Page 535 of 4770
56CHASSISÐMANUAL TRANSAXLE
MANUAL TRANSAXLE
� DESCRIPTION
�The 5S±FE engine model uses the same S51 manual transaxle as in the previous model.
�The 1MZ±FE engine model ahs newly adopted the E153 manual transaxle. The basic construction and operation
of the E153 manual transaxle are the same as those of the '95 MR2. However, the differential gear ratio has been
changed to accommodate the characteristics of the engine.
�Specifications�
Model
NewPrevious'95 MR2
Transaxle TypeS51E153S51E153
Engine Type5S FE1MZ FE5S FE3S GTEItem5S±FE1MZ±FE5S±FE3S±GTE
1st3.5383.2303.5383.230
Gear2nd1.9601.9131.9601.913Gear
Ratio3rd1.2501.2581.2501.258
4th0.9450.9180.9450.918
5th0.731uuu
Reverse3.1533.5453.15347
Differential Gear Ratio3.9443.9333.9444.285
Oil Capacity
liters (US qts, Imp. qts)2.6 (2.7, 2.3)4.2 (4.4, 3.7)2.6 (2.7, 2.3)4.2 (4.4, 3.7)
Oil ViscositySAE75W±90uuu
Oil Grade API, GL±4 OR GL±5uAPI GL±3, GL±4 OR GL±5u
Page 716 of 4770
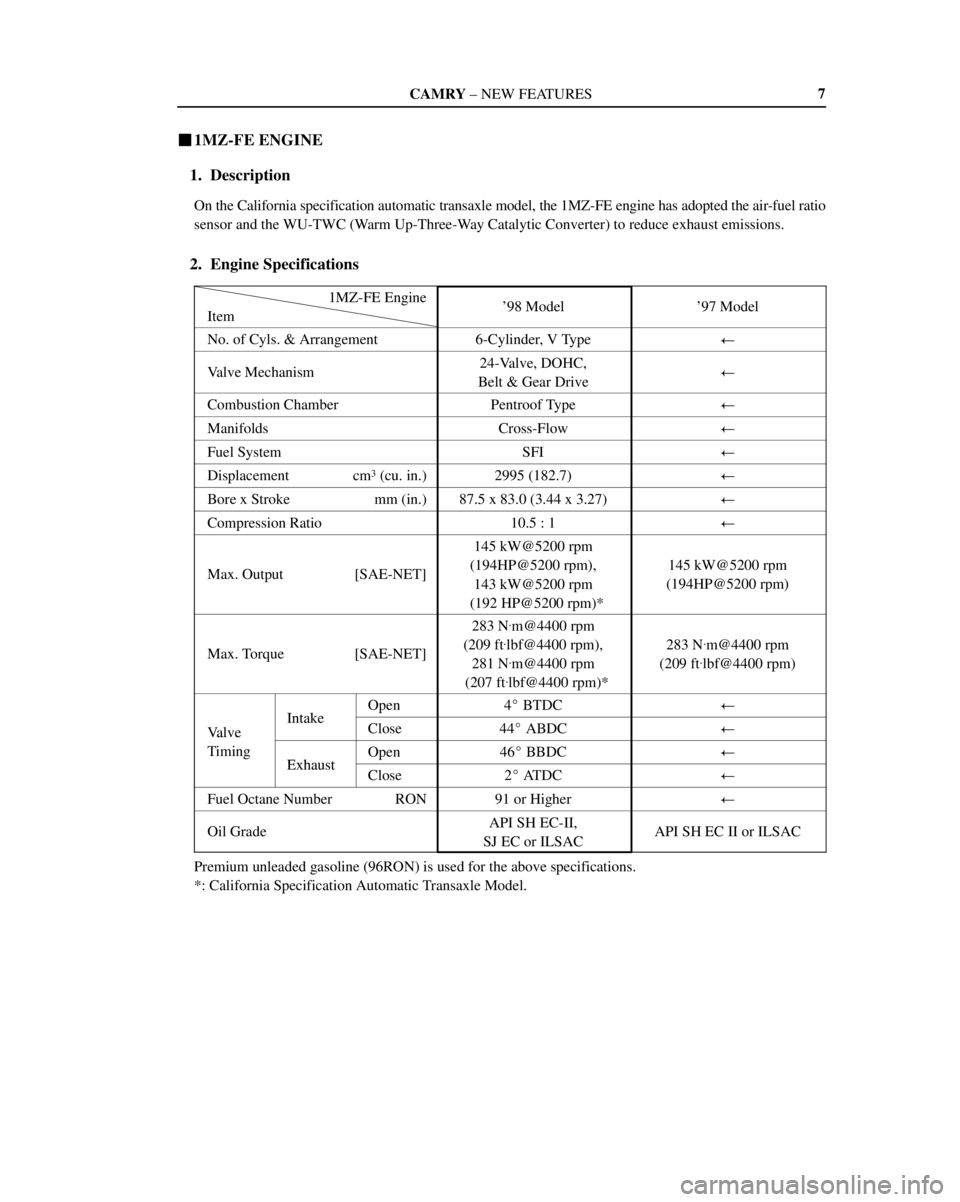
CAMRY ± NEW FEATURES7
�1MZ-FE ENGINE
1. Description
On the California specification automatic transaxle model, the 1MZ-FE engine has adopted the air-fuel ratio
sensor and the WU-TWC (Warm Up-Three-Way Catalytic Converter) to reduce exhaust emissions.
2. Engine Specifications
1MZ-FE Engine
Item'98 Model'97 Model
No. of Cyls. & Arrangement6-Cylinder, V Type�
Valve Mechanism24-Valve, DOHC,
Belt & Gear Drive�
Combustion ChamberPentroof Type�
ManifoldsCross-Flow�
Fuel SystemSFI�
Displacement cm3 (cu. in.)2995 (182.7)�
Bore x Stroke mm (in.)87.5 x 83.0 (3.44 x 3.27)�
Compression Ratio10.5 : 1�
Max. Output [SAE-NET]
145 kW@5200 rpm
(194HP@5200 rpm),
143 kW@5200 rpm
(192 HP@5200 rpm)*
145 kW@5200 rpm
(194HP@5200 rpm)
Max. Torque [SAE-NET]
283 N.m@4400 rpm
(209 ft
.lbf@4400 rpm),
281 N
.m@4400 rpm
(207 ft
.lbf@4400 rpm)*
283 N.m@4400 rpm
(209 ft
.lbf@4400 rpm)
IntakeOpen4� BTDC�
Valve
IntakeClose44� ABDC�Valve
Timing
ExhaustOpen46� BBDC�g
ExhaustClose2� AT D C�
Fuel Octane Number RON91 or Higher�
Oil GradeAPI SH EC-II,
SJ EC or ILSACAPI SH EC II or ILSAC
Premium unleaded gasoline (96RON) is used for the above specifications.
*: California Specification Automatic Transaxle Model.
Page 718 of 4770
CAMRY ± NEW FEATURES
150EG05 150EG08
� Front
WU-TWC
WU-TWC30 �m
Metallic Substrate
150EG09
9
Warm Up-Three-Way Catalytic Converter
�In addition to the TWC that is provided under the floor of the previous model, WU-TWCs are provided
to reduce exhaust emissions soon after the engine is started.
�The WU-TWC for the right bank is provided in the front exhaust pipe and in the exhaust manifold for
the left bank.
�The WU-TWC uses a thin-foil (foil thickness 50 �m � 30 �m) metallic substrate for weight reduction
and to improve warm-up performance.
5. Fuel System
Fuel Injector (California Specification Automatic Transaxle Model)
A compact 4-hole type injector has been adopted
to improve the atomization of fuel.
Page 720 of 4770
CAMRY ± NEW FEATURES
No.2 INJECTOR
SENSORS ACTUATORS
VG
RSO IGF NE
ECM
IGTI�
IGT3
#10
G22
THW
THA
VTA1
STA
SPD
AFR
AFL
OXS
EGLS
THG
KNKR
CF
NSW
A/C
ACIS
FC
ACT
MAFR
HAFL
HREL
#20
#30
#40
#50
#60
MASS AIR FLOW METER
R, 2, L KNKLIGSW
RSC
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
�Engine Speed Signal
�Crankshaft Angle Signal
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
�Crankshaft Angle Signal
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP.
SENSOR
INTAKE AIR TEMP. SENSOR
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
�Throttle Position Signal
IGNITION SWITCH
�Starting Signal
�Ignition Signal
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
COMBINATION METER
AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR
(Bank 1, Sensor 1)
AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR
(Bank 2, Sensor 1)
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(Bank 1, Sensor 2)
EGR VALVE POSITION SENSOR
EGR GAS TEMP. SENSOR
KNOCK SENSORS
PARK / NEUTRAL POSITION
SWITCH
�Neutral Start Signal
AIR CONDITIONING AMPLIFIER
�A / C Switch Signal
COOLING FAN RELAYNo.1 INJECTOR
No.3 INJECTOR
No.4 INJECTOR
No.5 INJECTOR
No.6 INJECTOR
ESA
IGNITER
IGNITION COILS
SPARK PLUGS
IAC
CONTROL VALVE
ACIS
VSV
FUEL PUMP CONTROL
CIRCUIT OPENING RELAY
AIR CONDITIONING CONTROL
AIR CONDITIONING
AMPLIFIER
AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR
HEATER CONTROL
AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR
HEATER RELAY
AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR
HEATER (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR
HEATER (Bank 1, Sensor 2)SFI
(Continued)
KNOCK SENSORS
11
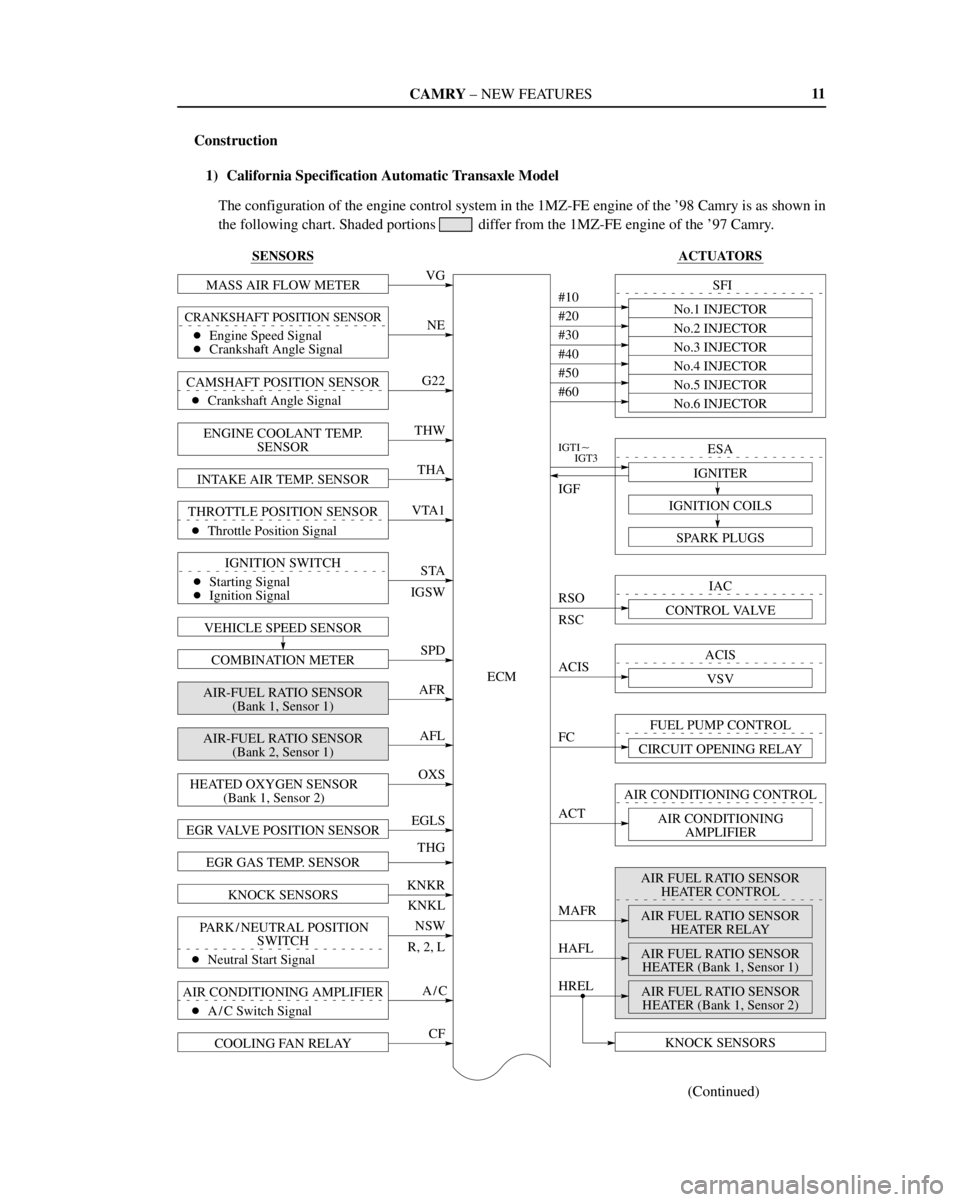
Construction
1) California Specification Automatic Transaxle Model
The configuration of the engine control system in the 1MZ-FE engine of the '98 Camry is as shown in
the following chart. Shaded portions
differ from the 1MZ-FE engine of the '97 Camry.
Page 721 of 4770
CAMRY ± NEW FEATURES
BATT
BATTERY
PS
IMLD
EGR
EVP1
TPC
W
ELS
STP
PTNK
TRC
TXCT
KSW
TC
SIL
EFI MAIN RELAY
+B
EFI ELS2 POWER STEERING OIL
PRESSURE SWITCH
TAILLIGHT & REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER
STOP LIGHT SWITCH
VAPOR PRESSURE SENSOR
ABS & TRAC ECU*
1
TRANSPONDER KEY
AMPLIFIER*2
UNLOCK WARNING SWITCH*2
DATALINK CONNECTOR 1
DATALINK CONNECTOR 3EGR CONTROL
VSV
EVAP CONTROL
VSV
VAPOR PRESSURE CONTROL
VSV
THEFT DETERRENT INDICATOR
LIGHT*2
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR
LAMP
HTSOXYGEN SENSOR HEATER
CONTROL
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
HEATER (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
RXCK
CODE
12
*1: Applicable only to vehicles equipped with the TRAC System.
*
2: Applicable only to vehicles equipped with the Engine Immobiliser System.
Page 732 of 4770
CAMRY ± NEW FEATURES
150NF116
Transponder Chip
Ignition KeyTransponder
Key Coil
Key
Cylinder
Transponder
Key AmplifierECMSpark Plug
Injector
150NF117
Transponder Key
AmplifierTransponder Key Coil
ECM
23
�ENGINE IMMOBILISER SYSTEM
1. General
The engine immobiliser system is a theft-deterrent system which disables the engine from starting using the
ignition key with an ID code that matches is the pre-registered code in the vehicle.
This system adopts a transponder system which uses a transponder chip embedded in the grip of the ignition
key. When the coil located around the ignition key cylinder receives the ID code signal transmitted by the
transponder chip, the computer included in the ECM determines whether or not the ID code matches the code
stored in the computer.
� System Diagram �
2. Layout of Components
The major function parts of the engine immobiliser system are shown below.
Page 733 of 4770
CAMRY ± NEW FEATURES
150NF118
BatteryIgnition Switch
EFI
Relay
Transponder
Key Coil
Transponder
Key AmplifierECMBody
ECU
DLC1
150NF119
Transponder Chip
24
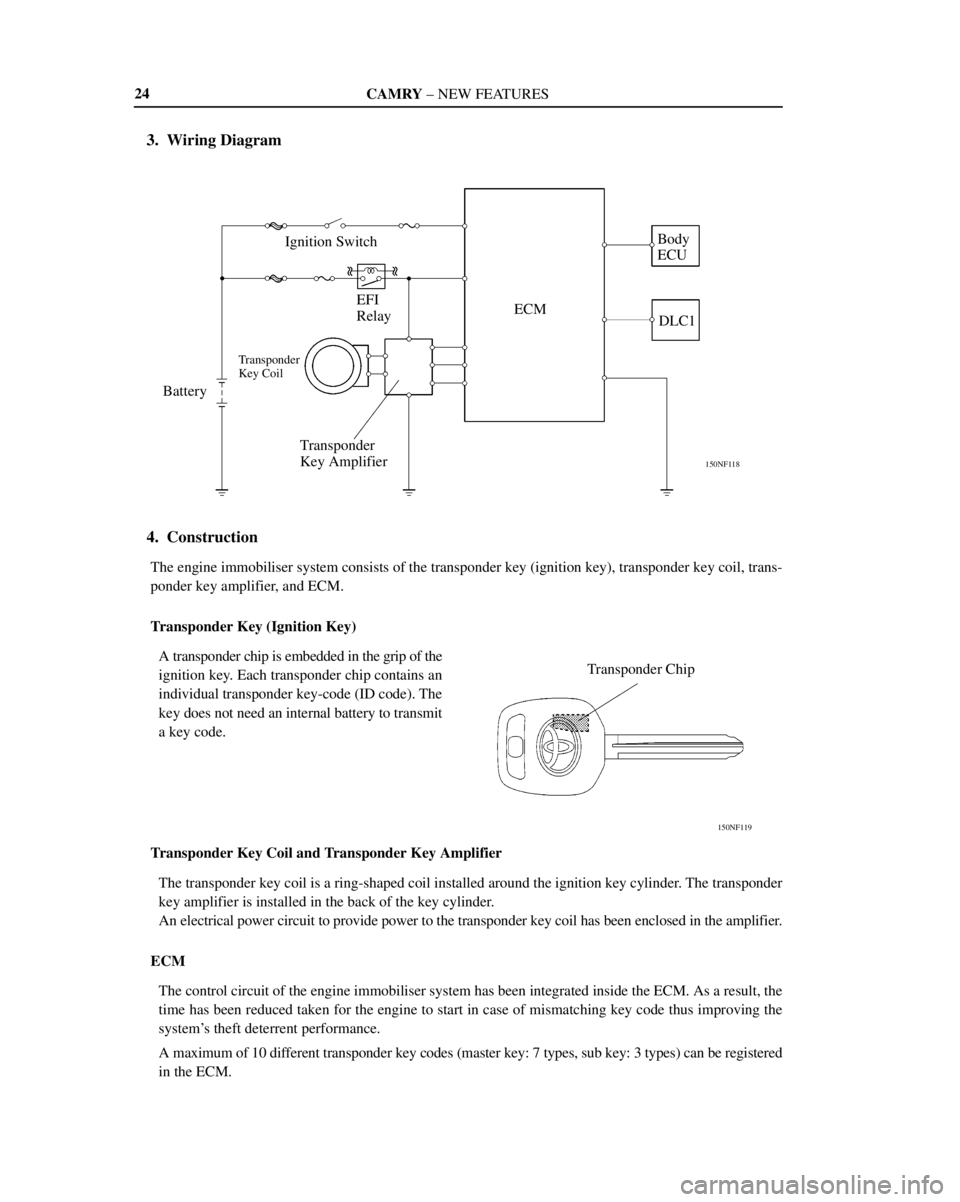
3. Wiring Diagram
4. Construction
The engine immobiliser system consists of the transponder key (ignition key), transponder key coil, trans-
ponder key amplifier, and ECM.
Transponder Key (Ignition Key)
A transponder chip is embedded in the grip of the
ignition key. Each transponder chip contains an
individual transponder key-code (ID code). The
key does not need an internal battery to transmit
a key code.
Transponder Key Coil and Transponder Key Amplifier
The transponder key coil is a ring-shaped coil installed around the ignition key cylinder. The transponder
key amplifier is installed in the back of the key cylinder.
An electrical power circuit to provide power to the transponder key coil has been enclosed in the amplifier.
ECM
The control circuit of the engine immobiliser system has been integrated inside the ECM. As a result, the
time has been reduced taken for the engine to start in case of mismatching key code thus improving the
system's theft deterrent performance.
A maximum of 10 different transponder key codes (master key: 7 types, sub key: 3 types) can be registered
in the ECM.
Page 734 of 4770
CAMRY ± NEW FEATURES
150NF120
Ignition KeyElectromagnetic
Energy
Transponder
ChipKey-Code
SignalTransponder Key
AmplifierECM
150NF121
Key-Code
SignalKey-Code
Transponder
Key AmplifierKey-CodeCode Memory Circuit
Code
Comparison
Circuit
ECMSpark Plug
Injector25
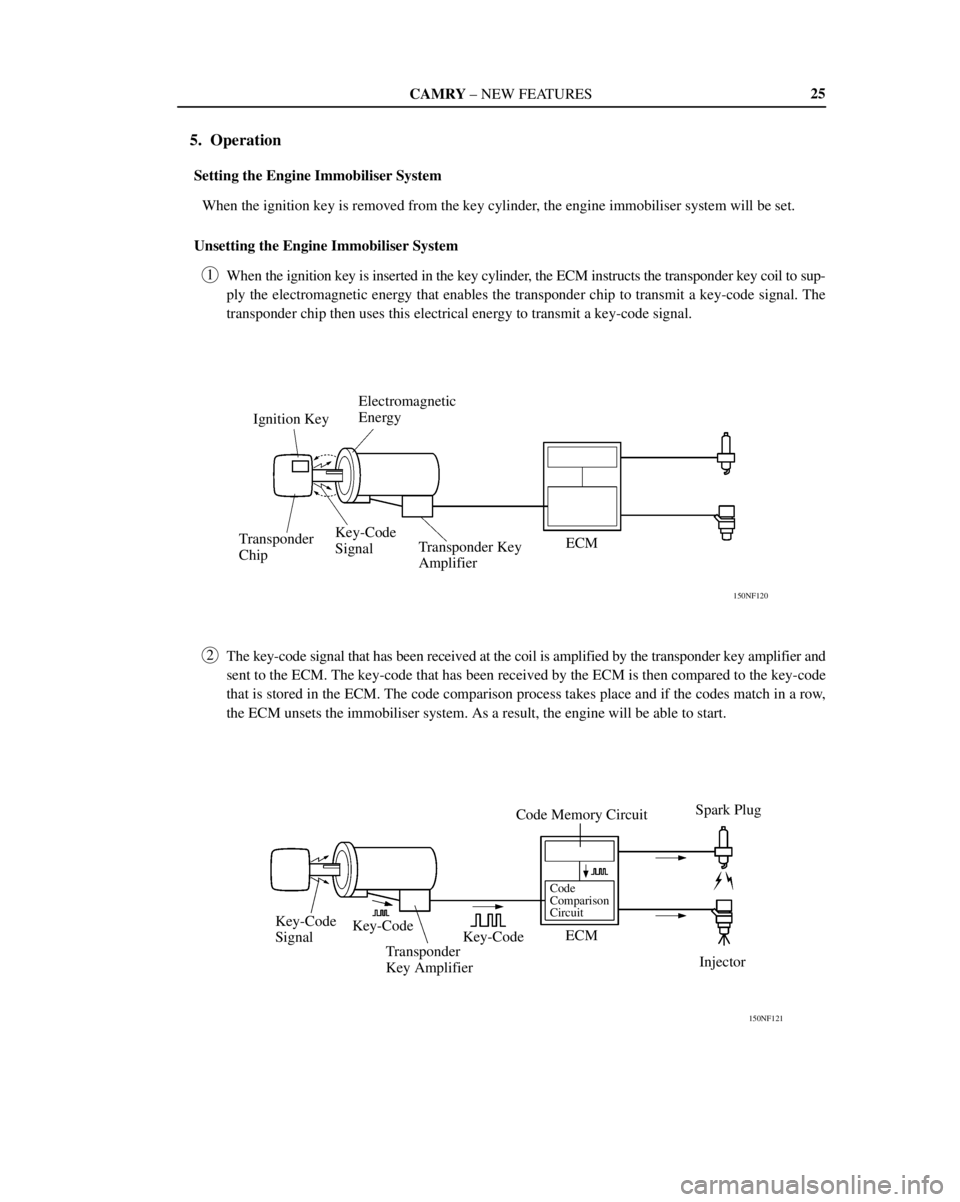
5. Operation
Setting the Engine Immobiliser System
When the ignition key is removed from the key cylinder, the engine immobiliser system will be set.
Unsetting the Engine Immobiliser System
1
When the ignition key is inserted in the key cylinder, the ECM instructs the transponder key coil to sup-
ply the electromagnetic energy that enables the transponder chip to transmit a key-code signal. The
transponder chip then uses this electrical energy to transmit a key-code signal.
2
The key-code signal that has been received at the coil is amplified by the transponder key amplifier and
sent to the ECM. The key-code that has been received by the ECM is then compared to the key-code
that is stored in the ECM. The code comparison process takes place and if the codes match in a row,
the ECM unsets the immobiliser system. As a result, the engine will be able to start.