2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 1658 of 4284

STANDARD PROCEDURE - BRAKE FLUID
LEVEL CHECKING
Check master cylinder reservoir fluid level a mini-
mum of twice annually.
Fluid reservoirs are marked with the words FULL
and ADD to indicate proper brake fluid fill level of
the master cylinder.
If necessary, add brake fluid to bring the level to
the bottom of the FULL mark on the side of the mas-
ter cylinder fluid reservoir.
Use only Mopartbrake fluid or equivalent from a
sealed container. Brake fluid must conform to DOT 3
specifications (DOT 4 or DOT 4+ are acceptable).
DO NOTuse brake fluid with a lower boiling
point, as brake failure could result during prolonged
hard braking.
Use only brake fluid that was stored in a tightly-
sealed container.
DO NOTuse petroleum-based fluid because seal
damage will result. Petroleum based fluids would be
items such as engine oil, transmission fluid, power
steering fluid etc.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID
The brake fluid used in this vehicle must conform
to DOT 3 specifications (DOT 4 and DOT 4+ are
acceptable) and SAE J1703 standards. No other type
of brake fluid is recommended or approved for usage
in the vehicle brake system. Use only MopartBrake
Fluid or equivalent from a tightly sealed container.
CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an container which has been left open. An
open container of brake fluid will absorb moisture
from the air and contaminate the fluid.
CAUTION: Never use any type of a petroleum-based
fluid in the brake hydraulic system. Use of such
type fluids will result in seal damage of the vehicle
brake hydraulic system causing a failure of the
vehicle brake system. Petroleum based fluids would
be items such as engine oil, transmission fluid,
power steering fluid, etc.
JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
A junction block is used on vehicles that are not
equipped with antilock brakes (ABS). The junction
block mounts in the same location as the integrated
control unit (ICU) does on vehicles equipped withABS. This allows for use of the same brake tube con-
figuration on all vehicles. The junction block is
located on the driver's side of the front suspension
cradle/crossmember below the master cylinder (Fig.
46).
It has six threaded ports to which the brake tubes
connect. Two are for the primary and secondary
brake tubes coming from the master cylinder. The
remaining four are for the chassis brake tubes going
to each brake assembly.
OPERATION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
The junction block distributes the brake fluid com-
ing from the master cylinder primary and secondary
ports to the four chassis brake tubes leading to the
brakes at each wheel. Since the junction block
mounts in the same location as the ABS integrated
control unit (ICU), it allows for the common use of
brake tubes going to the brakes whether the vehicle
is equipped with or without ABS.
NOTE: Although the brake tubes coming from the
master cylinder to the junction block or ABS ICU
may appear to be the same, they are not. They are
unique to each brake system application.
REMOVAL - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
(1) Using a brake pedal depressor, move and lock
the brake pedal to a position past its first 1 inch of
travel. This will prevent brake fluid from draining
out of the master cylinder when the brake tubes are
removed from the junction block.
(2) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(3) If the vehicle is equipped with speed control,
perform the following:
(a) Disconnect the battery positive cable.
(b) Remove the battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - REMOVAL).
(c) Disconnect the vacuum hose connector at the
tank built into the battery tray.
(d) Remove the screw securing the coolant filler
neck to the battery tray.
(e) Remove the battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - REMOVAL).
(f) Remove the fasteners and move the speed
control servo off to the side, out of the way.
CAUTION: Before removing the brake tubes from
the junction block, the junction block and the brake
tubes must be thoroughly cleaned. This is required
to prevent contamination from entering the brake
hydraulic system.
5 - 32 BRAKES - BASERS
FLUID (Continued)
Page 1706 of 4284

Use only brake fluid that was stored in a tightly-
sealed container.
DO NOTuse petroleum-based fluid because seal
damage will result. Petroleum based fluids would be
items such as engine oil, transmission fluid, power
steering fluid etc.
MASTER CYLINDER - RHD
DESCRIPTION
The master cylinder used on right hand drive
(RHD) vehicles functions similarly to that used on
left hand drive (LHD) vehicles. The RHD master cyl-
inder, as well as the RHD power brake booster, is
located in the same area, but lower in the engine
compartment than LHD models (Fig. 1). For that
reason an extension manifold is placed between the
fluid reservoir and master cylinder housing allowing
the fluid reservoir to be positioned in the same loca-
tion as on LHD models.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Vacuum in the power brake booster must
be pumped down (removed) before removing mas-
ter cylinder from power brake booster. This is nec-
essary to prevent the power brake booster from
sucking in any contamination as the master cylin-der is removed. This can be done simply by pump-
ing the brake pedal, with the vehicle's engine not
running, until a firm feeling brake pedal is achieved.
(1) With engine not running, pump brake pedal
until a firm pedal is achieved (4 or 5 strokes).
(2) Disconnect negative battery terminal.
(3) Disconnect positive battery terminal.
(4) Remove battery shield.
(5) Remove nut and clamp securing battery to tray,
remove battery.
(6) Thoroughly clean all surfaces of the brake fluid
reservoir and master cylinder. Use only solvent such
as MopartBrake Parts Cleaner or equivalent.
(7) Remove wiring harness connector from brake
fluid level switch in master cylinder brake fluid res-
ervoir (Fig. 1).
(8) Disconnect primary and secondary brake tubes
from master cylinder housing (Fig. 2). Install sealing
plugs in the now open brake tube outlet ports.
CAUTION: Before removing the master cylinder
from the power brake vacuum booster, the master
cylinder and vacuum booster must be thoroughly
cleaned. This must be done to prevent dirt particles
from falling into the power brake vacuum booster.
(9) Clean area where master cylinder assembly
attaches to power brake booster. Use only a solvent
such as MopartBrake Parts Cleaner or equivalent.
(10) Remove two nuts attaching master cylinder to
power brake booster (Fig. 2).
(11) Slide master cylinder straight out of power
brake booster.
Fig. 1 RHD MASTER CYLINDER AND POWER
BRAKE BOOSTER
1 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
2 - BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
3 - FLUID RESERVOIR
4 - MASTER CYLINDER
Fig. 2 RHD MASTER CYLINDER MOUNTING
1 - PRIMARY BRAKE TUBE NUT
2 - SECONDARY BRAKE TUBE NUT
3 - MASTER CYLINDER MOUNTING NUTS
5a - 2 BRAKES - BASERG
FLUID (Continued)
Page 1722 of 4284

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH SYSTEM
Clutch problem diagnosis will generally require a
road test to determine the type of fault. Component
inspection will then determine the problem after road
testing.
Drive the vehicle at normal speeds during road
test. Shift the transaxle through all gear ranges and
observe clutch action. If chatter, grab, slip, or
improper release is experienced, remove and inspect
the clutch components. If the problem is noise or
hard shifting, further diagnosis may be needed. The
transaxle or other driveline components may actually
be at fault.
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS - CLUTCH GRAB/CHATTER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CLUTCH DISC FACING
COVERED WITH OIL OR
GREASEOil leak at engine rear main or
transaxle input shaft seal.Correct leak and replace modular clutch
assembly (2.4L Gas) or clutch cover and
disc (2.5L TD).
Too much grease applied to splines
of disc and input shaft.Apply lighter coating of grease to splines.
NO FAULT FOUND WITH
CLUTCH
COMPONENTSProblem actually related to
suspension or driveline component.Further diagnosis required. Check
engine/transmission mounts, suspension
attaching parts and other driveline
components as needed.
Engine related problems. Check EFI and ignition systems.
PARTIAL ENGAGEMENT
OF CLUTCH DISCClutch cover, spring, or release
fingers bent, distorted (rough
handling, improper assembly).Replace modular clutch assembly (2.4L
Gas) or clutch cover and disc (2.5L TD).
Clutch disc damaged or distorted. Replace modular clutch assembly (2.4L
Gas) or clutch cover and disc (2.5L TD).
Clutch misalignment. Verify modular clutch pilot plate alignment
to crankshaft. Replace the modular clutch
assembly (2.4L Gas) or clutch cover and
disc (2.5L TD) if the pilot plate is loose or
bent.
Improper transaxle-to-engine
installation.Verify transaxle is properly installed to
engine.
Fig. 8 Release Bearing and Lever (RHD)
1 - RELEASE LEVER
2 - RELEASE BEARING
6a - 4 CLUTCHRG
CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1725 of 4284
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DRIVE PLATE
MISALIGNMENT
Common causes of misalignment are:
²Heat warping
²Mounting drive plate on a dirty crankshaft
flange
²Incorrect bolt tightening
²Improper seating on the crankshaft shoulder
²Loose crankshaft bolts
Clean the crankshaft flange before mounting the
drive plate. Dirt and grease on the flange surface
may misalign the flywheel, causing excessive runout.
Use new bolts when mounting drive plate to crank-
shaft. Tighten drive plate bolts to specified torque
only. Over-tightening can distort the drive plate hub
causing excessive runout.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH COVER
AND DISC RUNOUT
Check condition of the clutch cover before installa-
tion. A warped cover or diaphragm spring will cause
grab and/or incomplete release or engagement. Use
care when handling the clutch assembly. Impact can
distort the cover, diaphragm spring, and release fin-
gers.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH CHATTER
COMPLAINTS
For all clutch chatter complaints, perform the fol-
lowing:
(1) Check for loose, misaligned, or broken engine
and transmission mounts. If present, they should be
corrected at this time. Test vehicle for chatter. If
chatter is gone, there is no need to go any further.
(2) If chatter persists, check hydraulic clutch
release system is functioning properly.
(3) Check for loose connections in drivetrain. Cor-
rect any problems and determine if clutch chatter
complaints have been satisfied. If not:
(a) Remove transaxle.
(b) Check to see if the release bearing is sticky
or binding. Replace bearing, if needed.
(c) Check linkage for excessive wear on the pivot
stud and fork fingers. Replace all worn parts.
(d) Check clutch assembly for contamination
(dirt, oil). Replace clutch assembly, if required.
(e) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines
are damaged. Replace with new clutch assembly, if
necessary.
(f) Check input shaft splines for damage.
Replace, if necessary.
(g) Check for uneven wear on clutch fingers.
(h) Check for broken clutch cover diaphragm
spring fingers. Replace with new clutch assembly,
if necessary.
SPECIAL TOOLS
SPECIAL TOOLS - T850 TRANSAXLE
CLUTCH RELEASE CABLE -
LHD
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3)Diesel models:Remove underbody splash
shield.
(4) Remove clutch bellhousing cap.
(5) Some models will have a clutch cable retainer
clip at the transaxle to secure it to the case (Fig. 9).
If retainer clip is installed, dislodge clip from from
inside bellhousing using a suitable screwdriver (Fig.
10), pull outward on cable conduit, guiding cable core
wire through slot in bellhousing and disengaging
cable ªTº from clutch release lever (Fig. 11). If
retainer is not installed, disengage clutch cable from
transaxle by pulling outward on cable conduit, guid-
Disconnect Tool, 6638A
Remover/Installer, 6891
RGCLUTCH6a-7
CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1735 of 4284

COOLING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLING
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................3
COOLING SYSTEM LEAK TEST.............3
COOLING SYSTEM FLOW CHECK..........3
COOLING SYSTEM AERATION.............3
COOLING SYSTEM DEAERATION...........3
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................4COOLING SYSTEM - DRAINING............4
COOLING SYSTEM - REFILLING............4
COOLANT - ADDING ADDITIONAL...........4
COOLANT LEVEL CHECK - ROUTINE........5
SPECIFICATIONS.........................6
SPECIAL TOOLS..........................6
ACCESSORY DRIVE.......................7
ENGINE................................13
TRANSMISSION.........................36
COOLING
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system components consist of a radia-
tor, electric fan motors, shroud, pressure cap, thermo-
stat, transmission oil cooler, water pump, hoses,
clamps, coolant, and a coolant reserve system to com-
plete the circuit.
DESCRIPTION - HOSE CLAMPS
The cooling system uses spring type hose clamps.
If a spring type clamp replacement is necessary,
replace with the original Mopartequipment spring
type clamp.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only a original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter (Fig. 1).
OPERATION - COOLING SYSTEM
The engine cooling systems primary purpose is to
maintain engine temperature in a range that will
provide satisfactory engine performance and emission
levels under all expected driving conditions. It also
provides hot water (coolant) for heater performance
and cooling for automatic transmission oil. It does
this by transferring heat from engine metal to cool-
ant, moving this heated coolant to the radiator, and
then transferring this heat to the ambient air.²When engine is cold: thermostat is closed, cool-
ing system has no flow through the radiator. The
coolant bypass flows through the engine only.
²When engine is warm: thermostat is open, cool-
ing system has bypass flow and coolant flow through
radiator.
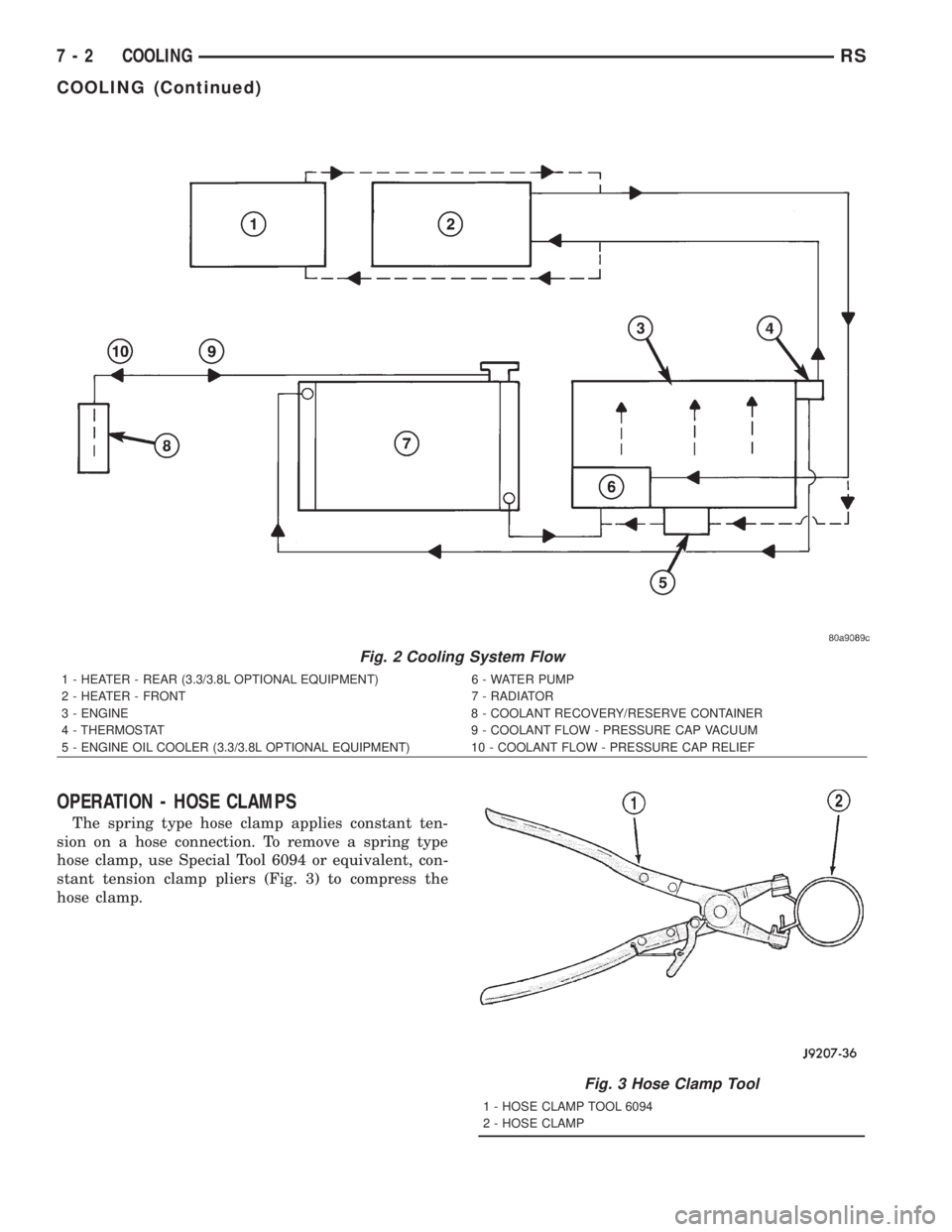
Coolant flow circuits for the 2.4L and 3.3/3.8L
engines are shown in (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 Spring Clamp Size Location
1 - SPRING CLAMP SIZE LOCATION
RSCOOLING7-1
Page 1736 of 4284
OPERATION - HOSE CLAMPS
The spring type hose clamp applies constant ten-
sion on a hose connection. To remove a spring type
hose clamp, use Special Tool 6094 or equivalent, con-
stant tension clamp pliers (Fig. 3) to compress the
hose clamp.
Fig. 2 Cooling System Flow
1 - HEATER - REAR (3.3/3.8L OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT) 6 - WATER PUMP
2 - HEATER - FRONT 7 - RADIATOR
3 - ENGINE 8 - COOLANT RECOVERY/RESERVE CONTAINER
4 - THERMOSTAT 9 - COOLANT FLOW - PRESSURE CAP VACUUM
5 - ENGINE OIL COOLER (3.3/3.8L OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT) 10 - COOLANT FLOW - PRESSURE CAP RELIEF
Fig. 3 Hose Clamp Tool
1 - HOSE CLAMP TOOL 6094
2 - HOSE CLAMP
7 - 2 COOLINGRS
COOLING (Continued)
Page 1737 of 4284

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
LEAK
WARNING: THE WARNING WORDS ªDO NOT OPEN
HOTº ON THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP IS A
SAFETY PRECAUTION. WHEN HOT, PRESSURE
BUILDS UP IN COOLING SYSTEM. TO PREVENT
SCALDING OR INJURY, THE RADIATOR CAP
SHOULD NOT BE REMOVED WHILE THE SYSTEM
IS HOT OR UNDER PRESSURE.
With engine not running, remove radiator pressure
cap and wipe the radiator filler neck sealing seat
clean. The radiator should be full.
Attach the Cooling System Tester 7700 or equiva-
lent to the radiator, as shown in (Fig. 4) and apply
104 kPa (15 psi) pressure. If the pressure drops more
than 13.8 kPa (2 psi) in 2 minutes, inspect all points
for external leaks.
All radiator and heater hoses should be shaken
while at 104 kPa (15 psi), since some leaks occur only
while driving due to engine movement.
If there are no external leaks, after the gauge dial
shows a drop in pressure, detach the tester. Start
engine and run until the thermostat opens, allowing
the coolant to expand. Reattach the cooling system
tester. If the needle on the dial fluctuates it indicates
a combustion leak, usually a head gasket leak.
WARNING: WITH TOOL IN PLACE, PRESSURE WILL
BUILD UP FAST. EXCESSIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP,
BY CONTINUOUS ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BERELEASED TO A SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER
PERMIT PRESSURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
If the needle on the dial does not fluctuate, raise
the engine rpm a few times. If an abnormal amount
of coolant or steam emits from the tailpipe, it may
indicate a coolant leak caused by a faulty head gas-
ket, cracked engine block, or cracked cylinder head.
There may be internal leaks that can be deter-
mined by removing the oil dipstick. If water globules
appear intermixed with the oil it will indicate an
internal leak in the engine. If there is an internal
leak, the engine must be disassembled for repair.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
FLOW
To determine whether coolant is flowing through
the cooling system, use the following procedures:
(1) If engine is cold, idle engine until normal oper-
ating temperature is reached. Then feel the upper
radiator hose. If it is hot, coolant is circulating.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE COOLING SYS-
TEM PRESSURE CAP WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND
UNDER PRESSURE BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS
FROM COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
(2) Remove pressure cap when engine is cold,
remove small amount of coolant Idle engine until
thermostat opens, you should observe coolant flow
while looking down the filler neck. Once flow is
detected install the pressure cap.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
AERATION
Low coolant level in a cross flow radiator will
equalize in both tanks with engine off. With engine
at running and at operating temperature, the high
pressure inlet tank runs full and the low pressure
outlet tank drops, resulting in cooling system aera-
tion. Aeration will draw air into the water pump
resulting in the following:
²High reading shown on the temperature gauge.
²Loss of coolant flow through the heater core.
²Corrosion in the cooling system.
²Water pump seal may run dry, increasing the
risk of premature seal failure.
²Combustion gas leaks into the coolant can also
cause the above problems.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
DEAERATION
As air is removed from the cooling system, it gath-
ers in the coolant bottle. This pressure is released
into the atmosphere through the pressure valve
located in the pressure cap when pressure reaches 96
Fig. 4 Pressure Testing
RSCOOLING7-3
COOLING (Continued)
Page 1739 of 4284
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT LEVEL
CHECK
NOTE: Do not remove radiator cap for routine cool-
ant level inspections.
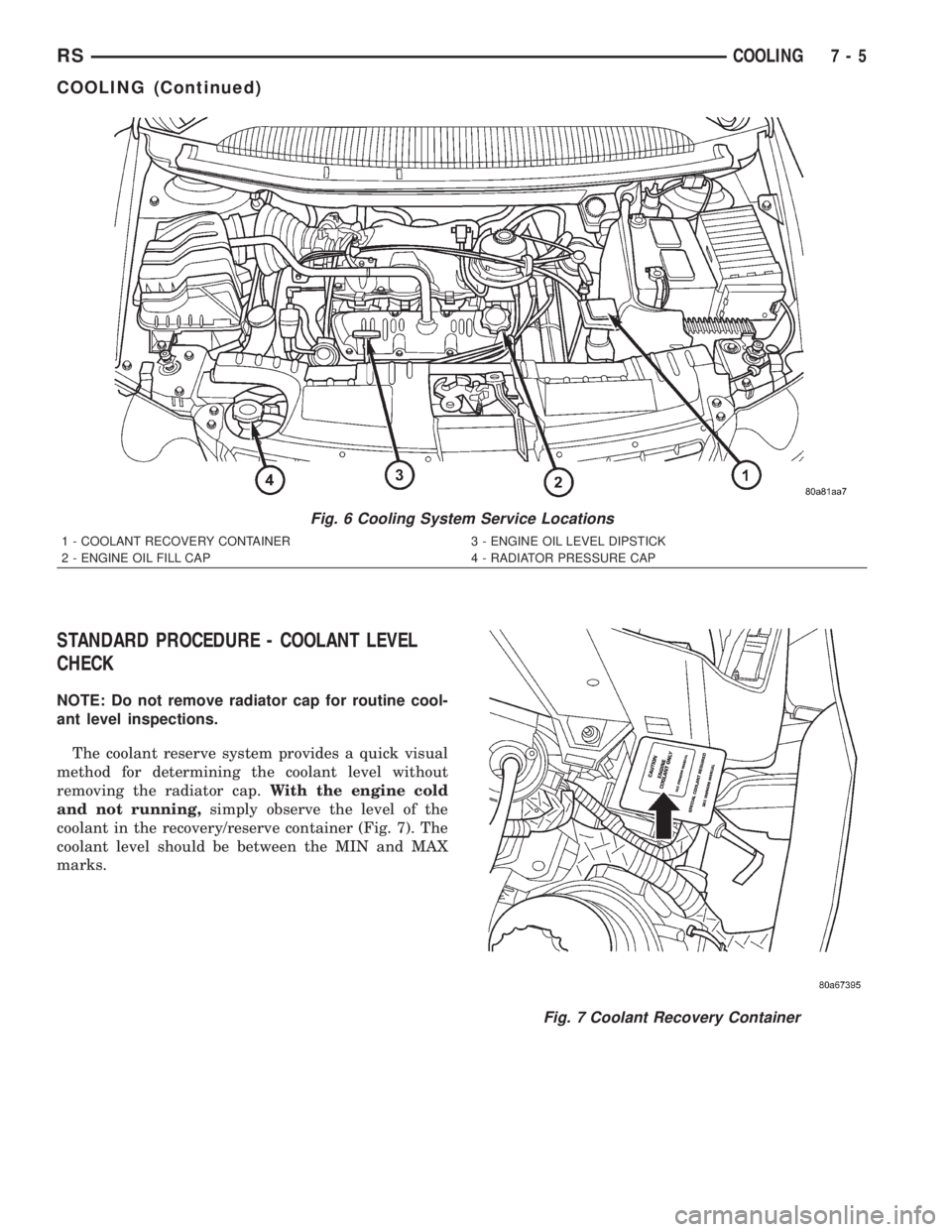
The coolant reserve system provides a quick visual
method for determining the coolant level without
removing the radiator cap.With the engine cold
and not running,simply observe the level of the
coolant in the recovery/reserve container (Fig. 7). The
coolant level should be between the MIN and MAX
marks.
Fig. 6 Cooling System Service Locations
1 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER 3 - ENGINE OIL LEVEL DIPSTICK
2 - ENGINE OIL FILL CAP 4 - RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
Fig. 7 Coolant Recovery Container
RSCOOLING7-5
COOLING (Continued)