1999 DODGE NEON change key battery
[x] Cancel search: change key batteryPage 331 of 1200
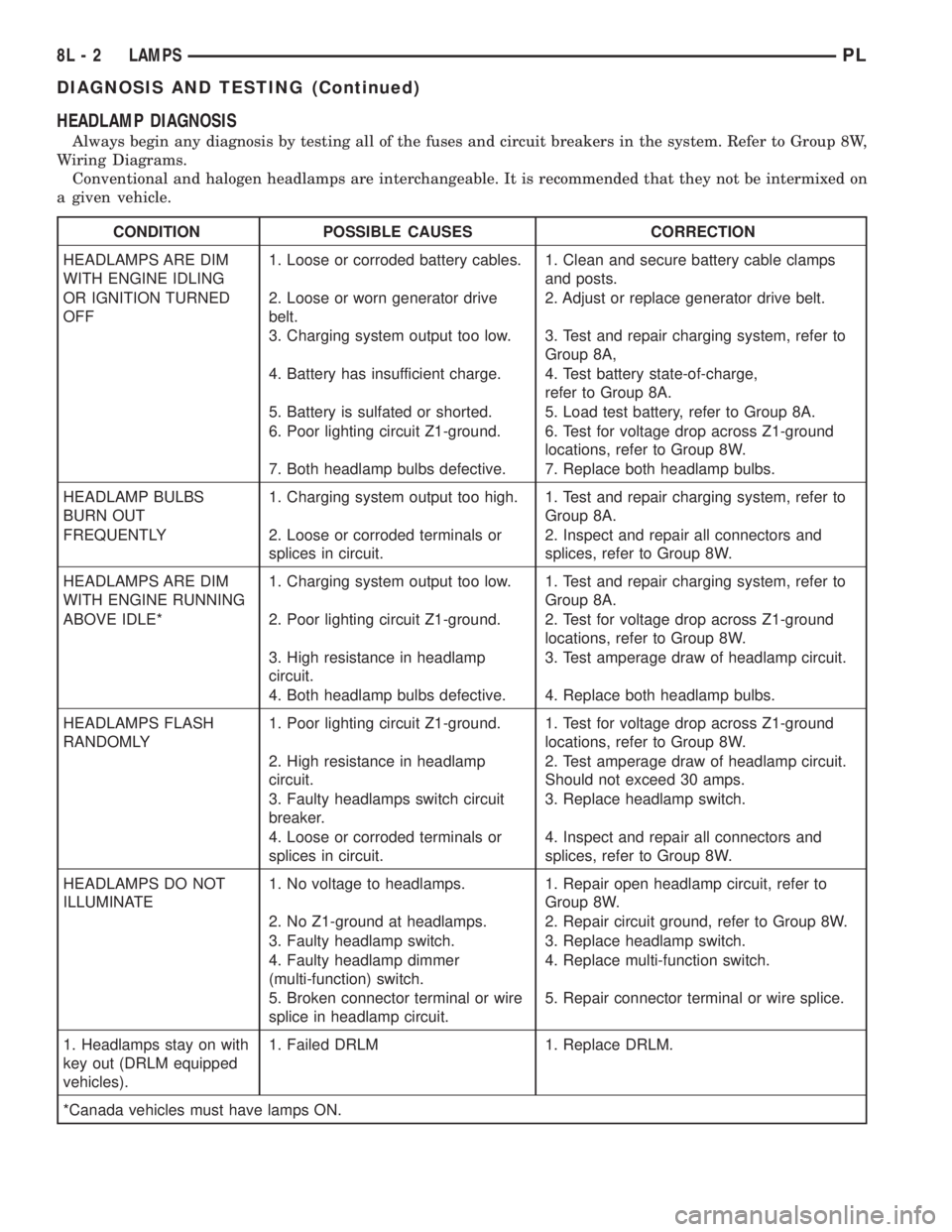
HEADLAMP DIAGNOSIS
Always begin any diagnosis by testing all of the fuses and circuit breakers in the system. Refer to Group 8W,
Wiring Diagrams.
Conventional and halogen headlamps are interchangeable. It is recommended that they not be intermixed on
a given vehicle.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HEADLAMPS ARE DIM
WITH ENGINE IDLING1. Loose or corroded battery cables. 1. Clean and secure battery cable clamps
and posts.
OR IGNITION TURNED
OFF2. Loose or worn generator drive
belt.2. Adjust or replace generator drive belt.
3. Charging system output too low. 3. Test and repair charging system, refer to
Group 8A,
4. Battery has insufficient charge. 4. Test battery state-of-charge,
refer to Group 8A.
5. Battery is sulfated or shorted. 5. Load test battery, refer to Group 8A.
6. Poor lighting circuit Z1-ground. 6. Test for voltage drop across Z1-ground
locations, refer to Group 8W.
7. Both headlamp bulbs defective. 7. Replace both headlamp bulbs.
HEADLAMP BULBS
BURN OUT1. Charging system output too high. 1. Test and repair charging system, refer to
Group 8A.
FREQUENTLY 2. Loose or corroded terminals or
splices in circuit.2. Inspect and repair all connectors and
splices, refer to Group 8W.
HEADLAMPS ARE DIM
WITH ENGINE RUNNING1. Charging system output too low. 1. Test and repair charging system, refer to
Group 8A.
ABOVE IDLE* 2. Poor lighting circuit Z1-ground. 2. Test for voltage drop across Z1-ground
locations, refer to Group 8W.
3. High resistance in headlamp
circuit.3. Test amperage draw of headlamp circuit.
4. Both headlamp bulbs defective. 4. Replace both headlamp bulbs.
HEADLAMPS FLASH
RANDOMLY1. Poor lighting circuit Z1-ground. 1. Test for voltage drop across Z1-ground
locations, refer to Group 8W.
2. High resistance in headlamp
circuit.2. Test amperage draw of headlamp circuit.
Should not exceed 30 amps.
3. Faulty headlamps switch circuit
breaker.3. Replace headlamp switch.
4. Loose or corroded terminals or
splices in circuit.4. Inspect and repair all connectors and
splices, refer to Group 8W.
HEADLAMPS DO NOT
ILLUMINATE1. No voltage to headlamps. 1. Repair open headlamp circuit, refer to
Group 8W.
2. No Z1-ground at headlamps. 2. Repair circuit ground, refer to Group 8W.
3. Faulty headlamp switch. 3. Replace headlamp switch.
4. Faulty headlamp dimmer
(multi-function) switch.4. Replace multi-function switch.
5. Broken connector terminal or wire
splice in headlamp circuit.5. Repair connector terminal or wire splice.
1. Headlamps stay on with
key out (DRLM equipped
vehicles).1. Failed DRLM 1. Replace DRLM.
*Canada vehicles must have lamps ON.
8L - 2 LAMPSPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 862 of 1200

GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
All engines used in this section have a sequential
Multi-Port Electronic Fuel Injection system. The MPI
system is computer regulated and provides precise
air/fuel ratios for all driving conditions. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) operates the fuel injec-
tion system.
The PCM regulates:
²Ignition timing
²Air/fuel ratio
²Emission control devices
²Cooling fan
²Charging system
²Idle speed
²Vehicle speed control
Various sensors provide the inputs necessary for
the PCM to correctly operate these systems. In addi-
tion to the sensors, various switches also provide
inputs to the PCM.
All inputs to the PCM are converted into signals.
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet chang-
ing operating conditions.
Fuel is injected into the intake port above the
intake valve in precise metered amounts through
electrically operated injectors. The PCM fires the
injectors in a specific sequence. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the PCM maintains an air fuel ratio
of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel by constantly adjust-
ing injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time the injector is open.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width by opening
and closing the ground path to the injector. Engine
RPM (speed) and manifold absolute pressure (air
density) are the primary inputs that determine injec-
tor pulse width.
MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). There are several differ-
ent modes of operation that determine how the PCM
responds to the various input signals.
There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP.
During OPEN LOOP modes the PCM receives
input signals and responds according to preset PCM
programming. Inputs from the upstream and down-
stream heated oxygen sensors are not monitored dur-
ing OPEN LOOP modes, except for heated oxygen
sensor diagnostics (they are checked for shorted con-
ditions at all times).During CLOSED LOOP modes the PCM monitors
the inputs from the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensors. The upstream heated oxygen
sensor input tells the PCM if the calculated injector
pulse width resulted in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7
to one. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen content
through the upstream heated oxygen sensor, the
PCM can fine tune injector pulse width. Fine tuning
injector pulse width allows the PCM to achieve opti-
mum fuel economy combined with low emissions.
For the PCM to enter CLOSED LOOP operation,
the following must occur:
(1) Engine coolant temperature must be over 35ÉF.
²If the coolant is over 35É the PCM will wait 44
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 50ÉF the PCM will wait 38
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 167ÉF the PCM will wait
11 seconds.
(2) For other temperatures the PCM will interpo-
late the correct waiting time.
(3) O2 sensor must read either greater than .745
volts or less than .1 volt.
(4) The multi-port fuel injection systems has the
following modes of operation:
²Ignition switch ON (Zero RPM)
²Engine start-up
²Engine warm-up
²Cruise
²Idle
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide Open Throttle
²Ignition switch OFF
(5) The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up,
deceleration with fuel shutoff and wide open throttle
modes are OPEN LOOP modes. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the acceleration, deceleration (with
A/C on), idle and cruise modes,with the engine at
operating temperatureare CLOSED LOOP modes.
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injec-
tion system, the following actions occur:
²The PCM monitors the engine coolant tempera-
ture sensor and throttle position sensor input. The
PCM determines basic fuel injector pulse width from
this input.
²The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to modify injector pulse
width.
When the key is in the ON position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the Auto Shutdown (ASD)
and fuel pump relays de-energize after approximately
1 second. Therefore, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel injectors and heated
oxygen sensors.
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 21
Page 875 of 1200

FUEL INJECTORSÐPCM OUTPUT
The 2.0L engine uses electrically operated top feed
fuel injectors (Fig. 26). The Automatic Shutdown
(ASD) relay supplies battery voltage to the fuel injec-
tors. The PCM controls the ground path for each
injector in sequence. By switching the ground paths
on and off, the PCM fine-tunes injector pulse width.
Injector pulse width refers to the amount of time an
injector operates.
The PCM determines injector synchronization from
the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position
sensor inputs. The PCM grounds the ASD and fuel
pump relays after receiving the camshaft position
sensor and crankshaft position sensor inputs.
The PCM energizes the injectors in a sequential
order during all engine operating conditions except
start-up. For the first injector pulse width during
start-up, all injectors are energized at the same time.
Once the PCM determines crankshaft position, it
begins energizing the injectors in sequence.
IGNITION COILÐPCM OUTPUT
The coil assembly consists of 2 coils molded
together. The coil assembly is mounted over the valve
cover (Fig. 27) or (Fig. 28). High tension leads route
to each cylinder from the coil. The coil fires two
spark plugs every power stroke. One plug is the cyl-
inder under compression, the other cylinder fires on
the exhaust stroke. Coil number one fires cylinders 1
and 4. Coil number two fires cylinders 2 and 3. The
PCM determines which of the coils to charge and fire
at the correct time.
The Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay provides battery
voltage to the ignition coil. The PCM provides a
ground contact (circuit) for energizing the coil. When
the PCM breaks the contact, the energy in the coil
primary transfers to the secondary causing the
spark. The PCM will de-energize the ASD relay if it
does not receive the crankshaft position sensor andcamshaft position sensor inputs. Refer to Auto Shut-
down (ASD) RelayÐPCM Output in this section for
relay operation.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR (CHECK ENGINE)
LAMPÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies the malfunction indicator (check
engine) lamp on/off signal to the instrument panel
through the CCD Bus. The CCD Bus is a communi-
cations port. Various modules use the CCD Bus to
exchange information.
The Check Engine lamp comes on each time the
ignition key is turned ON and stays on for 3 seconds
as a bulb test.
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) stays on
continuously, when the PCM has entered a Limp-In
mode or identified a failed emission component. Dur-
ing Limp-in Mode, the PCM attempts to keep the
system operational. The MIL signals the need for
immediate service. In limp-in mode, the PCM com-
pensates for the failure of certain components that
Fig. 26 Fuel Injector
Fig. 27 Ignition Coil PackÐSOHC
Fig. 28 Ignition Coil PackÐDOHC
14 - 34 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)