2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER coolant level
[x] Cancel search: coolant levelPage 3636 of 4284

Performance Temperature and Pressure
Ambient Temperature 21É C
(70É F)27É C
(80É F)32É C
(90É F)38É C
(100É F)43É C
(110É F)
Left Center Panel
Outlet Discharge Air
Temperature1to8ÉC
(34 to 46É F)3to9ÉC
(37 to 49É F)4 to 10ÉC
(39 to 50É F)6to11ÉC
(43 to 52É F)7 to 18É C
(45 to 65É F)
Discharge Pressure
(High Side Service
Port)1034 to 1724
kPa
(150 to 250
psi)1517 to 2275
kPa
(220 to 330
psi)1999 to 2620
kPa
(290 to 380
psi)2068 to 2965
kPa
(300 to 430
psi)2275 to 3421
kPa
(330 to 450 psi)
Suction Pressure (Low
Side Service Port)103 to 207 kPa
(15 to 30 psi)117 to 221 kPa
(17 to 32 psi)138 to 241 kPa
(20 to 35 psi)172 to 269 kPa
(25 to 39 psi)207 to 345 kPa
(30 to 50 psi)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE TEST
PRE-DIAGNOSTIC PREPARATIONS
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING FRONT - WARNING - HEATER PLUMB-
ING).
Check the coolant level, drive belt tension, radiator
air flow, and cooling fan operation. Start the engine
and allow it to warm up to normal temperature.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT: TEST AND ACTION
Engine coolant is provided to the heater system by
two 16 mm (5/8 inch inside diameter) heater hoses.
With the engine idling at normal running tempera-
ture, set the heater-A/C controls as follows. Temper-
ature control to full Heat, Mode control to Floor,
Blower control to the highest speed setting. Using a
test thermometer, check the air temperature coming
from the center floor outlets and compare this read-
ing to the Temperature Reference table.
TEMPERATURE REFERENCE
AMBIENT
TEMPERATUREMINIMUM FLOOR
OUTLET TEMPERATURE
CELSIUS FAHRENHEIT CELSIUS FAHRENHEIT
15.5É 60É 62.2É 144É
21.1É 70É 63.8É 147É
26.6É 80É 65.5É 150É
32.2É 90É 67.2É 153ÉIf the floor outlet air temperature is insufficient,
check that the cooling system is operating to specifi-
cations. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING). Both heater hoses should be
HOT to the touch (the coolant return hose should be
slightly cooler than the supply hose). If the coolant
return hose is much cooler than the supply hose,
locate and repair the engine coolant flow obstruction
in heater system.
POSSIBLE LOCATIONS OR CAUSE OF OBSTRUCTED
COOLANT FLOW
²Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
²Improper heater hose routing.
²Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports
at cooling system connections.
²Plugged heater core.
²Air locked heater core.
²Restrictor in backwards.
If coolant flow is verified and the heater floor out-
let temperature is insufficient, a mechanical problem
may exist.
POSSIBLE LOCATION OR CAUSE OF INSUFFICIENT HEAT
²Obstructed cowl air intake.
²Obstructed heater system outlets.
²Blend-air door not functioning properly.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If heater floor outlet temperature cannot be
adjusted with the heater-A/C control temperature
control lever, one of the following could require ser-
vice:
²Blend-air door binding.
²Faulty blend-air door motor.
²Improper engine coolant temperature.
²Faulty heater-A/C control.
24 - 6 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGRS
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 3692 of 4284

PLUMBING - FRONT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PLUMBING - FRONT
WARNING..............................62
CAUTION...............................63
COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................64
OPERATION.............................65
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................65
COMPRESSOR NOISE DIAGNOSIS.........65
REMOVAL..............................65
INSTALLATION...........................66
CONDENSER
DESCRIPTION...........................67
OPERATION.............................67
REMOVAL..............................68
INSTALLATION...........................69
DISCHARGE LINE
REMOVAL..............................70
INSTALLATION...........................70
EVAPORATOR
DESCRIPTION...........................71
OPERATION.............................71
REMOVAL..............................71
INSTALLATION...........................73
EXPANSION VALVE
DESCRIPTION...........................74
OPERATION.............................74
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................74
EXPANSION VALVE.....................74
REMOVAL..............................75
INSTALLATION...........................75
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION...........................76
OPERATION.............................76
REMOVAL..............................76INSTALLATION...........................79
HEATER HOSE
REMOVAL..............................80
INSTALLATION...........................82
LIQUID LINE
REMOVAL..............................82
INSTALLATION...........................84
RECEIVER/DRIER
DESCRIPTION...........................85
OPERATION.............................86
REMOVAL..............................86
INSTALLATION...........................86
REFRIGERANT
DESCRIPTION...........................87
OPERATION.............................87
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................87
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM CHARGE LEVEL....87
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM LEAKS...........89
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................89
SERVICE EQUIPMENT...................89
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM CHARGE.........90
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE........91
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY...............91
REFRIGERANT OIL
DESCRIPTION...........................91
OPERATION.............................92
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................92
REFRIGERANT OIL LEVEL................92
SUCTION LINE
REMOVAL..............................92
INSTALLATION...........................93
SERVICE PORTS
REMOVAL..............................94
INSTALLATION...........................95
PLUMBING - FRONT
WARNING
WARNING: THE ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM IS
DESIGNED TO DEVELOP INTERNAL PRESSURES
OF 97 TO 123 KILOPASCALS (14 TO 18 POUNDS
PER SQUARE INCH). DO NOT REMOVE OR
LOOSEN THE COOLANT PRESSURE CAP, CYLIN-
DER BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS, RADIATOR DRAIN,RADIATOR HOSES, HEATER HOSES, OR HOSE
CLAMPS WHILE THE SYSTEM IS HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. FAILURE TO OBSERVE THIS WARNING
CAN RESULT IN SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE
HEATED ENGINE COOLANT. ALLOW THE VEHICLE
TO COOL FOR A MINIMUM OF 15 MINUTES
BEFORE OPENING THE COOLING SYSTEM FOR
SERVICE.
24 - 62 PLUMBING - FRONTRS
Page 3730 of 4284

(2) Lubricate new rubber O-ring seals with clean
refrigerant oil and install them on the evaporator
tube fittings.
(3) Position the expansion valve onto the evapora-
tor tubes (Fig. 4).
(4) Install and tighten the two screws that secure
the expansion valve to the evaporator tube sealing
plate. Tighten the screws to 11 N´m (97 in. lbs.).
(5) If the vehicle is equipped with the optional
Automatic Temperature Control (ATC) system, recon-
nect the expansion valve solenoid pigtail wire connec-
tor to the rear HVAC wire harness connector for the
solenoid.
(6) Reinstall the rear evaporator line extension
onto the expansion valve. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - REAR/EVAPO-
RATOR - INSTALLATION - EVAPORATOR LINE
EXTENSION).
(7) Install the foam insulator wrap over the rear
expansion valve.
(8) Reinstall the rear heater-A/C unit housing into
the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/DISTRIBUTION - REAR/REAR HEATER-
A/C HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION
The rear heater core is located near the front of
the rear heater-A/C unit housing, behind the right
rear wheel house. It is a heat exchanger made ofrows of tubes and fins. One end of the core is fitted
with a molded plastic tank that includes integral
heater core inlet and outlet nipples. The heater core
can be serviced without removing the rear heater-A/C
unit housing from the vehicle. The heater core cannot
be repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
Engine coolant is circulated through heater hoses
to the heater core at all times. As the coolant flows
through the heater core, heat removed from the
engine is transferred to the heater core fins and
tubes. Air directed through the heater core picks up
the heat from the heater core fins. The blend air door
allows control of the heater output air temperature
by controlling how much of the air flowing through
the rear heater-A/C unit housing is directed through
the heater core.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEATER CORE
FILLING
In its final installed position, the rear heater core
is positioned higher than the radiator fill cap. There-
fore, when the cooling system is drained and refilled,
gravity will not refill the heater core with coolant to
the proper level. This may result in two problems:1.
Insufficient coolant level in the engine cooling sys-
tem, which may result in engine overheating.2.Air
entrapped within the rear heater core, which may
result in insufficient rear heater performance. There
are two methods that may be employed to prevent
these problems:1.Pre-filling of the rear heater core.
2.Thermal cycling of the engine cooling system. Fol-
lowing are descriptions of both prevention methods,
as well as a method to verify rear heater perfor-
mance.
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING FRONT - WARNING - HEATER PLUMB-
ING).
PRE-FILLING
If the rear heater core or the rear heater-A/C hous-
ing have been removed from the vehicle for service,
the rear heater core may be pre-filled with the proper
engine coolant mixture prior to reconnecting the
heater hoses to the heater core hose fittings.
(1) The heater core should be installed in the rear
heater-A/C unit housing, and the rear heater-A/C
unit housing should be installed in the vehicle.
Fig. 4 Expansion Valve
1 - SOLENOID
2 - SOLENOID CONNECTOR
3 - SEALING PLATE
4 - EXPANSION VALVE
5 - SEALING PLATE
6 - HVAC CONNECTOR
24 - 100 PLUMBING - REARRS
EXPANSION VALVE (Continued)
Page 3731 of 4284

(2) Take the proper precautions to protect the car-
peting below the rear heater core from spilled engine
coolant and have absorbent toweling readily avail-
able to mop up any spills.
(3) Insert the small end of an appropriate funnel
into the upper hose fitting of the heater core (Fig. 5).
(4) Carefully pour the proper pre-mixed engine
coolant solution into the rear heater core through a
funnel until coolant begins to appear at the lower
hose fitting of the heater core.
(5) Use absorbent toweling to clean up any engine
coolant spills from the preceding operation.
(6) Reconnect the heater hoses to the rear heater
core. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - REAR/HEATER HOSE - INSTAL-
LATION).
(7) Refill the engine cooling system. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM REFILL).
THERMAL CYCLING
If the rear heater core was emptied and was not
pre-filled, it will be necessary to thermal cycle the
vehicle at least two times to ensure that the rear
heater core is properly filled.
(1) Refill the engine cooling system. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM REFILL).
(2) Start the engine and allow it to operate until
the thermostat opens.
(3) Turn the engine off and allow it to cool.
(4) With the engine cold and not running, check
and top off the engine coolant level as necessary.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE
- COOLANT LEVEL CHECK) and (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT
- ADDING).(5) Start the engine and allow it to operate until
the thermostat opens again.
(6) Turn the engine off and allow it to cool down
again.
(7) With the engine cold and not running, check
and top off the engine coolant level as necessary.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE
- COOLANT LEVEL CHECK) and (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT
- ADDING).
(8) Check the performance of the rear heater.
Refer to REAR HEATER PERFORMANCE CHECK .
REAR HEATER PERFORMANCE CHECK
Successful completion of the rear heater perfor-
mance check will confirm that the rear heater core is
properly filled with engine coolant. If the check is not
successful, either there is still air trapped in the rear
heater core or the rear heater plumbing is restricted.
This check should be performed with the vehicle in a
shop where the ambient temperature is about 21É C
(70É F).
(1) Start the engine and allow it to idle until it
warms up to normal operating temperature.
(2) Adjust the heater-A/C controls so that the front
heater is turned Off, the rear heater is set for full
Heat, and the rear blower motor is at its highest
speed setting.
(3) Use an accurate test thermometer to measure
the temperature of the air being discharged from the
rear heater outlet located at the base of the right
C-pillar.
(4) Proper discharge air temperature readings
should be from 57É to 63É C (135É to 145É F).
REMOVAL
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING FRONT - WARNING - HEATER PLUMB-
ING).
(1) Drain the engine cooling system. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM DRAIN).
(2) Remove the right quarter trim panel and right
D-pillar trim panel from the quarter inner panel.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/QUARTER TRIM
PANEL - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the rear heater distribution duct from
the right quarter inner panel. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION -
REAR/REAR HEATER DISTRIBUTION DUCT -
REMOVAL).
Fig. 5 Pre-Filling Heater Core - Typical
1 - REAR HEATER CORE
RSPLUMBING - REAR24 - 101
HEATER CORE (Continued)
Page 3739 of 4284

HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PLUMBING - FRONT
WARNING...............................1
HEATER HOSES - DIESEL SUPPLEMENTAL
HEATER
REMOVAL...............................1
INSTALLATION............................2
HEATER PIPES - DIESEL SUPPLEMENTAL
HEATER
REMOVAL...............................2
INSTALLATION............................2
REFRIGERANT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................4
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - REFRIGERANT
CHARGE LEVEL 2.5L DIESEL...............4
DIESEL SUPPLEMENTAL HEATER - DCHA
DESCRIPTION............................5
OPERATION.............................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................6
DIESEL SUPPLEMENTAL HEATER - DCHA....6
EXHAUST TUBE
REMOVAL...............................6INSTALLATION............................7
FUEL DOSING PUMP
DESCRIPTION............................7
OPERATION.............................7
REMOVAL...............................7
INSTALLATION............................8
FUEL LINE
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................8
CLEANING.............................8
REMOVAL...............................8
INSTALLATION............................9
HEATER UNIT
REMOVAL..............................10
INSTALLATION...........................10
SUPPLEMENTAL DIESEL HEATER WIRING
REMOVAL..............................11
INSTALLATION...........................11
AIR INTAKE PIPE
REMOVAL..............................11
INSTALLATION...........................12
PLUMBING - FRONT
WARNING
WARNING:: DO NOT OPERATE DCHA IN AN
ENCLOSED AREA SUCH AS A GARAGE THAT
DOES NOT HAVE EXHAUST VENTILATION FACILI-
TIES. ALWAYS VENT THE DCHA'S EXHAUST WHEN
OPERATING THE DCHA. FAILURE TO FOLLOW
THESE INSTRUCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL
INJURY OR DEATH.
ALLOW THE DCHA ASSEMBLY TO COOL BEFORE
PERFORMING A COMPONENT INSPECTION/RE-
PAIR/REPLACEMENT. FAILURE TO FOLLOW THESE
INSTRUCTIONS MY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
VERIFY THAT ALL DCHA FUEL LINES ARE
SECURELY FASTENED TO THEIR RESPECTIVE
COMPONENTS BEFORE THIS PROCEDURE.
HEATER HOSES - DIESEL
SUPPLEMENTAL HEATER
REMOVAL
(1) Elevate vehicle on a lift taking note of the
exhaust tube flexible section.
(2) Drain cooling system(Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Lower heater unit from vehicle(Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CABIN HEAT-
ER/HEATER UNIT - REMOVAL).
NOTE: Complete removal of cabin heater from vehi-
cle is not required, lowering unit allows easier
access to coolant line clamps.
(4) Remove clamps from both flexible coolant line
ends.
(5) Remove both lines from vehicle.
NOTE: If either line is damaged it is recommended
that both flexible lines be replaced.
RGHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING24a-1
Page 3743 of 4284
(4) Raise the liquid line (discharge) pressure to
about 1793 kPa (260 psi) by placing a piece of card-
board over part of the front side of the condenser. To
place the cardboard properly, remove the upper radi-
ator sight shield from the front fascia. Cover only
enough of the condenser to raise and maintain the
liquid line pressure at the specified level.
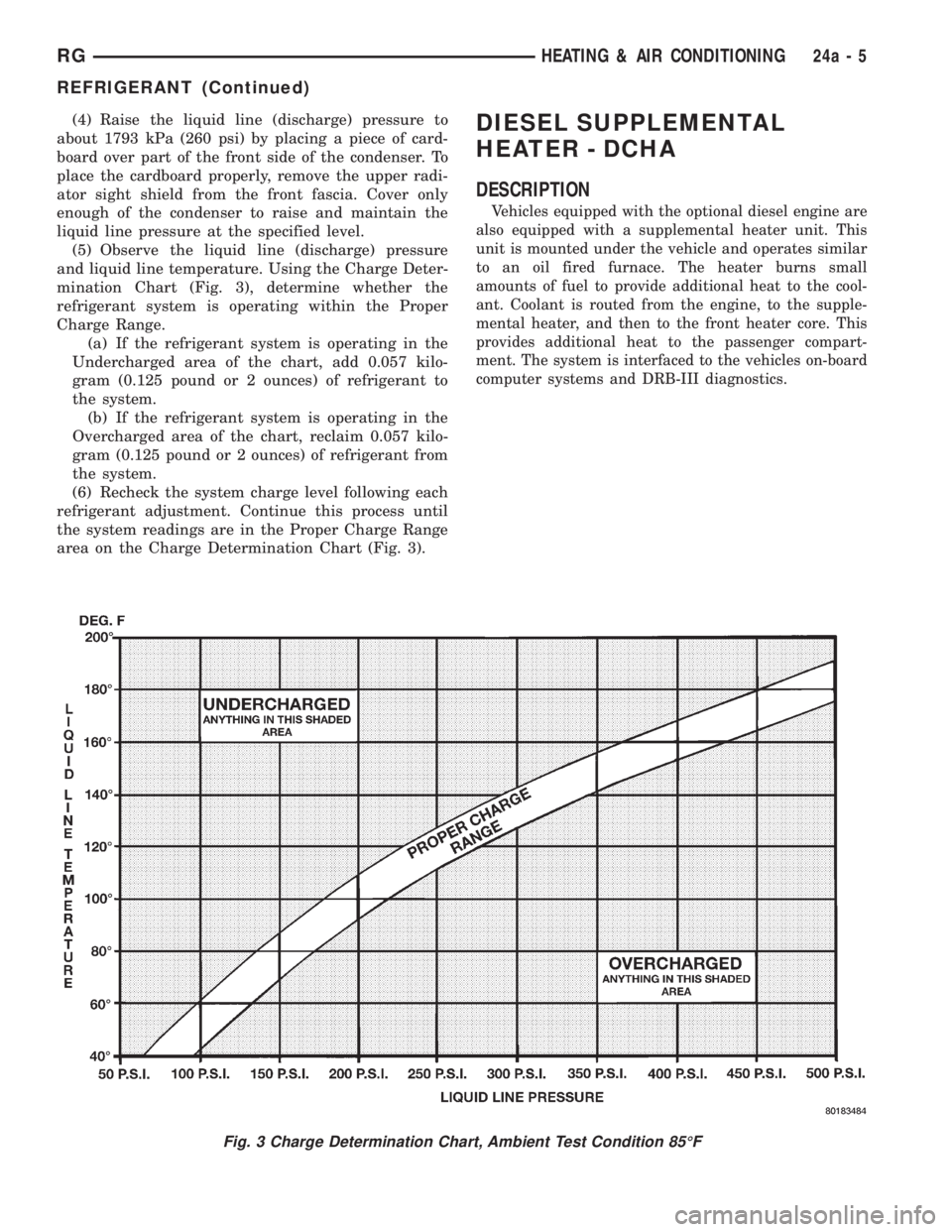
(5) Observe the liquid line (discharge) pressure
and liquid line temperature. Using the Charge Deter-
mination Chart (Fig. 3), determine whether the
refrigerant system is operating within the Proper
Charge Range.
(a) If the refrigerant system is operating in the
Undercharged area of the chart, add 0.057 kilo-
gram (0.125 pound or 2 ounces) of refrigerant to
the system.
(b) If the refrigerant system is operating in the
Overcharged area of the chart, reclaim 0.057 kilo-
gram (0.125 pound or 2 ounces) of refrigerant from
the system.
(6) Recheck the system charge level following each
refrigerant adjustment. Continue this process until
the system readings are in the Proper Charge Range
area on the Charge Determination Chart (Fig. 3).DIESEL SUPPLEMENTAL
HEATER - DCHA
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with the optional diesel engine are
also equipped with a supplemental heater unit. This
unit is mounted under the vehicle and operates similar
to an oil fired furnace. The heater burns small
amounts of fuel to provide additional heat to the cool-
ant. Coolant is routed from the engine, to the supple-
mental heater, and then to the front heater core. This
provides additional heat to the passenger compart-
ment. The system is interfaced to the vehicles on-board
computer systems and DRB-III diagnostics.
Fig. 3 Charge Determination Chart, Ambient Test Condition 85ÉF
RGHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING24a-5
REFRIGERANT (Continued)
Page 3751 of 4284

EMISSIONS CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................8EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS.................10
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION............20
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS.................23
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION - MONITORED COMPONENT
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (Check Engine) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum
and 1600 rpm.Any component that has an associated
limp in will set a fault after 1 trip with the malfunc-
tion present.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
The following is a list of the monitored compo-
nents:
²Comprehensive Components
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS
Along with the major monitors, OBD II requires
that the diagnostic system monitor any component
that could affect emissions levels. In many cases,
these components were being tested under OBD I.
The OBD I requirements focused mainly on testing
emissions-related components for electrical opens and
shorts.However, OBD II also requires that inputs from
powertrain components to the PCM be tested for
rationality, and that outputs to powertrain compo-
nents from the PCM be tested forfunctionality.
Methods for monitoring the various Comprehensive
Component monitoring include:
(1) Circuit Continuity
²Open
²Shorted high
²Shorted to ground
(2) Rationality or Proper Functioning
²Inputs tested for rationality
²Outputs tested for functionality
NOTE: Comprehensive component monitors are
continuous. Therefore, enabling conditions do not
apply.
Input RationalityÐWhile input signals to the
PCM are constantly being monitored for electrical
opens and shorts, they are also tested for rationality.
This means that the input signal is compared against
other inputs and information to see if it makes sense
under the current conditions.
PCM sensor inputs that are checked for rationality
include:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Oxygen Sensor (O2S)
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensors
²Power Steering Switch
²Oxygen Sensor Heater
²Engine Controller
²Brake Switch
²Leak Detection Pump Switch
²P/N Switch
²Trans Controls
Output FunctionalityÐPCM outputs are tested
for functionality in addition to testing for opens and
shorts. When the PCM provides a voltage to an out-
RSEMISSIONS CONTROL25-1
Page 3754 of 4284

PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the output of
the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxygen content
(lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a low content
of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL (check
engine lamp) will be illuminated.
Monitor OperationÐTo monitor catalyst effi-
ciency, the PCM expands the rich and lean switch
points of the heated oxygen sensor. With extended
switch points, the air/fuel mixture runs richer and
leaner to overburden the catalytic converter. Once
the test is started, the air/fuel mixture runs rich and
lean and the O2 switches are counted. A switch is
counted when an oxygen sensor signal goes from
below the lean threshold to above the rich threshold.
The number of Rear O2 sensor switches is divided by
the number of Front O2 sensor switches to determine
the switching ratio.
The test runs for 20 seconds. As catalyst efficiency
deteriorated over the life of the vehicle, the switch
rate at the downstream sensor approaches that of the
upstream sensor. If at any point during the test
period the switch ratio reaches a predetermined
value, a counter is incremented by one. The monitor
is enabled to run another test during that trip. When
the test fails three times, the counter increments to
three, a malfunction is entered, and a Freeze Frame
is stored. When the counter increments to three dur-ing the next trip, the code is matured and the MIL is
illuminated. If the test passes the first, no further
testing is conducted during that trip.
The MIL is extinguished after three consecutive
good trips. The good trip criteria for the catalyst
monitor is more stringent than the failure criteria. In
order to pass the test and increment one good trip,
the downstream sensor switch rate must be less than
80% of the upstream rate (60% for manual transmis-
sions). The failure percentages are 90% and 70%
respectively.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must typically be met before the PCM runs the cat-
alyst monitor. Specific times for each parameter may
be different from engine to engine.
²Accumulated drive time
²Enable time
²Ambient air temperature
²Barometric pressure
²Catalyst warm-up counter
²Engine coolant temperature
²Accumulated throttle position sensor
²Vehicle speed
²MAP
²RPM
²Engine in closed loop
²Fuel level
Pending ConditionsÐ
²Misfire DTC
²Front Oxygen Sensor Response
²Front Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Front Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Rationality (middle check)
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Fuel System Monitor
²All TPS faults
²All MAP faults
²All ECT sensor faults
²Purge flow solenoid functionality
²Purge flow solenoid electrical
²All PCM self test faults
²All CMP and CKP sensor faults
²All injector and ignition electrical faults
²Idle Air Control (IAC) motor functionality
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Brake switch
²Intake air temperature
ConflictÐThe catalyst monitor does not run if any
of the following are conditions are present:
²EGR Monitor in progress
²Fuel system rich intrusive test in progress
²EVAP Monitor in progress
²Time since start is less than 60 seconds
²Low fuel level
²Low ambient air temperature
25 - 4 EMISSIONS CONTROLRS
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)