2001 DODGE RAM height adjustment
[x] Cancel search: height adjustmentPage 219 of 2889

PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
Original Pinion
Gear Depth
VarianceReplacement Pinion Gear Depth Variance
þ4 þ3 þ2 þ1 0 +1 +2 +3 +4
+4+0.008 +0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0
+3+0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001
+2+0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002
+1+0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003
0+0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004
þ1+0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005
þ2+0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006
þ3+0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007
þ40 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007 þ0.008
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 6).(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 6737 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 6).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 7).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone-nut 6740
hand tight (Fig. 6).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 8).
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.
Fig. 6 Pinion Gear Depth Gauge Tools
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 7 Pinion Height Block
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
3 - 146 REAR AXLE - 267RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 267RBI (Continued)
Page 248 of 2889

PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
Original Pinion
Gear Depth
VarianceReplacement Pinion Gear Depth Variance
þ4 þ3 þ2 þ1 0 +1 +2 +3 +4
+4+0.008 +0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0
+3+0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001
+2+0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002
+1+0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003
0+0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004
þ1+0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005
þ2+0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006
þ3+0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007
þ40 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007 þ0.008
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion cups and pin-
ion bearings installed in housing. Take measure-
ments with a Pinion Gauge Set 6730 and Dial
Indicator C-3339 (Fig. 6).(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 6738 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 6).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 7).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone 6740
hand tight (Fig. 6).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 8).
Install differential bearing caps on Arbor Discs and
snug the bearing cap bolts. Then tighten cap bolts in
a criss-cross pattern to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 have different step diame-
ters to fit other axle sizes. Pick correct size step for
axle being serviced.
Fig. 6 Pinion Gear Depth Gauge
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 7 Pinion Height Block
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 286RBI 3 - 175
REAR AXLE - 286RBI (Continued)
Page 304 of 2889

The drum forces both brake shoes to move in the
same direction of rotation. Servo action begins with
the primary brake shoe which begins to wedge (or
wrap) itself against the rotating drum surface. This
force is transmitted equally to the secondary brake
shoe through the adjuster screw and anchor pin. The
net result is that each shoe helps the other exert
extra force against the drum. It is servo action that
creates the wedging (or wrap) effect which produces
increased force on the drum braking surface.
All drum brake assemblies are equipped with a self
adjusting mechanism. The components forming the
mechanism consist of the: adjuster screw, adjuster
lever, actuating lever (11 inch brake), lever return
spring and the adjuster lever spring. The adjuster
lever on the 12 inch brake, is also equipped with a
lever and tension spring.
The adjuster mechanism performs two important
functions. First, is in maintaining proper brake shoe
operating clearance. And second, is to maintain brake
pedal height. The mechanism does so, by adjusting
the shoes in small increments to compensate for lin-
ing wear. The adjustment process is continuous
throughout the useful life of the brake lining.
The adjuster components are all connected to the
secondary brake shoes. Actual adjustment only
occurs during reverse brake stops. Secondary brake
shoe movement (during reverse stops), is what acti-
vates the adjuster components.
In operation, secondary shoe movement causes the
adjuster lever spring to exert pull on the lever. This
pivots the lever away from the adjuster screw teeth.
When the stop is completed and the brakes released,
the adjuster lever pivots back to a normal position. It
is during this return movement of the lever when
adjustment occurs. At this point, the lever comes
back into contact with the adjuster screw teeth as it
moves upward. The lever will then rotate the
adjuster screw one or two teeth as needed for adjust-
ment.
NOTE: The adjustment process requires a complete
stop to actually occur. Rolling stops will NOT acti-
vate the adjuster components. In addition, the
adjuster screws are left and right hand parts and
must NOT be interchanged.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE DRUM
The maximum allowable diameter of the drum
braking surface is indicated on the drum outer edge.
Generally, a drum can be machined to a maximum of
1.52 mm (0.060 in.) oversize. Always replace the
drum if machining would cause drum diameter to
exceed the size limit indicated on the drum.
BRAKE DRUM RUNOUT
Measure drum diameter and runout with an accu-
rate gauge. The most accurate method of measure-
ment involves mounting the drum in a brake lathe
and checking variation and runout with a dial indi-
cator.
Variations in drum diameter should not exceed
0.069 mm (0.0028 in.). Drum runout should not
exceed 0.18 mm (0.007 in.) out of round. Machine the
drum if runout or variation exceed these values.
Replace the drum if machining causes the drum to
exceed the maximum allowable diameter.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BRAKE DRUM
MACHINING
The brake drums can be machined on a drum lathe
when necessary. Initial machining cuts should be lim-
ited to 0.12 - 0.20 mm (0.005 - 0.008 in.) at a time as
heavier feed rates can produce taper and surface
variation. Final finish cuts of 0.025 to 0.038 mm
(0.001 to 0.0015 in.) are recommended and will gen-
erally provide the best surface finish.
Be sure the drum is securely mounted in the lathe
before machining operations. A damper strap should
always be used around the drum to reduce vibration
and avoid chatter marks.
The maximum allowable diameter of the drum
braking surface is stamped or cast into the drum
outer edge.
CAUTION: Replace the drum if machining will cause
the drum to exceed the maximum allowable diame-
ter.
CLEANING
Clean the individual brake components, including
the support plate and wheel cylinder exterior, with a
water dampened cloth or with brake cleaner. Do not
use any other cleaning agents. Remove light rust and
scale from the brake shoe contact pads on the sup-
port plate with fine sandpaper.
INSPECTION
As a general rule, riveted brake shoes should be
replaced when worn to within 0.78 mm (1/32 in.) of
the rivet heads. Bonded lining should be replaced
when worn to a thickness of 1.6 mm (1/16 in.).
Examine the lining contact pattern to determine if
the shoes are bent or the drum is tapered. The lining
should exhibit contact across its entire width. Shoes
exhibiting contact only on one side should be
replaced and the drum checked for runout or taper.
Inspect the adjuster screw assembly. Replace the
assembly if the star wheel or threads are damaged,
or the components are severely rusted or corroded.
BR/BEBRAKES 5 - 33
DRUM (Continued)
Page 609 of 2889

SPORT
The fog lamps are serviced from the rearward side
of the front bumper.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Disengage fog lamp harness connector.
(3) Remove fog lamp to bumper attaching nuts
(Fig. 11).
(4) Separate fog lamp from bumper.
INSTALLATION
SLT
(1) Position fog lamp in bumper.
(2) Install fog lamp to bumper attaching nuts.
(3) Connect fog lamp harness connector.
(4) Check for proper operation and beam align-
ment.
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
SPORT
(1) Position fog lamp in fascia.
(2) Install screws attaching fog lamp to fascia.
(3) Connect wire connector to fog lamp.
(4) Check for proper operation and beam align-
ment.
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
ADJUSTMENTS
Prepare an alignment screen. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/HEAD-
LAMP UNIT - ADJUSTMENTS)
A properly aligned fog lamp will project a pattern
on the alignment screen 100 mm (4 in.) below the fog
lamp centerline and straight ahead (Fig. 12).
To adjust fog lamp aim, rotate adjustment screw on
the rear of fog lamp to achieve the specified height.
Fig. 11 Fog Lamp
1 - FOG LAMP
2 - BEAM ADJUSTER
3 - BUMPER
8L - 12 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORBR/BE
FOG LAMP UNIT (Continued)
Page 1174 of 2889

(1) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be
obtained.
(2) Measure the concentricity of valve seat using a
dial indicator. Total runout should not exceed 0.051
mm (0.002 in.) total indicator reading.
(3) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue, to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seat LIGHTLY with Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to the top edge of valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15É stone. If the blue is transferred to bottom
edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 60É stone.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake seats should be 1.016-1.524 mm (0.040-0.060
in.). The width of the exhaust seats should be 1.524-
2.032 mm (0.060-0.080 in.).
VALVE SPRINGS
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested. As an example the compression length of
the spring to be tested is 1-5/16 in.. Turn table of
Universal Valve Spring Tester Tool until surface is in
line with the 1-5/16 in. mark on the threaded stud.
Be sure the zero mark is to the front (Fig. 14). Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by 2. This will give the
spring load at test length. Fractional measurements
are indicated on the table for finer adjustments.
Refer to specifications to obtain specified height and
allowable tensions. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(2) Compress valve springs using Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD- 998772A and adapter 6716A.
(3) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(4) Before removing valves, remove any burrs from
valve stem lock grooves to prevent damage to the
valve guides. Identify valves to ensure installation in
original location.
CLEANING
Clean valves thoroughly. Discard burned, warped,
or cracked valves.
Remove carbon and varnish deposits from inside of
valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
INSPECTION
Measure valve stems for wear. If wear exceeds
0.051 mm (0.002 in.), replace the valve.
Measure valve stem guide clearance as follows:
(1) Install Valve Guide Sleeve Tool C-3973 over
valve stem and install valve (Fig. 15). The special
sleeve places the valve at the correct height for
checking with a dial indicator.
(2) Attach dial indicator Tool C-3339 to cylinder
head and set it at right angles to valve stem being
measured (Fig. 16).
(3) Move valve to and from the indicator. The total
dial indicator reading should not exceed 0.432 mm
(0.017 in.). Ream the guides for valves with oversize
stems if dial indicator reading is excessive or if the
stems are scuffed or scored.
Fig. 14 Testing Valve Spring for Compressed
Length
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - VALVE SPRING TESTER
Fig. 15 Positioning Valve with Tool C-3973
1 - VALVE
2 - SPACER TOOL
BR/BEENGINE 3.9L 9 - 27
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1231 of 2889

(1) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be
obtained.
(2) Measure the concentricity of valve seat using a
dial indicator. Total runout should not exceed 0.051
mm (0.002 in.) total indicator reading.
(3) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue, to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seat LIGHTLY with Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to the top edge of valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15É stone. If the blue is transferred to bottom
edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 60É stone.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake seats should be 1.016-1.524 mm (0.040-0.060
in.). The width of the exhaust seats should be 1.524-
2.032 mm (0.060-0.080 in.).
VALVE SPRINGS
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested. As an example the compression length of
the spring to be tested is 1-5/16 in.. Turn table of
Universal Valve Spring Tester Tool until surface is in
line with the 1-5/16 in. mark on the threaded stud.
Be sure the zero mark is to the front (Fig. 13). Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by 2. This will give the
spring load at test length. Fractional measurements
are indicated on the table for finer adjustments.
Refer to specifications to obtain specified height and
allowable tensions. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(2) Compress valve springs using Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD- 998772A and adapter 6716A.
(3) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(4) Before removing valves, remove any burrs from
valve stem lock grooves to prevent damage to the
valve guides. Identify valves to ensure installation in
original location.
CLEANING
Clean valves thoroughly. Discard burned, warped,
or cracked valves.
Remove carbon and varnish deposits from inside of
valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
INSPECTION
Measure valve stems for wear. If wear exceeds
0.051 mm (0.002 in.), replace the valve.
Measure valve stem guide clearance as follows:
(1) Install Valve Guide Sleeve Tool C-3973 over
valve stem and install valve (Fig. 14). The special
sleeve places the valve at the correct height for
checking with a dial indicator.
(2) Attach dial indicator Tool C-3339 to cylinder
head and set it at right angles to valve stem being
measured (Fig. 15).
(3) Move valve to and from the indicator. The total
dial indicator reading should not exceed 0.432 mm
(0.017 in.). Ream the guides for valves with oversize
stems if dial indicator reading is excessive or if the
stems are scuffed or scored.
Fig. 13 Testing Valve Spring for Compressed
Length
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - VALVE SPRING TESTER
Fig. 14 Positioning Valve with Tool C-3973
1 - VALVE
2 - SPACER TOOL
9 - 84 ENGINE 5.2LBR/BE
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1287 of 2889

VALVES
Inspect the remaining margin after the valves are
refaced (Fig. 11). Valves with less than 1.190 mm
(0.047 in.) margin should be discarded.
VALVE SEATS
CAUTION: DO NOT un-shroud valves during valve
seat refacing (Fig. 12).(1) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be
obtained.
(2) Measure the concentricity of valve seat using a
dial indicator. Total runout should not exceed 0.051
mm (0.002 in.) total indicator reading.
(3) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue, to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seat LIGHTLY with Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to the top edge of valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15É stone. If the blue is transferred to bottom
edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 60É stone.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake seats should be 1.016-1.524 mm (0.040-0.060
in.). The width of the exhaust seats should be 1.524-
2.032 mm (0.060-0.080 in.).
VALVE SPRINGS
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested. As an example the compression length of
the spring to be tested is 1-5/16 in.. Turn table of
Universal Valve Spring Tester Tool until surface is in
line with the 1-5/16 in. mark on the threaded stud.
Be sure the zero mark is to the front (Fig. 13). Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by 2. This will give the
spring load at test length. Fractional measurements
are indicated on the table for finer adjustments.
Refer to specifications to obtain specified height and
allowable tensions. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(2) Compress valve springs using Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD- 998772A and adapter 6716A.
(3) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(4) Before removing valves, remove any burrs from
valve stem lock grooves to prevent damage to the
valve guides. Identify valves to ensure installation in
original location.
CLEANING
Clean valves thoroughly. Discard burned, warped,
or cracked valves.
Remove carbon and varnish deposits from inside of
valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
Fig. 11 Intake and Exhaust Valves
1 - MARGIN
2 - VALVE SPRING RETAINER LOCK GROOVE
3 - STEM
4-FACE
Fig. 12 Refacing Valve Seats
1-STONE
2 - PILOT
3 - VALVE SEAT
4 - SHROUD
9 - 140 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1344 of 2889
(3) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seat LIGHTLY with Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to the top edge of valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15É stone. If the blue is transferred to bottom
edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 60É stone.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
valve seats should be 1.016-1.524 mm (0.040-0.060
inch).
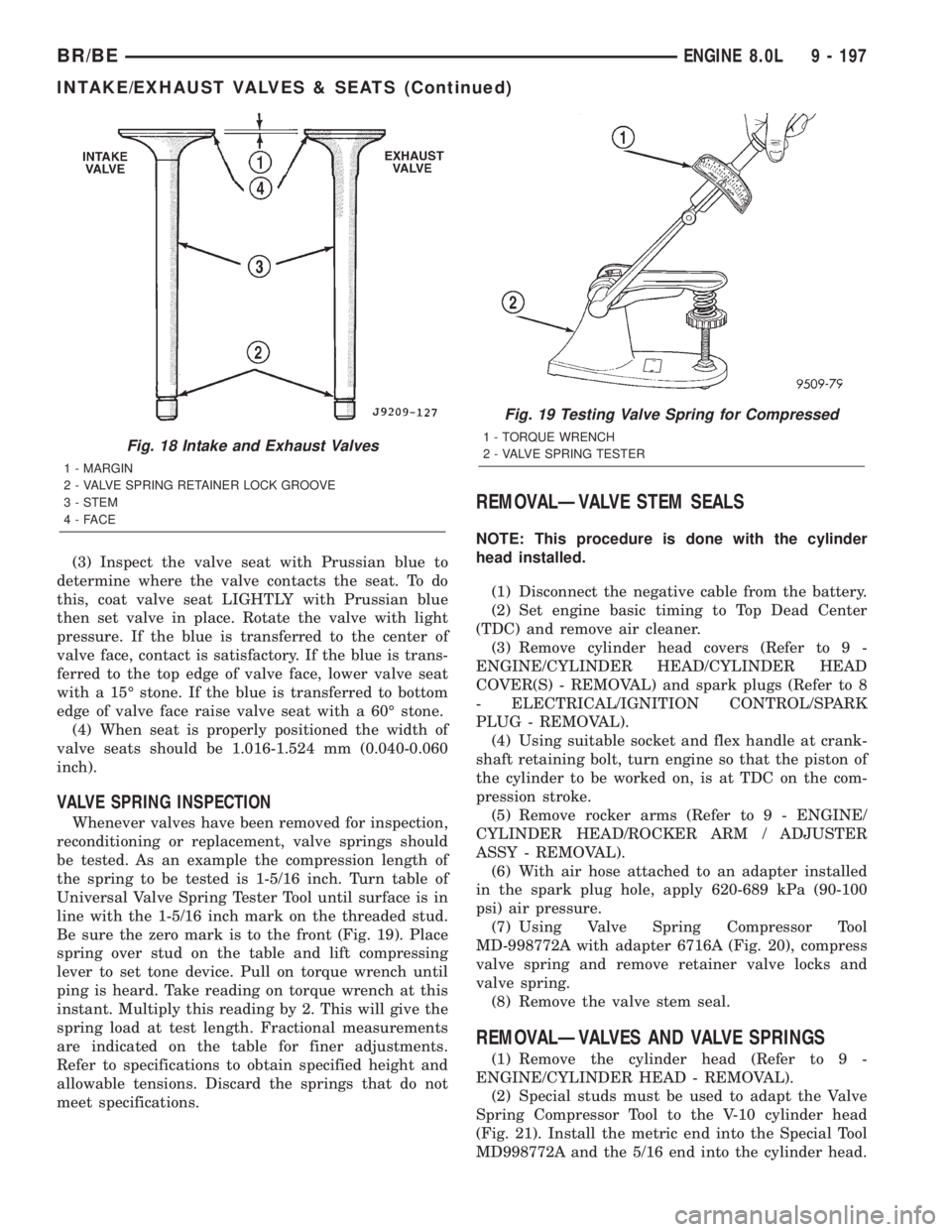
VALVE SPRING INSPECTION
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested. As an example the compression length of
the spring to be tested is 1-5/16 inch. Turn table of
Universal Valve Spring Tester Tool until surface is in
line with the 1-5/16 inch mark on the threaded stud.
Be sure the zero mark is to the front (Fig. 19). Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by 2. This will give the
spring load at test length. Fractional measurements
are indicated on the table for finer adjustments.
Refer to specifications to obtain specified height and
allowable tensions. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications.
REMOVALÐVALVE STEM SEALS
NOTE: This procedure is done with the cylinder
head installed.
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Set engine basic timing to Top Dead Center
(TDC) and remove air cleaner.
(3) Remove cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL) and spark plugs (Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK
PLUG - REMOVAL).
(4) Using suitable socket and flex handle at crank-
shaft retaining bolt, turn engine so that the piston of
the cylinder to be worked on, is at TDC on the com-
pression stroke.
(5) Remove rocker arms (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER
ASSY - REMOVAL).
(6) With air hose attached to an adapter installed
in the spark plug hole, apply 620-689 kPa (90-100
psi) air pressure.
(7) Using Valve Spring Compressor Tool
MD-998772A with adapter 6716A (Fig. 20), compress
valve spring and remove retainer valve locks and
valve spring.
(8) Remove the valve stem seal.
REMOVALÐVALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
(1) Remove the cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(2) Special studs must be used to adapt the Valve
Spring Compressor Tool to the V-10 cylinder head
(Fig. 21). Install the metric end into the Special Tool
MD998772A and the 5/16 end into the cylinder head.
Fig. 18 Intake and Exhaust Valves
1 - MARGIN
2 - VALVE SPRING RETAINER LOCK GROOVE
3 - STEM
4-FACE
Fig. 19 Testing Valve Spring for Compressed
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - VALVE SPRING TESTER
BR/BEENGINE 8.0L 9 - 197
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)