2000 DODGE NEON length
[x] Cancel search: lengthPage 407 of 1285
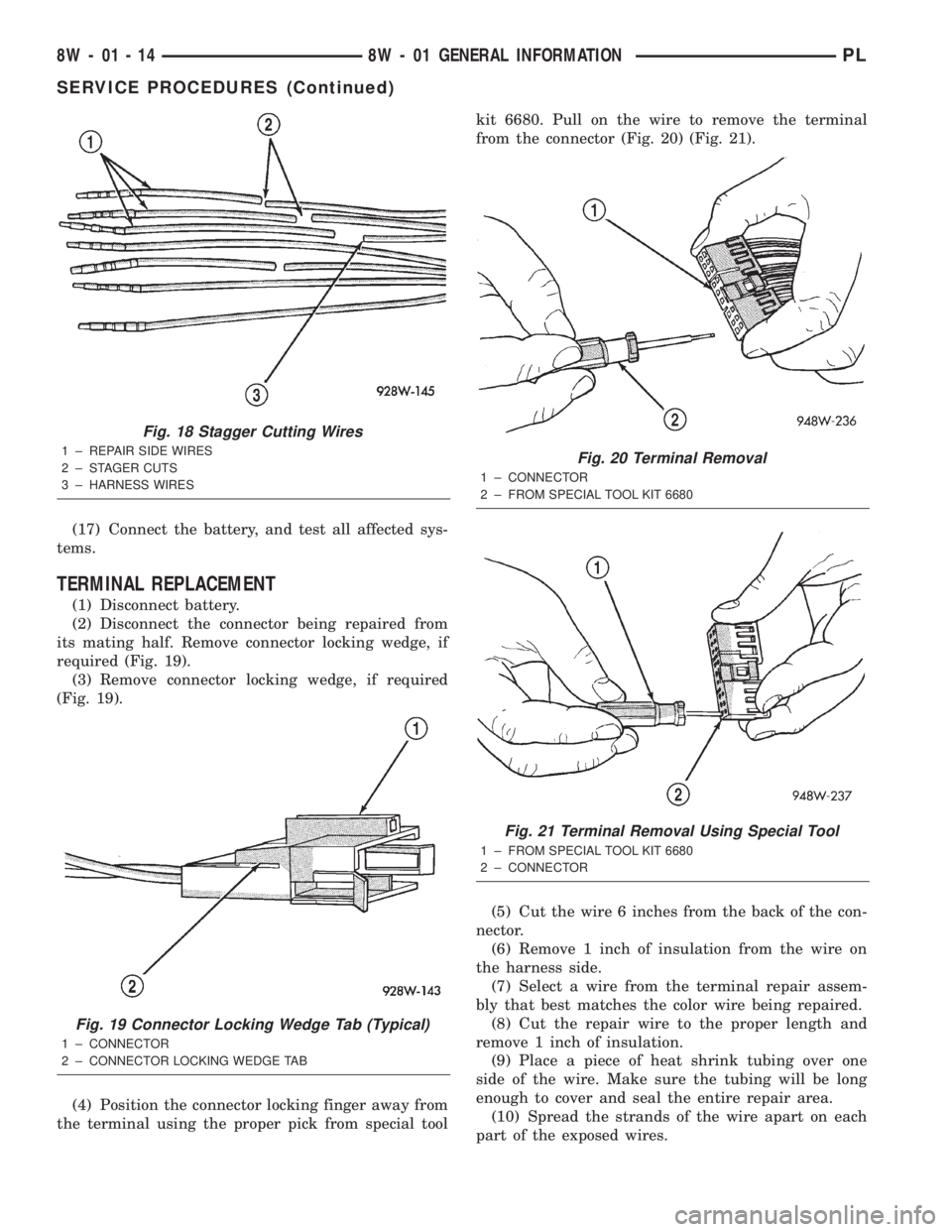
(17) Connect the battery, and test all affected sys-
tems.
TERMINAL REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect battery.
(2) Disconnect the connector being repaired from
its mating half. Remove connector locking wedge, if
required (Fig. 19).
(3) Remove connector locking wedge, if required
(Fig. 19).
(4) Position the connector locking finger away from
the terminal using the proper pick from special toolkit 6680. Pull on the wire to remove the terminal
from the connector (Fig. 20) (Fig. 21).
(5) Cut the wire 6 inches from the back of the con-
nector.
(6) Remove 1 inch of insulation from the wire on
the harness side.
(7) Select a wire from the terminal repair assem-
bly that best matches the color wire being repaired.
(8) Cut the repair wire to the proper length and
remove 1 inch of insulation.
(9) Place a piece of heat shrink tubing over one
side of the wire. Make sure the tubing will be long
enough to cover and seal the entire repair area.
(10) Spread the strands of the wire apart on each
part of the exposed wires.
Fig. 18 Stagger Cutting Wires
1 ± REPAIR SIDE WIRES
2 ± STAGER CUTS
3 ± HARNESS WIRES
Fig. 19 Connector Locking Wedge Tab (Typical)
1 ± CONNECTOR
2 ± CONNECTOR LOCKING WEDGE TAB
Fig. 20 Terminal Removal
1 ± CONNECTOR
2 ± FROM SPECIAL TOOL KIT 6680
Fig. 21 Terminal Removal Using Special Tool
1 ± FROM SPECIAL TOOL KIT 6680
2 ± CONNECTOR
8W - 01 - 14 8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATIONPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 740 of 1285
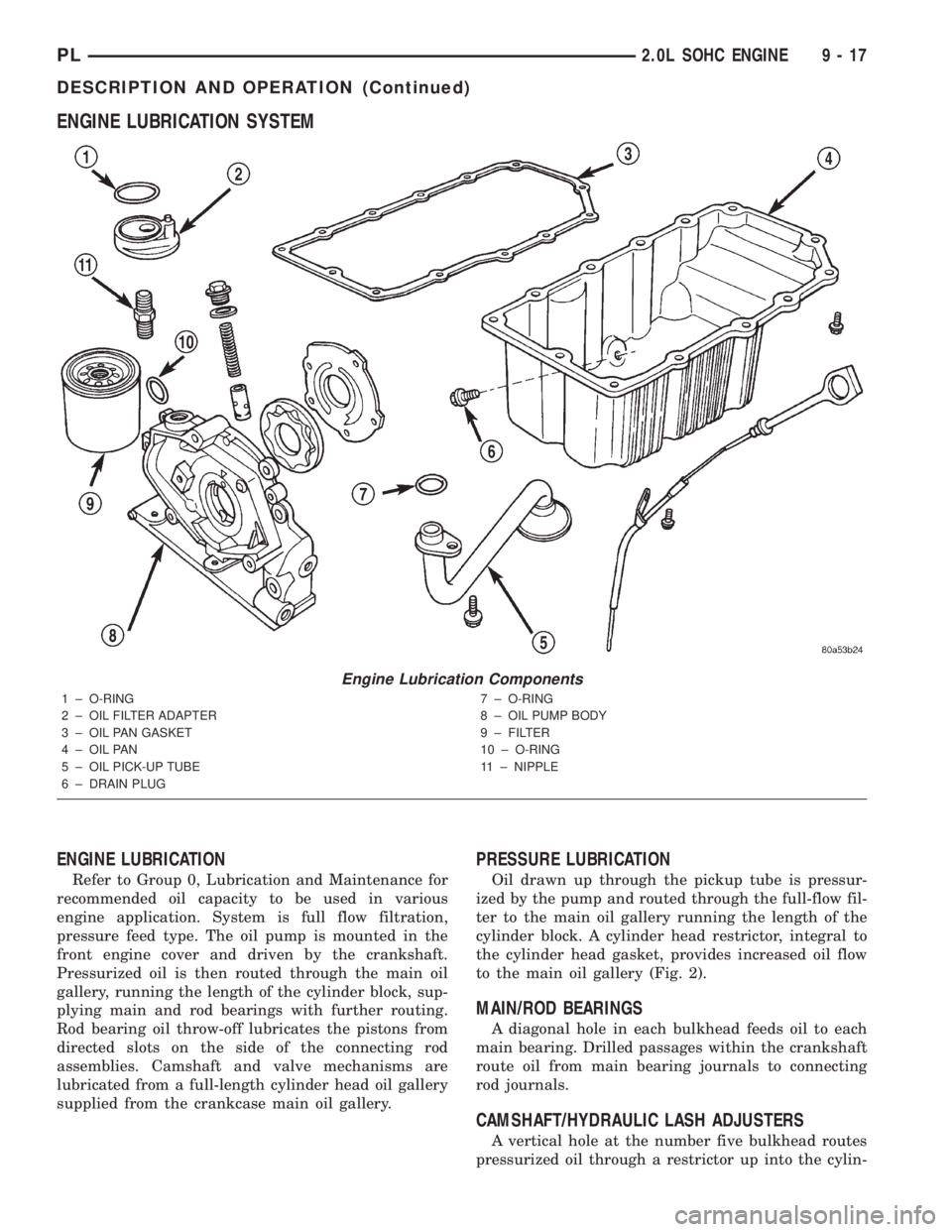
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM
ENGINE LUBRICATION
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
recommended oil capacity to be used in various
engine application. System is full flow filtration,
pressure feed type. The oil pump is mounted in the
front engine cover and driven by the crankshaft.
Pressurized oil is then routed through the main oil
gallery, running the length of the cylinder block, sup-
plying main and rod bearings with further routing.
Rod bearing oil throw-off lubricates the pistons from
directed slots on the side of the connecting rod
assemblies. Camshaft and valve mechanisms are
lubricated from a full-length cylinder head oil gallery
supplied from the crankcase main oil gallery.
PRESSURE LUBRICATION
Oil drawn up through the pickup tube is pressur-
ized by the pump and routed through the full-flow fil-
ter to the main oil gallery running the length of the
cylinder block. A cylinder head restrictor, integral to
the cylinder head gasket, provides increased oil flow
to the main oil gallery (Fig. 2).
MAIN/ROD BEARINGS
A diagonal hole in each bulkhead feeds oil to each
main bearing. Drilled passages within the crankshaft
route oil from main bearing journals to connecting
rod journals.
CAMSHAFT/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTERS
A vertical hole at the number five bulkhead routes
pressurized oil through a restrictor up into the cylin-
Engine Lubrication Components
1 ± O-RING
2 ± OIL FILTER ADAPTER
3 ± OIL PAN GASKET
4 ± OIL PAN
5 ± OIL PICK-UP TUBE
6 ± DRAIN PLUG7 ± O-RING
8 ± OIL PUMP BODY
9 ± FILTER
10 ± O-RING
11 ± NIPPLE
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 17
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 783 of 1285

(10) Install connecting rod lower bearing half and
cap. InstallNewbolts and tighten to 27 N´m (20 ft.
lbs.) plus 1/4 turn.
(11) Install cylinder head and oil pan. Refer to pro-
cedures in this section.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
OIL PUMP
(1) To remove the relief valve, proceed as follows:
(2) Remove the threaded plug and gasket from the
oil pump (Fig. 116).
CAUTION: Oil pump pressure relief valve must be
installed as shown in (Fig. 116) or serious damage
may occur.
(3) Remove spring and relief valve (Fig. 116).
(4) Remove oil pump cover screws, and lift off
cover.
(5) Remove pump rotors.
(6) Wash all parts in a suitable solvent and inspect
carefully for damage or wear (Fig. 117).
VALVE SERVICE WITH THE CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVED
REMOVAL
(1) With cylinder head removed, compress valve
springs using Special Tool C-3422-B with Adaptor
6526.(2) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(3) Before removing valves,remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent dam-
age to the valve guides.Identify valves to insure
installation in original location.
VALVE INSPECTION
(1) Clean valves thoroughly and discard burned,
warped and cracked valves.
(2) Measure valve stems for wear. Measure stem
about 60 mm beneath the valve lock grooves.
(3) If valve stems are worn more than 0.05 mm
(0.002 in.), replace valve.
VALVE GUIDES
(1) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(2) Using a small hole gauge and a micrometer,
measure valve guides in 3 places top, middle and bot-
tom (Fig. 118). Replace guides if they are not within
specification. For specifications, refer to Engine Spec-
ifications in this section.
(3) Check valve guide height (Fig. 119).
TESTING VALVE SPRINGS
(1) Whenever valves have been removed for inspec-
tion, reconditioning or replacement, valve springs
should be tested Special Tool C-647. As an example,
the compression length of the spring to be tested is
33.34 mm (1-5/16 in.). Turn tool table until surface is
in line with the 33.34 mm (1-5/16 in.) mark on the
threaded stud and the zero mark on the front. Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device (Fig. 120). Pull on torque
Fig. 116 Oil Pressure Relief Valve
1 ± RETAINER CAP
2 ± GASKET
3 ± OIL PUMP BODY
4 ± RELIEF VALVE
5 ± SPRING
Fig. 117 Oil Pump
1 ± OIL PUMP BODY
2 ± OIL PUMP COVER
3 ± OUTER ROTOR
4 ± INNER ROTOR
9 - 60 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 784 of 1285
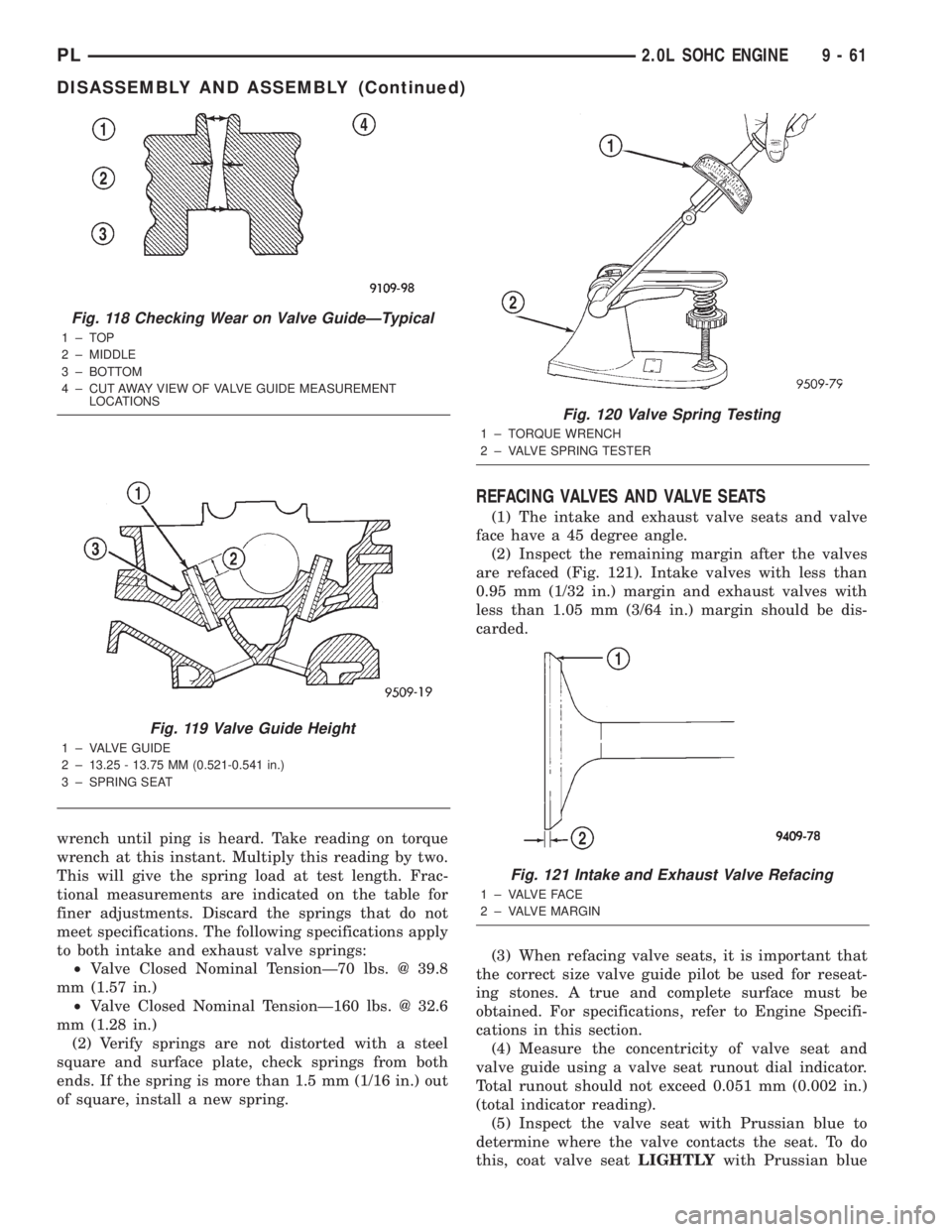
wrench until ping is heard. Take reading on torque
wrench at this instant. Multiply this reading by two.
This will give the spring load at test length. Frac-
tional measurements are indicated on the table for
finer adjustments. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications. The following specifications apply
to both intake and exhaust valve springs:
²Valve Closed Nominal TensionÐ70 lbs. @ 39.8
mm (1.57 in.)
²Valve Closed Nominal TensionÐ160 lbs. @ 32.6
mm (1.28 in.)
(2) Verify springs are not distorted with a steel
square and surface plate, check springs from both
ends. If the spring is more than 1.5 mm (1/16 in.) out
of square, install a new spring.
REFACING VALVES AND VALVE SEATS
(1) The intake and exhaust valve seats and valve
face have a 45 degree angle.
(2) Inspect the remaining margin after the valves
are refaced (Fig. 121). Intake valves with less than
0.95 mm (1/32 in.) margin and exhaust valves with
less than 1.05 mm (3/64 in.) margin should be dis-
carded.
(3) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be
obtained. For specifications, refer to Engine Specifi-
cations in this section.
(4) Measure the concentricity of valve seat and
valve guide using a valve seat runout dial indicator.
Total runout should not exceed 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
(total indicator reading).
(5) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seatLIGHTLYwith Prussian blue
Fig. 118 Checking Wear on Valve GuideÐTypical
1±TOP
2 ± MIDDLE
3 ± BOTTOM
4 ± CUT AWAY VIEW OF VALVE GUIDE MEASUREMENT
LOCATIONS
Fig. 119 Valve Guide Height
1 ± VALVE GUIDE
2 ± 13.25 - 13.75 MM (0.521-0.541 in.)
3 ± SPRING SEAT
Fig. 120 Valve Spring Testing
1 ± TORQUE WRENCH
2 ± VALVE SPRING TESTER
Fig. 121 Intake and Exhaust Valve Refacing
1 ± VALVE FACE
2 ± VALVE MARGIN
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 61
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 786 of 1285

a 0.762 mm (0.030 in.) spacer under the valve spring
seat to bring spring height back within specification.
(5) Install rocker arm shafts as previously
described in this section.
(6) Checking dry lash. Dry lash is the amount of
clearance that exists between the base circle of an
installed cam and the rocker arm roller when the
adjuster is drained of oil and completely collapsed.
Specified dry lash is 1.17 mm (0.046 in.) for intake
and 1.28 mm (0.050 in.) for exhaust. After performing
dry lash check, refill adjuster with oil and allow 10
minutes for adjuster(s) to bleed down before rotating
cam.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
INTAKE MANIFOLD
CLEAN AND INSPECT
Check for:
²Inspect manifold for cracks or distortions.
²Check for torn or missing O-rings at the mating
surface of the manifold (Fig. 125).
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
CLEAN AND INSPECT
(1) Discard gasket and clean all gasket surfaces of
manifolds and cylinder head.
(2) Test manifold gasket surfaces for flatness with
straight edge. Surface must be flat within 0.15 mm
per 300 mm (.006 in. per foot) of manifold length.
(3) Inspect manifolds for cracks or distortion.
Replace manifold if necessary.
CYLINDER HEAD AND CAMSHAFT JOURNALS
CLEANING
Remove all gasket material from cylinder head. Be
careful not to gouge or scratch the aluminum head
sealing surface. Clean all engine oil passages.
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
Neveruse the following to clean aluminum gasket
surfaces:
²Metal scraper
²Abrasive pad or paper to clean cylinder block
and head
²High speed power tool with an abrasive pad or a
wire brush (Fig. 126)
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets
require a scratch free sealing surface.
Only use the following for cleaning gasket surfaces:
²Solvent or a commercially available gasket
remover
²Plastic or wood scraper (Fig. 126)
²Drill motor with 3M RolocyBristle Disc (white
or yellow) (Fig. 126)
CAUTION: Excessive pressure or high RPM can
damage the sealing surfaces. The mild (white, 120
grit) bristle disc is recommended. If necessary, the
medium (yellow, 80 grit) bristle disc may be used
on cast iron surfaces with care.
Fig. 125 Intake Manifold O-Rings
1 ± INTAKE MANIFOLD O-RING GASKETS
Fig. 126 Proper Tool Usage For Surface Preparation
1 ± ABRASIVE PAD
2 ± 3M ROLOCYBRISTLE DISC
3 ± PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 63
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 788 of 1285

mm (0.015 inch.) or more, replace housing only if
outer rotor is in specification.
(6) Install inner rotor into pump housing. If clear-
ance between inner and outer rotors (Fig. 132) is
0.203 mm (0.008 inch) or more, replace both rotors.(7) Place a straightedge across the face of the
pump housing, between bolt holes. If a feeler gauge
of 0.102 mm (0.004 inch) or more can be inserted
between rotors and the straightedge, replace pump
assembly (Fig. 133).ONLYif rotors are in specs.
(8) Inspect oil pressure relief valve plunger for
scoring and free operation in its bore. Small marks
may be removed with 400-grit wet or dry sandpaper.
(9) The relief valve spring has a free length of
approximately 60.7 mm (2.39 inches) it should test
between 18 and 19 pounds when compressed to 40.5
mm (1.60 inches). Replace spring that fails to meet
specifications.
(10) If oil pressure is low and pump is within spec-
ifications, inspect for worn engine bearings, damaged
or missing oil pick-up tube O-ring, clogged oil pick-up
tube screen, clogged oil filter and stuck open pres-
sure relief valve or other reasons for oil pressure
loss.
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BORE
(1) Clean cylinder block thoroughly and check all
core hole plugs for evidence of leaking.
(2) If new core plugs are installed, refer to Engine
Core Plugs in this section.
(3) Examine block and cylinder bores for cracks or
fractures.
Fig. 131 Measuring Outer Rotor Clearance in
Housing
1 ± FEELER GAUGE
2 ± OUTER ROTOR
Fig. 132 Measuring Clearance Between Rotors
1 ± FEELER GAUGE
2 ± INNER ROTOR
3 ± OUTER ROTOR
Fig. 133 Measuring Clearance Over Rotors
1 ± FEELER GAUGE
2 ± STRAIGHT EDGE
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 65
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 791 of 1285

SPECIFICATIONS
2.0L SOHC ENGINE
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
General Specification
Type In-Line OHV, SOHC
Number of Cylinders 4
Displacement 2.0 Liters
(122 cu. in.)
Bore 87.5 mm
(3.445 in.)
Stroke 83.0 mm
(3.268 in.)
Compression Ratio 9.8:1
Firing Order 1-3-4-2
Compression Pressure 1172±1551 kPa
(170±225 psi)
Max. Variation Between
Cylinders25%
Cylinder Block
Cylinder Bore Diameter 87.4924±87.5076 mm
(3.4446±3.4452 in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.) 0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)
Taper (Max.) 0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)
Pistons (Federal Emission)
Piston Diameter 87.463±87.481 mm
(3.4434±3.4441 in.)
Clearance 17.5 mm
(11/16 in.) from bottom of
skirt0.012±0.044 mm
(0.0004±0.0017 in.)
Weight 325±335 grams
(11.47±11.82 oz.)
Land Clearance
(Diametrical)0.734±0.797 mm
(0.029±0.031 in.)
Piston Length 64 mm
(2.520 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 13.989±4.188 mm
(0.157±0.165 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 24.462±4.661 mm
(0.176±0.184 in.)
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 33.847±4.131 mm
(0.151±0.163 in.)
Pistons (Low Emission VehicleÐLEV/ULEV)
Piston Diameter 87.456±87.474 mm
(3.4432±3.4439 in.)
Clearance 10.42 mm
(0.42 in.) from bottom of
skirt0.018±0.50 mm
(0.0008±0.0020 in.)
Weight 320±329 grams
(11.29±11.60 oz.)
Land Clearance
(Diametrical)0.758±0.790 mm
(0.0299±0.0312 in.)
Piston Length 55.8 mm
(2.197 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 13.989±4.188 mm
(0.157±0.165 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 24.462±4.661 mm
(0.176±0.184 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 33.847±4.131 mm
(0.151±0.163 in.)
Piston Pins
Clearance in Piston 0.008±0.015 mm
(0.0003±0.0006 in.)
Clearance in Connecting
RodInterference
Diameter 21.000±21.003 mm
(0.8268±0.8269 in.)
End Play None
Length 74.75±75.25 mm
(2.943±2.963 in.)
Piston Rings
Ring GapÐTop
Compression Ring0.23±0.52 mm
(0.009±0.020 in.)
Wear Limit 0.8 mm
(0.031 in.)
Ring GapÐ2nd
Compression Ring0.49±0.78 mm
(0.019±0.031 in.)
Wear Limit 1.0 mm
(0.039 in.)
Ring GapÐOil Control
Steel Rails0.23±0.66 mm
(0.009±0.026 in.)
9 - 68 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
Page 793 of 1285

DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
No. 3 41.928±41.947 mm
(1.650±1.651 in.)
No. 4 42.328±42.374 mm
(1.666±1.668 in.)
No. 5 42.728±42.747 mm
(1.682±1.6829 in.)
Bearing ClearanceÐ
Diametrical0.053±0.093 mm
(0.0027±0.003 in.)
Bearing Clearance (Max.
allowable)0.12 mm
(0.0047 in.)
End Play 0.05±0.39 mm
(0.002±0.015 in.)
Lift (Zero Lash)
Intake 7.2 mm
(0.283 in.)
Exhaust 7.03 mm
(0.277 in.)
Exhaust Valve Timing*
Closes (ATDC) 5.4É
Opens (BBDC) 43.7É
Duration 229.1É
Intake Valve Timing*
Closes (ABDC) 41.1É
Opens (ATDC) 13.9É
Duration 207.2É
Valve Overlap 84.8É
*All readings in crankshaft degrees, at 0.5 mm (0.019
in.) of valve lift.
Cylinder Head
Material Cast Aluminum
Gasket Thickness
(Compressed)1.15 mm
(0.045 in.)
Valve Seat
Angle 45É
Seat DiameterÐIntake 33 mm
(1.299 in.)
Seat DiameterÐExhaust 28 mm
(1.102 in.)
Runout (Max.) 0.05 mm
(0.002 in.)
Valve Seat WidthÐIntake
and Exhaust0.9±1.3 mm
(0.035±0.051 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Service LimitÐIntake 2.0 mm
(0.079 in.)
Service LimitÐExhaust 2.5 mm
(0.098 in.)
Valve Guide
Diameter I. D. 5.975±6.000 mm
(0.235±0.236 in.)
Guide Bore Diameter
(Std.)11.0±11.02 mm
(0.4330±0.4338 in.)
Guide Height (spring seat
to guide tip)13.25±13.75 mm
(0.521±0.541 in.)
Valves
Face Angle Intake and
Exhaust45±45.5É
Head DiameterÐIntake 32.12±33.37 mm
(1.303±1.313 in.)
Head DiameterÐExhaust 28.57±28.83 mm
(1.124±1.135 in.)
Valve Margin
Intake 1.15±1.48 mm
(0.0452±0.0583 in.)
Service Limit 0.95 mm
(1/32 in.)
Exhaust 1.475±1.805 mm
(0.058±0.071 in.)
Service Limit 1.05 mm
(3/64 in.)
Valve Length (Overall)
Intake 114.69±115.19 mm
(4.515±4.535 in.)
Exhaust 116.94±117.44 mm
(4.603±4.623 in.)
Valve Stem Tip Height
Intake 45.01±46.07 mm
(1.77±1.81 in.)
Exhaust 43.51±44.57 mm
(1.71±1.75 in.)
Valve Stem Diameter
Intake 5.934±5.952 mm
(0.2337±0.2344 in.)
9 - 70 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)