Page 67 of 558
ENGINE – Rocker Arms and Camshaft11-42
(9) Remove the lash adjuster from the container, then stand
the lash adjuster with its plunger at the top. Push the
plunger firmly and check that it does not move. Also,
check that the lash adjuster’s height matches that of a
new lash adjuster.
NOTE
If lash adjuster contracts, perform the operations (7)
through (9) again to fill it with diesel fuel completely.
Replace the lash adjuster if it still contracts after performing
these steps.
(10)Stand the lash adjuster upright to prevent diesel fuel from
spilling out. Do not allow the lash adjuster to become
contaminated by dirt or other foreign matter. Fit the lash
adjuster onto the engine as soon as possible.
Page 68 of 558
ENGINE – Cylinder Head and Valves11-43
CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVES
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Apply engine oil to all
moving parts before
installation.78 Nm → Loosen completely → 20 Nm + 90� + 90�
1
2
3 4
5
6
78
9
10
11 12
1314
15
1617
1819 20
Removal steps
�A��D�1. Cylinder head bolt
2. Cylinder head assembly
3. Cylinder head gasket
�B��C�4. Retainer lock
5. Valve spring retainer
�B�6. Valve spring
7. Intake valve
�B��C�8. Retainer lock
9. Valve spring retainer
�B�10. Valve spring�C�11. Exhaust valve
�A�12. Valve stem seal
13. Valve spring seat
�A�14. Valve stem seal
15. Valve spring seat
16. Intake valve guide
17. Exhaust valve guide
18. Intake valve seat
19. Exhaust valve seat
20. Cylinder head
Page 69 of 558

ENGINE – Cylinder Head and Valves11-44
REMOVAL SERVICE POINTS
PRECAUTION FOR REMOVED PARTS
Keep removed parts in order according to the cylinder number
and intake/exhaust.
�A�CYLINDER HEAD BOLTS REMOVAL
Using the special tool, loosen the cylinder head bolts. Loosen
evenly, little by little.
�B�RETAINER LOCK REMOVAL
Store removed valves, springs and other parts, tagged to
indicate their cylinder No. and location for reassembly.
�C�VALVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
(1) Sodium reacts violently with water or moisture generation
heat and liberating hydrogen. It must be handled with
utmost care because otherwise the following dangerous
conditions may result:
Loss of eyesight if sodium gets in eyes.
Burns if soduim contact skin.
Fire hazard.
(2) Handling of Soduim-filled Exhaust Valves
Soduim-filled exhaust valves are not dangerous and may
be handled in the same way as ordinary valves unless
they are broken.
Never try to break the valves and expose soduim to the
air. When worn exhaust valves are to be discarded, have
them disposed of by a salvage company equipped with
special disposal system, notifying them that the valves
contain soduim.
Should the exhaust valves be broken, neutralize soduim
using the method described below, and discard the valves
in the same way as ordinary valves.
MB991654
MD998772
MD998735
Page 70 of 558

ENGINE – Cylinder Head and Valves11-45
(3) How to Neutralize Sodium
Place a container filled with more than 10 liters of water
in a well ventilated large space.
Wear rubber gloves and goggles, and carefully take out
broken valves from the cylinder head.
Put a broken valve in the water-filled container and quickly
get away from the container at least 2 or 3 m.
Caution
1. Valves must be neutralized one at a time.
2. Put a valve in the container only after soduim
in the preceding one has completely reacted with
water.
Keep fire away from the container during the
neutralization. The resulting hydrogen gas is highly
explosive.
When the reaction has finished (there is no more
generation of hydrogen gas), take the valves out of the
container with large tweezers or the like.
NOTE
The reaction occurs when water enters the cavity in the
valve. Hydrogen gas may be trapped inside the valve,
temporarily blocking the water passage. In such a case,
wait until hydrogen gas in released and remaining soduim
reacts with water.
After the neutralization of soduim, water in the container
contains soduim hydroxide and is highly alkaline. The
water solution should be disposed of according to local
regulations.
Caution
1. Do not let the solution contact the eyes or the
skin.
2. Should it get in the eyes, immediately flush them
with clean water thoroughly, and receive medical
attention. When it contacts the skin, wash with
ample amounts of clean water.
INSTALLATION SERVICE POINTS
�A�VALVE STEM SEAL INSTALLATION
(1) Install the valve spring seat.
(2) The special tool must be used to install the valve stem
seal. Improper installation could result in oil leaks past
the valve guide.
Caution
Do not reuse removed valve stem seals.
MD998737
Page 71 of 558
ENGINE – Cylinder Head and Valves11-46
�B�VALVE SPRING INSTALLATION
Direct the valve spring end with identification color toward
the spring retainer.
�C�RETAINER LOCK INSTALLATION
The valve spring, if excessively compressed, causes the
bottom end of the retainer to be in contact with, and damage,
the stem seal.
�D�CYLINDER HEAD BOLT INSTALLATION
(1) When installing the cylinder head bolts, check that the
shank length of each bolt meets the limit. If the limit is
exceeded, replace the bolt.
Limit: Max. 99.4 mm
(2) Apply engine oil to the bolt threads and to the washers.
(3) Using the special tool (MB991654) and according to the
tightening sequence, tighten the bolts to the specified
torque.
Tightening torque: 78 Nm
(4) Loosen all bolts fully.
(5) Retighten the loosened bolts to a torque of 20 Nm in
the specified tightening sequence.
MD998772
MD998735
6EN0782
Shank length
Timing belt side
Page 72 of 558

ENGINE – Cylinder Head and Valves11-47
(6) Make paint marks on the cylinder head bolt heads and
cylinder head.
(7) Give a 90° turn to the cylinder head bolts in the specified
tightening sequence.
(8) Give another 90° turn to the cylinder head bolts and make
sure that the paint mark on the head of each cylinder
head bolt and that on the cylinder head are on the same
straight line.
Caution
1. If the bolt is turned less than 90°, proper fastening
performance may not be expected. When
tightening the bolt, therefore, be careful to give
a sufficient turn to it.
2. If the bolt is overtightened, loosen the bolt
completely and then retighten it by repeating the
tightening procedure from step (1).
INSPECTION
CYLINDER HEAD
(1) Check the cylinder head gasket surface for flatness by
using a straightedge and thickness gauge.
Standard value: 0.05 mm
Limit: 0.2 mm
(2) If the service limit is exceeded, correct to meet
specification.
Grinding limit: *0.2 mm
* Includes combined with cylinder block grinding.
Cylinder head height (Specification when new):
131.9 – 132.1 mm
6AE0297
90°
Paint mark
90°
9EN0064
Page 73 of 558

ENGINE – Cylinder Head and Valves11-48
VA LV E
(1) Check the valve face for correct contact. If incorrect, reface
using a valve refacer. Valve seat contact should be
maintained uniform at the center of valve face.
(2) If the margin exceeds the service limit, replace the valve.
ItemStandard value mmLimit mm
Intake1.00.5
Exhaust1.51.0
(3) Measure valve’s total length. If measurement is less than
specified, replace the valve.
ItemStandard value mmLimit mm
Intake109.5109.0
Exhaust109.7109.2
VALVE SPRING
(1) Measure the free height of spring and, if it is smaller
than the limit, replace.
Standard value mmLimit mm
48.347.3
(2) Measure the squareness of the spring and, if the limit
is exceeded, replace.
Standard valueLimit
1.5°4°
VALVE GUIDE
Measure the clearance between the valve guide and valve
stem. If the limit is exceeded, replace the valve guide or
valve, or both.
ItemStandard value mmLimit mm
Intake0.02 – 0.050.10
Exhaust0.05 – 0.090.15
1EN0264
Free
height
Out of
square
Valve
guide
Page 74 of 558
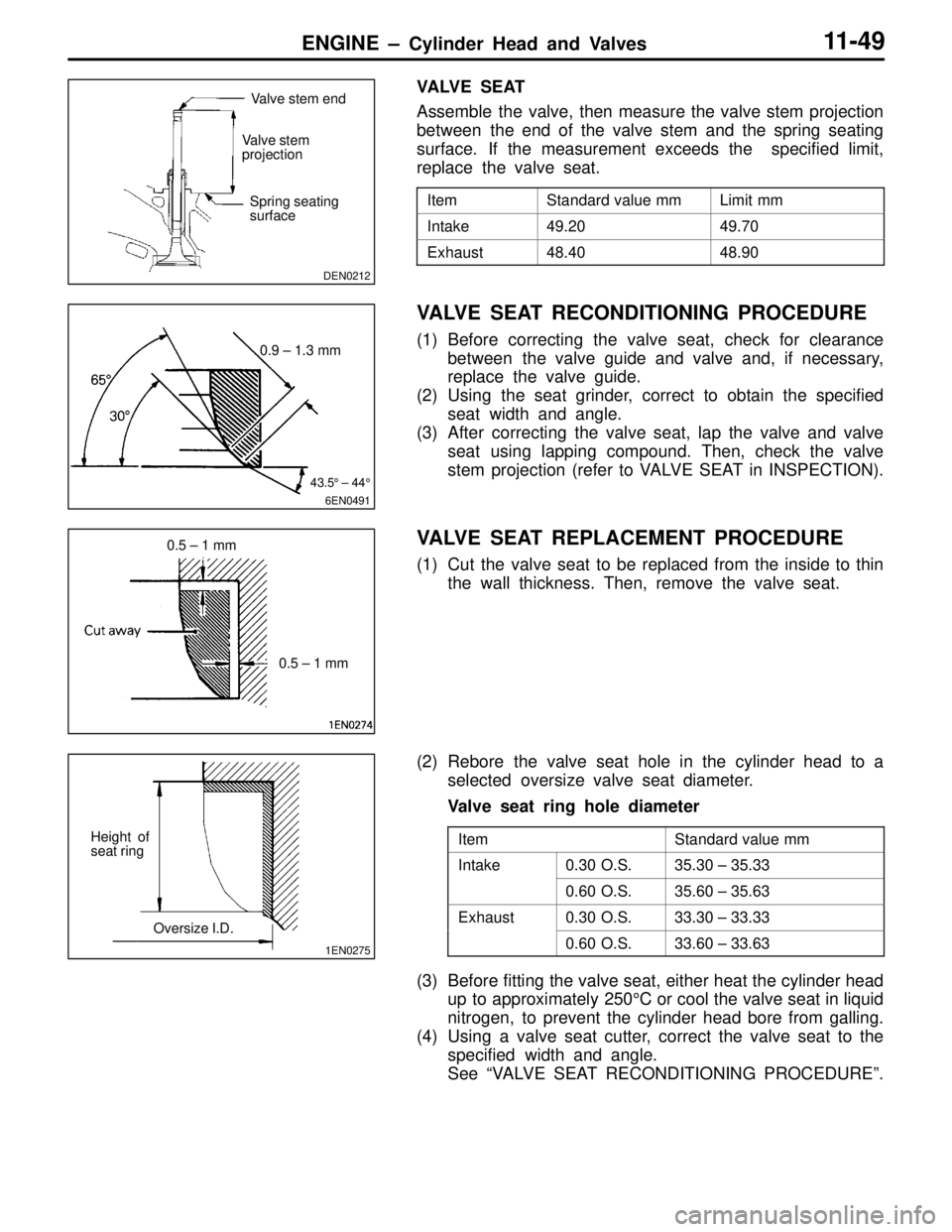
ENGINE – Cylinder Head and Valves11-49
VA LV E S E AT
Assemble the valve, then measure the valve stem projection
between the end of the valve stem and the spring seating
surface. If the measurement exceeds the specified limit,
replace the valve seat.
ItemStandard value mmLimit mm
Intake49.2049.70
Exhaust48.4048.90
VALVE SEAT RECONDITIONING PROCEDURE
(1) Before correcting the valve seat, check for clearance
between the valve guide and valve and, if necessary,
replace the valve guide.
(2) Using the seat grinder, correct to obtain the specified
seat width and angle.
(3) After correcting the valve seat, lap the valve and valve
seat using lapping compound. Then, check the valve
stem projection (refer to VALVE SEAT in INSPECTION).
VALVE SEAT REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Cut the valve seat to be replaced from the inside to thin
the wall thickness. Then, remove the valve seat.
(2) Rebore the valve seat hole in the cylinder head to a
selected oversize valve seat diameter.
Valve seat ring hole diameter
ItemStandard value mm
Intake0.30 O.S.35.30 – 35.33
0.60 O.S.35.60 – 35.63
Exhaust0.30 O.S.33.30 – 33.33
0.60 O.S.33.60 – 33.63
(3) Before fitting the valve seat, either heat the cylinder head
up to approximately 250°C or cool the valve seat in liquid
nitrogen, to prevent the cylinder head bore from galling.
(4) Using a valve seat cutter, correct the valve seat to the
specified width and angle.
See “VALVE SEAT RECONDITIONING PROCEDURE”.
DEN0212
Valve stem end
Valve stem
projection
Spring seating
surface
6EN0491
0.9 – 1.3 mm
43.5° – 44°
0.5 – 1 mm
0.5 – 1 mm
1EN0275
Height of
seat ring
Oversize I.D.