2000 DODGE NEON fuse
[x] Cancel search: fusePage 654 of 1285
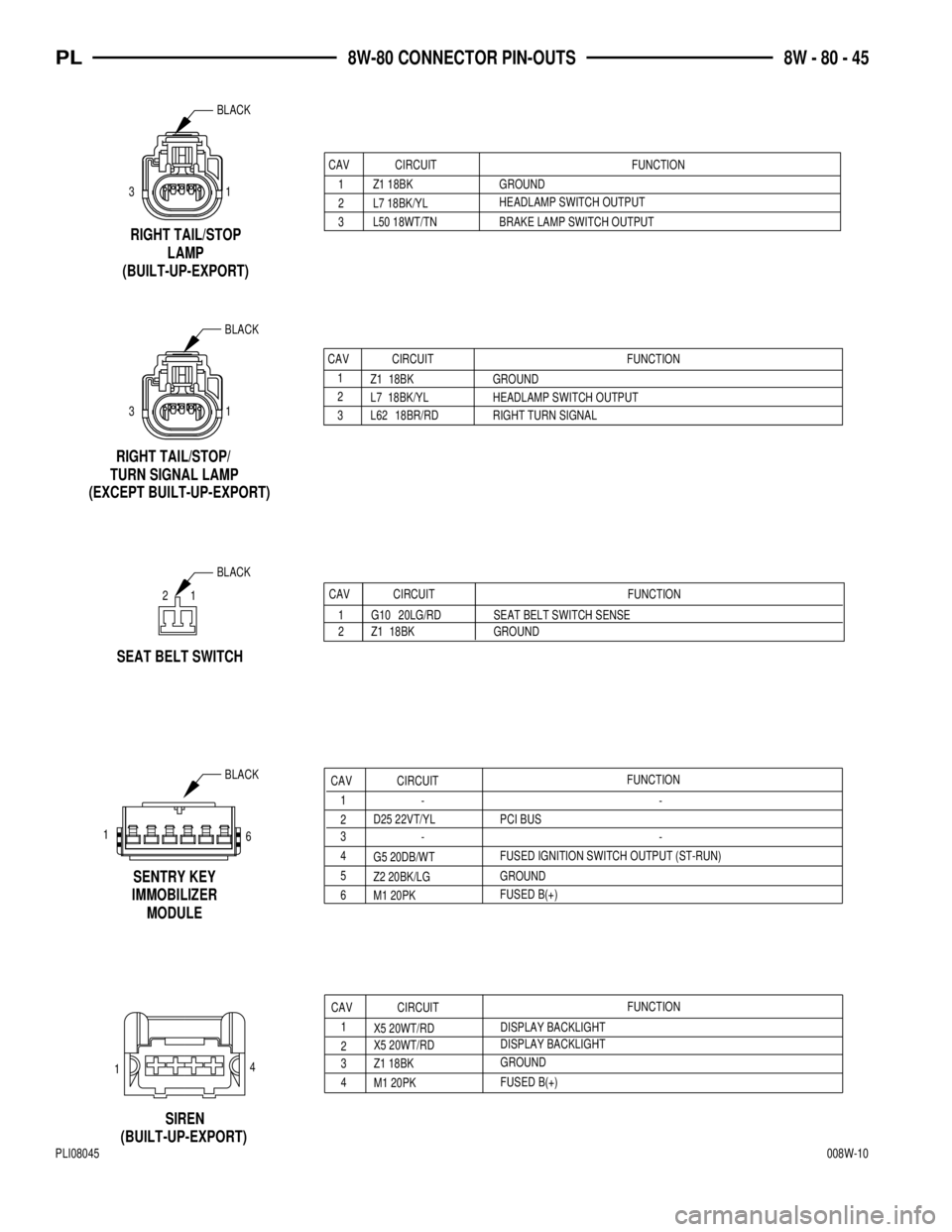
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1
Z1 18BK GROUND
2
L7 18BK/YL HEADLAMP SWITCH OUTPUT
3 L62 18BR/RD RIGHT TURN SIGNAL
RIGHT TAIL/STOP/
TURN SIGNAL LAMP
SEAT BELT SWITCH
1 2
BLACK
SEAT BELT SWITCH SENSE 20LG/RD G10 1
GROUND 18BK Z1 2
FUNCTION CIRCUIT CAV
(EXCEPT BUILT-UP-EXPORT)
M1 20PKFUSED B(+) GROUND
Z1 18BK X5 20WT/RDDISPLAY BACKLIGHT
4
1
SIREN
DISPLAY BACKLIGHT
X5 20WT/RDFUNCTION
CAV CIRCUIT
1
2
4 3
MODULE IMMOBILIZER
- -- -
FUSED B(+)
M1 20PKGROUND
Z2 20BK/LGFUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (ST-RUN)
G5 20DB/WTPCI BUS D25 22VT/YL1
6
SENTRY KEY
FUNCTION
CAV CIRCUIT
1
2
4 3
6 5
RIGHT TAIL/STOP
LAMP
(BUILT-UP-EXPORT)
1 3
HEADLAMP SWITCH OUTPUTGROUND Z1 18BK
3
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1
L50 18WT/TN BRAKE LAMP SWITCH OUTPUT 2 L7 18BK/YL
(BUILT-UP-EXPORT)
31
BLACK
BLACK
BLACK
PL8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTS 8W - 80 - 45
PLI08045008W-10
Page 655 of 1285
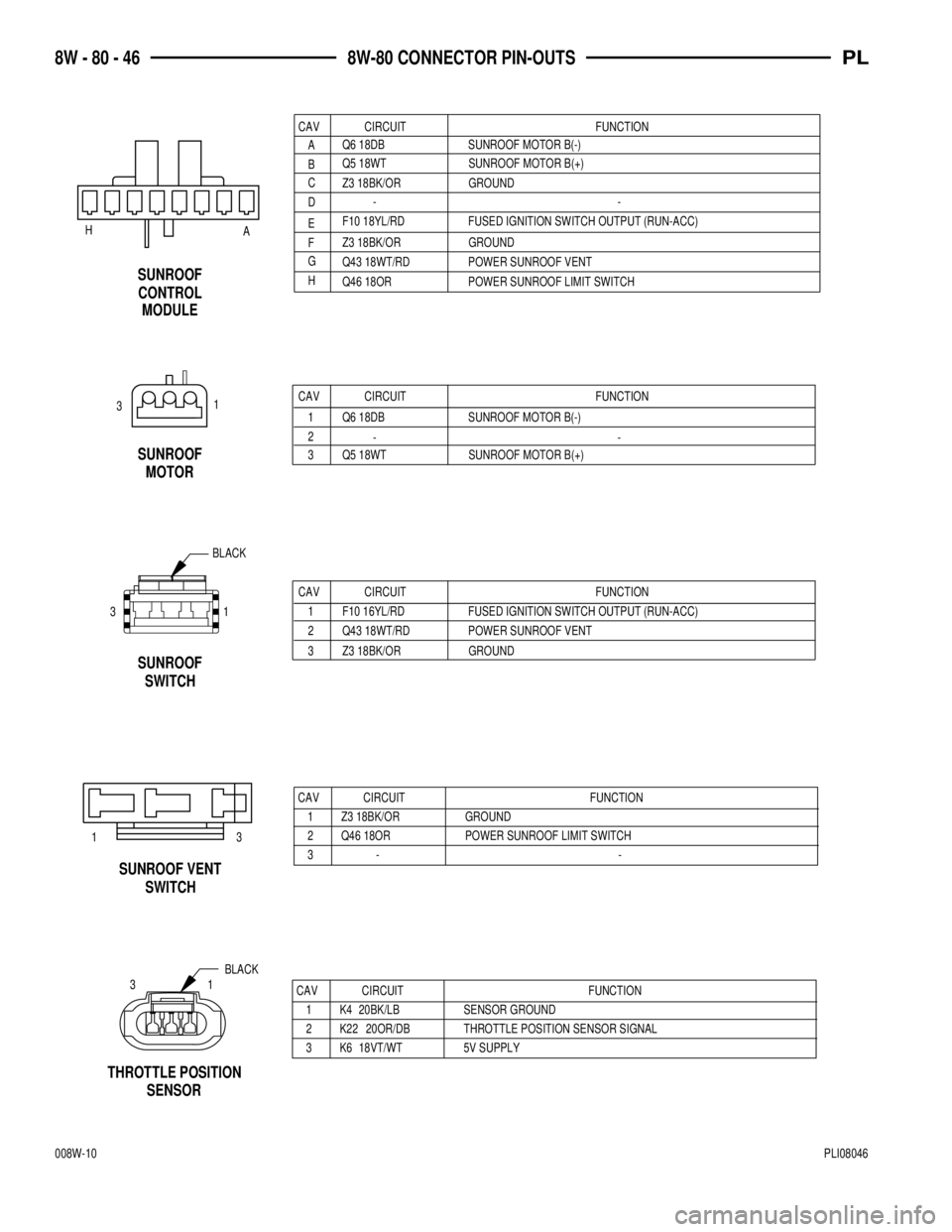
1 F10 16YL/RD FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN-ACC)
SWITCH SUNROOF
POWER SUNROOF VENT Q43 18WT/RD 2
GROUND Z3 18BK/OR 3
FUNCTION CIRCUIT CAV
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
3 Q5 18WT SUNROOF MOTOR B(+)
1 Q6 18DB SUNROOF MOTOR B(-)
SUNROOF
MOTOR
CIRCUIT CAV FUNCTION
A
Q5 18WT SUNROOF MOTOR B(+)
BQ6 18DB SUNROOF MOTOR B(-)
Z3 18BK/OR GROUND
F10 18YL/RD FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN-ACC)
Z3 18BK/OR GROUND
Q43 18WT/RD POWER SUNROOF VENT
Q46 18OR POWER SUNROOF LIMIT SWITCH D C
H G F E--
SUNROOF
CONTROL
MODULE
A H
31
BLACK
3
1
SWITCH SUNROOF VENT
-
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 Z3 18BK/OR GROUND
2 Q46 18OR POWER SUNROOF LIMIT SWITCH
3-132
--
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 K4 20BK/LB SENSOR GROUND
2 K22 20OR/DB THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR SIGNAL
3 K6 18VT/WT 5V SUPPLY
BLACK
31
THROTTLE POSITION
SENSOR
8W - 80 - 46 8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTSPL
008W-10PLI08046
Page 656 of 1285
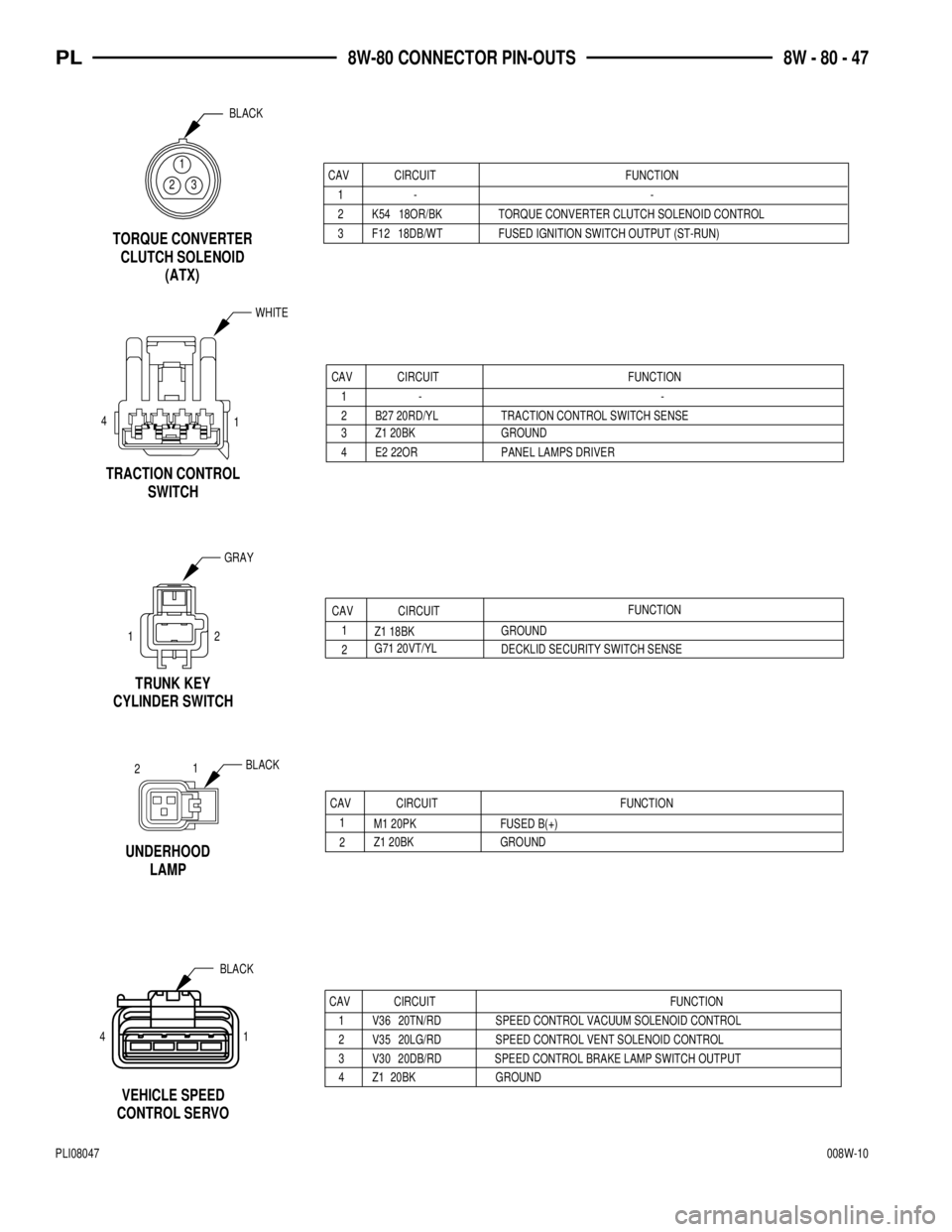
Z1 20BK
2 CAV
1CIRCUIT
GROUNDFUNCTION
M1 20PK FUSED B(+)
UNDERHOOD
LAMP
CONTROL SERVOVEHICLE SPEED
41BLACK
GROUND 20BK Z1 4SPEED CONTROL BRAKE LAMP SWITCH OUTPUT 20DB/RD V30 3
SPEED CONTROL VENT SOLENOID CONTROL 20LG/RD V35 2
SPEED CONTROL VACUUM SOLENOID CONTROL 20TN/RD V36 1
FUNCTION CIRCUIT CAV
21
3 Z1 20BK GROUND
4 E2 22OR PANEL LAMPS DRIVER 4
1
SWITCH TRACTION CONTROL
TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH SENSE B27 20RD/YL 2- 1
FUNCTION CIRCUIT CAV
-
2
1
DECKLID SECURITY SWITCH SENSE G71 20VT/YL
GROUND
Z1 18BKFUNCTION
CAV CIRCUIT
1
2
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1- -
2 K54 18OR/BK TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID CONTROL
3 F12 18DB/WT FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (ST-RUN)
BLACK
1
23
TORQUE CONVERTER
CLUTCH SOLENOID
(ATX)
TRUNK KEY
CYLINDER SWITCH
BLACK
GRAY
WHITE
PL8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTS 8W - 80 - 47
PLI08047008W-10
Page 657 of 1285
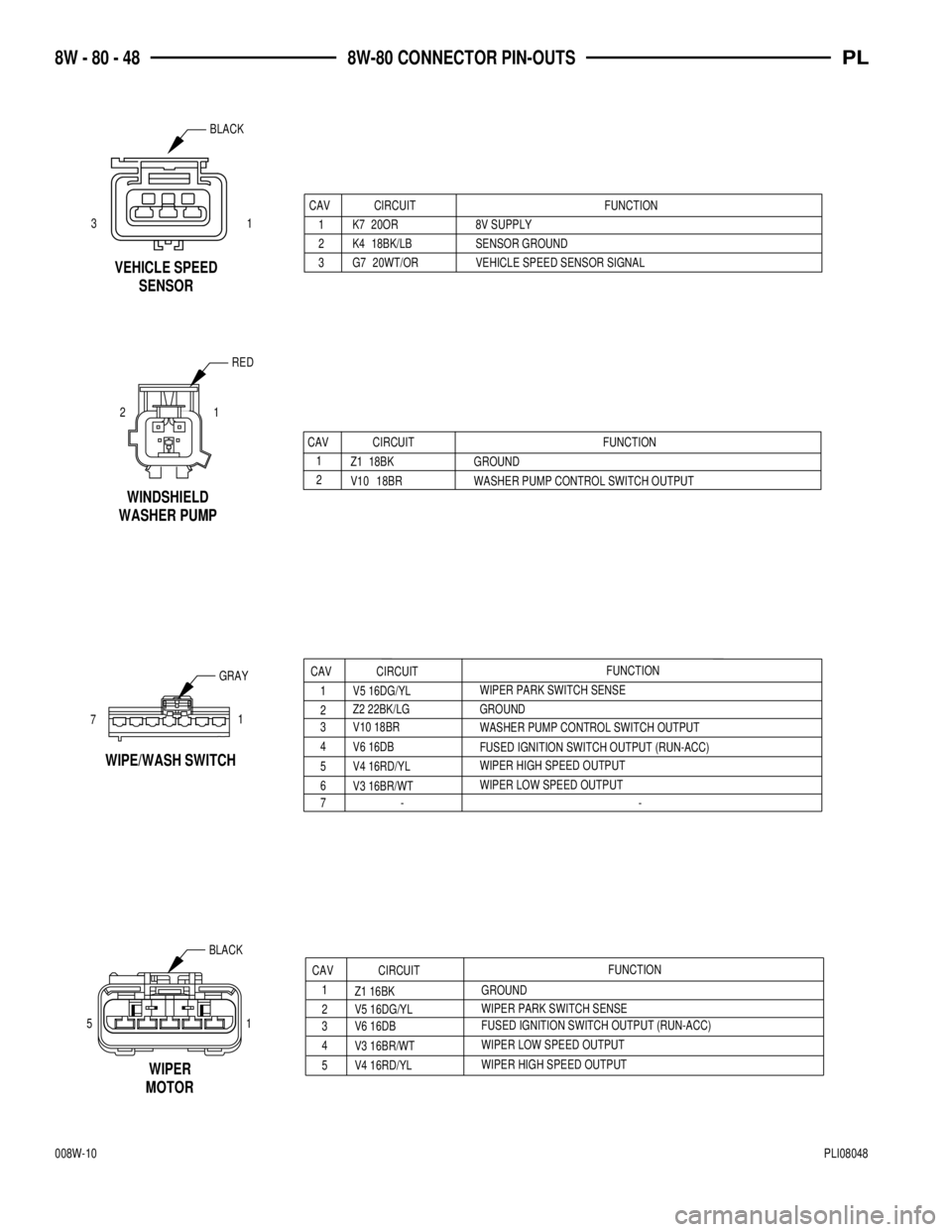
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1
V10 18BR WASHER PUMP CONTROL SWITCH OUTPUT 2Z1 18BK GROUND
WINDSHIELD
WASHER PUMP
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 K7 20OR 8V SUPPLY
2 K4 18BK/LB SENSOR GROUND
3 G7 20WT/OR VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR SIGNAL
VEHICLE SPEED
SENSOR
1 2
RED
WIPER HIGH SPEED OUTPUT
V4 16RD/YLWIPER LOW SPEED OUTPUT
V3 16BR/WTFUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN-ACC)
V6 16DBWIPER PARK SWITCH SENSE
V5 16DG/YL
51
MOTORWIPER
GROUND
Z1 16BKFUNCTION
CAV CIRCUIT
1
2
4 3
5
- FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN-ACC)
WIPER HIGH SPEED OUTPUT
WIPER LOW SPEED OUTPUT V6 16DB
V3 16BR/WT Z2 22BK/LG V5 16DG/YL
GROUND WIPER PARK SWITCH SENSEFUNCTION- V4 16RD/YL 71
CAV CIRCUIT
1
2
4 3
7 6 5
WIPE/WASH SWITCH
V10 18BR
WASHER PUMP CONTROL SWITCH OUTPUT
BLACK
31
GRAY
BLACK
8W - 80 - 48 8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTSPL
008W-10PLI08048
Page 833 of 1285

REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY
The relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) (Fig. 12). The PDC is located next to the
battery in the engine compartment. For the location
of the relay within the PDC, refer to the PDC cover
for location. Check electrical terminals for corrosion
and repair as necessary.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC. The
inside top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay
and fuse location.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
REMOVAL
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VENTILATED AREAS
AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES. NEVER SMOKE
WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE.
(1) Drain the fuel. Refer to Draining Fuel Tank in
the Fuel Tank section of this group.
WARNING: THE FUEL RESERVOIR OF THE FUEL
PUMP MODULE DOES NOT EMPTY OUT WHEN THE
TANK IS DRAINED. THE FUEL IN THE RESERVOIR
WILL SPILL OUT WHEN THE MODULE IS
REMOVED.
(2) Remove fuel tank, refer to the Fuel Tank
removal/installation section.
(3) Lower tank.(4) Use Special Tool 6856 to remove fuel pump
module locknut (Fig. 15).
(5) Remove fuel pump and O-ring seal from tank.
Discard old seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Wipe seal area of tank clean and place a new
seal in position in the tank opening.
(2) Position fuel pump in the tank. Make sure the
alignment tab on the underside of the fuel pump
module flange sits in the notch on the fuel tank (Fig.
14).
(3) Position the locknut over the fuel pump mod-
ule.
Fig. 12 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
Fig. 13 Fuel Pump Module Removal
1 ± FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 ± FUEL LINE
3 ± LOCKNUT
Fig. 14 Alignment Tab
14 - 12 FUEL SYSTEMPL
Page 845 of 1285

²All inputs monitored for proper voltage range.
²All monitored components (refer to the Emission
section for On-Board Diagnostics).
The PCM compares the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensor inputs to measure catalytic
convertor efficiency. If the catalyst efficiency drops
below the minimum acceptable percentage, the PCM
stores a diagnostic trouble code in memory.
During certain idle conditions, the PCM may enter
a variable idle speed strategy. During variable idle
speed strategy the PCM adjusts engine speed based
on the following inputs.
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Battery temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine run time
²Power steering pressure switch
²Vehicle mileage
ACCELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in Throttle Position sensor
output voltage or MAP sensor output voltage as a
demand for increased engine output and vehicle
acceleration. The PCM increases injector pulse width
in response to increased fuel demand.
DECELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²A/C pressure transducer
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Exhaust gas oxygen content (upstream heated
oxygen sensor)
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Power steering pressure switch
²Throttle position
²IAC motor control changes in response to MAP
sensor feedback.
The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) when it senses an
abrupt decrease in manifold pressure. This indicates
a hard deceleration. In response, the PCM may
momentarily turn off the injectors. This helps
improve fuel economy, emissions and engine braking.
If decel fuel shutoff is detected, downstream oxy-
gen sensor diagnostics is performed.WIDE-OPEN-THROTTLE MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide-open-
throttle operation, the following inputs are received
by the PCM:
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine speed
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position
When the PCM senses a wide-open-throttle condi-
tion through the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) it de-
energizes the A/C compressor clutch relay. This
disables the air conditioning system.
The PCM does not monitor the heated oxygen sen-
sor inputs during wide-open-throttle operation except
for downstream heated oxygen sensor and both
shorted diagnostics. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width to supply a predetermined amount of addi-
tional fuel.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When the operator turns the ignition switch to the
OFF position, the following occurs:
²All outputs are turned off, unless 02 Heater
Monitor test is being run. Refer to the Emission sec-
tion for On-Board Diagnostics.
²No inputs are monitored except for the heated
oxygen sensors. The PCM monitors the heating ele-
ments in the oxygen sensors and then shuts down.
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
OPERATION
The PCM can test many of its own input and out-
put circuits. If the PCM senses a fault in a major
system, the PCM stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) in memory.
For DTC information see On-Board Diagnostics.
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
The Power Distribution Center (PDC) is located
next to the battery (Fig. 1). The PDC contains the
starter relay, radiator fan relay, A/C compressor
clutch relay, auto shutdown relay, fuel pump relay
and several fuses.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 2). The
PCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors that are referred to as PCM Inputs.
Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts various
engine and vehicle operations through devices that
are referred to as PCM Outputs.
PCM Inputs:
14 - 24 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 859 of 1285

Like all Hall-effect sensors, the electronics of the
sensor needs a power source. This power source is
provided by the PCM. It is the same 8 volt power
supply that is used by the CKP and CMP sensors.
The vehicle speed sensor generates 8 pulses per
sensor revolution. This signal, in conjunction with a
closed throttle signal from the throttle position sen-
sor, indicates a closed throttle deceleration to the
PCM. Under deceleration conditions, the PCM
adjusts the Idle Air Control (IAC) motor to maintain
a desired MAP value.
When the vehicle is stopped at idle, a closed throt-
tle signal is received by the PCM (but a speed sensor
signal is not received). Under idle conditions, the
PCM adjusts the IAC motor to maintain a desired
engine speed.
AIR CONDITIONING CLUTCH RELAYÐPCM
OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
The air conditioning clutch relay is located in the
PDC. The inside top of the PDC cover has a label
showing relay and fuse location.
OPERATION
The PCM controls the air conditioning clutch relay
ground circuit. The A/C clutch relay coil side contains
a 10 amp fuse between the buss bar in the Power
Distribution Center (PDC) and the relay. The power
side of this relay is fused with a 40 amp fuse. When
the PCM receives an air conditioning input, it
grounds the A/C compressor clutch relay and the
radiator fan relay.
When the PCM senses low idle speeds or wide open
throttle through the throttle position sensor, it
removes the ground for the A/C compressor clutch
relay. When the relay de-energizes, the contacts open
preventing air conditioning clutch engagement. Also,
if the PCM senses a part throttle launch condition, it
disables the A/C compressor clutch for several sec-
onds.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAYÐPCM
OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
The ASD relay is located in the PDC. The inside
top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay and
fuse location.
OPERATION
The automatic shutdown (ASD) relay supplies bat-
tery voltage to the fuel injectors, electronic ignition
coil and the heating elements in the oxygen sensors
generator field and PCM sense circuit.A buss bar in the power distribution center (PDC)
supplies voltage to the solenoid side and contact side
of the relay. The ASD relay power circuit contains a
fuse between the buss bar in the PDC and the relay.
The fuse also protects the power circuit for the fuel
pump relay and pump. The fuse is located in the
PDC. Refer to the Wiring Diagrams for circuit infor-
mation.
The PCM controls the relay by switching the
ground path for the solenoid side of the relay on and
off. The PCM turns the ground path off when the
ignition switch is in the Off position unless the 02
Heater Monitor test is being run. When the ignition
switch is in the On or Crank position, the PCM mon-
itors the crankshaft position sensor and camshaft
position sensor signals to determine engine speed
and ignition timing (coil dwell). If the PCM does not
receive the crankshaft position sensor and camshaft
position sensor signals when the ignition switch is in
the Run position, it will de-energize the ASD relay.
CHARGING SYSTEM INDICATOR LAMPÐPCM
OUTPUT
OPERATION
The PCM turns the instrument panel Charging
System Lamp on. Refer to the Charging system sec-
tion information.
FUEL PUMP RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC. The
inside top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay
and fuse location.
OPERATION
The fuel pump relay supplies battery voltage to the
fuel pump. A buss bar in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) supplies voltage to the solenoid side and
contact side of the relay. The fuel pump relay power
circuit contains a fuse between the buss bar in the
PDC and the relay. The fuse also protects the power
circuit for the Automatic Shutdown (ASD) relay. The
fuse is located in the PDC. Refer to the Wiring Dia-
grams for circuit information.
The PCM controls the fuel pump relay by switch-
ing the ground path for the solenoid side of the relay
on and off. The PCM turns the ground path off when
the ignition switch is in the Off position. When the
ignition switch is in the On position, the PCM ener-
gizes the fuel pump. If the crankshaft position sensor
does not detect engine rotation, the PCM de-ener-
gizes the relay after approximately one second.
14 - 38 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1115 of 1285

The check valves are one-way valves. The first
check valve is used to draw outside air into the lower
chamber of the LDP (the space that is below the
pump diaphragm). The second check valve is used to
vent this outside air, which has become pressurized
from the fall of the pump diaphragm, into the evap-
orative system.
The spring loaded vent seal valve, inside the LDP
is used to seal off the evaporative system. When the
pump diaphragm is in the ªupº position the spring
pushes the vent seal valve closed. The vent seal valve
opens only when the pump diaphragm is in its ªfull
downº position. When the pump assembly is in its
pump mode the pump diaphragm is not allowed to
descend (fall) so far as to allow the vent seal valve to
open. This allows the leak detection pump to develop
the required pressure within the evaporative system
for system leak testing.
A pressure build up within the evaporative system
may cause pressure on the lower side of the LDP dia-
phragm. This will cause the LDP diaphragm to
remain in its ªupº position (stuck in the up position).
This condition can occur even when the solenoid
valve is deenergized. This condition can be caused by
previous cycling (pumping) of the LDP by the techni-
cian (dealer test). Another way that this condition is
created is immediately following the running of the
vehicle evaporative system monitor. In this case, the
PCM has not yet opened the proportional purge sole-
noid in order to vent the pressure that has been built
up in the evaporative system to the engine combus-
tion system. The technician will need to vent the
evaporative system pressure via the vehicle fuel filler
cap and its fuel filler secondary seal (if so equipped
in the fuel filler neck). This will allow the technician
to cycle the LDP and to watch switch state changes.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained until the purge sys-
tem is activated, in effect creating a leak. If the dia-
phragm falls (as is expected), causing the reed switch
to change state, then the diagnostic test is completed.
When of the evaporative system leak monitor
begins its various tests, a test is performed to deter-
mine that no part of the evaporative system is
blocked. In this test, the LDP is cycled (pumped) a
calibrated (few) number of times. Pressure should not
build up in the evaporative system. If pressure is
present, then LDP diaphragm is forced to stay in its
ªupº position. The reed switch now stays open and
the PCM senses this open (incorrect) state. The evap-
orative system monitor will fail the test because of a
detected obstruction within the system.
Possible causes:
²Open or shorted LDP switch sense circuit
²Leak Detection Pump switch failure²Open fused ignition switch output
²Restricted, disconnected, or blocked manifold
vacuum source
²Obstruction of hoses or lines
²PCM failure
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION (PCV)
SYSTEMS
DESCRIPTION
OPERATION
Intake manifold vacuum removes crankcase vapors
and piston blow-by from the engine. The emissions
pass through the PCV valve into the intake manifold
where they become part of the calibrated air-fuel
mixture. They are burned and expelled with the
exhaust gases. The air cleaner supplies make up air
when the engine does not have enough vapor or
blow-by gases. In this system, fresh air does not
enter the crankcase.
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION VALVE
OPERATION
The PCV valve contains a spring loaded plunger.
The plunger meters the amount of crankcase vapors
routed into the combustion chamber based on intake
manifold vacuum.
When the engine is not operating or during an
engine backfire, the spring forces the plunger back
against the seat. This prevents vapors from flowing
through the valve (Fig. 4).
When the engine is at idle or cruising, high mani-
fold vacuum is present. At these times manifold vac-
uum is able to completely compress the spring and
Fig. 3 PCV System
25 - 28 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)