2000 DODGE NEON fuel type
[x] Cancel search: fuel typePage 831 of 1285
(3) Squeeze retainer tabs together and pull fuel
tube/quick-connect fitting assembly off of fuel tube
nipple. The retainer will remain on fuel tube.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Never install a quick-connect fitting
without the retainer being either on the fuel tube or
already in the quick-connect fitting. In either case,
ensure the retainer locks securely into the quick-
connect fitting by firmly pulling on fuel tube and fit-
ting to ensure it is secured.
(1) Using a clean lint free cloth, clean the fuel tube
nipple and retainer.
(2) Prior to connecting the fitting to the fuel tube,
coat the fuel tube nipple with clean 30 weight engine
oil.
(3) Push the quick-connect fitting over the fuel
tube until theretainer seats and a click is heard.
(4) The plastic quick-connect fitting has windows
in the sides of the casing. When the fitting com-
pletely attaches to the fuel tube, the retainer locking
ears and the fuel tube shoulder are visible in the
windows. If they are not visible, the retainer was not
properly installed (Fig. 9).Do not rely upon the
audible click to confirm a secure connection.
(5) Connect negative cable to battery or auxiliary
jumper terminal.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or
until the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion.(6) Use the DRB scan tool ASD Fuel System Test
to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
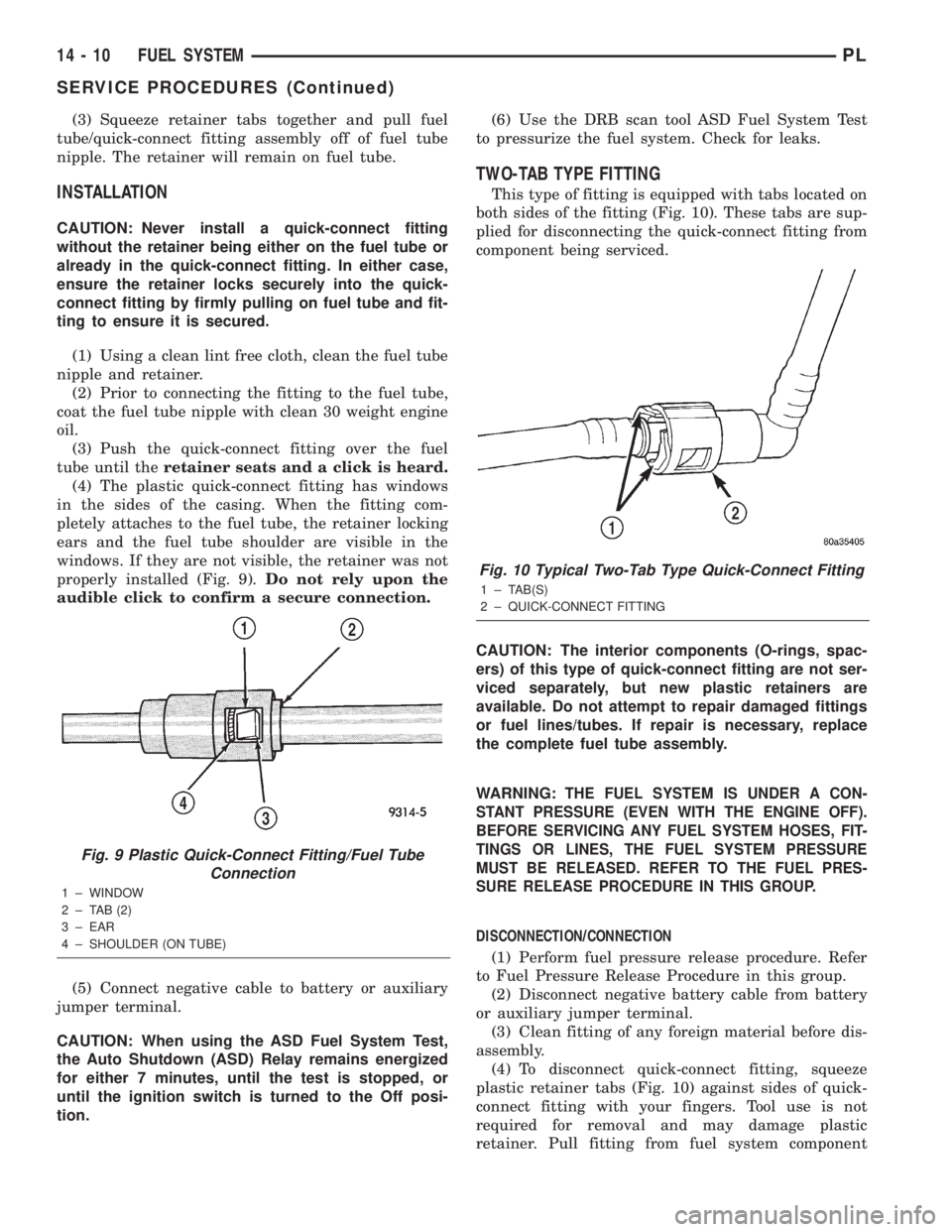
TWO-TAB TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting is equipped with tabs located on
both sides of the fitting (Fig. 10). These tabs are sup-
plied for disconnecting the quick-connect fitting from
component being serviced.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers) of this type of quick-connect fitting are not ser-
viced separately, but new plastic retainers are
available. Do not attempt to repair damaged fittings
or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is necessary, replace
the complete fuel tube assembly.
WARNING:
THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES, FIT-
TINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS GROUP.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this group.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
or auxiliary jumper terminal.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4) To disconnect quick-connect fitting, squeeze
plastic retainer tabs (Fig. 10) against sides of quick-
connect fitting with your fingers. Tool use is not
required for removal and may damage plastic
retainer. Pull fitting from fuel system component
Fig. 9 Plastic Quick-Connect Fitting/Fuel Tube
Connection
1 ± WINDOW
2 ± TAB (2)
3 ± EAR
4 ± SHOULDER (ON TUBE)
Fig. 10 Typical Two-Tab Type Quick-Connect Fitting
1 ± TAB(S)
2 ± QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
14 - 10 FUEL SYSTEMPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 832 of 1285

being serviced. The plastic retainer will remain on
component being serviced after fitting is discon-
nected. The O-rings and spacer will remain in quick-
connect fitting connector body.
(5) Inspect quick-connect fitting body and compo-
nent for damage. Replace as necessary.
CAUTION:
When the quick-connect fitting was dis-
connected, the plastic retainer will remain on the com-
ponent being serviced. If this retainer must be
removed, very carefully release the retainer from the
component with two small screwdrivers. After removal,
inspect the retainer for cracks or any damage.
(6) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(7) Insert quick-connect fitting to component being
serviced and into plastic retainer. When a connection
is made, a click will be heard.
(8) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(9) Connect negative cable to battery or auxiliary
jumper terminal.
(10) Start engine and check for leaks.
PLASTIC RETAINER RING TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting can be identified by the use of a
full-round plastic retainer ring (Fig. 11) usually black
in color.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers, retainers) of this type of quick-connect fitting
are not serviced separately. Do not attempt to repair
damaged fittings or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is nec-
essary, replace the complete fuel tube assembly.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
THIS GROUP.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this section.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
or auxiliary jumper terminal.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4) To release fuel system component from quick-
connect fitting, firmly push fitting towards compo-nent being serviced while firmly pushing plastic
retainer ring into fitting (Fig. 11). With plastic ring
depressed, pull fitting from component.The plastic
retainer ring must be pressed squarely into fit-
ting body. If this retainer is cocked during
removal, it may be difficult to disconnect fit-
ting. Use an open-end wrench on shoulder of
plastic retainer ring to aid in disconnection.
(5) After disconnection, plastic retainer ring will
remain with quick-connect fitting connector body.
(6) Inspect fitting connector body, plastic retainer
ring and fuel system component for damage. Replace
as necessary.
(7) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(8) Insert quick-connect fitting into component
being serviced until a click is felt.
(9) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(10) Connect negative battery cable to battery or
auxiliary jumper terminal.
(11) Start engine and check for leaks.
Fig. 11 Plastic Retainer Ring Type Fitting
1 ± FUEL TUBE
2 ± QUICK CONNECT FITTING
3 ± PUSH
4 ± PLASTIC RETAINER
5 ± PUSH
6 ± PUSH
7 ± PUSH
8 ± PUSH
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 11
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 854 of 1285
grammed (fixed) values and inputs from other sen-
sors.
DOWNSTREAM OXYGEN SENSOR 1/2
The Downstream O2 Sensor has two functions.
One function is measuring catalyst efficiency. This is
an OBD II requirement. The oxygen content of theexhaust gasses has significantly less fluctuation than
at the inlet if the converter is working properly. The
PCM compares upstream and Downstream O2 Sen-
sor switch rates under specific operating conditions
to determine if the catalyst is functioning properly.
The other function is a downstream fuel control
which was introduced in 1996. The upstream O2 goal
varies within the window of operation of the O2 Sen-
sor. In the past the goal was a preprogrammed fixed
value based upon where it believed the catalyst oper-
ated most efficiently.
While the Upstream O2 Sensor input is used to
maintain the 14.7:1 air/fuel ratio, variations in
engines, exhaust systems and catalytic converters
may cause this ratio to not be the most ideal for a
particular catalyst and engine. To help maintain the
catalyst operating at maximum efficiency, the PCM
will fine tune the air/fuel ratio entering the catalyst
based upon the oxygen content leaving the catalyst.
This is accomplished by modifying the Upstream O2
Sensor voltage goal.
If the exhaust leaving the catalyst has too much
oxygen (lean ) the PCM increases the upstream O2
goal which increases fuel in the mixture causing less
oxygen to be left over. Conversely, if the oxygen con-
tent leaving the catalyst has is too little oxygen (rich)
the PCM decreases the upstream O2 goal down
which removes fuel from the mixture causing more
oxygen to be left over. This function only occurs dur-
ing downstream closed loop mode operation.
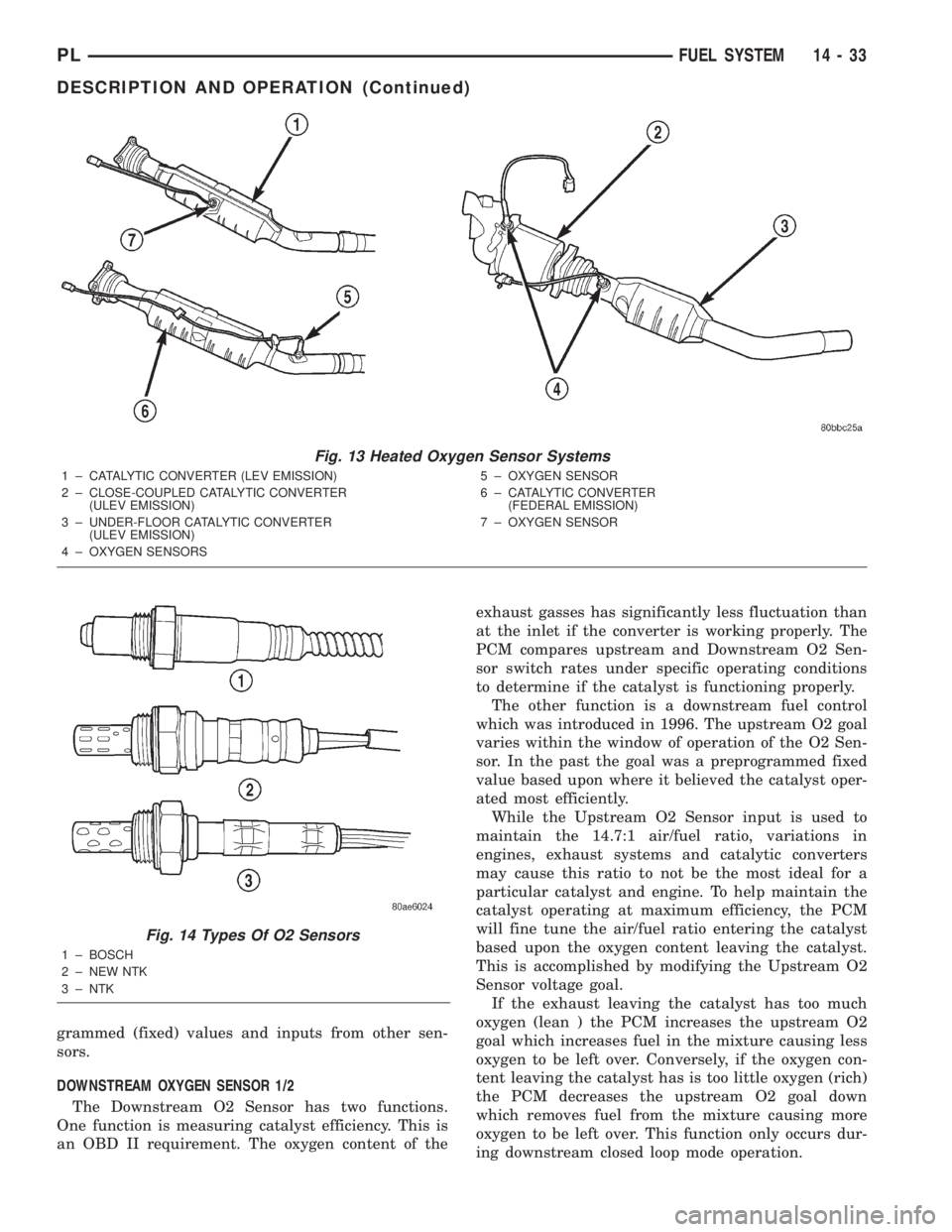
Fig. 13 Heated Oxygen Sensor Systems
1 ± CATALYTIC CONVERTER (LEV EMISSION)
2 ± CLOSE-COUPLED CATALYTIC CONVERTER
(ULEV EMISSION)
3 ± UNDER-FLOOR CATALYTIC CONVERTER
(ULEV EMISSION)
4 ± OXYGEN SENSORS5 ± OXYGEN SENSOR
6 ± CATALYTIC CONVERTER
(FEDERAL EMISSION)
7 ± OXYGEN SENSOR
Fig. 14 Types Of O2 Sensors
1 ± BOSCH
2 ± NEW NTK
3 ± NTK
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 33
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)