1998 OPEL FRONTERA battery
[x] Cancel search: batteryPage 4847 of 6000

6E–190
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0327 KS Sensor Circuit
D06RW035
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) uses the knock
sensor to detect engine detonation, allowing the PCM to
retard ignition control (IC) spark timing based on the
knock sensor (KS) signal being received. The knock
sensor produces an AC signal so that under a no knock
condition the signal on the KS circuit measures about
0.007 V AC. The signal amplitude and frequency are
dependent upon the amount of knock being experienced.
The PCM monitors the KS signal and can diagnose the
KS sensor and circuitry.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Engine running for at least 10 seconds.
The TP sensor is greater than 5%.
The ECT sensor is greater than 60C (140F).
Engine speed is between 2000 and 4000 RPM.
The knock sensor signal voltage is less than 0.20 volts,
or greater than 4.8 volts.
All conditions are present for more than 15 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
The PCM will use a calculated spark retard value to
minimize knock during conditions when knock is likely
to occur. The calculated value will vary based on
engine speed and load.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0327 can be cleared by using Tech 2 “Clear Info”
function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. Ensures that the fault is present.
4. The knock sensor is attached to a short jumper
harness, so it can be tested without removing the
intake manifold. A 2-wire connector for the knock
sensor is accessible behind the left rear fuel injector.
Page 4848 of 6000
6E–191 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
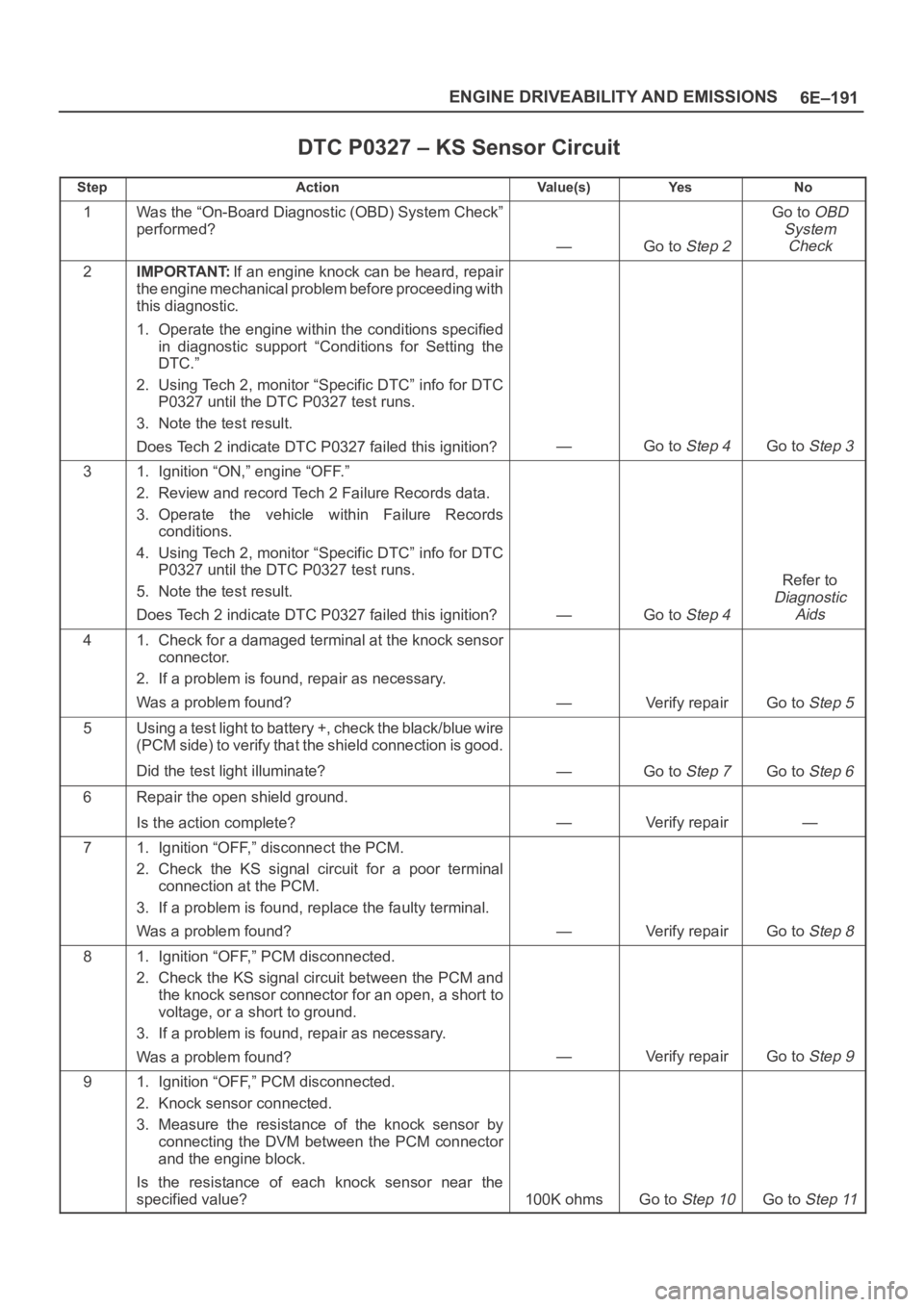
DTC P0327 – KS Sensor Circuit
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2IMPORTANT:If an engine knock can be heard, repair
the engine mechanical problem before proceeding with
this diagnostic.
1. Operate the engine within the conditions specified
in diagnostic support “Conditions for Setting the
DTC.”
2. Using Tech 2, monitor “Specific DTC” info for DTC
P0327 until the DTC P0327 test runs.
3. Note the test result.
Does Tech 2 indicate DTC P0327 failed this ignition?
—Go to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions.
4. Using Tech 2, monitor “Specific DTC” info for DTC
P0327 until the DTC P0327 test runs.
5. Note the test result.
Does Tech 2 indicate DTC P0327 failed this ignition?
—Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Check for a damaged terminal at the knock sensor
connector.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 5
5Using a test light to battery +, check the black/blue wire
(PCM side) to verify that the shield connection is good.
Did the test light illuminate?
—Go to Step 7Go to Step 6
6Repair the open shield ground.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
71. Ignition “OFF,” disconnect the PCM.
2. Check the KS signal circuit for a poor terminal
connection at the PCM.
3. If a problem is found, replace the faulty terminal.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Ignition “OFF,” PCM disconnected.
2. Check the KS signal circuit between the PCM and
the knock sensor connector for an open, a short to
voltage, or a short to ground.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
91. Ignition “OFF,” PCM disconnected.
2. Knock sensor connected.
3. Measure the resistance of the knock sensor by
connecting the DVM between the PCM connector
and the engine block.
Is the resistance of each knock sensor near the
specified value?
100K ohmsGo to Step 10Go to Step 11
Page 4850 of 6000
6E–193 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0336 58X Reference Signal Circuit
D06RW032
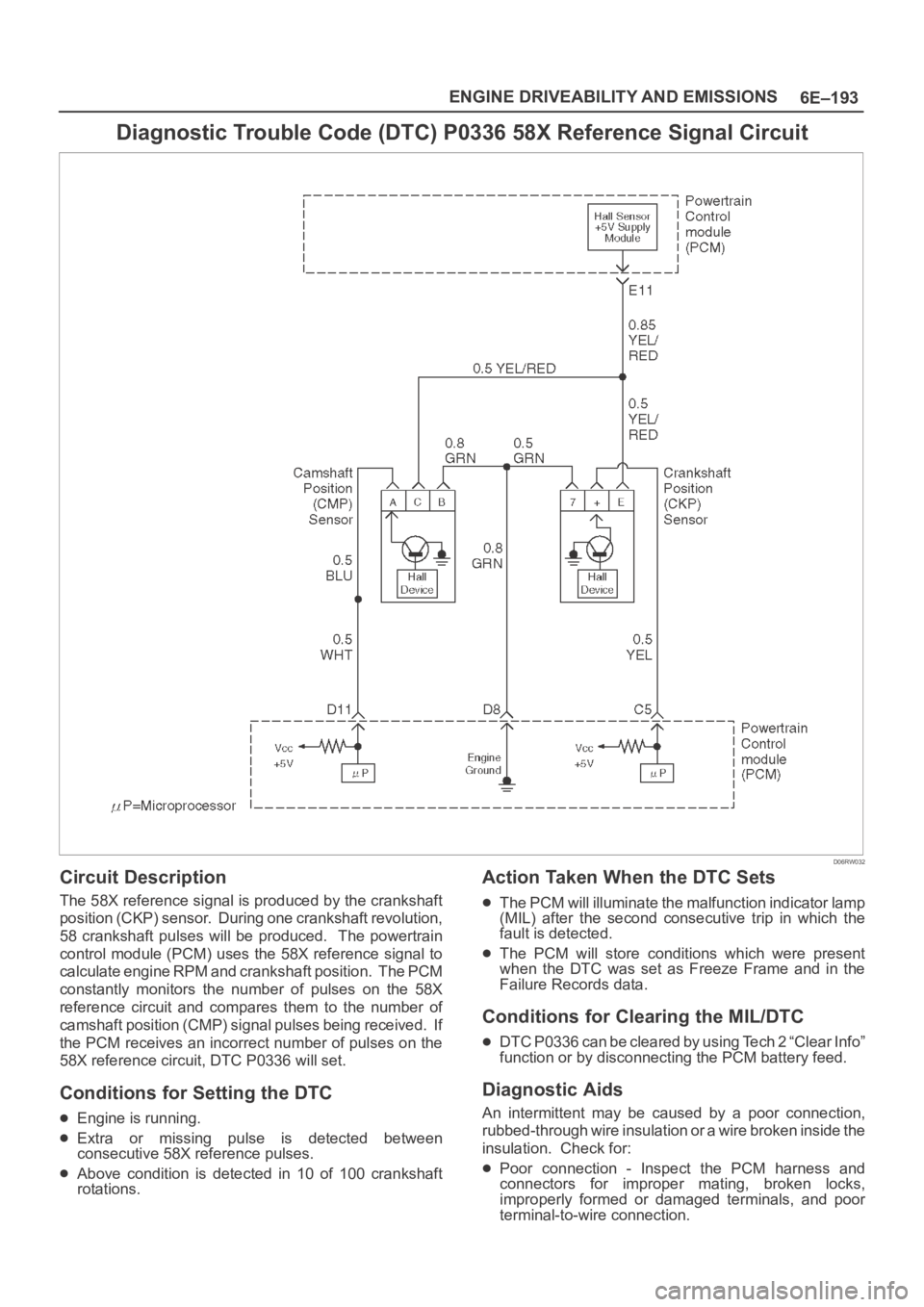
Circuit Description
The 58X reference signal is produced by the crankshaft
position (CKP) sensor. During one crankshaft revolution,
58 crankshaft pulses will be produced. The powertrain
control module (PCM) uses the 58X reference signal to
calculate engine RPM and crankshaft position. The PCM
constantly monitors the number of pulses on the 58X
reference circuit and compares them to the number of
camshaft position (CMP) signal pulses being received. If
the PCM receives an incorrect number of pulses on the
58X reference circuit, DTC P0336 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Engine is running.
Extra or missing pulse is detected between
consecutive 58X reference pulses.
Above condition is detected in 10 of 100 crankshaft
rotations.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0336 can be cleared by using Tech 2 “Clear Info”
function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
Poor connection - Inspect the PCM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal-to-wire connection.
Page 4852 of 6000
6E–195 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0337 CKP Sensor Circuit Low Frequency
D06RW032
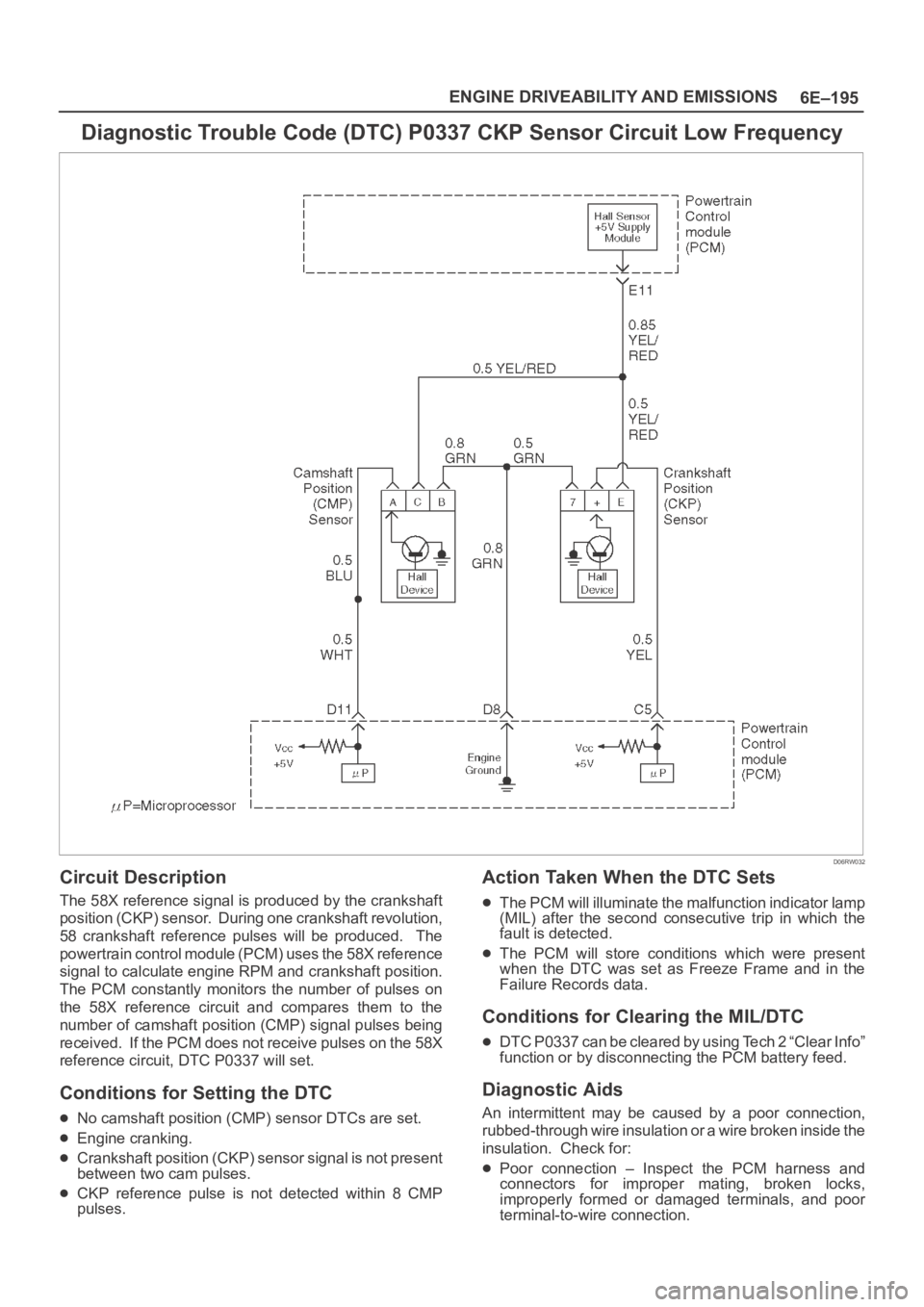
Circuit Description
The 58X reference signal is produced by the crankshaft
position (CKP) sensor. During one crankshaft revolution,
58 crankshaft reference pulses will be produced. The
powertrain control module (PCM) uses the 58X reference
signal to calculate engine RPM and crankshaft position.
The PCM constantly monitors the number of pulses on
the 58X reference circuit and compares them to the
number of camshaft position (CMP) signal pulses being
received. If the PCM does not receive pulses on the 58X
reference circuit, DTC P0337 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No camshaft position (CMP) sensor DTCs are set.
Engine cranking.
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor signal is not present
between two cam pulses.
CKP reference pulse is not detected within 8 CMP
pulses.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0337 can be cleared by using Tech 2 “Clear Info”
function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
Poor connection – Inspect the PCM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal-to-wire connection.
Page 4856 of 6000

6E–199 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0341 can be cleared by using Tech 2 “Clear Info”
function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
Poor connection – Inspect the PCM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect
the PCM, turn the ignition on and observe a voltmeter
connected to the CMP signal circuit at the PCM
harness connector while moving connectors andwiring harnesses related to the ICM and the CMP
sensor. A change in voltage will indicate the location
of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. Ensures that the fault is present.
12.Determines whether the fault is being caused by a
missing camshaft magnet or a faulty sensor. The
voltage measured in this step should read around 4
volts, toggling to near 0 volts when the CMP sensor
interfaces with the camshaft magnet.
Page 4860 of 6000
6E–203 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0342 can be cleared by using Tech 2 “Clear Info”
function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
Poor connection – Inspect the PCM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal to wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect
the PCM, turn the ignition on and observe a voltmeterconnected to the CMP signal circuit at the PCM
harness connector while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the ICM and the CMP
sensor. A change in voltage will indicate the location
of the fault.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. Ensures that the fault is present.
14.Determines whether the fault is being caused by a
missing camshaft magnet or a faulty PCM. The
voltage measured in this step should read around 4
volts, toggling to near 0 volts when the CMP sensor
interfaces with the camshaft magnet.
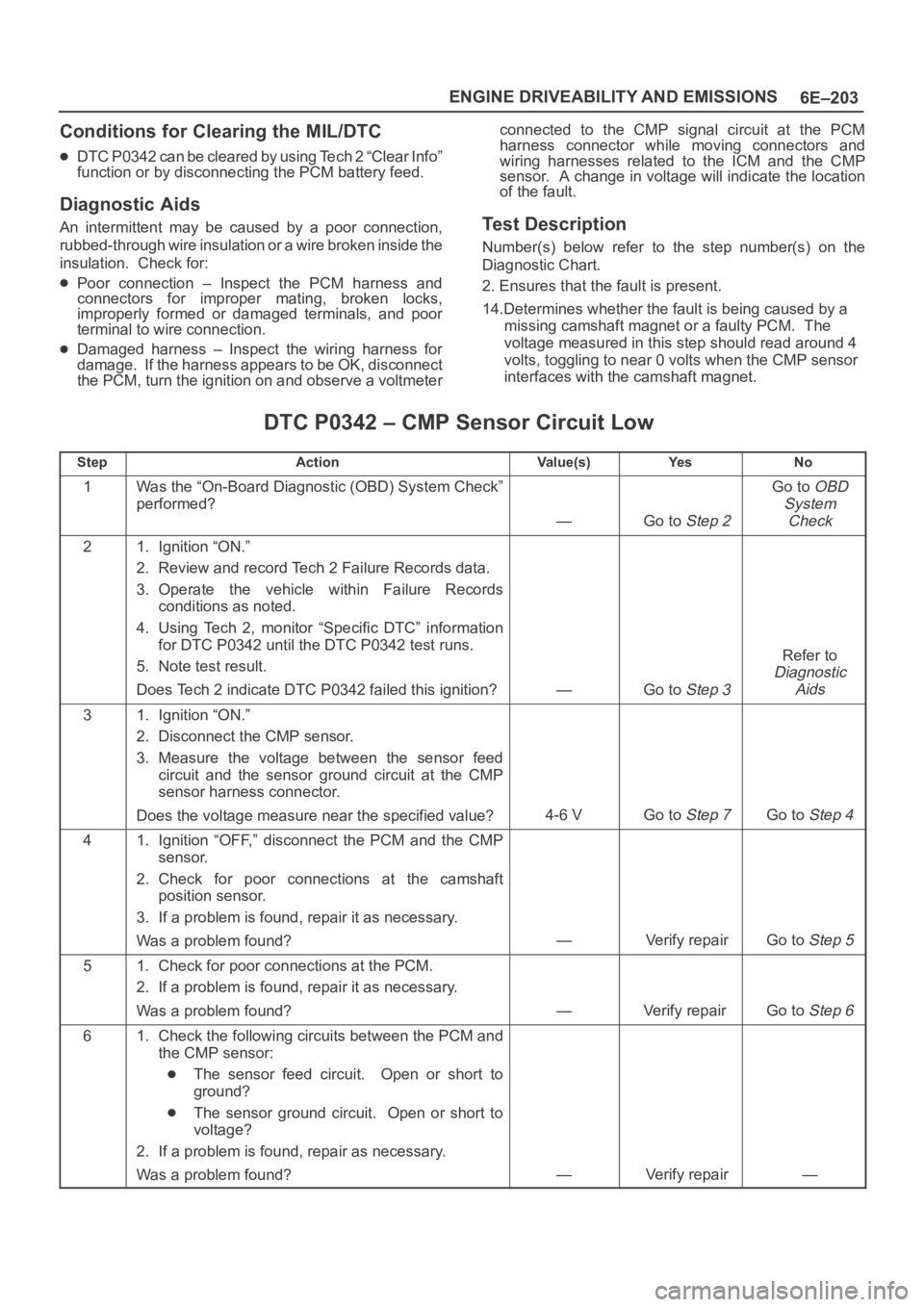
DTC P0342 – CMP Sensor Circuit Low
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition “ON.”
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using Tech 2, monitor “Specific DTC” information
for DTC P0342 until the DTC P0342 test runs.
5. Note test result.
Does Tech 2 indicate DTC P0342 failed this ignition?
—Go to Step 3
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
31. Ignition “ON.”
2. Disconnect the CMP sensor.
3. Measure the voltage between the sensor feed
circuit and the sensor ground circuit at the CMP
sensor harness connector.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value?
4-6 VGo to Step 7Go to Step 4
41. Ignition “OFF,” disconnect the PCM and the CMP
sensor.
2. Check for poor connections at the camshaft
position sensor.
3. If a problem is found, repair it as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 5
51. Check for poor connections at the PCM.
2. If a problem is found, repair it as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repair Go to Step 6
61. Check the following circuits between the PCM and
the CMP sensor:
The sensor feed circuit. Open or short to
ground?
The sensor ground circuit. Open or short to
voltage?
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repair—
Page 4863 of 6000
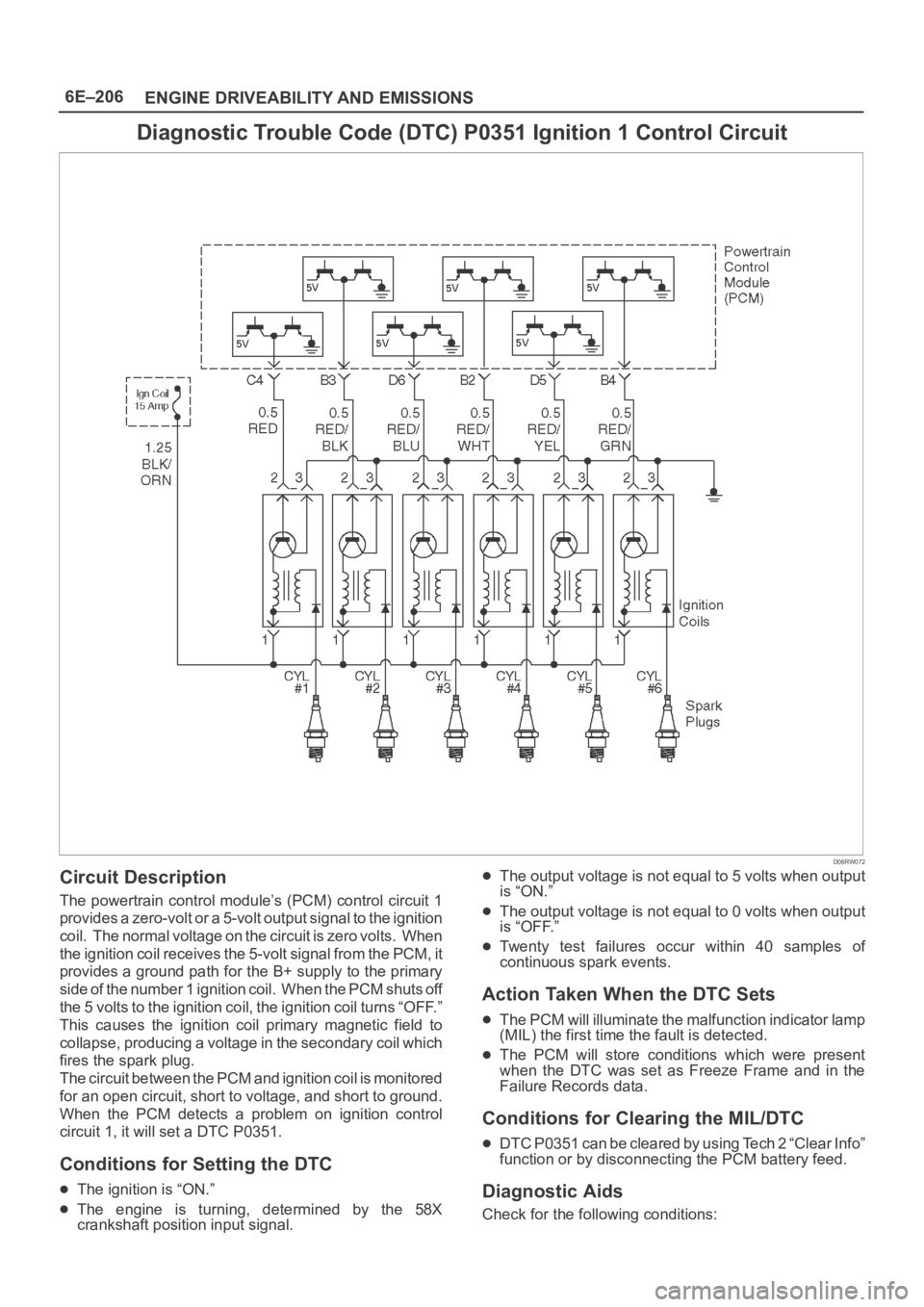
6E–206
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0351 Ignition 1 Control Circuit
D06RW072
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module’s (PCM) control circuit 1
provides a zero-volt or a 5-volt output signal to the ignition
coil. The normal voltage on the circuit is zero volts. When
the ignition coil receives the 5-volt signal from the PCM, it
provides a ground path for the B+ supply to the primary
side of the number 1 ignition coil. When the PCM shuts off
the 5 volts to the ignition coil, the ignition coil turns “OFF.”
This causes the ignition coil primary magnetic field to
collapse, producing a voltage in the secondary coil which
fires the spark plug.
The circuit between the PCM and ignition coil is monitored
for an open circuit, short to voltage, and short to ground.
When the PCM detects a problem on ignition control
circuit 1, it will set a DTC P0351.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ignition is “ON.”
The engine is turning, determined by the 58X
crankshaft position input signal.
The output voltage is not equal to 5 volts when output
is “ON.”
The output voltage is not equal to 0 volts when output
is “OFF.”
Twenty test failures occur within 40 samples of
continuous spark events.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0351 can be cleared by using Tech 2 “Clear Info”
function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Page 4866 of 6000
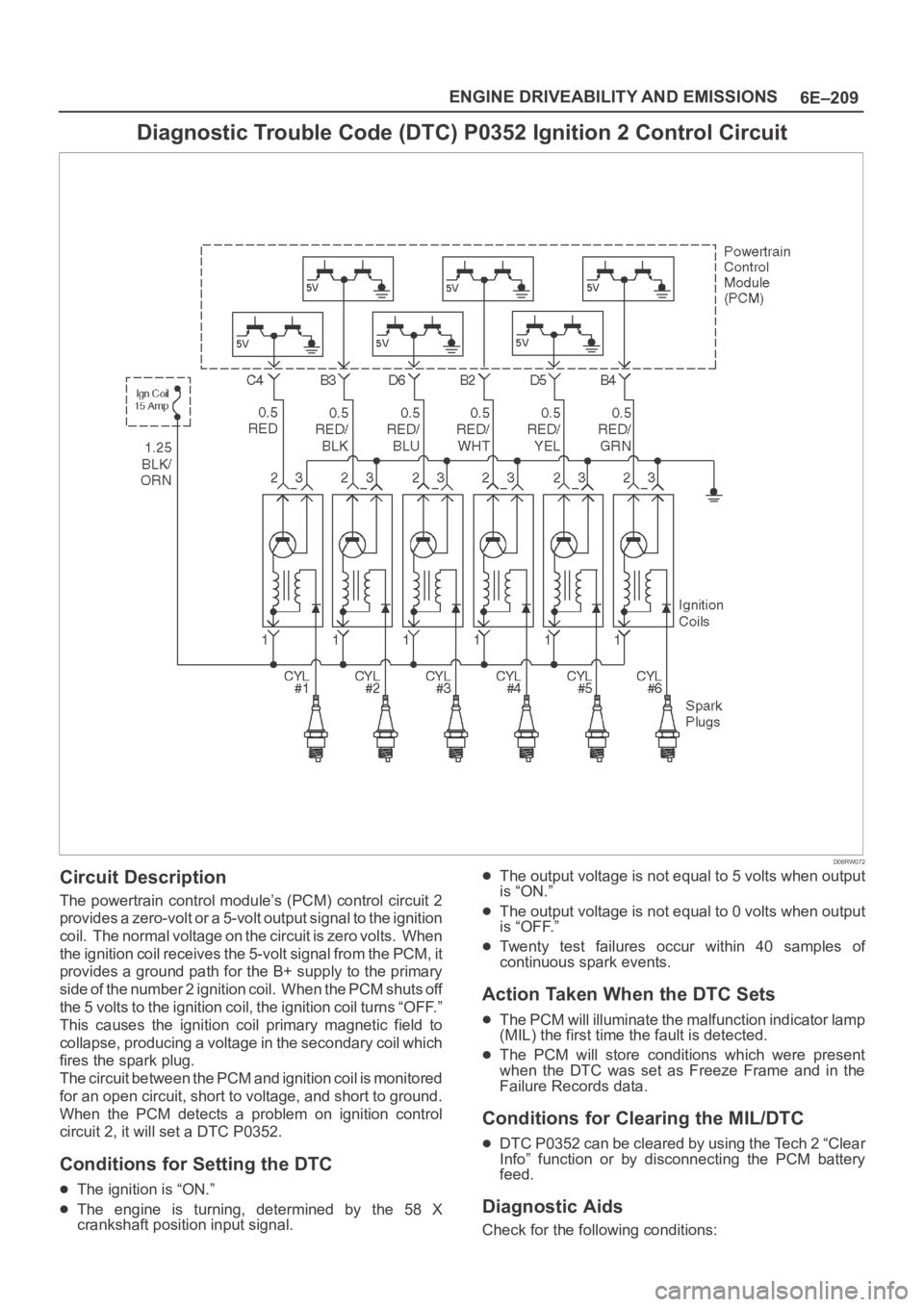
6E–209 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0352 Ignition 2 Control Circuit
D06RW072
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module’s (PCM) control circuit 2
provides a zero-volt or a 5-volt output signal to the ignition
coil. The normal voltage on the circuit is zero volts. When
the ignition coil receives the 5-volt signal from the PCM, it
provides a ground path for the B+ supply to the primary
side of the number 2 ignition coil. When the PCM shuts off
the 5 volts to the ignition coil, the ignition coil turns “OFF.”
This causes the ignition coil primary magnetic field to
collapse, producing a voltage in the secondary coil which
fires the spark plug.
The circuit between the PCM and ignition coil is monitored
for an open circuit, short to voltage, and short to ground.
When the PCM detects a problem on ignition control
circuit 2, it will set a DTC P0352.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ignition is “ON.”
The engine is turning, determined by the 58 X
crankshaft position input signal.
The output voltage is not equal to 5 volts when output
is “ON.”
The output voltage is not equal to 0 volts when output
is “OFF.”
Twenty test failures occur within 40 samples of
continuous spark events.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0352 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions: