1999 LAND ROVER DEFENDER air filter
[x] Cancel search: air filterPage 231 of 667

18ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION SENSOR - AMBIENT AIR PRESSURE AND
TEMPERATURE (AAP)
The AAP sensor is located in the top of the air filter housing. It provides a voltage signal relative to ambient air
pressure to the ECM. The AAP sensor works on the piezo crystal principal. Piezo crystals are pressure sensitive
and will oscillate in accordance to changes in air pressure. The AAP sensor produces a voltage between 0 and 5
volts proportional to the pressure level of the air in the air filter housing. A reading of 0 volts indicates low pressure
and a reading of 5 volts a high pressure. The ECM uses this signal for the following functions.
To maintain manifold boost pressure.
To reduce exhaust smoke emissions while driving at high altitudes.
Control of the EGR system.
Inputs / Outputs
The ECM (C0158-8) supplies the AAP sensor (C0188-3) with a 5 volt feed on a pink/purple wire. The output signal
from the AAP sensor (C0188-2) is sent to the ECM (C0158-10) on a white/yellow wire. The AAP sensor is earthed
(C0188-1) via the ECM (C0158-30) on a pink/black wire.
The AAP sensor can fail, or supply an incorrect signal if one or more of the following occurs:
Sensor open circuit.
Short circuit to vehicle supply.
Short circuit to vehicle earth.
Contaminated sensor element.
Damaged sensor element.
Resistance in wiring harness.
In the event of an AAP sensor signal failure, any of the following symptoms may be observed:
Altitude compensation inoperative (engine will produce black smoke).
Active boost control inoperative.
Turbocharger boost pressure limited to 1 bar (14.5 lbf.in
2).
EGR altitude compensation inoperative.
In the event of a AAP sensor failure, the ECM will use a fixed default value from its memory.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 250 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
27
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION The turbocharger is exposed to extremely high operating temperatures (up to 1000°C, 1832°F) because of the
hot exhaust gases and the high speed revolution of the turbine (up to 15,000 rev/min). In order to resist wear of
the turbine bearings a flow of lubrication oil is supplied from the engine lubrication system to keep the bearings
cool. Oil is supplied from a tapping at the front of the full-flow filter adaptor housing via a metal pipe with banjo
connections. Oil is returned to the sump via a metal pipe which connects to the cylinder block at a port below the
turbocharger assembly.
A heatshield is attached to the LH side of the engine to protect adjacent components from the heat generated at
the turbocharger. The heatshield is attached to the engine by 2 bolts. An additional bolt attaches the heatshield to
the turbocharger casting.
The ECM controls the amount of boost pressure the engine receives by way of the turbocharger. When full boost
is reached a control signal is sent to the wastegate modulator, and a vacuum is applied to the wastegate valve.
The wastegate valve opens, bypassing some of the exhaust gases away from the turbine to be output to the
exhaust system.
The engine should be allowed to idle for 15 seconds following engine start up and before the engine is switched
off to protect the turbocharger by maintaining oil supply to the turbine bearings.
INTERCOOLER
The intercooler is an air-to-air heat exchanger which lowers the intake air temperature to obtain a higher air
density for better combustion efficiency. The intercooler receives compressed air from the turbocharger via a
metal pipe. It cools the intake air via the intercooler matrix and delivers it to the intake manifold by means of a
rubber hose which connects between the intercooler outlet and the intake manifold. The rubber hose is connected
to ports at each end by metal clips.
The intercooler is located at the front of the engine bay, forward of the radiator.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 254 of 667

19 - FUEL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
Page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COMPONENT LOCATION 1...................................................................................
DESCRIPTION 2.....................................................................................................
FUEL PUMP AND FUEL GAUGE SENDER 3........................................................
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR 5........................................................................
INJECTORS 7.........................................................................................................
FUEL FILTER 9.......................................................................................................
WATER SENSOR 10..............................................................................................
OPERATION 11......................................................................................................
ADJUSTMENT
HEATER PLUG TEST 1..........................................................................................
FUEL SYSTEM - BLEED 1.....................................................................................
FUEL TANK - DRAIN 2...........................................................................................
REPAIR
ELEMENT - AIR FILTER 1......................................................................................
SENSOR - FUEL TEMPERATURE 1......................................................................
SWITCH - INERTIA - FUEL CUT OFF 2.................................................................
SENSOR - MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) 2....................................................................
SENSOR - COMBINED MAP AND IAT 3................................................................
SENSOR - AMBIENT AIR PRESSURE (AAP) 3.....................................................
ELEMENT - FUEL FILTER 4...................................................................................
COOLER - FUEL 4..................................................................................................
TURBOCHARGER 5...............................................................................................
FILTER ASSEMBLY - AIR 6...................................................................................
INJECTOR - SET 7.................................................................................................
HEATER PLUGS - SET 9.......................................................................................
INTERCOOLER 9...................................................................................................
POTENTIOMETER - THROTTLE 10......................................................................
PUMP - FUEL 10.....................................................................................................
REGULATOR - FUEL PRESSURE 11....................................................................
FUEL TANK 12.......................................................................................................
NECK - FUEL TANK FILLER 14.............................................................................
ProCarManuals.com
Page 256 of 667

FUEL SYSTEM
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION COMPONENT LOCATION
1.HP stage
2.LP stage
3.Filters
4.Jet pump
5.Fuel pump and fuel gauge sender unit
6.LP return connection
7.LP feed connection8.HP feed connection
9.Air bleed connection
10.Fuel filter
11.Water sensor
12.Fuel cooler
13.Fuel pressure regulator
14.Electronic Unit Injectors
ProCarManuals.com
Page 257 of 667

19FUEL SYSTEM
2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
General
The fuel delivery system comprises a fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, five injectors and a fuel filter.
The system is controlled by the ECM, which energises the fuel pump relay and controls the operation and timing
of each injector solenoid.
Unlike other Diesel engines, the Td5 has no injection pump. The diesel direct injection system receives fuel at
pressure from a two stage fuel pump located in the fuel tank. The system incorporates a fuel return to the fuel
pump, via a fuel cooler attached to the inlet manifold, and a fuel filter. A fuel pressure regulator is located in a
housing on the rear of the cylinder head. The regulator maintains the fuel delivered to the injectors at a constant
pressure and returns excess fuel back to the fuel filter and pump via the fuel cooler.
A fuel filter is positioned on the chassis longitudinal, below the RH rear wheel arch. The fuel feed and return to and
from the engine passes through the filter. The filter also incorporates a water sensor, which illuminates a warning
lamp in the instrument pack.
A moulded fuel tank is located at the rear underside of the vehicle between the chassis longitudinals. The tank
provides the attachment for the fuel pump and the fuel gauge sender unit, which is located inside the tank.
Fuel Tank and Breather
The fuel tank and breather system is a major part of the fuel delivery system. The fuel tank and breathers are
located at the rear of the vehicle between the chassis longitudinals.
Fuel Tank
The moulded fuel tank is made from High Molecular Weight (HMW) High Density Polyethylene (HDPE), and is
manufactured using a proportion of recycled plastic.
The tank is held in position by a metal cradle which is secured to the chassis cross members by four bolts, two
holding the front of the cradle in position, two holding the rear. The fuel tank has a useable capacity of 75 litres
(16.5 gallons).
An aperture in the top surface of the tank allows for the fitment of the fuel pump and fuel gauge sender unit, which
is retained with a locking ring. A reflective metallic covering is attached to the tank with three scrivets to shield the
tank from heat generated by the exhaust system.
Fuel Tank Breather System
The fuel tank filler tube incorporates a tank vent which allows air and fuel vapour displaced from the tank when
filling to vent to atmosphere via the filler neck.
A breather spout within the tank controls the tank’Full’height. When fuel covers the spout it prevents fuel vapour
and air from escaping from the tank. This causes the fuel to’back-up’in the filler tube and shuts off the filler gun.
The position of the spout ensures that when the filler gun shuts off, a vapour space of approximately 10% of the
tanks total capacity remains. The vapour space ensures that the Roll Over Value (ROV) is always above the fuel
level and vapour can escape and allow the tank to breathe.
The ROV is welded to the top surface of the tank. It is connected by a tube to the filler tube, which in turn is
connected to the atmospheric vent pipe. The ROV allows fuel vapour to pass through it during normal vehicle
operation. In the event of the vehicle being overturned the valve shuts off, sealing the tank and preventing fuel
from spilling from the atmospheric vent pipe.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 258 of 667

FUEL SYSTEM
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION FUEL PUMP AND FUEL GAUGE SENDER
1.Fuel burning heater feed pipe (not used)
2.Air bleed connection (natural)
3.HP feed connection (green)
4.LP feed connection (blue)
5.LP return connection (black)
6.Pump feed pipe.
7.Spring
8.Fuel gauge sender unit9.Swirl pot
10.Gauze filter
11.Fuel gauge sender float
12.Electrical connections
13.HP/LP two stage pump
14.Pump LP return pipe
15.Electrical connector
The fuel pump is a self priming, wet type, two stage pump, which is emersed in fuel in the tank. It operates at all
times when the ignition switch is in position’II’. If the engine is not started, the ECM will’time-out’after three
minutes and de-energise the fuel pump relay.
The fuel pump assembly is retained with a locking ring and sealed with a rubber seal. The locking ring requires a
special tool for removal and refitment. The fuel gauge sender is integral with the fuel pump. The sender is
submerged in the fuel and is operated by a float which moves with the fuel level in the tank.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 264 of 667
FUEL SYSTEM
9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION FUEL FILTER
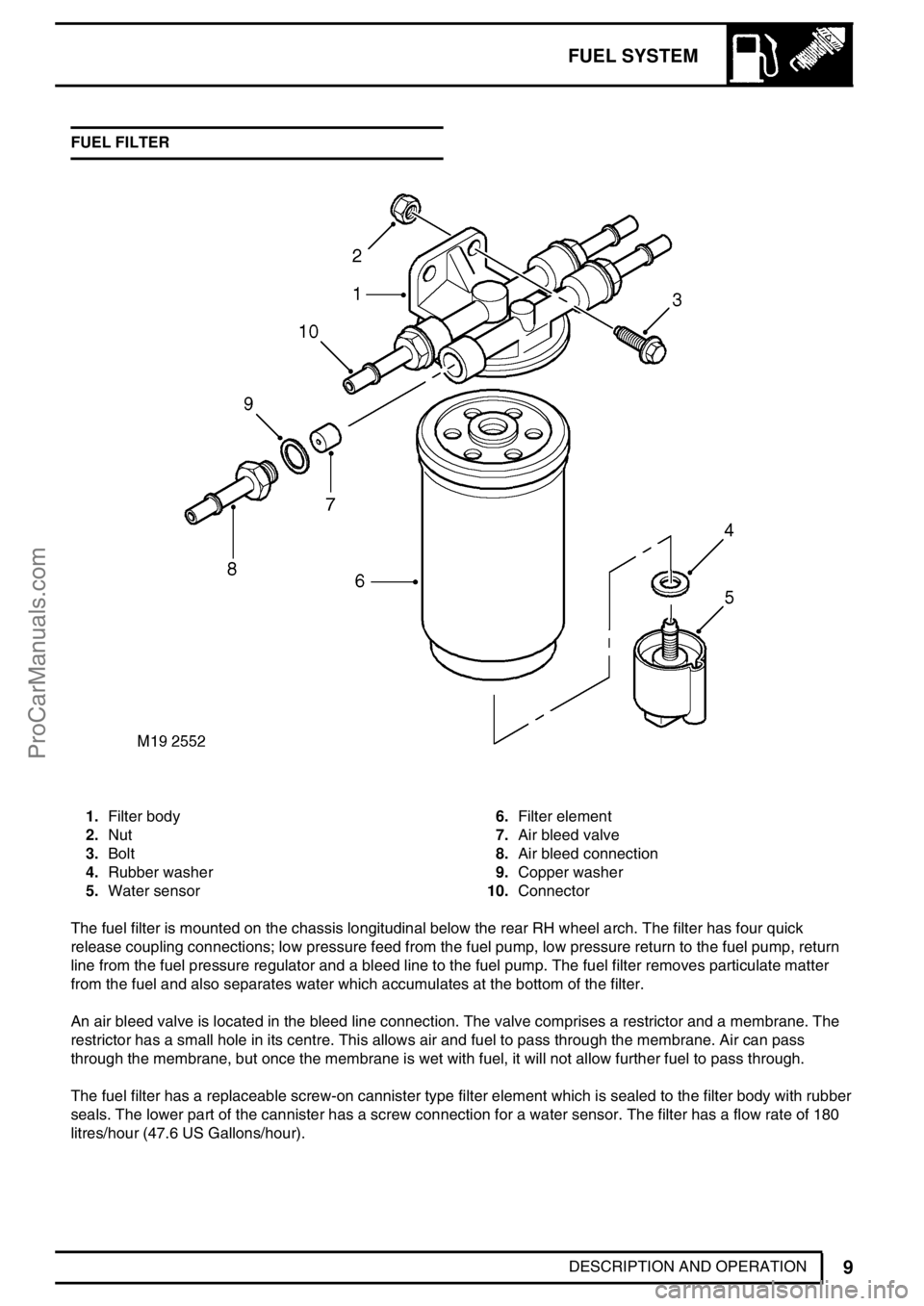
1.Filter body
2.Nut
3.Bolt
4.Rubber washer
5.Water sensor6.Filter element
7.Air bleed valve
8.Air bleed connection
9.Copper washer
10.Connector
The fuel filter is mounted on the chassis longitudinal below the rear RH wheel arch. The filter has four quick
release coupling connections; low pressure feed from the fuel pump, low pressure return to the fuel pump, return
line from the fuel pressure regulator and a bleed line to the fuel pump. The fuel filter removes particulate matter
from the fuel and also separates water which accumulates at the bottom of the filter.
An air bleed valve is located in the bleed line connection. The valve comprises a restrictor and a membrane. The
restrictor has a small hole in its centre. This allows air and fuel to pass through the membrane. Air can pass
through the membrane, but once the membrane is wet with fuel, it will not allow further fuel to pass through.
The fuel filter has a replaceable screw-on cannister type filter element which is sealed to the filter body with rubber
seals. The lower part of the cannister has a screw connection for a water sensor. The filter has a flow rate of 180
litres/hour (47.6 US Gallons/hour).
ProCarManuals.com
Page 270 of 667
FUEL SYSTEM
1
REPAIR ELEMENT - AIR FILTER
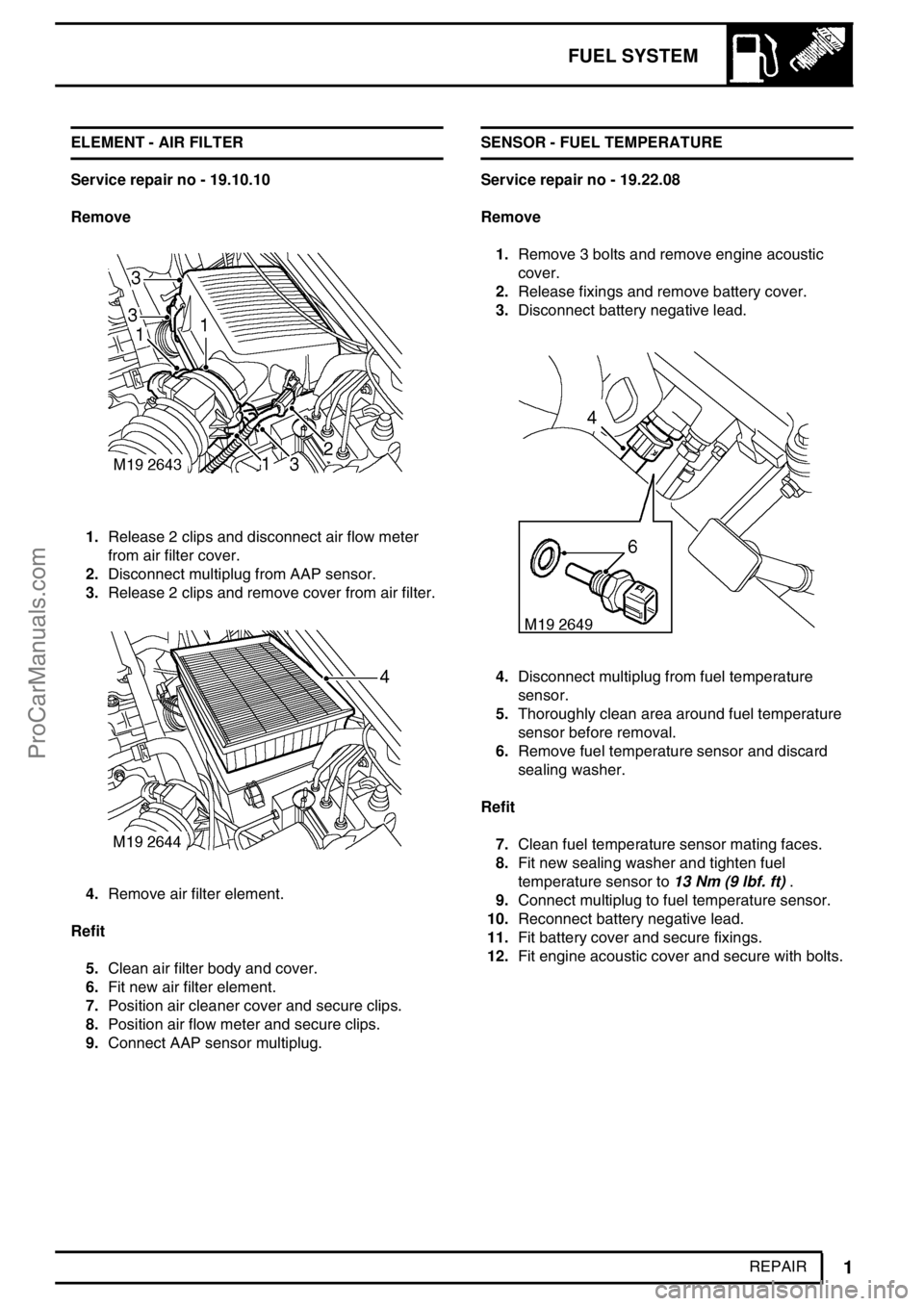
Service repair no - 19.10.10
Remove
1.Release 2 clips and disconnect air flow meter
from air filter cover.
2.Disconnect multiplug from AAP sensor.
3.Release 2 clips and remove cover from air filter.
4.Remove air filter element.
Refit
5.Clean air filter body and cover.
6.Fit new air filter element.
7.Position air cleaner cover and secure clips.
8.Position air flow meter and secure clips.
9.Connect AAP sensor multiplug.SENSOR - FUEL TEMPERATURE
Service repair no - 19.22.08
Remove
1.Remove 3 bolts and remove engine acoustic
cover.
2.Release fixings and remove battery cover.
3.Disconnect battery negative lead.
4.Disconnect multiplug from fuel temperature
sensor.
5.Thoroughly clean area around fuel temperature
sensor before removal.
6.Remove fuel temperature sensor and discard
sealing washer.
Refit
7.Clean fuel temperature sensor mating faces.
8.Fit new sealing washer and tighten fuel
temperature sensor to13 Nm (9 lbf. ft).
9.Connect multiplug to fuel temperature sensor.
10.Reconnect battery negative lead.
11.Fit battery cover and secure fixings.
12.Fit engine acoustic cover and secure with bolts.
ProCarManuals.com