Page 193 of 557
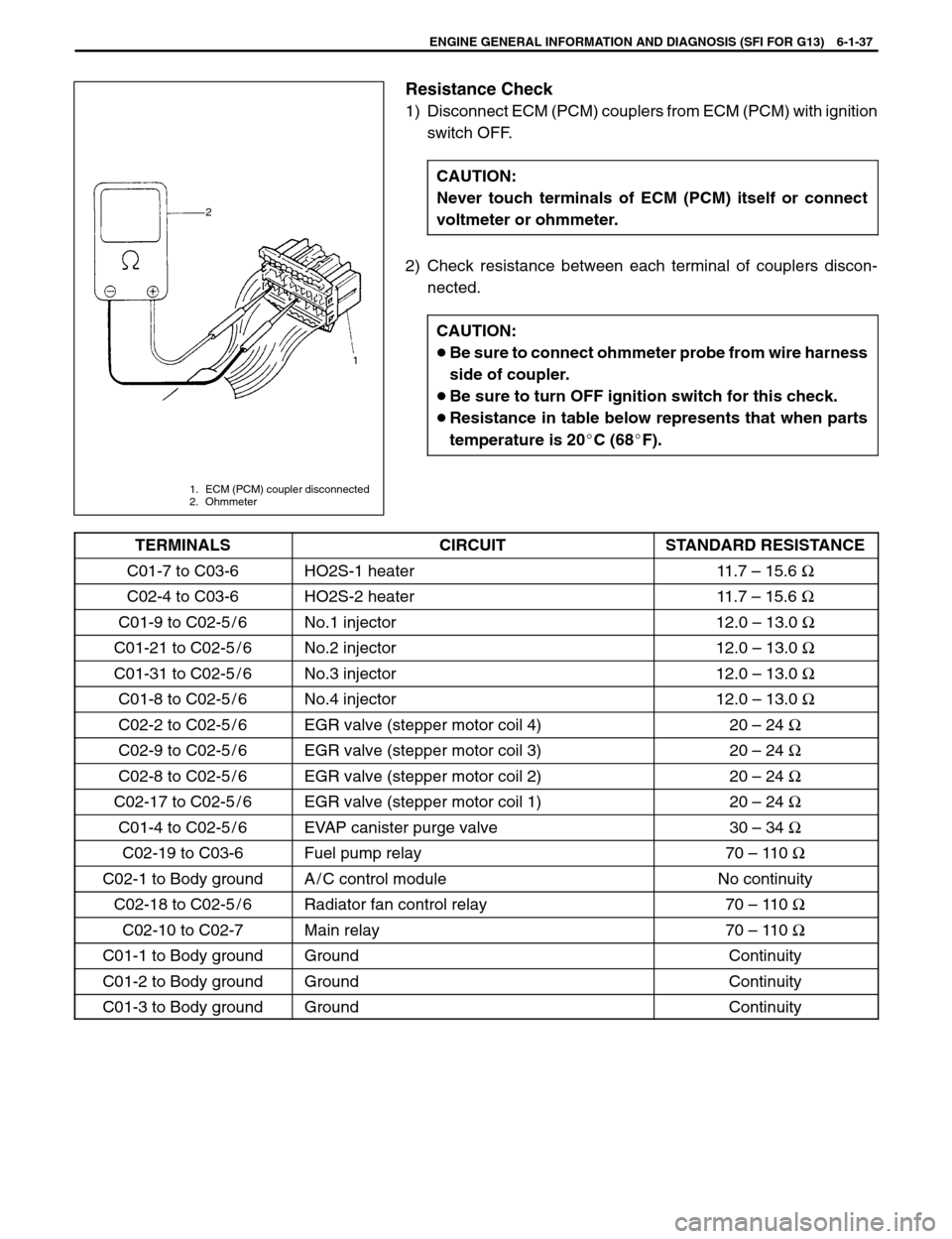
1 2
1. ECM (PCM) coupler disconnected
2. Ohmmeter
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13) 6-1-37
Resistance Check
1) Disconnect ECM (PCM) couplers from ECM (PCM) with ignition
switch OFF.
CAUTION:
Never touch terminals of ECM (PCM) itself or connect
voltmeter or ohmmeter.
2) Check resistance between each terminal of couplers discon-
nected.
CAUTION:
�Be sure to connect ohmmeter probe from wire harness
side of coupler.
�Be sure to turn OFF ignition switch for this check.
�Resistance in table below represents that when parts
temperature is 20�C (68�F).
TERMINALSCIRCUITSTANDARD RESISTANCE
C01-7 to C03-6HO2S-1 heater11.7 – 15.6 Ω
C02-4 to C03-6HO2S-2 heater11.7 – 15.6 Ω
C01-9 to C02-5 / 6No.1 injector12.0 – 13.0 Ω
C01-21 to C02-5 / 6No.2 injector12.0 – 13.0 Ω
C01-31 to C02-5 / 6No.3 injector12.0 – 13.0 Ω
C01-8 to C02-5 / 6No.4 injector12.0 – 13.0 Ω
C02-2 to C02-5 / 6EGR valve (stepper motor coil 4)20 – 24 Ω
C02-9 to C02-5 / 6EGR valve (stepper motor coil 3)20 – 24 Ω
C02-8 to C02-5 / 6EGR valve (stepper motor coil 2)20 – 24 Ω
C02-17 to C02-5 / 6EGR valve (stepper motor coil 1)20 – 24 Ω
C01-4 to C02-5 / 6EVAP canister purge valve30 – 34 Ω
C02-19 to C03-6Fuel pump relay70 – 110 Ω
C02-1 to Body groundA / C control moduleNo continuity
C02-18 to C02-5 / 6Radiator fan control relay70 – 110 Ω
C02-10 to C02-7Main relay70 – 110 Ω
C01-1 to Body groundGroundContinuity
C01-2 to Body groundGroundContinuity
C01-3 to Body groundGroundContinuity
Page 194 of 557
INFORMATION SENSORS
-1. MAP sensor
-2. TP sensor
-3. IAT sensor
-4. ECT sensor
-5. Heated oxygen sensor-1
5-1. Heated oxygen sensor-2
-6. VSS (A / T)
-7. Transmission range switch (A / T)
-8. Battery
-9. CMP sensor
-10. CKP sensor
-11. Fuel level sensor (gauge) (in fuel tank)
-12. PSP switch
-13. A / C control module (if equipped)
-14. VSS (speedometer) (M / T)OTHERS
A: ECM (PCM)
B: Main relay
C: EVAP canister
D: Data link connector CONTROL DEVICES
a: Fuel injector
b: EVAP canister purge valve
c: Fuel pump relay
d: EGR valve (step motor)
e: Malfunction indicator lamp
f: Ignition coil assembly
g: Radiator fan control relay
h: IAC valve
6-1-38 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13)
COMPONENT LOCATION
Page 208 of 557

6-1-52 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13)
Throttle
position
sensorTo other sensors
To other sensors
DTC P0121 THROTTLE POSITION CIRCUIT RANGE / PERFORMANCE
PROBLEM
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC DETECTING CONDITIONPOSSIBLE CAUSE
�After engine warmed up.
�While vehicle running at specified engine speed.
�No change in intake manifold pressure (constant throttle opening)
�Difference between actual throttle opening (detected from TP sensor)
and opening calculated by ECM (PCM) (Obtained on the basis of
engine speed and intake manifold pressure) in larger than specified
value.
�2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitoring�TP sensor malfunction
�High resistance in the circuit
�ECM (PCM) malfunction
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
WARNING:
�When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident
and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
�Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF. Clear DTC with ignition switch ON, check vehicle and environmental condition for:
–Indication of fuel level meter in combination meter: 1 / 4 or more
–Altitude (barometric pressure): 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
–Intake air temp.: between –10�C and 80�C (14�F and 176�F)
–Engine coolant temp.: 70�C, 158�F or higher
2) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
3) Increase vehicle speed to 30 – 40 mph, 50 – 60 km / h in 3rd gear or “D” range and hold throttle valve at that
opening position for 1 min.
4) Stop vehicle.
5) Check DTC in “DTC” mode and pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode.
Page 213 of 557

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13) 6-1-57
Fig. 1 for Step 3
DTC P0134 HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S) CIRCUIT NO ACTIVITY
DETECTED (SENSOR-1)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION – Refer to DTC P0130 section.
DTC DETECTING CONDITIONPOSSIBLE CAUSE
�Engine warmed up.
�While running under other than high load and high
engine speed conditions or at specified idle speed
(engine is in closed loop condition), HO2S-1 output
voltage is high or low continuously.
�2 driving cycle detection logic, Continuous
monitoring.�“G” or “R” circuit open or short
�Heated oxygen sensor malfunction
�Fuel system malfunction
�Exhaust gas leakage
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE – Refer to DTC P0130 section.
INSPECTION
STEPACTIONYESNO
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” performed?Go to Step 2.Go to “ENGINE
DIAG. FLOW
TABLE”.
2Is there DTC(s) other than Fuel system
(DTC P0171 / P0172) and HO2S-1 (DTC P0134)?Go to applicable
DTC Diag. Flow
Table.Go to Step 3.
3Check HO2S-1 and Its Circuit.
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch OFF.
2) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature and
keep it at 2000 r / min. for 60 sec.
3) Repeat racing engine (Repeat depressing accelerator
pedal 5 to 6 times continuously and take foot off from
pedal to enrich and enlean A / F mixture). See Fig. 1.
Does HO2S-1 output voltage deflect between 0.3 V and
over 0.6 V repeatedly?Go to DTC P0171
and P0172 Diag.
Flow Table (Fuel
System Check).Check “R” and “G”
wires for open
and short, and
connections for
poor connection.
If wires and
connections are
OK, replace
HO2S-1.
Page 216 of 557
6-1-60 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13)
To other sensor
Main
fuseIgnition
switch
Heater
To HO2S-1
heater
DTC P0136 HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S) CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
(SENSOR-2)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC DETECTING CONDITIONPOSSIBLE CAUSE
DTC will set when A or B condition is detected.
A. Max. output voltage of HO2S-2 is lower than specified value or
Min. output voltage is higher than specified value while vehicle
driving.
B. Engine is warmed up and HO2S-2 voltage is 4.5 V or more.
(circuit open)
�2 driving cycle detection logic, monitoring once / 1 driving.�Exhaust gas leakage
�“G” or “R” circuit open or short
�Heated oxygen sensor-2 malfunction
�Fuel system malfunction
Page 217 of 557
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13) 6-1-61
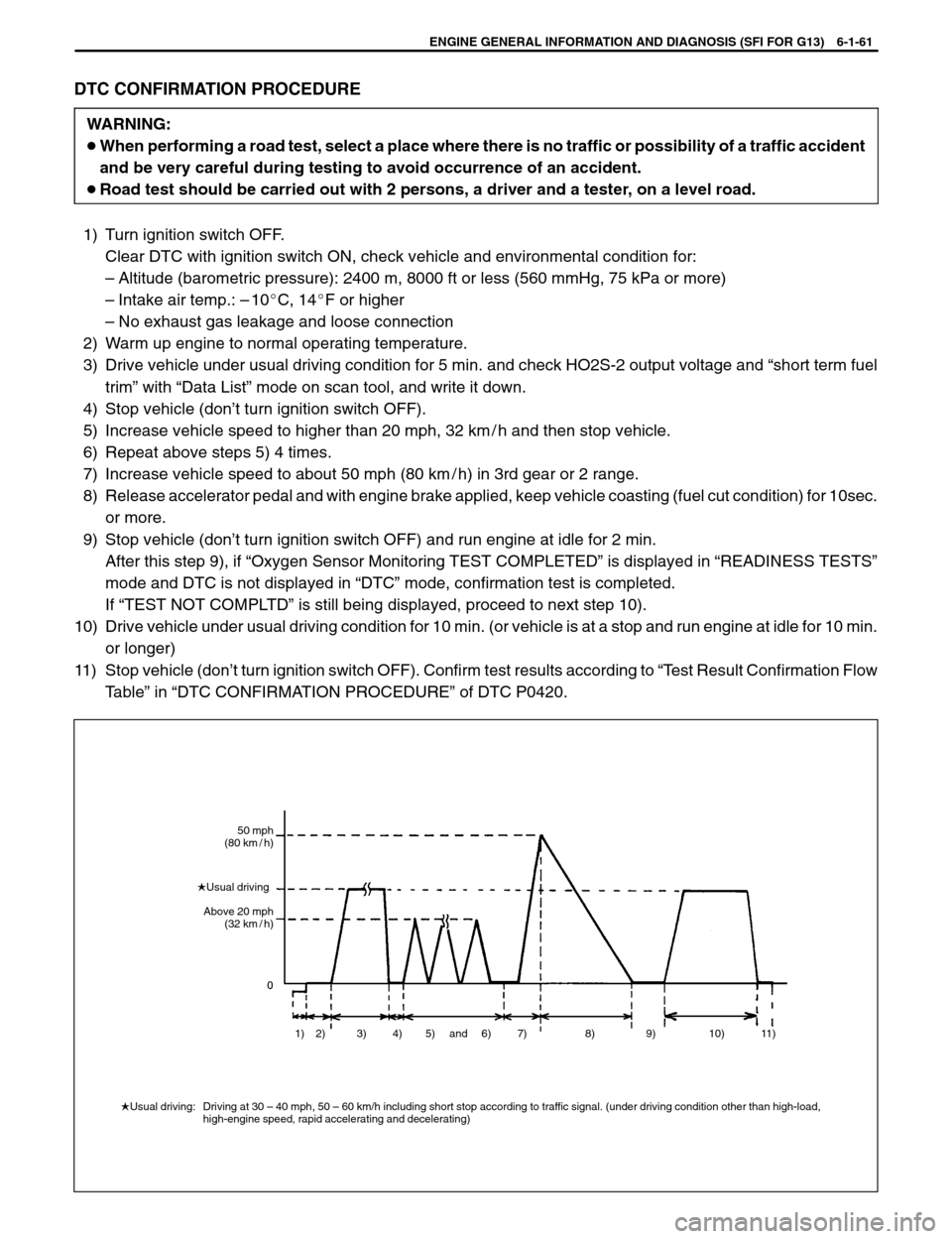
�Usual driving: Driving at 30 – 40 mph, 50 – 60 km/h including short stop according to traffic signal. (under driving condition other than high-load,
high-engine speed, rapid accelerating and decelerating)1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11)and 50 mph
(80 km / h)
Above 20 mph
(32 km / h) �Usual driving
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
WARNING:
�When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident
and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
�Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
Clear DTC with ignition switch ON, check vehicle and environmental condition for:
–Altitude (barometric pressure): 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
–Intake air temp.: –10�C, 14�F or higher
–No exhaust gas leakage and loose connection
2) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
3) Drive vehicle under usual driving condition for 5 min. and check HO2S-2 output voltage and “short term fuel
trim” with “Data List” mode on scan tool, and write it down.
4) Stop vehicle (don’t turn ignition switch OFF).
5) Increase vehicle speed to higher than 20 mph, 32 km / h and then stop vehicle.
6) Repeat above steps 5) 4 times.
7) Increase vehicle speed to about 50 mph (80 km / h) in 3rd gear or 2 range.
8) Release accelerator pedal and with engine brake applied, keep vehicle coasting (fuel cut condition) for 10sec.
or more.
9) Stop vehicle (don’t turn ignition switch OFF) and run engine at idle for 2 min.
After this step 9), if “Oxygen Sensor Monitoring TEST COMPLETED” is displayed in “READINESS TESTS”
mode and DTC is not displayed in “DTC” mode, confirmation test is completed.
If “TEST NOT COMPLTD” is still being displayed, proceed to next step 10).
10) Drive vehicle under usual driving condition for 10 min. (or vehicle is at a stop and run engine at idle for 10 min.
or longer)
11) Stop vehicle (don’t turn ignition switch OFF). Confirm test results according to “Test Result Confirmation Flow
Table” in “DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE” of DTC P0420.
Page 218 of 557
6-1-62 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13)
INSPECTION
STEPACTIONYESNO
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” performed?Go to Step 2.Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2Check exhaust system for leakage, loose
connection and damage.
Is it good condition?Go to Step 3.Repair or replace.
3Check HO2S-2 and Its Circuit.
Was HO2S-2 output voltage indicated on scan
tool in step 3) of DTC confirmation test less
than 1.275 V?Go to Step 4.“G” or “R” circuit open or
HO2S-2 malfunction.
4Check Short Term Fuel Trim.
Did short term fuel trim very within –20 – + 20%
range in step 3) of DTC confirmation test?Check “R” and “G” wire
for open and short, and
connection for poor
connection. If wire and
connection are OK,
replace HO2S-2.Check fuel system. Go
to DTC P0171 / P0172
Diag. Flow Table.
Page 221 of 557
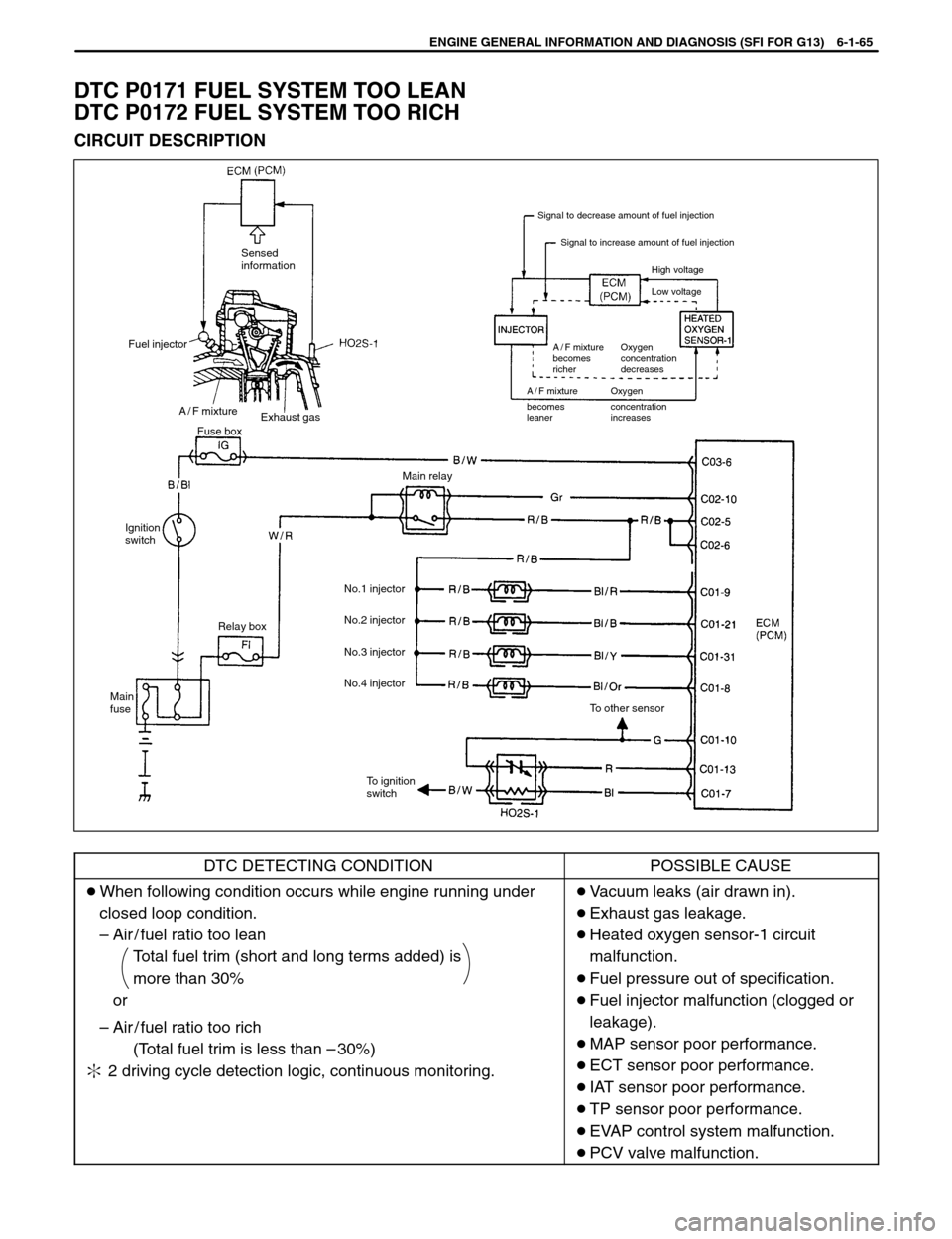
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13) 6-1-65
Ignition
switch
Main
fuseMain relay
To ignition
switchTo other sensor Relay boxNo.1 injector
No.2 injector
No.3 injector
No.4 injector Fuse box
Signal to decrease amount of fuel injection
Signal to increase amount of fuel injection
High voltage
Low voltage
A / F mixture
becomes
richerOxygen
concentration
decreases
A / F mixture Oxygen
Fuel injectorSensed
information
A / F mixture
Exhaust gas
becomes
leanerconcentration
increases
DTC P0171 FUEL SYSTEM TOO LEAN
DTC P0172 FUEL SYSTEM TOO RICH
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC DETECTING CONDITIONPOSSIBLE CAUSE
�When following condition occurs while engine running under
closed loop condition.
–Air / fuel ratio too lean
Total fuel trim (short and long terms added) is
more than 30%
or
–Air / fuel ratio too rich
(Total fuel trim is less than –30%)
�2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitoring.�Vacuum leaks (air drawn in).
�Exhaust gas leakage.
�Heated oxygen sensor-1 circuit
malfunction.
�Fuel pressure out of specification.
�Fuel injector malfunction (clogged or
leakage).
�MAP sensor poor performance.
�ECT sensor poor performance.
�IAT sensor poor performance.
�TP sensor poor performance.
�EVAP control system malfunction.
�PCV valve malfunction.