2001 DODGE RAM transmission oil
[x] Cancel search: transmission oilPage 1887 of 2889

No upshift to fourth gear will occur if any of the fol-
lowing are true:
²The transmission fluid temperature is below 10É
C (50É F) or above 121É C (250É F).
²The shift to third is not yet complete.
²Vehicle speed is too low for the 3-4 shift to occur.
²Battery temperature is below -5É C (23É F).
ADJUSTMENT
Check linkage adjustment by starting engine in
PARK and NEUTRAL. Adjustment is acceptable if
the engine starts in only these two positions. Adjust-
ment is incorrect if the engine starts in one position
but not both positions
If the engine starts in any other position, or if the
engine will not start in any position, the park/neutral
switch is probably faulty.
LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
Check condition of the shift linkage (Fig. 227). Do
not attempt adjustment if any component is loose,
worn, or bent. Replace any suspect components.
Replace the grommet securing the shift rod or
torque rod in place if either rod was removed from
the grommet. Remove the old grommet as necessary
and use suitable pliers to install the new grommet.
(1) Shift transmission into PARK.
(2) Raise and support vehicle.
(3) Loosen lock bolt in front shift rod adjusting
swivel (Fig. 227).
(4) Ensure that the shift rod slides freely in the
swivel. Lube rod and swivel as necessary.
(5) Move transmission shift lever fully rearward to
the Park detent.
(6) Center adjusting swivel on shift rod.
(7) Tighten swivel lock bolt to 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.).
(8) Lower vehicle and verify proper adjustment.
SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The typical electrical solenoid used in automotive
applications is a linear actuator. It is a device that
produces motion in a straight line. This straight line
motion can be either forward or backward in direc-
tion, and short or long distance.
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that uses
a magnetic force to perform work. It consists of a coil
of wire, wrapped around a magnetic core made from
steel or iron, and a spring loaded, movable plunger,
which performs the work, or straight line motion.
The solenoids used in transmission applications
are attached to valves which can be classified asnor-
mally openornormally closed. Thenormally
opensolenoid valve is defined as a valve whichallows hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is
applied to the solenoid. Thenormally closedsole-
noid valve is defined as a valve which does not allow
hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is applied
to the solenoid. These valves perform hydraulic con-
trol functions for the transmission and must there-
fore be durable and tolerant of dirt particles. For
these reasons, the valves have hardened steel pop-
pets and ball valves. The solenoids operate the valves
directly, which means that the solenoids must have
very high outputs to close the valves against the siz-
able flow areas and line pressures found in current
transmissions. Fast response time is also necessary
to ensure accurate control of the transmission.
The strength of the magnetic field is the primary
force that determines the speed of operation in a par-
ticular solenoid design. A stronger magnetic field will
cause the plunger to move at a greater speed than a
weaker one. There are basically two ways to increase
the force of the magnetic field:
²Increase the amount of current applied to the
coil or
²Increase the number of turns of wire in the coil.
The most common practice is to increase the num-
ber of turns by using thin wire that can completely
fill the available space within the solenoid housing.
The strength of the spring and the length of the
Fig. 227 Linkage Adjustment Components
1 - FRONT SHIFT ROD
2 - TORQUE SHAFT ASSEMBLY
3 - TORQUE SHAFT ARM
4 - ADJUSTING SWIVEL
5 - LOCK BOLT
21 - 252 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
SHIFT MECHANISM (Continued)
Page 1888 of 2889

plunger also contribute to the response speed possi-
ble by a particular solenoid design.
A solenoid can also be described by the method by
which it is controlled. Some of the possibilities
include variable force, pulse-width modulated, con-
stant ON, or duty cycle. The variable force and pulse-
width modulated versions utilize similar methods to
control the current flow through the solenoid to posi-
tion the solenoid plunger at a desired position some-
where between full ON and full OFF. The constant
ON and duty cycled versions control the voltage
across the solenoid to allow either full flow or no flow
through the solenoid's valve.
OPERATION
When an electrical current is applied to the sole-
noid coil, a magnetic field is created which produces
an attraction to the plunger, causing the plunger to
move and work against the spring pressure and the
load applied by the fluid the valve is controlling. The
plunger is normally directly attached to the valve
which it is to operate. When the current is removed
from the coil, the attraction is removed and the
plunger will return to its original position due to
spring pressure.
The plunger is made of a conductive material and
accomplishes this movement by providing a path for
the magnetic field to flow. By keeping the air gap
between the plunger and the coil to the minimum
necessary to allow free movement of the plunger, the
magnetic field is maximized.
SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The speed sensor (Fig. 228) is located in the over-
drive gear case. The sensor is positioned over the
park gear and monitors transmission output shaft
rotating speed.
OPERATION
Speed sensor signals are triggered by the park
gear lugs as they rotate past the sensor pickup face.
Input signals from the sensor are sent to the trans-
mission control module for processing. Signals from
this sensor are shared with the powertrain control
module.
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
DESCRIPTION
Transmission throttle valve cable (Fig. 229) adjust-
ment is extremely important to proper operation.
This adjustment positions the throttle valve, which
controls shift speed, quality, and part-throttle down-
shift sensitivity.
If cable setting is too loose, early shifts and slip-
page between shifts may occur. If the setting is too
tight, shifts may be delayed and part throttle down-
shifts may be very sensitive.
The transmission throttle valve is operated by a
cam on the throttle lever. The throttle lever is oper-
ated by an adjustable cable (Fig. 230). The cable is
attached to an arm mounted on the throttle lever
shaft. A retaining clip at the engine-end of the cable
Fig. 228 Transmission Output Speed Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION OUTPUT SHAFT SPEED SENSOR
2 - SEAL
Fig. 229 Throttle Valve Cable Attachment - At
Engine
1 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
2 - CABLE BRACKET
3 - THROTTLE BODY LEVER
4 - ACCELERATOR CABLE
5 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 253
SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 1891 of 2889

TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 234) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The torque
converter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid)
pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid. If the fluid
is contaminated, flush the all transmission fluid
cooler(s) and lines.
Fig. 234 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - FRONT COVER
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
7 - DRIVE PLATE
21 - 256 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
Page 1892 of 2889
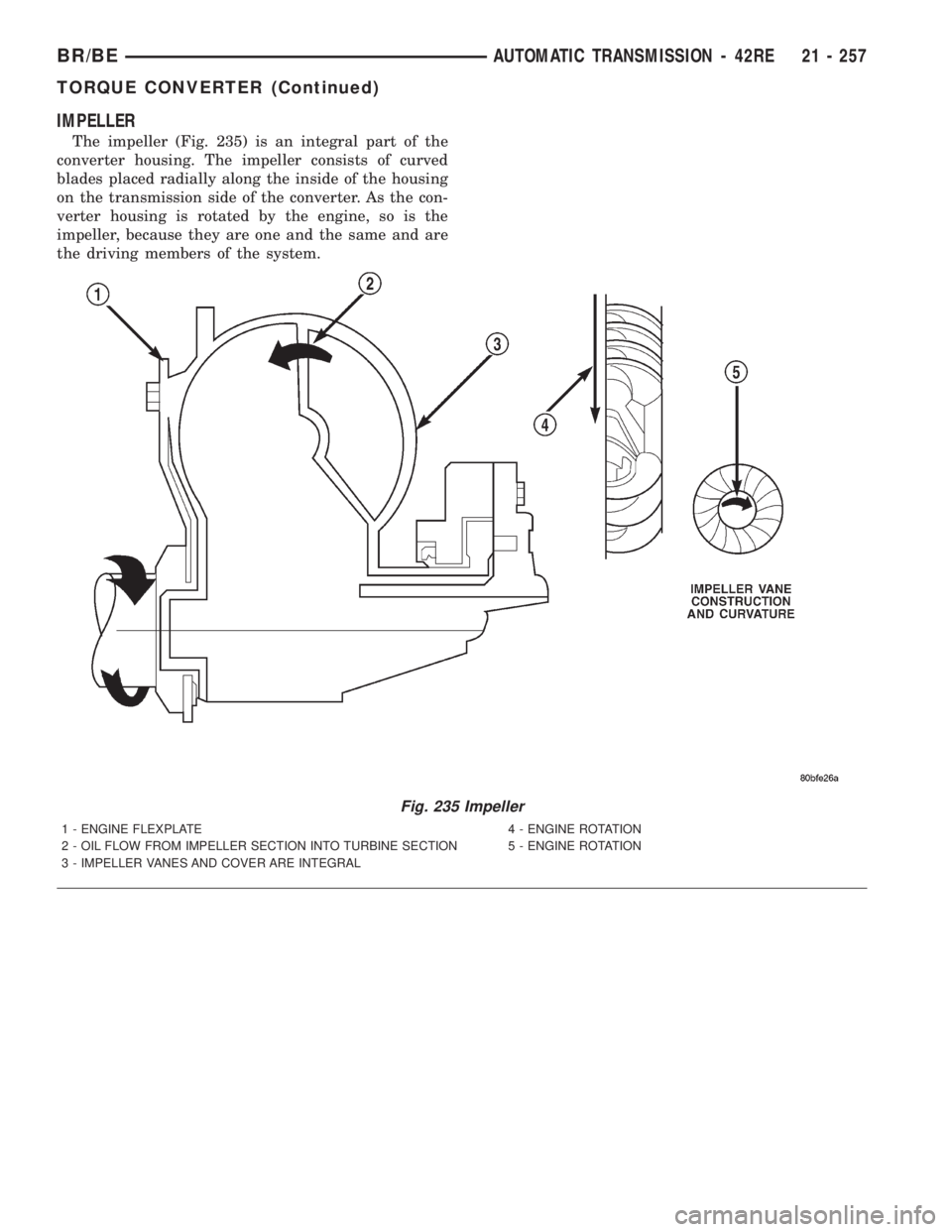
IMPELLER
The impeller (Fig. 235) is an integral part of the
converter housing. The impeller consists of curved
blades placed radially along the inside of the housing
on the transmission side of the converter. As the con-
verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the
impeller, because they are one and the same and are
the driving members of the system.
Fig. 235 Impeller
1 - ENGINE FLEXPLATE 4 - ENGINE ROTATION
2 - OIL FLOW FROM IMPELLER SECTION INTO TURBINE SECTION 5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - IMPELLER VANES AND COVER ARE INTEGRAL
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 257
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1893 of 2889

TURBINE
The turbine (Fig. 236) is the output, or driven,
member of the converter. The turbine is mounted
within the housing opposite the impeller, but is not
attached to the housing. The input shaft is inserted
through the center of the impeller and splined into
the turbine. The design of the turbine is similar to
the impeller, except the blades of the turbine are
curved in the opposite direction.
Fig. 236 Turbine
1 - TURBINE VANE 4 - PORTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER COVER
2 - ENGINE ROTATION 5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - INPUT SHAFT 6 - OIL FLOW WITHIN TURBINE SECTION
21 - 258 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1894 of 2889
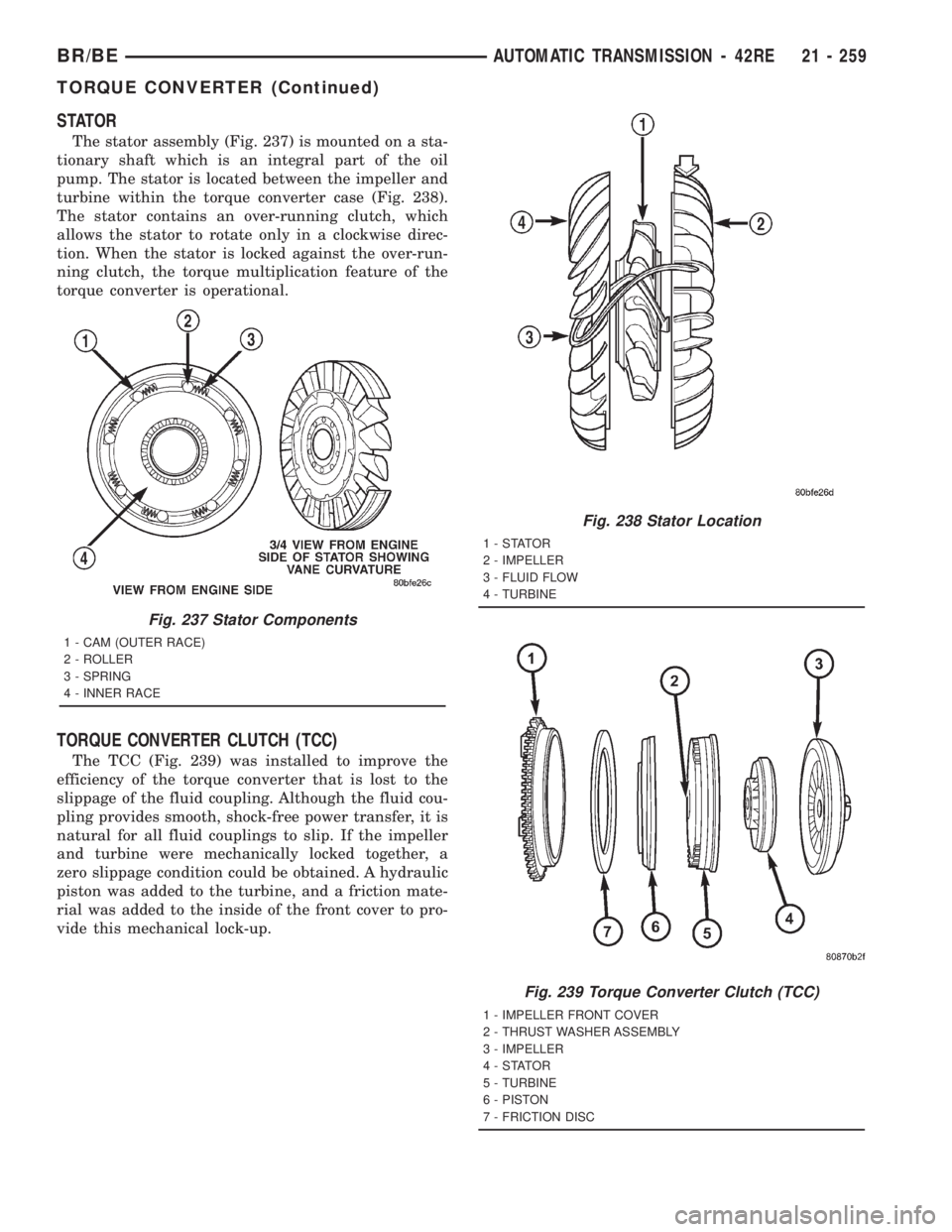
STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 237) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 238).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 239) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston was added to the turbine, and a friction mate-
rial was added to the inside of the front cover to pro-
vide this mechanical lock-up.
Fig. 237 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 238 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 239 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 259
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1895 of 2889

OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 240) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 241).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-clockwise direction. When this happens the overrun-
ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The torque converter clutch is hydraulically
applied and is released when fluid is vented from the
hydraulic circuit by the torque converter control
(TCC) solenoid on the valve body. The torque con-
verter clutch is controlled by the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The torque converter clutch engages
in fourth gear, and in third gear under various con-
ditions, such as when the O/D switch is OFF, when
the vehicle is cruising on a level surface after the
vehicle has warmed up. The torque converter clutch
will disengage momentarily when an increase in
engine load is sensed by the PCM, such as when the
Fig. 240 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
21 - 260 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1896 of 2889

vehicle begins to go uphill or the throttle pressure is
increased.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 242). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
Fig. 241 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
Fig. 242 Checking Torque Converter Seating -
Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 261
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)