2001 DODGE RAM fuel filter
[x] Cancel search: fuel filterPage 1098 of 2889
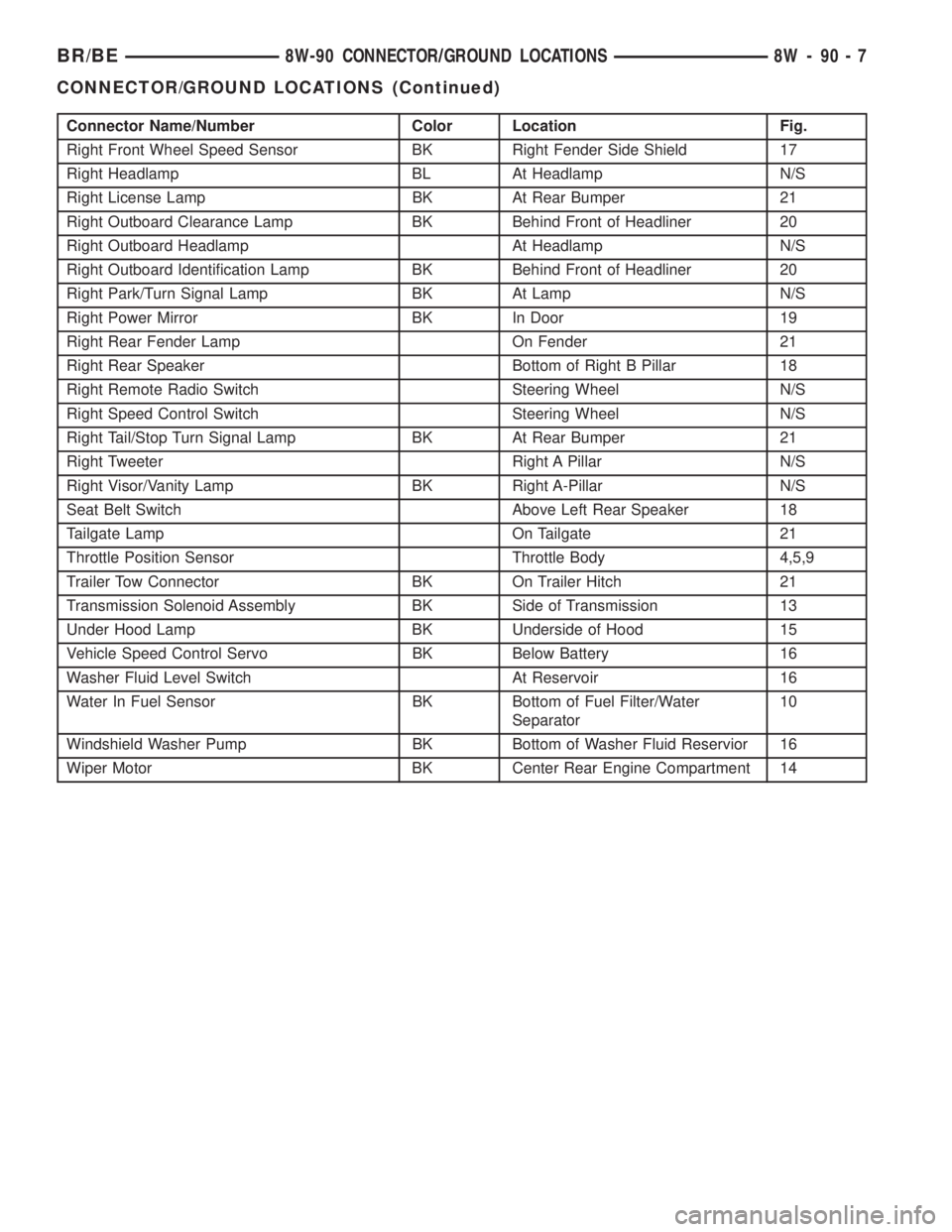
Connector Name/Number Color Location Fig.
Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor BK Right Fender Side Shield 17
Right Headlamp BL At Headlamp N/S
Right License Lamp BK At Rear Bumper 21
Right Outboard Clearance Lamp BK Behind Front of Headliner 20
Right Outboard Headlamp At Headlamp N/S
Right Outboard Identification Lamp BK Behind Front of Headliner 20
Right Park/Turn Signal Lamp BK At Lamp N/S
Right Power Mirror BK In Door 19
Right Rear Fender Lamp On Fender 21
Right Rear Speaker Bottom of Right B Pillar 18
Right Remote Radio Switch Steering Wheel N/S
Right Speed Control Switch Steering Wheel N/S
Right Tail/Stop Turn Signal Lamp BK At Rear Bumper 21
Right Tweeter Right A Pillar N/S
Right Visor/Vanity Lamp BK Right A-Pillar N/S
Seat Belt Switch Above Left Rear Speaker 18
Tailgate Lamp On Tailgate 21
Throttle Position Sensor Throttle Body 4,5,9
Trailer Tow Connector BK On Trailer Hitch 21
Transmission Solenoid Assembly BK Side of Transmission 13
Under Hood Lamp BK Underside of Hood 15
Vehicle Speed Control Servo BK Below Battery 16
Washer Fluid Level Switch At Reservoir 16
Water In Fuel Sensor BK Bottom of Fuel Filter/Water
Separator10
Windshield Washer Pump BK Bottom of Washer Fluid Reservior 16
Wiper Motor BK Center Rear Engine Compartment 14
BR/BE8W-90 CONNECTOR/GROUND LOCATIONS 8W - 90 - 7
CONNECTOR/GROUND LOCATIONS (Continued)
Page 1150 of 2889

ENGINE 3.9L
DESCRIPTION
The 3.9 Liter (238 CID) six-cylinder engine is a
V-Type, lightweight, single cam, overhead valve
engine with hydraulic roller tappets. This engine is
designed to use unleaded fuel.
The engine lubrication system consists of a rotor
type oil pump and a full-flow oil filter.
The cylinders are numbered from front to rear; 1,
3, 5 on the left bank and 2, 4, 6 on the right bank.
The firing order is 1-6-5-4-3-2 (Fig. 1).
The engine serial number is stamped into a
machined pad located on the left front corner of the
cylinder block. When component part replacement is
necessary, use the engine type and serial number for
reference (Fig. 2).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING - Preformance) or (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAG-
NOSIS AND TESTING - Mechanical). Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM for fuel system diagnosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
²Lash Adjuster (Tappet) Noise Diagnosis
²Engine Oil Leak Inspection
Fig. 1 Firing Order
Fig. 2 Engine Identification (Serial) Number
BR/BEENGINE 3.9L 9 - 3
ENGINE 3.9L (Continued)
Page 1151 of 2889
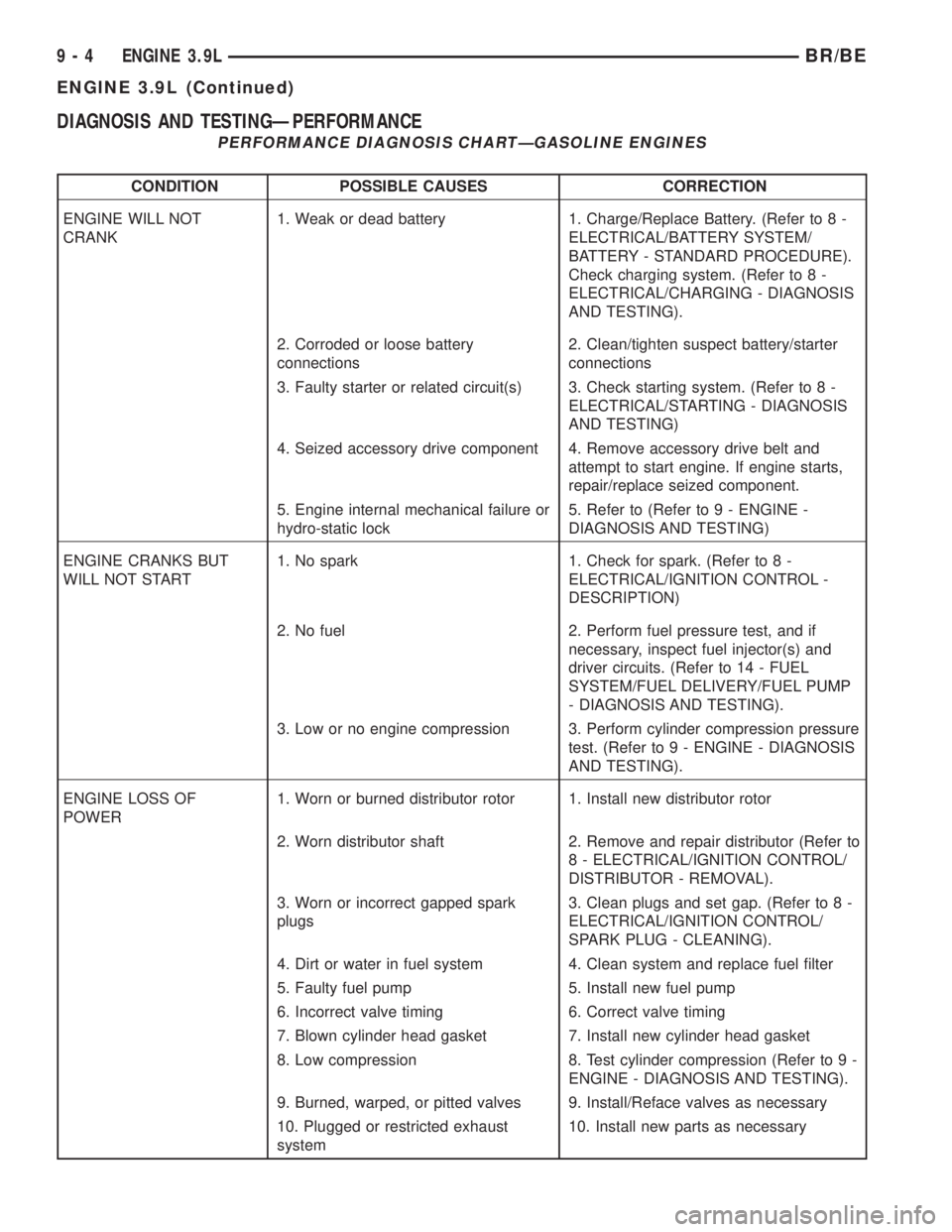
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐPERFORMANCE
PERFORMANCE DIAGNOSIS CHARTÐGASOLINE ENGINES
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT
CRANK1. Weak or dead battery 1. Charge/Replace Battery. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/
BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check charging system. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/CHARGING - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections2. Clean/tighten suspect battery/starter
connections
3. Faulty starter or related circuit(s) 3. Check starting system. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)
4. Seized accessory drive component 4. Remove accessory drive belt and
attempt to start engine. If engine starts,
repair/replace seized component.
5. Engine internal mechanical failure or
hydro-static lock5. Refer to (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
ENGINE CRANKS BUT
WILL NOT START1. No spark 1. Check for spark. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL -
DESCRIPTION)
2. No fuel 2. Perform fuel pressure test, and if
necessary, inspect fuel injector(s) and
driver circuits. (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL PUMP
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
3. Low or no engine compression 3. Perform cylinder compression pressure
test. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
ENGINE LOSS OF
POWER1. Worn or burned distributor rotor 1. Install new distributor rotor
2. Worn distributor shaft 2. Remove and repair distributor (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
DISTRIBUTOR - REMOVAL).
3. Worn or incorrect gapped spark
plugs3. Clean plugs and set gap. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
SPARK PLUG - CLEANING).
4. Dirt or water in fuel system 4. Clean system and replace fuel filter
5. Faulty fuel pump 5. Install new fuel pump
6. Incorrect valve timing 6. Correct valve timing
7. Blown cylinder head gasket 7. Install new cylinder head gasket
8. Low compression 8. Test cylinder compression (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
9. Burned, warped, or pitted valves 9. Install/Reface valves as necessary
10. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system10. Install new parts as necessary
9 - 4 ENGINE 3.9LBR/BE
ENGINE 3.9L (Continued)
Page 1158 of 2889

(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 50É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐHYDROSTATIC
LOCK
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the spark plugs.
(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(7) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(15) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐREPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐFORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS & SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN II
MopartEngine RTV GEN II is used to seal com-
ponents exposed to engine oil. This material is a spe-
cially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTV
MopartATF RTV is a specifically designed black
silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and seal-
ing properties to seal components exposed to auto-
matic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKER
MopartGasket Maker is an anaerobic type gasket
material. The material cures in the absence of air
when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The anaerobic
BR/BEENGINE 3.9L 9 - 11
ENGINE 3.9L (Continued)
Page 1207 of 2889

FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................100
INSTALLATION..........................100
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................101
INSTALLATION..........................101
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION..........................102
OPERATION............................102
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................104
ENGINE OIL LEAKS....................104
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE................104
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................104
ENGINE OIL..........................104
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL.............................105
INSTALLATION..........................105
OIL PAN
REMOVAL.............................105
CLEANING.............................106
INSPECTION...........................106
INSTALLATION..........................106
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL.............................107
DISASSEMBLY..........................107INSPECTION...........................107
ASSEMBLY............................109
INSTALLATION..........................109
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION..........................109
OPERATION............................109
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................110
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE............110
REMOVAL.............................110
CLEANING.............................110
INSPECTION...........................110
INSTALLATION..........................111
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION..........................112
OPERATION............................112
REMOVAL.............................112
CLEANING.............................112
INSPECTION...........................112
INSTALLATION..........................113
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
REMOVAL.............................113
INSTALLATION..........................113
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS
REMOVAL.............................114
INSPECTION...........................114
INSTALLATION..........................115
ENGINE 5.2L
DESCRIPTION
The 5.2 Liter (318 CID) eight-cylinder engine is a
V-Type lightweight, single cam, overhead valve
engine with hydraulic roller tappets. This engine is
designed for unleaded fuel.
Engine lubrication system consists of a rotor type
oil pump and a full flow oil filter.The cylinders are numbered from front to rear; 1,
3, 5, 7 on the left bank and 2, 4, 6, 8 on the right
bank. The firing order is 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2 (Fig. 1).
The engine serial number is stamped into a
machined pad located on the left, front corner of the
cylinder block. When component part replacement is
necessary, use the engine type and serial number for
reference (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 Firing Order
Fig. 2 Engine Identification (Serial) Number
9 - 60 ENGINE 5.2LBR/BE
Page 1209 of 2889

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
3. Worn or incorrect gapped spark
plugs3. Clean plugs and set gap. (Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
SPARK PLUG - CLEANING).
4. Dirt or water in fuel system 4. Clean system and replace fuel filter
5. Faulty fuel pump 5. Install new fuel pump
6. Incorrect valve timing 6. Correct valve timing
7. Blown cylinder head gasket 7. Install new cylinder head gasket
8. Low compression 8. Test cylinder compression (Refer to
9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
9. Burned, warped, or pitted valves 9. Install/Reface valves as necessary
10. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system10. Install new parts as necessary
11. Faulty ignition cables 11. Replace any cracked or shorted
cables
12. Faulty ignition coil 12. Test and replace, as necessary
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION
CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
REMOVAL).
ENGINE STALLS OR
ROUGH IDLE1. Carbon build-up on throttle plate 1. Remove throttle body and de-
carbon. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL INJECTION/THROTTLE BODY -
REMOVAL).
2. Engine idle speed too low 2. Check Idle Air Control circuit. (Refer
to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/IDLE AIR CONTROL
MOTOR - DESCRIPTION)
3. Worn or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs3. Replace or clean and re-gap spark
plugs (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING)
4. Worn or burned distributor rotor 4. Install new distributor rotor
5. Spark plug cables defective or
crossed5. Check for correct firing order or
replace spark plug cables. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
SPARK PLUG CABLE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)
6. Faulty coil 6. Test and replace, if necessary (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION
CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
REMOVAL)
7. Intake manifold vacuum leak 7. Inspect intake manifold gasket and
vacuum hoses (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
9 - 62 ENGINE 5.2LBR/BE
ENGINE 5.2L (Continued)
Page 1216 of 2889

(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the spark plugs.
(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(7) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(15) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐCYLINDER BORE
HONING
Before honing, stuff plenty of clean shop towels
under the bores and over the crankshaft to keep
abrasive materials from entering the crankshaft
area.
(1) Used carefully, the Cylinder Bore Sizing Hone
C-823, equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best tool
for this job. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round, as well as removing light
scuffing, scoring and scratches. Usually, a few strokes
will clean up a bore and maintain the required lim-
its.
CAUTION: DO NOT use rigid type hones to remove
cylinder wall glaze.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done if
the cylinder bore is straight and round. Use a cylin-
der surfacing hone, Honing Tool C-3501, equipped
with 280 grit stones (C-3501-3810). about 20-60strokes, depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Using honing
oil C-3501-3880, or a light honing oil, available from
major oil distributors.
CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits, or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.
The hone marks should INTERSECT at 50É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 3).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 50É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Recover refrigerant from a/c system, if
equipped (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Remove the a/c condenser, if equipped (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
A/C CONDENSER - REMOVAL).
Fig. 3 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
1 - CROSSHATCH PATTERN
2 - INTERSECT ANGLE
BR/BEENGINE 5.2L 9 - 69
ENGINE 5.2L (Continued)
Page 1264 of 2889

FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................156
INSTALLATION..........................156
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................157
INSTALLATION..........................158
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION..........................158
OPERATION............................158
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................160
ENGINE OIL LEAKS....................160
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE................160
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................160
ENGINE OIL..........................160
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL.............................161
INSTALLATION..........................161
OIL PAN
REMOVAL.............................161
CLEANING.............................162
INSPECTION...........................162
INSTALLATION..........................162
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL.............................162
DISASSEMBLY..........................163INSPECTION...........................163
ASSEMBLY............................165
INSTALLATION..........................165
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION..........................165
OPERATION............................165
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................165
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE............165
REMOVAL.............................166
CLEANING.............................166
INSPECTION...........................166
INSTALLATION..........................166
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION..........................168
OPERATION............................168
REMOVAL.............................168
CLEANING.............................168
INSPECTION...........................168
INSTALLATION..........................168
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
REMOVAL.............................169
INSTALLATION..........................169
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS
REMOVAL.............................170
INSPECTION...........................170
INSTALLATION..........................170
ENGINE 5.9L
DESCRIPTION
The 5.9 Liter (360 CID) eight-cylinder engine is a
V-Type lightweight, single cam, overhead valve
engine with hydraulic roller tappets. This engine is
designed for unleaded fuel.
The engine lubrication system consists of a rotor
type oil pump and a full flow oil filter.
The cylinders are numbered from front to rear; 1,
3, 5, 7 on the left bank and 2, 4, 6, 8 on the right
bank. The firing order is 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2 (Fig. 1).The engine serial number is stamped into a
machined pad located on the left, front corner of the
cylinder block. When component part replacement is
necessary, use the engine type and serial number for
reference (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 Firing Order
Fig. 2 Engine Identification Number
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 117