rotated
and tilted into position while removing.
REMOVALÐWATER TO OIL COOLER
CAUTION: If a leak should occur in the water-to-oil
cooler mounted to the side of the engine block,
engine coolant may become mixed with transmis-
sion fluid. Transmission fluid may also enter engine
cooling system. Both cooling system and transmis-
sion should be drained and inspected in case of oil
cooler leakage.
(1) Disconnect both battery negative cables.
(2) Remove air cleaner assembly and air cleaner
intake hoses.
(3) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Disconnect coolant lines from cooler.
(5) Disconnect transmission oil lines from cooler.
Plug cooler lines to prevent oil leakage.
(6) Remove oil cooler mounting straps (Fig. 9).
Fig. 8 Auxiliary Transmission Oil CoolerÐDiesel
Engine
1 - CHARGE AIR COOLER (INTERCOOLER)
2 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS (2)
3 - MOUNTING NUTS (2)
4 - MOUNTING BOLT
5 - TRANSMISSION OIL COOLER
BR/BETRANSMISSION 7 - 87
TRANS COOLER - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 500 of 2889

BATTERY TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) is attached
to the battery tray located under the battery.
OPERATION
The BTS is used to determine the battery temper-
ature and control battery charging rate. This temper-
ature data, along with data from monitored line
voltage, is used by the PCM to vary the battery
charging rate. System voltage will be higher at colder
temperatures and is gradually reduced at warmer
temperatures.
The PCM sends 5 volts to the sensor and is
grounded through the sensor return line. As temper-
ature increases, resistance in the sensor decreases
and the detection voltage at the PCM increases.
The BTS is also used for OBD II diagnostics. Cer-
tain faults and OBD II monitors are either enabled
or disabled, depending upon BTS input (for example,
disable purge and enable Leak Detection Pump
(LDP) and O2 sensor heater tests). Most OBD II
monitors are disabled below 20ÉF.
REMOVAL
The battery temperature sensor is located under
the vehicle battery (Fig. 1) and is attached (snapped
into) a mounting hole on battery tray. On models
equipped with a diesel engine (dual batteries), only
one sensor is used. The sensor is located under the
battery on drivers side of vehicle.
(1) Remove battery. Refer to 8, Battery for proce-
dures.
(2) Disconnect sensor pigtail harness from engine
wire harness.
(3) Pry sensor straight up from battery tray
mounting hole.
INSTALLATION
The battery temperature sensor is located under
the vehicle battery (Fig. 1) and is attached (snapped
into) a mounting hole on battery tray. On models
equipped with a diesel engine (dual batteries), only
one sensor is used. The sensor is located under the
battery on drivers side of vehicle.
(1) Feed pigtail harness through mounting hole in
top of battery tray and press sensor into top of tray
(snaps in).
(2) Connect pigtail harness.
(3) Install battery. Refer to 8A, Battery for proce-
dures.
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION
The generator is belt-driven by the engine using a
serpentine type drive belt. It is serviced only as a
complete assembly. If the generator fails for any rea-
son, the entire assembly must be replaced.
OPERATION
As the energized rotor begins to rotate within the
generator, the spinning magnetic field induces a cur-
rent into the windings of the stator coil. Once the
generator begins producing sufficient current, it also
provides the current needed to energize the rotor.
The Y type stator winding connections deliver the
induced alternating current to 3 positive and 3 neg-
ative diodes for rectification. From the diodes, recti-
fied direct current is delivered to the vehicle
electrical system through the generator battery ter-
minal.
Fig. 1 Battery Temperature Sensor Location
1 - BATT. TEMP. SENSOR
2 - BATTERY HOLD DOWN STRAP
3 - PIGTAIL HARNESS
4 - U-NUT
5 - U-NUT
6 - ELEC. CONNEC.
BR/BECHARGING 8F - 29
Page 503 of 2889

STARTING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STARTING
DESCRIPTION...........................32
OPERATION.............................32
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................33
STARTING SYSTEM.....................33
SPECIFICATIONS........................38
ENGINE STARTER MOTOR
DESCRIPTION...........................39
OPERATION.............................39
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................39STARTERMOTOR......................39
REMOVAL..............................40
INSTALLATION...........................41
ENGINE STARTER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION...........................42
OPERATION.............................42
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................42
STARTER RELAY.......................42
REMOVAL..............................43
INSTALLATION...........................43
STARTING
DESCRIPTION
The starting system consists of:
²Starter relay
²Starter motor (including an integral starter sole-
noid)
Other components to be considered as part of start-
ing system are:
²Battery
²Battery cables
²Ignition switch and key lock cylinder
²Clutch pedal position switch (manual transmis-
sion)
²Park/neutral position switch (automatic trans-
mission)
²Wire harnesses and connections.
The Battery, Starting, and Charging systems oper-
ate in conjunction with one another, and must be
tested as a complete system. For correct operation of
starting/charging systems, all components used in
these 3 systems must perform within specifications.
When attempting to diagnose any of these systems, it
is important that you keep their interdependency in
mind.
The diagnostic procedures used in each of these
groups include the most basic conventional diagnostic
methods, to the more sophisticated On-Board Diag-
nostics (OBD) built into the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM). Use of an induction-type milliampere
ammeter, volt/ohmmeter, battery charger, carbon pile
rheostat (load tester), and 12-volt test lamp may be
required.
Certain starting system components are monitored
by the PCM and may produce a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC). Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes for
additional information and a list of codes.
OPERATION
The starting system components form two separate
circuits. A high-amperage feed circuit that feeds the
starter motor between 150 and 350 amperes (700
amperes - diesel engine), and a low-amperage control
circuit that operates on less than 20 amperes. The
high-amperage feed circuit components include the
battery, the battery cables, the contact disc portion of
the starter solenoid, and the starter motor. The low-
amperage control circuit components include the igni-
tion switch, the clutch pedal position switch (manual
transmission), the park/neutral position switch (auto-
matic transmission), the starter relay, the electro-
magnetic windings of the starter solenoid, and the
connecting wire harness components.
If the vehicle is equipped with a manual transmis-
sion, it has a clutch pedal position switch installed in
series between the ignition switch and the coil bat-
tery terminal of the starter relay. This normally open
switch prevents the starter relay from being ener-
gized when the ignition switch is turned to the
momentary Start position, unless the clutch pedal is
depressed. This feature prevents starter motor oper-
ation while the clutch disc and the flywheel are
engaged. The starter relay coil ground terminal is
always grounded on vehicles with a manual trans-
mission.
If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic trans-
mission, battery voltage is supplied through the low-
amperage control circuit to the coil battery terminal
of the starter relay when the ignition switch is
turned to the momentary Start position. The park/
neutral position switch is installed in series between
the starter relay coil ground terminal and ground.
This normally open switch prevents the starter relay
from being energized and the starter motor from
operating unless the automatic transmission gear
selector is in the Neutral or Park positions.
8F - 32 STARTINGBR/BE
Page 509 of 2889
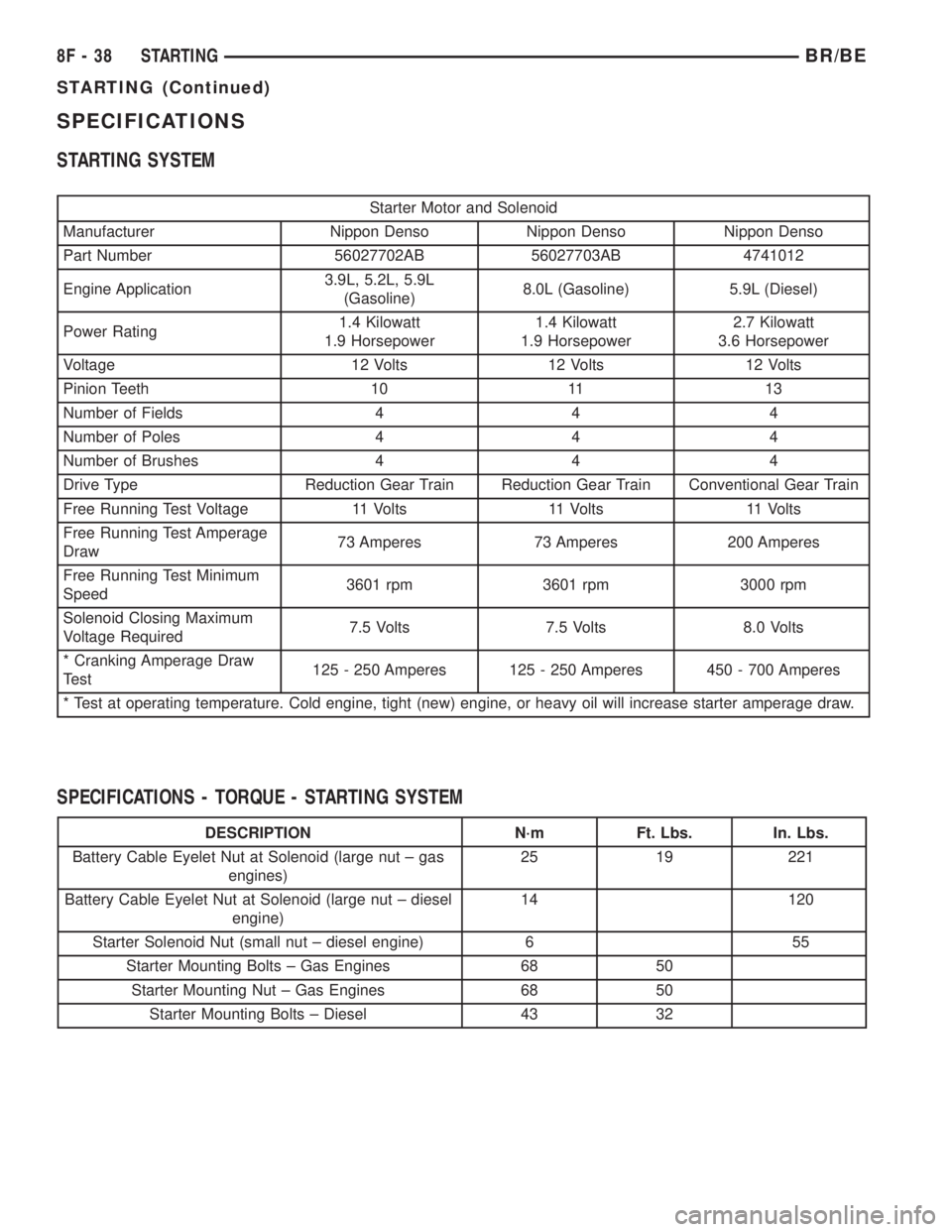
SPECIFICATIONS
STARTING SYSTEM
Starter Motor and Solenoid
Manufacturer Nippon Denso Nippon Denso Nippon Denso
Part Number 56027702AB 56027703AB 4741012
Engine Application3.9L, 5.2L, 5.9L
(Gasoline)8.0L (Gasoline) 5.9L (Diesel)
Power Rating1.4 Kilowatt
1.9 Horsepower1.4 Kilowatt
1.9 Horsepower2.7 Kilowatt
3.6 Horsepower
Voltage 12 Volts 12 Volts 12 Volts
Pinion Teeth 10 11 13
Number of Fields 4 4 4
Number of Poles 4 4 4
Number of Brushes 4 4 4
Drive Type Reduction Gear Train Reduction Gear Train Conventional Gear Train
Free Running Test Voltage 11 Volts 11 Volts 11 Volts
Free Running Test Amperage
Draw73 Amperes 73 Amperes 200 Amperes
Free Running Test Minimum
Speed3601 rpm 3601 rpm 3000 rpm
Solenoid Closing Maximum
Voltage Required7.5 Volts 7.5 Volts 8.0 Volts
* Cranking Amperage Draw
Test125 - 250 Amperes 125 - 250 Amperes 450 - 700 Amperes
* Test at operating temperature. Cold engine, tight (new) engine, or heavy oil will increase starter amperage draw.
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - STARTING SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Battery Cable Eyelet Nut at Solenoid (large nut ± gas
engines)25 19 221
Battery Cable Eyelet Nut at Solenoid (large nut ± diesel
engine)14 120
Starter Solenoid Nut (small nut ± diesel engine) 6 55
Starter Mounting Bolts ± Gas Engines 68 50
Starter Mounting Nut ± Gas Engines 68 50
Starter Mounting Bolts ± Diesel 43 32
8F - 38 STARTINGBR/BE
STARTING (Continued)
Page 533 of 2889

tion on the high-line or premium CTM. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY - GEN-
ERAL INFORMATION) for more information on the
VTSS. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER LOCKS -
GENERAL INFORMATION) for more information on
the RKE system.
HORN
DESCRIPTION
The standard single, low-note, electromagnetic dia-
phragm-type horn is secured with a bracket to the
right front fender wheel house extension in the
engine compartment. The high-note horn for the
optional dual-note horn system is connected in paral-
lel with and secured with a bracket just forward of
the low-note horn. Each horn is grounded through its
wire harness connector and circuit to a ground splice
joint connector, and receives battery feed through the
closed contacts of the horn relay.
The horns cannot be repaired or adjusted and, if
faulty or damaged, they must be individually replaced.
OPERATION
Within the two halves of the molded plastic horn
housing are a flexible diaphragm, a plunger, an elec-
tromagnetic coil and a set of contact points. The dia-
phragm is secured in suspension around its
perimeter by the mating surfaces of the horn hous-
ing. The plunger is secured to the center of the dia-
phragm and extends into the center of the
electromagnet. The contact points control the current
flow through the electromagnet.
When the horn is energized, electrical current
flows through the closed contact points to the electro-
magnet. The resulting electromagnetic field draws
the plunger and diaphragm toward it until that
movement mechanically opens the contact points.
When the contact points open, the electromagnetic
field collapses allowing the plunger and diaphragm to
return to their relaxed positions and closing the con-
tact points again. This cycle continues repeating at a
very rapid rate producing the vibration and move-
ment of air that creates the sound that is directed
through the horn outlet.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN
For complete circuit diagrams, refer to the appro-
priate wiring information. The wiring information
includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and connector
repair procedures, details of wire harness routing
and retention, connector pin-out information andlocation views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.
(1) Disconnect the wire harness connector(s) from
the horn connector receptacle(s). Measure the resis-
tance between the ground circuit cavity of the horn(s)
wire harness connector(s) and a good ground. There
should be no measurable resistance. If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground
as required.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the horn relay out-
put circuit cavity of the horn(s) wire harness connec-
tor(s). There should be zero volts. If OK, go to Step 3.
If not OK, repair the shorted horn relay output cir-
cuit or replace the faulty horn relay as required.
(3) Depress the horn switch. There should now be
battery voltage at the horn relay output circuit cavity
of the horn(s) wire harness connector(s). If OK,
replace the faulty horn(s). If not OK, repair the open
horn relay output circuit to the horn relay as
required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Disconnect the wire harness connector(s) from
the horn connector receptacle(s) (Fig. 1) .
(3) Remove the screw that secures the horn and
mounting bracket unit(s) to the right fender wheel
house front extension.
(4) Remove the horn and mounting bracket unit(s)
from the right fender wheel house front extension.
Fig. 1 Horns Remove/Install
1 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 - SCREWS
3 - INNER FENDER
4 - LOW NOTE HORN
5 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
6 - WHEELHOUSE EXTENSION
7 - HIGH NOTE HORN
8H - 2 HORNBR/BE
HORN (Continued)
Page 535 of 2889

(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to the common feed terminal (30) in the ener-
gized position. This terminal supplies battery voltage
to the horn(s). There should be continuity between
the cavity for relay terminal 87 and the horn relay
output circuit cavity of each horn wire harness con-
nector at all times. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK,
repair the open circuit to the horn(s) as required.
(4) The coil battery terminal (86) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is connected to bat-
tery voltage and should be hot at all times. Check for
battery voltage at the cavity for relay terminal 86. If
OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the open circuit to
the fuse in the PDC as required.
(5) The coil ground terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is grounded
through the horn switch when the horn switch is
depressed. On vehicles equipped with the Vehicle
Theft Security System (VTSS), the horn relay coil
ground terminal can also be grounded by the Central
Timer Module (CTM) in response to certain inputs
related to the VTSS or Remote Keyless Entry (RKE)
system. Check for continuity to ground at the cavity
for relay terminal 85. There should be continuity
with the horn switch depressed, and no continuity
with the horn switch released. If not OK, (Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/HORN/HORN SWITCH - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 3) .(3) See the fuse and relay layout label affixed to
the underside of the PDC cover for horn relay iden-
tification and location.
(4) Remove the horn relay from the PDC.
INSTALLATION
(1) See the fuse and relay layout label affixed to
the underside of the PDC cover for the proper horn
relay location.
(2) Position the horn relay in the proper receptacle
in the PDC.
(3) Align the horn relay terminals with the termi-
nal cavities in the PDC receptacle.
(4) Push down firmly on the horn relay until the
terminals are fully seated in the terminal cavities in
the PDC receptacle.
(5) Install the cover onto the PDC.
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
HORN SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
A center-blow, normally open, resistive membrane-
type horn switch is secured with heat stakes to the
back side of the driver side airbag module trim cover
in the center of the steering wheel (Fig. 4) . The
switch consists of two plastic membranes, one that is
flat and one that is slightly convex. These two mem-
branes are secured to each other around the perime-
ter. Inside the switch, the centers of the facing
surfaces of these membranes each has a grid made
with an electrically conductive material applied to it.
One of the grids is connected to a circuit that pro-
vides it with continuity to ground at all times. The
grid of the other membrane is connected to the horn
relay control circuit.
Fig. 2 Horn Relay
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 3 Power Distribution Center
1 - COVER
2 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
8H - 4 HORNBR/BE
HORN RELAY (Continued)
Page 540 of 2889

SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCE
MINIMUM MAXIMUM
250 Ohms Per Inch 1000 Ohms Per Inch
3000 Ohms Per Foot 12,000 Ohms Per Foot
SPARK PLUGS
ENGINE PLUG TYPE ELECTRODE GAP
3.9L V-6 RC12LC4 1.01 mm (.040 in.)
5.2L/5.9L V-8 RC12LC4 1.01 mm (.040 in.)
8.0L V-10 QC9MC4 1.14 mm (.045 in.)
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCEÐ3.9L/5.2L/5.9L ENGINES
COIL MANUFACTURERPRIMARY RESISTANCE
21-27ÉC (70-80ÉF)SECONDARY RESISTANCE 21-27ÉC
(70-80ÉF)
Diamond 0.97 - 1.18 Ohms 11,300 - 15,300 Ohms
Toyodenso 0.95 - 1.20 Ohms 11,300 - 13,300 Ohms
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCEÐ8.0L V-10
ENGINE
Primary Resistance: 0.53-0.65 Ohms. Test across the
primary connector. Refer to text for test procedures.
Secondary Resistance: 10.9-14.7K Ohms. Test
across the individual coil towers. Refer to text for test
procedures.
IGNITION TIMING
Ignition timing is not adjustable on any engine.
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN
RELAY
DESCRIPTION - PCM OUTPUT
The 5±pin, 12±volt, Automatic Shutdown (ASD)
relay is located in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT
The ASD relay supplies battery voltage (12+ volts)
to the fuel injectors and ignition coil(s). With certain
emissions packages it also supplies 12±volts to the
oxygen sensor heating elements.
The ground circuit for the coil within the ASD
relay is controlled by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM operates the ASD relay by switch-
ing its ground circuit on and off.The ASD relay will be shut±down, meaning the
12±volt power supply to the ASD relay will be de-ac-
tivated by the PCM if:
²the ignition key is left in the ON position. This
is if the engine has not been running for approxi-
mately 1.8 seconds.
²there is a crankshaft position sensor signal to
the PCM that is lower than pre-determined values.
OPERATION - ASD SENSE - PCM INPUT
A 12 volt signal at this input indicates to the PCM
that the ASD has been activated. The relay is used to
connect the oxygen sensor heater element, ignition
coil and fuel injectors to 12 volt + power supply.
This input is used only to sense that the ASD relay
is energized. If the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) does not see 12 volts at this input when the
ASD should be activated, it will set a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ASD AND FUEL
PUMP RELAYS
The following description of operation and
tests apply only to the Automatic Shutdown
(ASD) and fuel pump relays. The terminals on the
bottom of each relay are numbered. Two different
types of relays may be used, (Fig. 1) or (Fig. 2).
²Terminal number 30 is connected to battery volt-
age. For both the ASD and fuel pump relays, termi-
nal 30 is connected to battery voltage at all times.
BR/BEIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 3
IGNITION CONTROL (Continued)