2000 DODGE NEON light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 1086 of 1285

(3) Grasp the wheel cover and pull straight out-
ward. This will remove the wheel cover from the
wheel.
(4) Remove the wheel mounting nuts from the
studs (Fig. 16).
(5) Remove the tire and wheel assembly from the
hub.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Installing the wheel mounting nuts with-
out having good metal-to-mental contact between
the back of the wheel and the hub mounted brake
disc or drum could cause the wheel to bind and
eventually cause loosening of the wheel mounting
nuts.
(1) Install the tire and wheel assembly on the hub
studs against the hub mounted brake disc or drum
using the hub pilot as a guide.
CAUTION: When installing the tire and wheel
assembly, never use oil or grease on studs or nuts.
(2) Install and lightly tighten the wheel nuts in
the proper sequence (Fig. 17).
(3) Lower the vehicle.
(4) Progressively tighten the 5 wheel nuts in the
proper sequence until tightened to half of the speci-
fied torque (Fig. 17). Finally, tighten the wheel nutsin the proper sequence to a torque of 135 N´m (100
ft. lbs.).
(5) Align the valve notch in the wheel cover with
the valve stem on the wheel (Fig. 15). Align the
wheel cover retaining nuts with the externally
threaded wheel nuts.
(6) By hand, start to thread all 5 of the wheel
cover retaining nuts onto the externally threaded
wheel nuts.
NOTE: When tightening the wheel cover retaining
nuts it is recommended that a hand wrench be used
and not an impact wrench. Use of an impact wrench
could result in damage to the lock-on wheel cover
retaining nuts.
(7) Tighten each of the wheel cover retaining nuts.
If the retaining nut ªjumpsº a thread (slips), which is
an override feature of the retaining nut, retighten
the retaining nut to a point just prior to this occur-
ring. To avoid rattling of the wheel cover be sure all
five retaining nuts are correctly tightened.
SPECIFICATIONS
WHEEL SPECIFICATIONS
Wheel:
Wheel Mounting Stud Size...... M12x1.5mm
Wheel Mounting Nut Hex Size......... 19mm
Wheel Mounting Nut Torque..... 115±155 N´m
(85 to 115 ft. lbs.)
Fig. 16 Wheel Nuts
1 ± WHEEL
2 ± EXTERNALLY THREADED WHEEL NUTS
3 ± TIRE
Fig. 17 Wheel Nut Tightening Sequence
PLTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 17
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1103 of 1285

²200 revolution increments for immediate cata-
lyst damage
²1000 revolution increments for emissions viola-
tion and Inspection/Maintenance (I/M) test failure
NOTE: The percent of misfire for malfunction crite-
ria varies due to RPM and load. As the engine
speed increases or load decreases, the effects of a
misfire diminishes due to crankshaft momentum.
Failure percentages also vary from engine to
engine.
Monitor OperationÐThe PCM utilizes the
Crankshaft Speed Fluctuation method to monitor for
misfire. The misfire monitor utilizes a crankshaft
position sensor to determine engine RPM. The sensor
can detect slight variations in engine speed due to
misfire. Misfire is continuously monitored once the
enabling conditions are met.
Once enabling conditions are met, the PCM counts
the number of misfires in every 200 revolutions of
the crankshaft. If, duringfive200 counters, the mis-
fire percentage exceeds a predetermined value, a
maturing code is set and a Freeze Frame is entered.
Freeze Frame data is recorded during the last 200
revolutions of the 1000 revolution period. A failure on
the second consecutive trip matures the code and a
DTC is set.
If misfire continues during the initial trip, the MIL
is not illuminated. However, the MIL flashes when
the misfire percentage exceeds the malfunction per-
centage, in any 200 revolution period, that would
cause permanent catalyst damage. This is a one trip
monitor. If misfire reaches a point in which catalyst
damage is likely to occur, the MIL flashes and a DTC
is stored in a Freeze Frame. The engine defaults to
open loop operation to prevent increased fuel flow to
the cylinders. Once misfire is below the predeter-
mined percentage, the MIL stops flashing but
remains illuminated.
The 1000 revolution counters are two trip moni-
tors. As with the fuel system monitor, Freeze Frame
data is from the original fault, and MIL extinguish-
ing requires the monitor to pass under similar condi-
tions.
The Adaptive NumeratorÐThe Misfire Monitor
takes into account component wear, sensor fatigue
and machining tolerances. The PCM compares the
crankshaft in the vehicle to data on an ideal crank
and uses this as a basis to determine variance. To do
this, the crankshaft sensor monitors the reference
notches in the crank. The PCM uses the first signal
set as a point of reference. It then measures where
the second set of signals is, compared to where engi-
neering data has determined it should be. This vari-
ance is the Adaptive Numerator. The monitor will not
run if the numerator is not set.If the Adaptive Numerator is equal to the default
value, the adaptive Numerator has not been learned
and the Misfire Monitor does not run. If the Adaptive
Numerator exceeds its limits, the PCM sets a DTC
for Adaptive Numerator and illuminates the MIL.
RPM ErrorÐThe PCM also checks the machining
tolerances for each group of slots. By monitoring the
speed of the crank from the first slot to the last slot
in a group, the PCM can calculate engine RPM. The
variance between groups of slots is know as the RPM
error. In order for the PCM to run the Misfire Mon-
itor, RPM error must be less than approximately 5%.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must be met before the PCM runs the Misfire Moni-
tor:
²RPM
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
²Barometric Pressure (MAP)
²Fuel level
²Ambient air Temperature
Pending ConditionsÐThe Misfire Monitor does
not run when the MIL is illuminated for any of the
following:
²Limp in mode for
Ð MAP
Ð TPS
Ð Crankshaft Sensor
Ð Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Speed Sensor DTC
²EGR Electrical
²EVAP Electrical
²Idle Speed Faults
²Intake Air Temperature
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Electrical
Conflict ConditionsÐIf any of the following con-
ditions conflict with the Misfire Monitor, the monitor
will not run:
²Low fuel level
²MAP voltage rapidly changing
²Severe engine decel
²TPS toggling OPEN/CLOSED
²Engine RPM too low (RPM levels by vehicle)
²Engine RPM too high (RPM levels vary by vehi-
cle)
²Full Lean or Decel Fuel Shut-off
²Cold start
FUEL SYSTEM MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide. The catalyst works best
when the air fuel (A/F) ratio is at or near the opti-
mum of 14.7 to 1.
25 - 16 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1118 of 1285

BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PAINT................................... 1
STATIONARY GLASS........................ 4
SEATS ................................... 8BODY COMPONENTS...................... 12
SPECIFICATIONS......................... 60
PAINT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
PAINT CODE.............................1
BASE COAT/CLEAR COAT FINISH.............1
WET SANDING, BUFFING, AND POLISHING.....1PAINTED SURFACE TOUCH-UP..............1
SPECIFICATIONS
AFTERMARKET PAINT REPAIR PRODUCTS.....2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
PAINT CODE
A paint code is provided on the body code plate
located in the engine compartment. Refer to the
Introduction section at the front of this manual for
body code plate description. The paint and trim codes
are also included on the Vehicle Safety Label located
on the driver's door end frame.
BASE COAT/CLEAR COAT FINISH
On most vehicles a two-part paint application (base
coat/clear coat) is used. Color paint that is applied to
primer is called base coat. The clear coat protects the
base coat from ultraviolet light and provides a dura-
ble high-gloss finish.
CAUTION: Do not use abrasive chemicals or com-
pounds on painted surfaces. Damage to finish can
result.
Do not use harsh alkaline based cleaning sol-
vents on painted surfaces. Damage to finish or
color can result.
WET SANDING, BUFFING, AND POLISHING
Minor acid etching, orange peel, or smudging in
clear coat or single-stage finishes can be reduced
with light wet sanding, hand buffing, and polishing.
If the finish has been wet sanded in the past, itcannot be repeated. Wet sanding operation
should be performed by a trained automotive
paint technician.
CAUTION: Do not remove clear coat finish, if
equipped. Base coat paint must retain clear coat for
durability.
PAINTED SURFACE TOUCH-UP
When a painted metal surface has been scratched
or chipped, it should be touched-up as soon as possi-
ble to avoid corrosion. For best results, use Mopart
Scratch Filler/Primer, Touch-Up Paints and Clear Top
Coat. Refer to Introduction group of this manual for
Body Code Plate information.
CAUTION: USE A OSHA APPROVED BREATHING
FILTER WHEN SPRAYING PAINT OR SOLVENTS IN
A CONFINED AREA. PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
TOUCH-UP PROCEDURE
(1) Scrape loose paint and corrosion from inside
scratch or chip.
(2) Clean affected area with MopartTar/Road Oil
Remover, and allow to dry.
(3) Fill the inside of the scratch or chip with a coat
of filler/primer. Do not overlap primer onto good sur-
PLBODY 23 - 1
Page 1119 of 1285

face finish. The applicator brush should be wet
enough to puddle-fill the defect without running. Do
not stroke brush applicator on body surface. Allow
the filler/primer to dry hard.
(4) Cover the filler/primer with color touch-up
paint. Do not overlap touch-up color onto the original
color coat around the scratch or chip. Butt the new
color to the original color, if possible. Do not stroke
applicator brush on body surface. Allow touch-up
paint to dry hard.
(5) On vehicles without clear coat, the touch-up
color can be lightly wet sanded (1500 grit) and pol-
ished with rubbing compound.(6) On vehicles with clear coat, apply clear top coat
to touch-up paint with the same technique as
described in Step 4. Allow clear top coat to dry hard.
If desired, Step 5 can be performed on clear top coat.
CAUTION: AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT
WITH PETROLEUM OR ALCOHOL ± BASED CLEAN-
ING SOLVENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
SPECIFICATIONS
AFTERMARKET PAINT REPAIR PRODUCTS
EXTERIOR COLORS
EXTERIOR
COLORCHRY
CODE*PPG DUPONTS-W
M-S **A-N/S ** S-H ** ICI **
Black Clear
CoatDX8 9700 F0206 34858 CHA85:DX8 73328 TC60B
Bright White
Clear CoatGW7 4037 B8833 37298 CHA88:GW7 11751 TA45B
Bright Silver
Metallic Clear
CoatWS2 5464 F7999 56150 CHA99:WS2 74611 KDP8B
Cinnamon
Glaze Metallic
Clear CoatVLB 5313 B9824 54469 CHA98:VLB 80758 HMT2B
Deep
Amethyst
Pearl CoatTCN5246 B9751 52566 CHA97:TCN 54755 FNE4B
Deep
Cranberry
Pearl CoatVMT5359 B9842 54119 CHA98:VMT 33686 GJX2B
Flame Red
Clear CoatPR4 4679 B9326 46916 CHA93:PR4 30116 2NNGB
Forest Green
Pearl CoatSG8 5065 B9609 51062 CHA95:SG8 61633 7MR8B
Patriot Blue
Pearl CoatWB75512 F7991 56683 CHA99:WB7 56580 LEC6B
Salsa Red
Pearl CoatWE5 5442 F7998 56147 CHA99:WE5 34462 5WS8B
*BASF, Glasurit, and Standox use the DaimlerChrysler paint code.
** S-W = Sherwin Williams, M-S = Martin Senour,
A-N/S = Akzo Nobel/Sikkens, S-H = Spies Hecker and ICI = Autocolor
23 - 2 BODYPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1135 of 1285

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing,
improper body component alignment, body seam
porosity, missing plugs, or blocked drain holes. Cen-
trifugal and gravitational force can cause water to
drip from a location away from the actual leak point,
making leak detection difficult. All body sealing
points should be water tight in normal wet-driving
conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of
the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water-test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body
drains are clear, and body components are properly
aligned and sealed. If component alignment or seal-
ing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of
this group for proper procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: DO NOT USE ELECTRIC SHOP LIGHTS
OR TOOLS IN WATER TEST AREA. PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT.
When the conditions causing a water leak have
been determined, simulate the conditions as closely
as possible.
²If a leak occurs with the vehicle parked in a
steady light rain, flood the leak area with an open-
ended garden hose.
²If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds
in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable
velocity stream or fan spray of water. Direct the
spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
²If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an
incline, hoist the end or side of the vehicle to simu-
late this condition. This method can be used when
the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or
turns. If the leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the
front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking,
hoist the back of the vehicle. If the leak occurs on left
turns, hoist the left side of the vehicle. If the leak
occurs on right turns, hoist the right side of the vehi-cle. For hoisting recommendations refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance, General Information
section.
WATER LEAK DETECTION
To detect a water leak point-of-entry, do a water
test and watch for water tracks or droplets forming
on the inside of the vehicle. If necessary, remove inte-
rior trim covers or panels to gain visual access to the
leak area. If the hose cannot be positioned without
being held, have someone help do the water test.
Some water leaks must be tested for a considerable
length of time to become apparent. When a leak
appears, find the lowest point of the water track or
drop. After leak point has been found, repair the leak
and water test to verify that the leak has stopped.
Locating the entry point of water that is leaking
into a cavity between panels can be difficult. The
trapped water may splash or run from the cavity,
often at a distance from the entry point. Most water
leaks of this type become apparent after accelerating,
stopping, turning, or when on an incline.
MIRROR INSPECTION METHOD
When a leak point area is visually obstructed, use
a suitable mirror to gain visual access. A mirror can
also be used to deflect light to a limited-access area
to assist in locating a leak point.
BRIGHT LIGHT LEAK TEST METHOD
Some water leaks in the luggage compartment can
be detected without water testing. Position the vehi-
cle in a brightly lit area. From inside the darkened
luggage compartment inspect around seals and body
seams. If necessary, have a helper direct a drop light
over the suspected leak areas around the luggage
compartment. If light is visible through a normally
sealed location, water could enter through the open-
ing.
PRESSURIZED LEAK TEST METHOD
When a water leak into the passenger compart-
ment cannot be detected by water testing, pressurize
the passenger compartment and soap test exterior of
the vehicle. To pressurize the passenger compart-
ment, close all doors and windows, start engine, and
set heater control to high blower in HEAT position. If
engine can not be started, connect a charger to the
battery to ensure adequate voltage to the blower.
With interior pressurized, apply dish detergent solu-
tion to suspected leak area on the exterior of the
vehicle. Apply detergent solution with spray device or
soft bristle brush. If soap bubbles occur at a body
seam, joint, seal or gasket, the leak entry point could
be at that location.
23 - 18 BODYPL
Page 1137 of 1285

SAFETY PRECAUTION AND WARNINGS
WARNING: EYE PROTECTION SHOULD BE USED
WHEN SERVICING RTM AND SMC COMPONENTS.
PERSONAL INJURE CAN RESULT.
USE AN OSHA APPROVED BREATHING DEVICE
WHEN MIXING EPOXY, GRINDING RTM AND SMC,
AND SPRAYING PAINT OR SOLVENTS IN A CON-
FINED AREA. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT WITH
EPOXY RESIN, PETROLEUM, OR ALCOHOL BASED
SOLVENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
DO NOT VENTURE UNDER A HOISTED VEHICLE
THAT IS NOT PROPERLY SUPPORTED ON SAFETY
STANDS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
²When holes must be drilled or cut in body pan-
els, verify locations of internal body components and
electrical wiring. Damage to vehicle can result.
²Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds on
undamaged painted surfaces around repair areas.
Damage to finish can result.
PANEL SECTIONING
If it is required to section a large panel for an SMC
or RTM repair, it will be necessary to reinforce the
panel with epoxy structural adhesive (rigid repair
adhesive) (Fig. 2). To bond two plastic panels
together, a reinforcement must overlap both panels.
The panels must be ªV'dº at a 20 degree angle. The
area to be reinforced should be washed, then sanded.
Be sure to wipe off any excess soap and water when
finished. Lightly sand or abrade the plastic with an
abrasive pad or sandpaper. Blow off any dust with
compressed air or wipe with a clean dry rag.When bonding SMC or RTM panels, use a two-part
epoxy adhesive. Properly mix parts A and B, and
apply it to the panels being repaired. Be sure that
enough adhesive has been applied to allow squeeze
out and to fill the full bond line. Once the pieces
have been brought together, do not move them until
the adhesive is cured. The assembly can be held
together with clamps, rivets, etc. A faster cure can be
obtained by heating with a heat lamp or heat gun.
After the parts have been bonded and have had
time to cure, rough sand the seam and apply the
final adhesive filler to the area being repaired.
Smooth the filler with a spatula, wooden tongue
depressor, or squeegee. For fine texturing, a small
amount of water can be applied to the filler surface
while smoothing. The cured filler can be sanded as
necessary and, as a final step, cleanup can be done
withy soapy water. Wipe the surface clean with a dry
cloth allowing time for the panel to dry before mov-
ing on with the repair.
PANEL REINFORCEMENT
Structural repair procedures for rigid panels such
as Sheet Molded compound (SMC) or Resin Transfer
Molded (RTM) with large cracks and holes will
require a reinforcement backing. Reinforcements can
be made with several applications of glass cloth sat-
urated with epoxy structural adhesive, semirigid or
flexible repair materials should be used for semirigid
or flexible part repairs (Fig. 3) and (Fig. 4). Open
meshed fiberglass dry wall tape can be used to form
a reinforcement. The dry wall tape allows the resin
to penetrate through and make a good bond between
the panel and the epoxy adhesive. Structurally, the
more dry wall tape used, the stronger the repair.
Another kind of repair that can be done to repair
large cracks and holes is to use a scrap piece of sim-
ilar plastic and bond with structural adhesive. The
reinforcement should cover the entire break and
should have a generous amount of overlap on either
side of the cracked or broken area.
When repairing plastic, the damaged area is first
ªV'dº out, or beveled. Large bonding areas are desir-
able when repairing plastic because small repairs are
less likely to hold permanently. Beveling the area
around a crack at a 20 degree angle will increase the
bonding surface for a repair (Fig. 5). It is recom-
mended that sharp edges be avoided because the
joint may show through after the panel is refinished.
²Panel repair for both flexible and rigid panels
are basically the same. The primary difference
between flexible panel repair and rigid panel repair
is in the adhesive materials used (Fig. 6).
²The technician should first decide what needs to
be done when working on any type of body panel.
One should determine if it is possible to return the
Fig. 2 Panel Sectioning
1 ± EXISTING PANEL
2 ± NEW PANEL
3 ± PANEL ADHESIVE
4 ± BONDING STRIP
23 - 20 BODYPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1174 of 1285

warning label applied to the sun visor, verify label
availability and ensure the label is installed.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove sun visor from center support.
(2) Remove screws attaching sun visor to roof
header.
(3) Remove sun visor from header.
(4) If equipped, disconnect wire connector from
body harness.
(5) Remove sun visor from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place sun visor in position.
(2) If equipped, connect wire connector from body
harness.
(3) Install screws attaching sun visor to header.
(4) Install sun visor into center support.
HEADLINER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove screws attaching sun visors to roof
header panel.
(2) Disconnect wire connector from lighted vanity
mirror, if so equipped.
(3) Remove sun visors from vehicle.
(4) Remove A-pillar trim covers.
(5) Remove B-pillar trim panels.
(6) Remove (upper) quarter panel trim panels.
(7) Remove assist handle, if so equipped.
(8) Remove sun visor hooks.
(9) Remove coat hooks, if so equipped.
(10) Remove three push in fasteners at rear of
headliner.
(11) Disengage dome lamp wire connector, at rear
of headliner.
(12) Remove push in fastener attaching wiring to
C-pillar.
(13) Remove headliner through door opening (Fig.
73).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position headliner in vehicle.
(2) Install sun visor hooks, if so equipped.
(3) Install coat hooks, if so equipped.
(4) Install three push in fastener at rear of head-
liner.
(5) Install assist handles, if so equipped.
(6) Install push in fastener attaching headliner
wiring to C-pillar.
(7) Connect dome lamp wire connector, at rear of
headliner.
(8) Install (upper) quarter panel trim panel.
(9) Install B-pillar trim panels.
(10) Install A-pillar trim covers.(11) Install sun visors, lighted vanity mirror wire
connector, if so equipped, and screws attaching sun
visors to roof header panel.
INSIDE REAR VIEW MIRROR
REMOVAL
(1) Loosen the mirror base set screw (Fig. 74).
(2) Slide the mirror base upward and off the
bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the mirror base at the bracket and
slide it downward onto the support bracket.
(2) Tighten the setscrew 1 N´m (15 in. lbs.) torque.
REAR SHELF TRIM PANEL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove quarter trim panels as necessary.
(2) Remove rear seat cushion and back.
(3) Disengage seat belt bezels from rear shelf trim
panel.
(4) Remove rear seat shoulder belt from the shelf
by sliding belt through the slot.
(5) Remove rear shelf trim panel from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place into position rear shelf trim panel.
(2) Slide the rear seat shoulder belt through the
slot in the rear shelf trim panel.
(3) Engage seat belt bezels to rear shelf trim
panel.
Fig. 73 Headliner
1 ± HEADLINER TO REAR HEADER FASTENERS
2 ± HEADLINER
3 ± VISORS
PLBODY 23 - 57
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1175 of 1285
(4) Install rear seat cushion and back.
(5) Install quarter trim.
BODY VENT
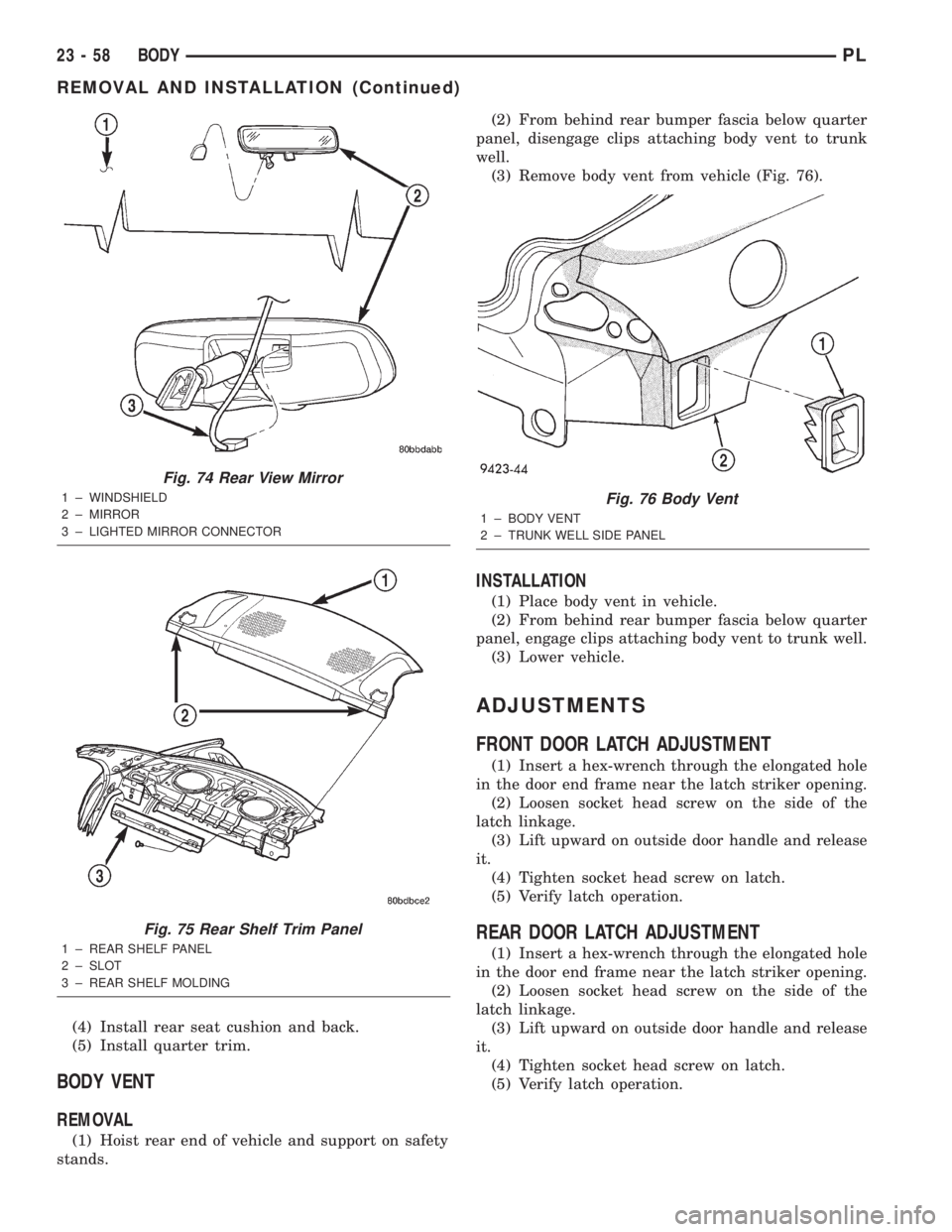
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist rear end of vehicle and support on safety
stands.(2) From behind rear bumper fascia below quarter
panel, disengage clips attaching body vent to trunk
well.
(3) Remove body vent from vehicle (Fig. 76).
INSTALLATION
(1) Place body vent in vehicle.
(2) From behind rear bumper fascia below quarter
panel, engage clips attaching body vent to trunk well.
(3) Lower vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
FRONT DOOR LATCH ADJUSTMENT
(1) Insert a hex-wrench through the elongated hole
in the door end frame near the latch striker opening.
(2) Loosen socket head screw on the side of the
latch linkage.
(3) Lift upward on outside door handle and release
it.
(4) Tighten socket head screw on latch.
(5) Verify latch operation.
REAR DOOR LATCH ADJUSTMENT
(1) Insert a hex-wrench through the elongated hole
in the door end frame near the latch striker opening.
(2) Loosen socket head screw on the side of the
latch linkage.
(3) Lift upward on outside door handle and release
it.
(4) Tighten socket head screw on latch.
(5) Verify latch operation.
Fig. 74 Rear View Mirror
1 ± WINDSHIELD
2 ± MIRROR
3 ± LIGHTED MIRROR CONNECTOR
Fig. 75 Rear Shelf Trim Panel
1 ± REAR SHELF PANEL
2 ± SLOT
3 ± REAR SHELF MOLDING
Fig. 76 Body Vent
1 ± BODY VENT
2 ± TRUNK WELL SIDE PANEL
23 - 58 BODYPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)