2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER service indicator
[x] Cancel search: service indicatorPage 3062 of 4284

FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL AND
CONDITION CHECK
NOTE: The transmission and differential sump have
a common oil sump with a communicating opening
between the two.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground. This will assure complete oil level sta-
bilization between differential and transmis-
sion.The fluid should be at normal operating
temperature (approximately 82 C. or 180 F.). The
fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT region (cross-
hatched area) on the fluid level indicator (Fig. 165).
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, the air bubbles can cause overheat-
ing, fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can inter-
fere with normal valve, clutch, and servo operation.
Foaming can also result in fluid escaping from the
transaxle dipstick where it may be mistaken for a
leak.Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle overhaul is needed.
Be sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick closely.
If there is any doubt about its condition, drain out a
sample for a double check.
FLUID CONDITION
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle recondition is needed.
Be sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick closely.
If there is any doubt about its condition, drain out a
sample for a double check.
Moparž ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid-
Type 9602) when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed
red so it can be identified from other fluids used in
the vehicle such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red
color is not permanent and is not an indicator of fluid
condition. As the vehicle is driven, the ATF will begin
to look darker in color and may eventually become
brown. This is normal. A dark brown/black fluid
accompanied with a burnt odor and/or deterioration
in shift quality may indicate fluid deterioration or
transmission component failure.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
CHANGE
NOTE: For the recommended maintenance (fluid/fil-
ter change) intervals for this transaxle, (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE
SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION)
NOTE: Only fluids of the type labeled Moparž
ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid) Type 9602
should be used. A filter change should be made at
the time of the transmission oil change. The magnet
(on the inside of the oil pan) should also be cleaned
with a clean, dry cloth.
NOTE: If the transaxle is disassembled for any rea-
son, the fluid and filter should be changed.
FLUID/FILTER SERVICE (RECOMMENDED)
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist. Place a drain con-
tainer with a large opening, under transaxle oil pan.
Fig. 165 Fluid Level Indicator Markings
1 - TRANSAXLE DIPSTICK
21 - 98 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
Page 3130 of 4284
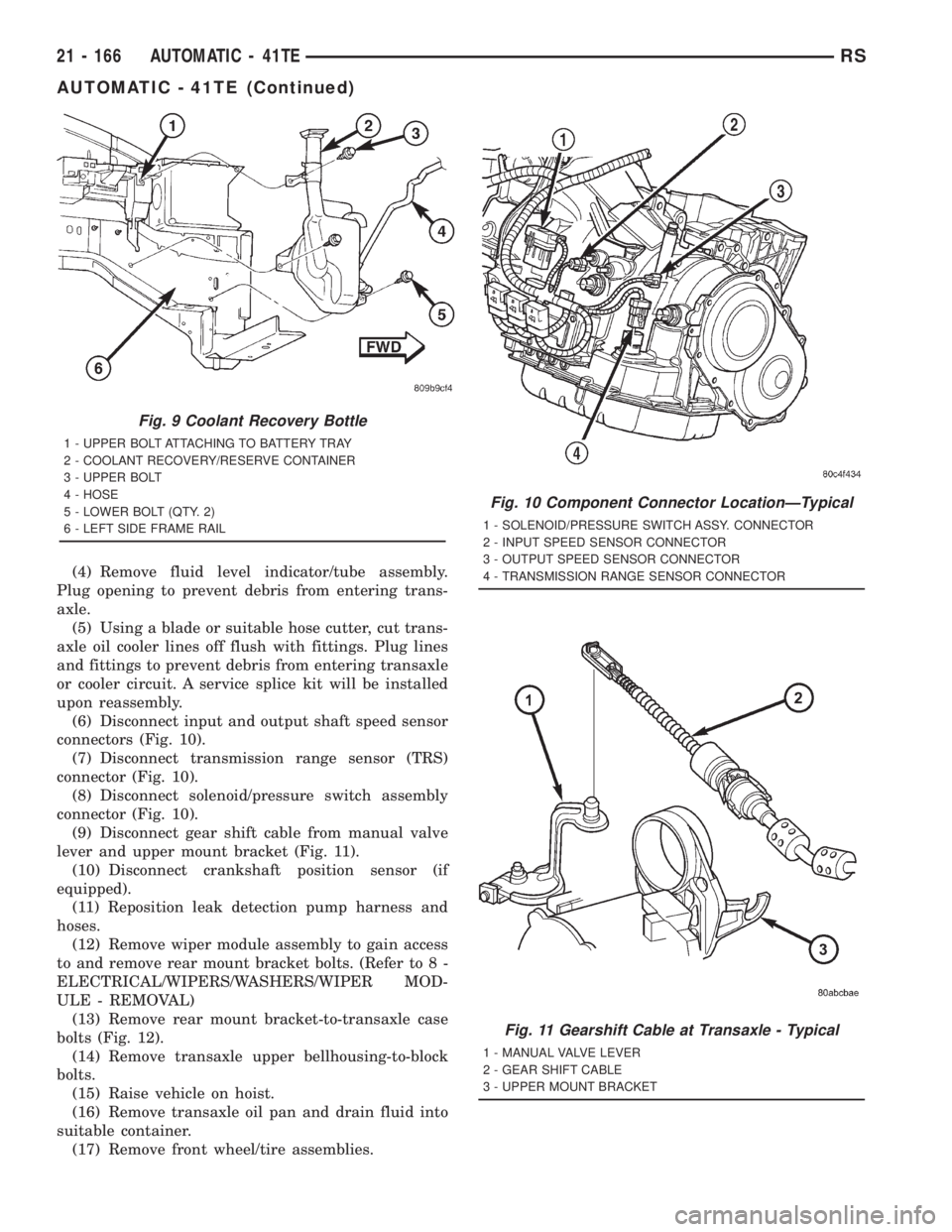
(4) Remove fluid level indicator/tube assembly.
Plug opening to prevent debris from entering trans-
axle.
(5) Using a blade or suitable hose cutter, cut trans-
axle oil cooler lines off flush with fittings. Plug lines
and fittings to prevent debris from entering transaxle
or cooler circuit. A service splice kit will be installed
upon reassembly.
(6) Disconnect input and output shaft speed sensor
connectors (Fig. 10).
(7) Disconnect transmission range sensor (TRS)
connector (Fig. 10).
(8) Disconnect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
connector (Fig. 10).
(9) Disconnect gear shift cable from manual valve
lever and upper mount bracket (Fig. 11).
(10) Disconnect crankshaft position sensor (if
equipped).
(11) Reposition leak detection pump harness and
hoses.
(12) Remove wiper module assembly to gain access
to and remove rear mount bracket bolts. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MOD-
ULE - REMOVAL)
(13) Remove rear mount bracket-to-transaxle case
bolts (Fig. 12).
(14) Remove transaxle upper bellhousing-to-block
bolts.
(15) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(16) Remove transaxle oil pan and drain fluid into
suitable container.
(17) Remove front wheel/tire assemblies.
Fig. 9 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - UPPER BOLT ATTACHING TO BATTERY TRAY
2 - COOLANT RECOVERY/RESERVE CONTAINER
3 - UPPER BOLT
4 - HOSE
5 - LOWER BOLT (QTY. 2)
6 - LEFT SIDE FRAME RAIL
Fig. 10 Component Connector LocationÐTypical
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY. CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 11 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle - Typical
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
21 - 166 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
AUTOMATIC - 41TE (Continued)
Page 3173 of 4284

INSTALLATION
NOTE: If transaxle assembly has been replaced or
overhauled (clutch and/or seal replacement), it is
necessary to perfrom the TCM Quick Learn proce-
dure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
NOTE: If torque converter assembly has been
replaced, it is necessary to reset the TCC Break-In
Strategy. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Using a transmission jack and a helper, posi-
tion transaxle assembly to engine. Install and torque
bolts to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install upper mount assembly to transaxle and
torque bolts to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 164).
(3) Raise engine/transaxle assembly into position.
Install and torque upper mount-to-bracket thru-bolt
to 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 164).
(4) Remove transmission jack and screw jack.
(5) Secure left wheelhouse splash shield.
(6) Install torque converter-to-drive plate bolts and
torque to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.)
(7) Install inspection cover.(8) Install lateral bending brace.
(9) Install starter motor.
(10) Install front mount/bracket assembly.
(11) Install rear mount and bracket assembly into
position (Fig. 165).
(12) Install and torque rear mount bolts to 54 N´m
(40 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 166).
(13) Lower vehicle.
(14) Install and torque rear mount bracket-to-tran-
saxle vertical bolts (Fig. 165) to 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.).
(15) Raise vehicle.
(16) Install rear mount bracket-to-transaxle hori-
zontal bolt (Fig. 165) and torque to 102 N´m (75 ft.
lbs.).
(17) Install rear mount thru-bolt and torque to 54
N´m (40 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 166).
(18) Install rear mount heat shield (Fig. 167).
(19) AWD models: Install power transfer unit.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
POWER TRANSFER UNIT - INSTALLATION)
(20) Install cradle plate.
(21) Install exhaust pipe to manifold (Fig. 168).
(22) Install left and right halfshaft assemblies.
(Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF
SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(23) Install front wheel/tire assemblies.
(24) Lower vehicle.
(25) Install transaxle upper bellhousing-to-block
bolts and torque to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(26) Install wiper module assembly. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MOD-
ULE - INSTALLATION)
(27) Connect crank position sensor (if equipped).
(28) Connect gearshift cable to upper mount
bracket and transaxle manual valve lever (Fig. 169).
(29) Connect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
(Fig. 170).
(30) Connect transmission range sensor connector
(Fig. 170).
(31) Connect input and output speed sensor con-
nectors (Fig. 170).
(32) Remove plugs and install transaxle oil cooler
line service splice kit. Refer to instructions included
with kit.
(33) Remove plug and Install fluid level indicator/
tube assembly.
(34) Install coolant recovery bottle (Fig. 171).
(35) Install battery shield.
(36) Connect battery cables.
(37) Fill transaxle with suitable amount of ATF+4
(Automatic Transmission FluidÐType 9602). (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 164 Left Mount to Bracket and Transaxle
1 - BOLT - BRACKET TO FRAME RAIL 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
2 - BOLT - MOUNT TO RAIL THRU 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.)
3 - BOLT - LEFT MOUNT TO TRANSAXLE 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
4 - TRANSAXLE
5 - MOUNT - LEFT
6 - BRACKET - LEFT MOUNT
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 209
AUTOMATIC - 41TE (Continued)
Page 3197 of 4284

OPERATION
The function of an accumulator is to cushion the
application of a frictional clutch element. When pres-
surized fluid is applied to a clutch circuit, the appli-
cation force is dampened by fluid collecting in the
respective accumulator chamber against the piston
and spring(s). The intended result is a smooth, firm
clutch application.
AUTOSTICK SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
Autostick is a driver-interactive transaxle feature
that offers manual gear shifting capability. The con-
trol switch is part of the transaxle gear shift lever as
shown in (Fig. 175). It can only be serviced by replac-
ing the gearshift lever assembly. (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/GEAR SHIFT LEVER -
REMOVAL)
OPERATION
When the shift lever is moved into the Autostick
position (as indicated by the Shift Lever Position
Indicator in the cluster), the transaxle remains in
whatever gear it was using before Autostick was acti-
vated. The TCM sends a 5 volt signal through the
switch and then monitors the signal for voltage drop.
Each switch state (driver command) results in a spe-
cific voltage reading sensed by the TCM. The TCM
then determines transaxle operation (upshift/down-
shift/OD Lockout) based on their corresponding volt-
age. Refer to the following chart for corresponding
switch states and voltage readings:
Switch State Voltage Reading
Autostick DOWN
depressed0.3V-1.6V
Autostick UP depressed 1.6V-2.8V
Overdrive OFF9Lockout9
depressed2.8V-3.8V
All switches open 3.8V-4.8V
-Voltage values <.3V and >4.8V are considered
INVALID and will result in a DTC
Moving the switch up causes an upshift and mov-
ing the switch down causes a downshift. The instru-
ment cluster will illuminate the selected gear. The
vehicle can be launched in 1st, 2nd, or 3rd gear while
in the Autostick mode. The speed control is operable
Fig. 173 Low/Reverse Accumulator Assembly
1 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
2 - SEAL RINGS
3 - RETURN SPRINGS
4 - (NOTE NOTCH)
Fig. 174 2/4 Accumulator Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - RETAINER PLATE
3 - DETENT SPRING
4 - SPRINGS
5 - SEALS
6 - PISTON
Fig. 175 Autostick Switch Location (if equipped)
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 233
ACCUMULATOR (Continued)
Page 3210 of 4284

FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL AND
CONDITION CHECK
NOTE: Only transmission fluid of the type labeled
Mopar ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid±Type
9602) should be used in this transaxle.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The transmission sump has a fluid level indicator
(dipstick) to check oil similar to most automatic
transmissions. It is located on the left side of the
engine. Be sure to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle
before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground.At normal operating temperature (approxi-
mately 82 C. or 180 F.), the fluid level is correct if it
is in the HOT region (cross-hatched area) on the oil
level indicator (Fig. 214). The fluid level should be
within the WARM range of the dipstick at 70É F fluid
temperature.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK USING DRB
NOTE: Engine and Transaxle should be at normal
operating temperature before performing this proce-
dure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Hook up DRB scan tool and select transmis-
sion.(3) Select sensors.
(4) Read the transmission temperature value.
(5) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
fluid temperature chart (Fig. 215).
(6) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
indicator according to the chart.
(7) Check transmission for leaks.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transaxle vent where it may be mistaken
for a leak.
FLUID CONDITION
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle recondition is proba-
bly required. Be sure to examine the fluid on the dip-
stick closely. If there is any doubt about its condition,
drain out a sample for a double check.
Moparž ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid-
Type 9602) when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed
red so it can be identified from other fluids used in
the vehicle such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red
color is not permanent and is not an indicator of fluid
condition. As the vehicle is driven, the ATF will begin
to look darker in color and may eventually become
brown. This is normal. A dark brown/black fluid
accompanied with a burnt odor and/or deterioration
in shift quality may indicate fluid deterioration or
transmission component failure.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
SERVICE
NOTE: Refer to the maintenance schedules in
LUBRICATION and MAINTENANCE, or the vehicle
owner's manual, for the recommended maintenance
(fluid/filter change) intervals for this transaxle.
Fig. 214 Transaxle Fluid Level Indicator
1 - TRANSAXLE DIPSTICK
21 - 246 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
Page 3212 of 4284
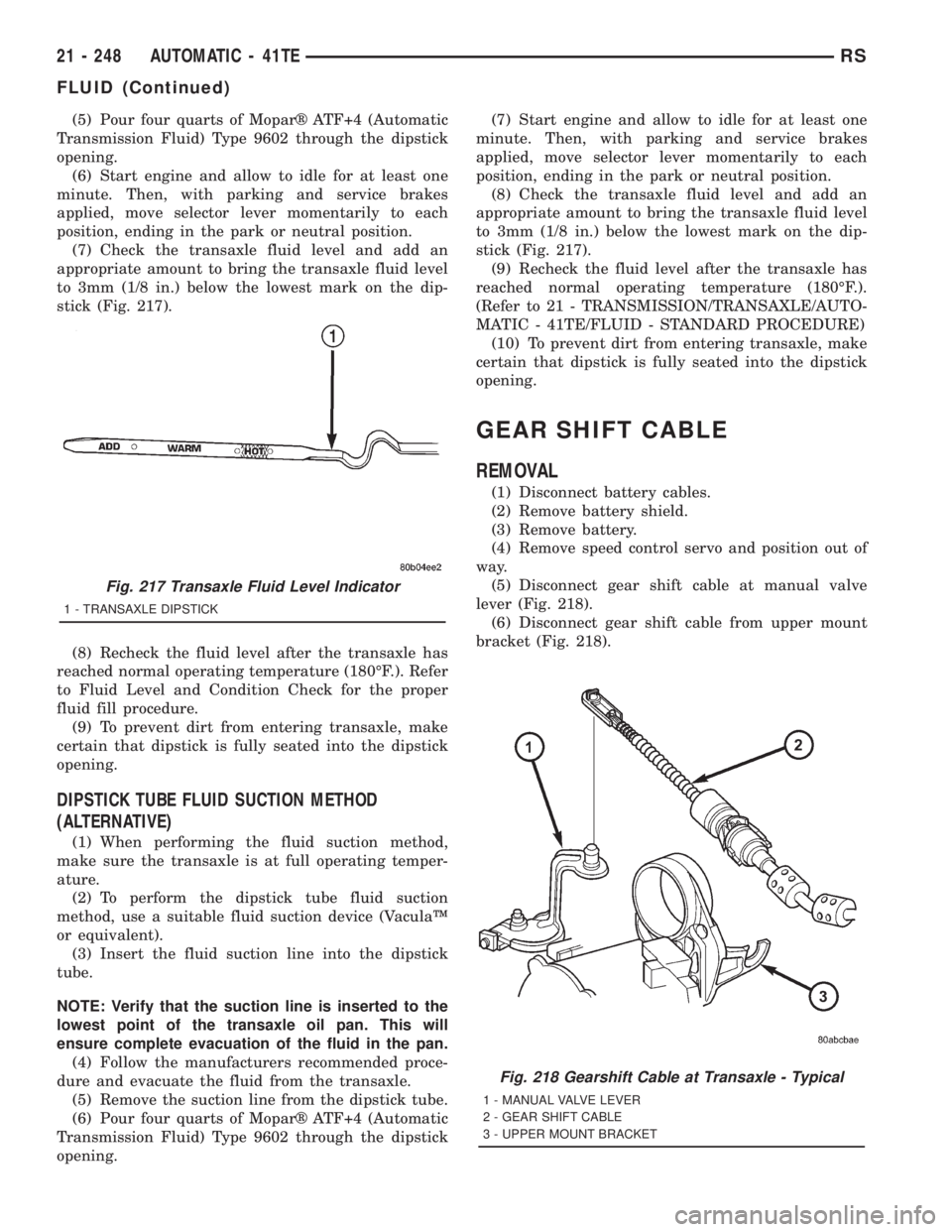
(5) Pour four quarts of Moparž ATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission Fluid) Type 9602 through the dipstick
opening.
(6) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.
(7) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 217).
(8) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.). Refer
to Fluid Level and Condition Check for the proper
fluid fill procedure.
(9) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
DIPSTICK TUBE FLUID SUCTION METHOD
(ALTERNATIVE)
(1) When performing the fluid suction method,
make sure the transaxle is at full operating temper-
ature.
(2) To perform the dipstick tube fluid suction
method, use a suitable fluid suction device (VaculaŸ
or equivalent).
(3) Insert the fluid suction line into the dipstick
tube.
NOTE: Verify that the suction line is inserted to the
lowest point of the transaxle oil pan. This will
ensure complete evacuation of the fluid in the pan.
(4) Follow the manufacturers recommended proce-
dure and evacuate the fluid from the transaxle.
(5) Remove the suction line from the dipstick tube.
(6) Pour four quarts of Moparž ATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission Fluid) Type 9602 through the dipstick
opening.(7) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.
(8) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 217).
(9) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.).
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(10) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
GEAR SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery cables.
(2) Remove battery shield.
(3) Remove battery.
(4) Remove speed control servo and position out of
way.
(5) Disconnect gear shift cable at manual valve
lever (Fig. 218).
(6) Disconnect gear shift cable from upper mount
bracket (Fig. 218).
Fig. 217 Transaxle Fluid Level Indicator
1 - TRANSAXLE DIPSTICK
Fig. 218 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle - Typical
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
21 - 248 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
FLUID (Continued)
Page 3772 of 4284

A failed or malfunctioning EGR system can cause
engine spark knock, sags or hesitation, rough idle,
engine stalling and increased emissions.
REMOVAL - 2.4L
The EGR valve and Electrical EGR Transducer are
serviced as an assembly (Fig. 1).(1) Disconnect vacuum tube from electric EGR
transducer. Inspect vacuum tube for damage.
(2) Remove electrical connector from solenoid.
(3) Remove EGR tube bolts from EGR valve.
(4) Remove EGR valve from cylinder head adaptor.
(5) Clean gasket surface and discard old gasket.
Check for any signs of leakage or cracked surfaces.
Repair or replace as necessary.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
The EGR valve and Electrical EGR Transducer are
serviced as an assembly (Fig. 2).
(1) Disconnect vacuum tube from electric EGR
transducer. Inspect vacuum tube for damage.
(2) Remove electrical connector from solenoid.
(3) Remove EGR tube bolts from EGR valve.
(4) Remove EGR valve from cylinder head adaptor.
(5) Clean gasket surface and discard old gasket.
Check for any signs of leakage or cracked surfaces.
Repair or replace as necessary.
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
The EGR valve and Electrical EGR Transducer are
serviced as an assembly (Fig. 1).
(1) Assemble EGR valve with new gasket onto the
cylinder head adaptor.
(2) Loose assemble the bolts from EGR valve to
EGR tube.
(3) Loose assemble the bolts from EGR valve to
cylinder head.
(4) Tighten bolts from EGR valve to cylinder head
to 22.8 N´m (200625 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Tighten bolts from EGR valve to EGR tube to
11.9 N´m (105620 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Reconnect vacuum hose and electrical connec-
tor to electrical EGR transducer.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
The EGR valve and Electrical EGR Transducer are
serviced as an assembly (Fig. 2).
(1) Loose assemble the bolts from EGR valve to
EGR tube.
(2) Loose assemble the bolts from EGR valve to
cylinder head adaptor.
(3) Tighten bolts from EGR valve to EGR tube to
11.9 N´m (105620 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Tighten bolts from EGR valve to cylinder head
to 22.9 N´m (200625 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Reconnect vacuum hose and electrical connec-
tor to electrical EGR transducer.
Fig. 3 EGR Valve and Transducer - Typical
1 - DIAPHRAGM
2 - PISTON
3 - SPRING
4 - EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY
5 - VACUUM MOTOR
6 - VACUUM MOTOR FITTING
7 - VACUUM OUTLET FITTING TO EGR VALVE
8 - EGR VALVE CONTROL ASSEMBLY
9 - ELECTRIC SOLENOID PORTION OF VALVE CONTROL
10 - VACUUM INLET FITTING FROM ENGINE
11 - BACK-PRESSURE HOSE
12 - TRANSDUCER PORTION OF VALVE CONTROL
13 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTION POINT
14 - EGR VALVE BACK-PRESSURE FITTING
15 - EXHAUST GAS INLET
16 - STEM PROTECTOR AND BUSHING
17 - BASE
18 - MOVEMENT INDICATOR
19 - POPPET VALVE
20 - SEAT
21 - EXHAUST GAS OUTLET
25 - 22 EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATIONRS
VALVE (Continued)
Page 4071 of 4284

POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST VER - 2 APPLICABILITY
1. NOTE: If the PCM has been replaced and the correct VIN and mileage have not
been programmed, a DTC will be set in the ABS Module, Airbag Module and the
SKIM.
2. NOTE: If the vehicle is equipped with a Sentry Key Immobilizer System, Secret
Key data must be updated. Refer to the Service Information for the PCM, SKIM and
the Transponder (ignition key) for programming information.
3. Inspect the vehicle to ensure that all components related to the repair are connected
properly.
4. With the DRBIIIt, clear DTCs and Reset Memory all engine values.
5. Run the engine for one warm-up cycle to verify proper operation.
6. Road test the vehicle. Use all accessories that may be related to this repair.
7. With the DRBIIIt, confirm that no DTC's or Secondary Indicators are present and that all
components are functioning properly.
8. If this test is being performed after a No Trouble Code test, verify the symptom is no longer
present.
9. If the symptom is still present, or any other symptom or DTC is present refer to the
appropriate category and perform the corresponding symptom.
10. Refer to any Technical Service Bulletins that may apply.
11. If there are no DTCs present and all components are functional properly, the repair is
complete.
Are any DTCs present?All
Ye s®Repair is not complete, refer to appropriate symptom.
No®Repair is complete.
POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST VER - 3 APPLICABILITY
1. NOTE: If the PCM has been replaced and the correct VIN and mileage have not
been programmed, a DTC will be set in the ABS Module, Airbag Module and the
SKIM.
2. NOTE: If the vehicle is equipped with a Sentry Key Immobilizer System, Secret
Key data must be updated. Refer to the Service Information for the PCM, SKIM and
the Transponder (ignition key) for programming information.
3. Inspect the vehicle to ensure that all components related to the repair are connected
properly.
4. With the DRBIIIt, clear DTCs.
5. Perform generator output test. Refer to the appropriate service information as necessary.
6. Start the engine and set engine speed to 2000 RPM for at least thirty seconds.
7. Cycle the ignition key off and on.
8. With the DRBIIIt, read the DTCs. If the DTC returns, or any other symptom or DTC is
present, refer to the appropriate category and perform the corresponding symptom.
9. If there are no DTCs present and all components are functioning properly, the repair is
complete.
Are any DTCs present?All
Ye s®Repair is not complete, refer to appropriate symptom.
No®Repair is complete.
277
VERIFICATION TESTS
VERIFICATION TESTS ÐContinued