1998 OPEL FRONTERA battery
[x] Cancel search: batteryPage 4739 of 6000
6E–82
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Engine Cranks But Will Not Run
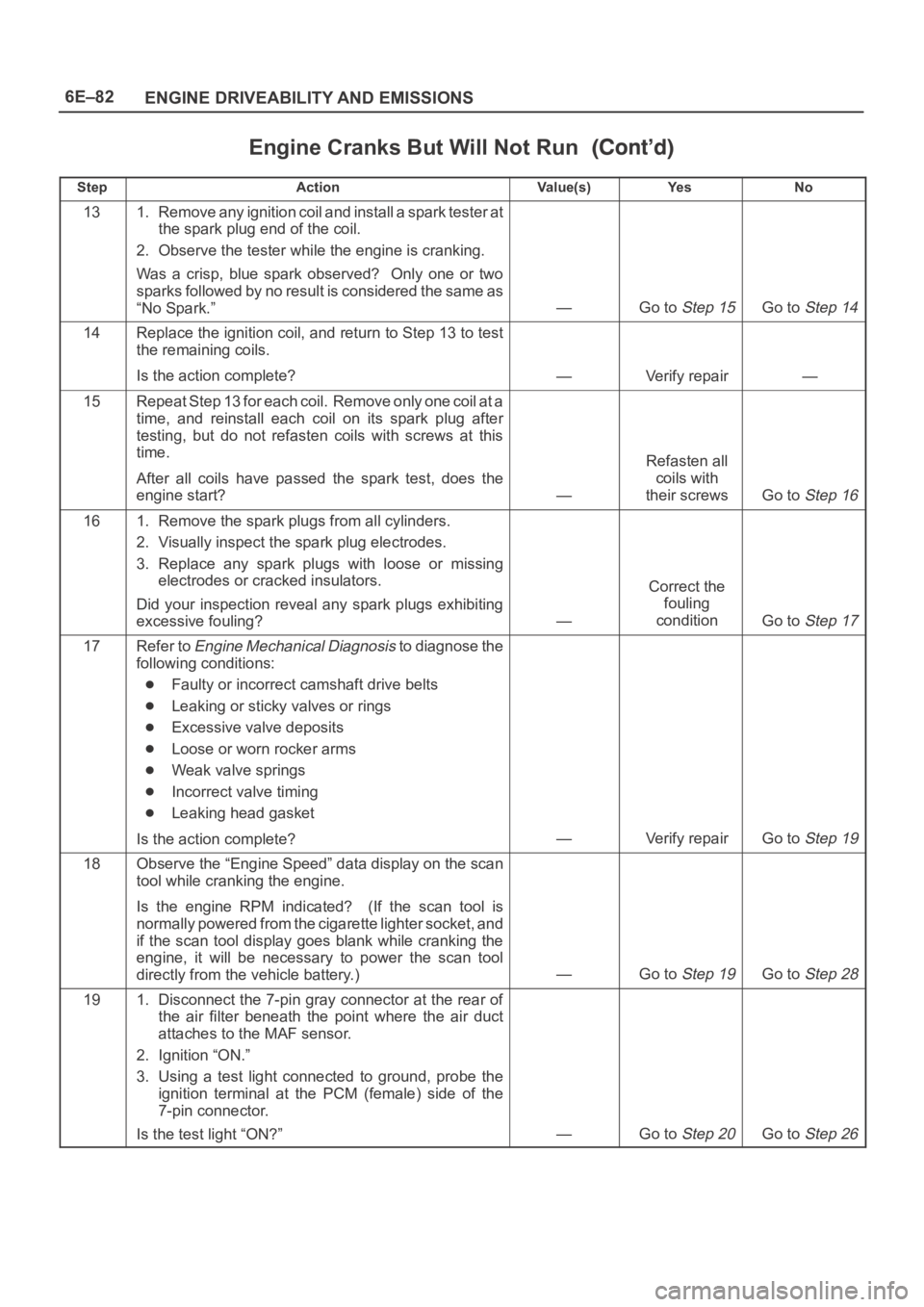
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
131. Remove any ignition coil and install a spark tester at
the spark plug end of the coil.
2. Observe the tester while the engine is cranking.
Was a crisp, blue spark observed? Only one or two
sparks followed by no result is considered the same as
“No Spark.”
—Go to Step 15Go to Step 14
14Replace the ignition coil, and return to Step 13 to test
the remaining coils.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
15Repeat Step 13 for each coil. Remove only one coil at a
time, and reinstall each coil on its spark plug after
testing, but do not refasten coils with screws at this
time.
After all coils have passed the spark test, does the
engine start?
—
Refasten all
coils with
their screws
Go to Step 16
161. Remove the spark plugs from all cylinders.
2. Visually inspect the spark plug electrodes.
3. Replace any spark plugs with loose or missing
electrodes or cracked insulators.
Did your inspection reveal any spark plugs exhibiting
excessive fouling?
—
Correct the
fouling
condition
Go to Step 17
17Refer to Engine Mechanical Diagnosis to diagnose the
following conditions:
Faulty or incorrect camshaft drive belts
Leaking or sticky valves or rings
Excessive valve deposits
Loose or worn rocker arms
Weak valve springs
Incorrect valve timing
Leaking head gasket
Is the action complete?
—Verify repairGo to Step 19
18Observe the “Engine Speed” data display on the scan
tool while cranking the engine.
Is the engine RPM indicated? (If the scan tool is
normally powered from the cigarette lighter socket, and
if the scan tool display goes blank while cranking the
engine, it will be necessary to power the scan tool
directly from the vehicle battery.)
—Go to Step 19Go to Step 28
191. Disconnect the 7-pin gray connector at the rear of
the air filter beneath the point where the air duct
attaches to the MAF sensor.
2. Ignition “ON.”
3. Using a test light connected to ground, probe the
ignition terminal at the PCM (female) side of the
7-pin connector.
Is the test light “ON?”
—Go to Step 20Go to Step 26
Page 4743 of 6000
6E–86
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
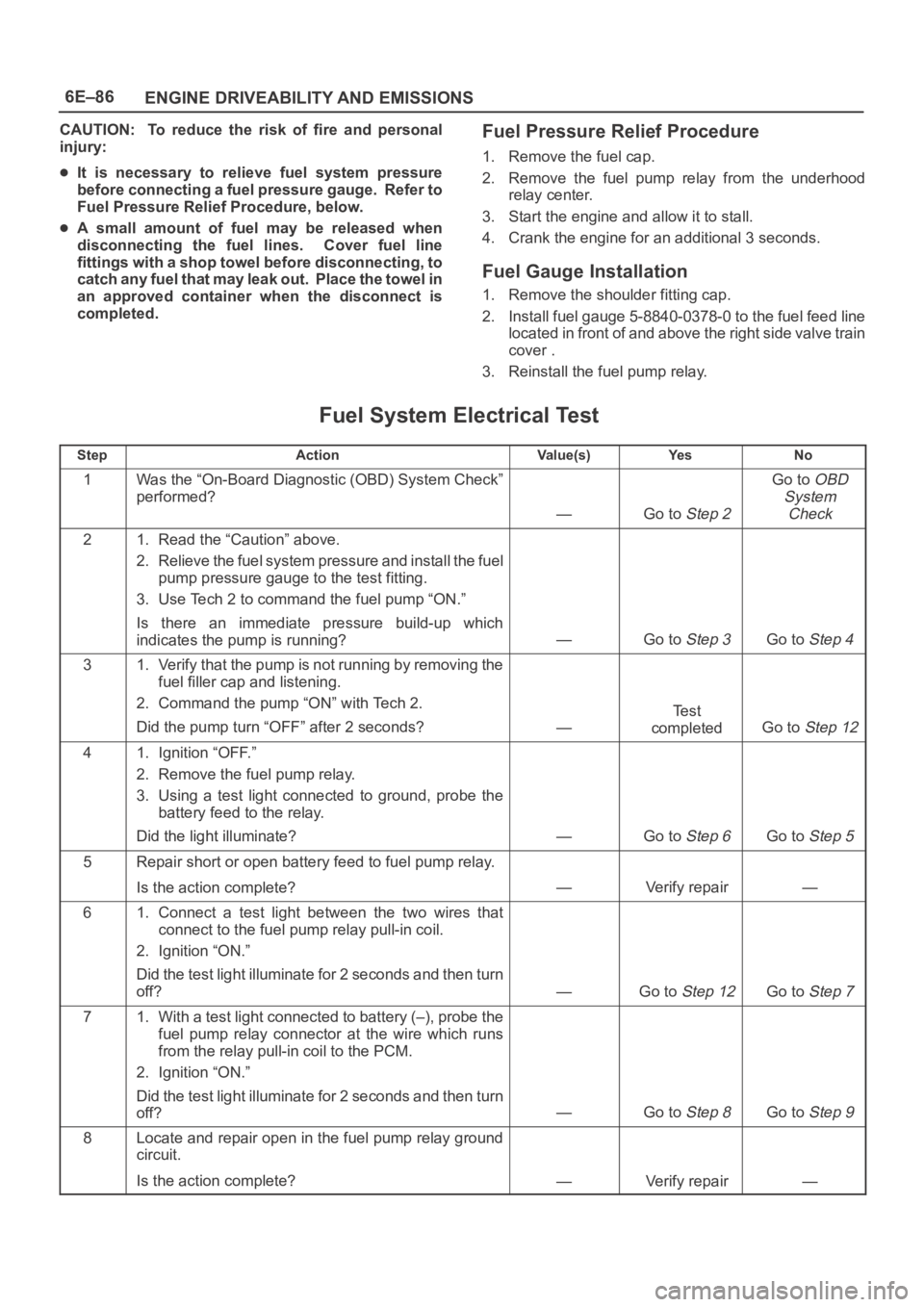
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury:
It is necessary to relieve fuel system pressure
before connecting a fuel pressure gauge. Refer to
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure, below.
A small amount of fuel may be released when
disconnecting the fuel lines. Cover fuel line
fittings with a shop towel before disconnecting, to
catch any fuel that may leak out. Place the towel in
an approved container when the disconnect is
completed.
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
1. Remove the fuel cap.
2. Remove the fuel pump relay from the underhood
relay center.
3. Start the engine and allow it to stall.
4. Crank the engine for an additional 3 seconds.
Fuel Gauge Installation
1. Remove the shoulder fitting cap.
2. Install fuel gauge 5-8840-0378-0 to the fuel feed line
located in front of and above the right side valve train
cover .
3. Reinstall the fuel pump relay.
Fuel System Electrical Test
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Read the “Caution” above.
2. Relieve the fuel system pressure and install the fuel
pump pressure gauge to the test fitting.
3. Use Tech 2 to command the fuel pump “ON.”
Is there an immediate pressure build-up which
indicates the pump is running?
—Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
31. Verify that the pump is not running by removing the
fuel filler cap and listening.
2. Command the pump “ON” with Tech 2.
Did the pump turn “OFF” after 2 seconds?
—
Te s t
completed
Go to Step 12
41. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Remove the fuel pump relay.
3. Using a test light connected to ground, probe the
battery feed to the relay.
Did the light illuminate?
—Go to Step 6Go to Step 5
5Repair short or open battery feed to fuel pump relay.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
61. Connect a test light between the two wires that
connect to the fuel pump relay pull-in coil.
2. Ignition “ON.”
Did the test light illuminate for 2 seconds and then turn
off?
—Go to Step 12Go to Step 7
71. With a test light connected to battery (–), probe the
fuel pump relay connector at the wire which runs
from the relay pull-in coil to the PCM.
2. Ignition “ON.”
Did the test light illuminate for 2 seconds and then turn
off?
—Go to Step 8Go to Step 9
8Locate and repair open in the fuel pump relay ground
circuit.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 4755 of 6000
6E–98
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
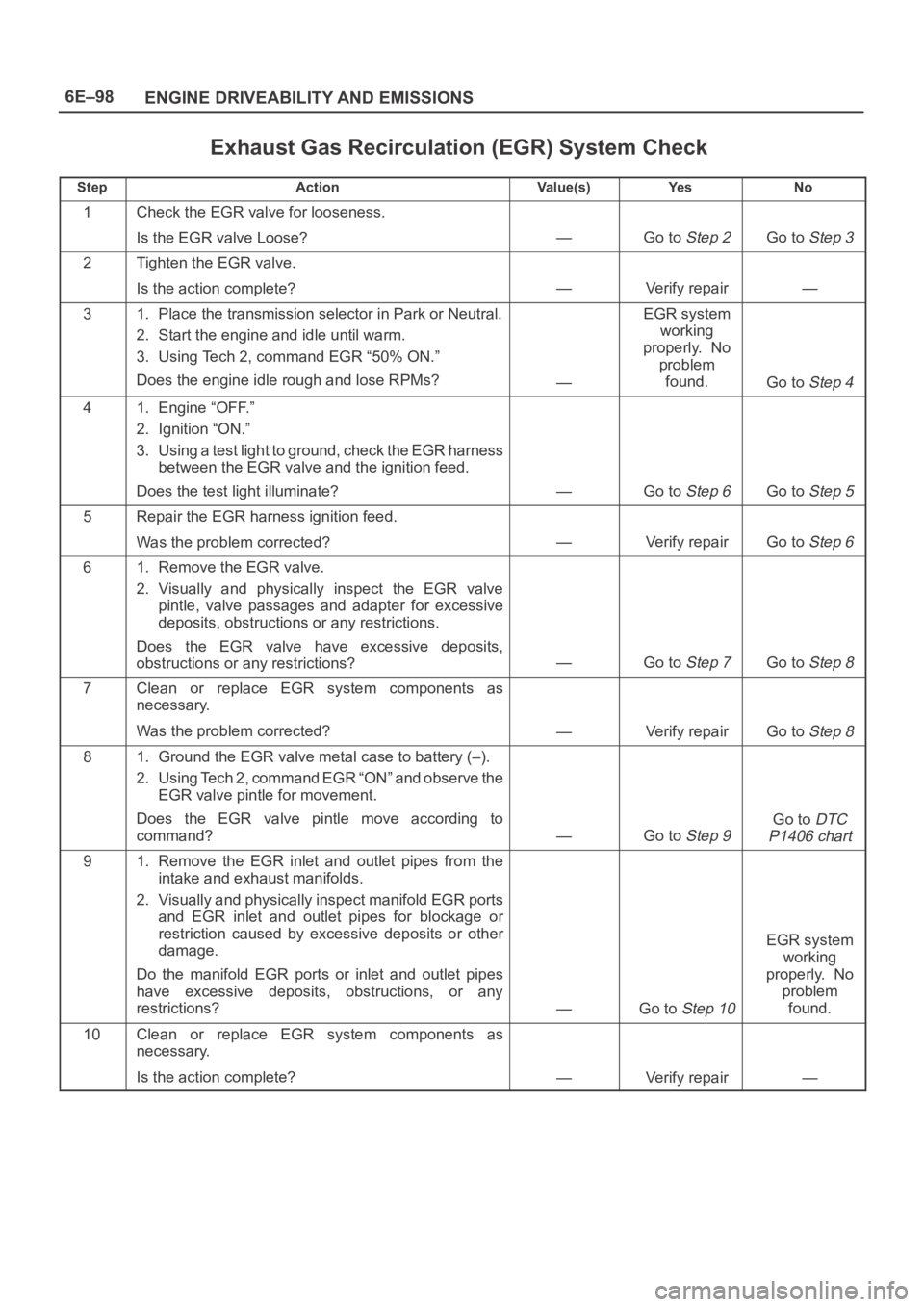
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Check
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Check the EGR valve for looseness.
Is the EGR valve Loose?
—Go to Step 2Go to Step 3
2Tighten the EGR valve.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
31. Place the transmission selector in Park or Neutral.
2. Start the engine and idle until warm.
3. Using Tech 2, command EGR “50% ON.”
Does the engine idle rough and lose RPMs?
—
EGR system
working
properly. No
problem
found.
Go to Step 4
41. Engine “OFF.”
2. Ignition “ON.”
3. Using a test light to ground, check the EGR harness
between the EGR valve and the ignition feed.
Does the test light illuminate?
—Go to Step 6Go to Step 5
5Repair the EGR harness ignition feed.
Was the problem corrected?
—Verify repairGo to Step 6
61. Remove the EGR valve.
2. Visually and physically inspect the EGR valve
pintle, valve passages and adapter for excessive
deposits, obstructions or any restrictions.
Does the EGR valve have excessive deposits,
obstructions or any restrictions?
—Go to Step 7Go to Step 8
7Clean or replace EGR system components as
necessary.
Was the problem corrected?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Ground the EGR valve metal case to battery (–).
2. Using Tech 2, command EGR “ON” and observe the
EGR valve pintle for movement.
Does the EGR valve pintle move according to
command?
—Go to Step 9
Go to DTC
P1406 chart
91. Remove the EGR inlet and outlet pipes from the
intake and exhaust manifolds.
2. Visually and physically inspect manifold EGR ports
and EGR inlet and outlet pipes for blockage or
restriction caused by excessive deposits or other
damage.
Do the manifold EGR ports or inlet and outlet pipes
have excessive deposits, obstructions, or any
restrictions?
—Go to Step 10
EGR system
working
properly. No
problem
found.
10Clean or replace EGR system components as
necessary.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 4761 of 6000

6E–104
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0101 MAF System Performance
D06RW103
Circuit Description
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of
air which passes through it into the engine during a given
time. The powertrain control module (PCM) uses the
mass air flow information to monitor engine operating
conditions for fuel delivery calculations. A large quantity
of air entering the engine indicates an acceleration or high
load situation, while a small quantity or air indicates
deceleration or idle.
The MAF sensor produces a frequency signal which can
be monitored using a Tech 2. DTC P0101 will be set if the
signal from the MAF sensor does not match a predicted
value based on throttle position and engine RPM.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The engine is running.
No TP sensor or MAP sensor DTCs are set.
The throttle is steady, TP angle doesn’t change by
more than 1%.
System voltage is between 11.5 volts and 16 volts.
Calculated air flow is between 25 g/second and 40
g/second.
Above conditions present for at least 1 second.
MAF signal frequency indicates an airflow significantly
higher or lower than a predicted value based on throttle
position and engine RPM for a total of 12.5 seconds
over a 25-second period of time.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
The PCM calculates an airflow value based on idle air
control valve position, throttle position, RPM and
barometric pressure.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0101 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by the following:
Poor connections.
Mis-routed harness.
Rubbed through wire insulation.
Broken wire inside the insulation.
Refer to Intermittents under service category Symptoms.
Any un-metered air may cause this DTC to set. Check for
the following:
The duct work at the MAF sensor for leaks.
An engine vacuum leak.
The PCV system for vacuum leaks.
An incorrect PCV valve.
Page 4764 of 6000
6E–107 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
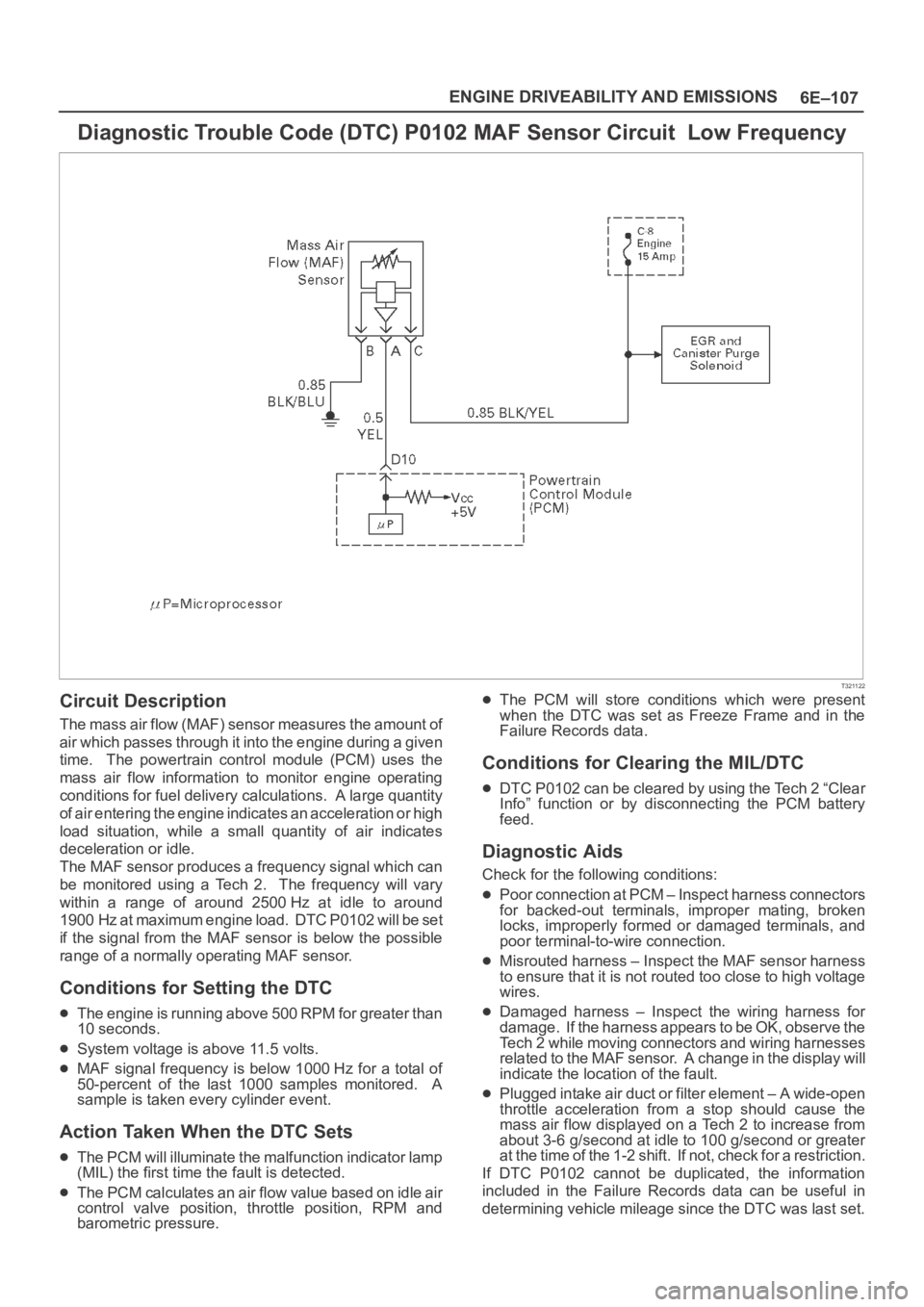
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0102 MAF Sensor Circuit Low Frequency
T321122
Circuit Description
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of
air which passes through it into the engine during a given
time. The powertrain control module (PCM) uses the
mass air flow information to monitor engine operating
conditions for fuel delivery calculations. A large quantity
of air entering the engine indicates an acceleration or high
load situation, while a small quantity of air indicates
deceleration or idle.
The MAF sensor produces a frequency signal which can
be monitored using a Tech 2. The frequency will vary
within a range of around 2500 Hz at idle to around
1900 Hz at maximum engine load. DTC P0102 will be set
if the signal from the MAF sensor is below the possible
range of a normally operating MAF sensor.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The engine is running above 500 RPM for greater than
10 seconds.
System voltage is above 11.5 volts.
MAF signal frequency is below 1000 Hz for a total of
50-percent of the last 1000 samples monitored. A
sample is taken every cylinder event.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM calculates an air flow value based on idle air
control valve position, throttle position, RPM and
barometric pressure.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0102 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Misrouted harness – Inspect the MAF sensor harness
to ensure that it is not routed too close to high voltage
wires.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
Tech 2 while moving connectors and wiring harnesses
related to the MAF sensor. A change in the display will
indicate the location of the fault.
Plugged intake air duct or filter element – A wide-open
throttle acceleration from a stop should cause the
mass air flow displayed on a Tech 2 to increase from
about 3-6 g/second at idle to 100 g/second or greater
at the time of the 1-2 shift. If not, check for a restriction.
If DTC P0102 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Page 4765 of 6000
6E–108
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. This step verifies that the problem is present at idle.4. A voltage reading of less than 4 or over 5 volts at the
MAF sensor signal circuit indicates a fault in the
wiring or a poor connection.
5. This verifies that ignition feed voltage and a good
ground are available at the MAF sensor.
DTC P0102 – MAF Sensor Circuit Low Frequency
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Start the engine.
2. With the engine idling, monitor “MAF Frequency”
display on the Tech 2.
Is the “MAF Frequency” below the specified value?
3g/SecGo to Step 4Go to Step 5
31. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor “DTC” info for DTC P0102.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P0102 failed this
ignition?
—Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Disconnect the MAF sensor connector.
3. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
4. Using a DVM, measure voltage between the MAF
sensor signal circuit and battery ground.
Is the voltage near the specified value?
5 VGo to Step 5Go to Step 8
5Connect a test light between the MAF sensor ignition
feed and ground circuits at the MAF sensor harness
connector.
Is the test light “ON?”
—Go to Step 13Go to Step 6
6Connect a test light between the MAF sensor ignition
feed circuit and battery ground.
Is the test light “ON?”
—Go to Step 12Go to Step 7
71. Check for a poor connection at the MAF sensor.
2. If a poor connection is found, replace the faulty
terminal(s).
Was a poor connection found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 11
81. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Disconnect the MAF sensor.
3. Disconnect the PCM connector for the MAF signal
circuit.
4. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
5. With the DVM, measure the voltage between the
MAF signal terminal at the PCM and battery ground.
Is the voltage under the specified value?
4 VGo to Step 9Go to Step 10
Page 4767 of 6000
6E–110
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
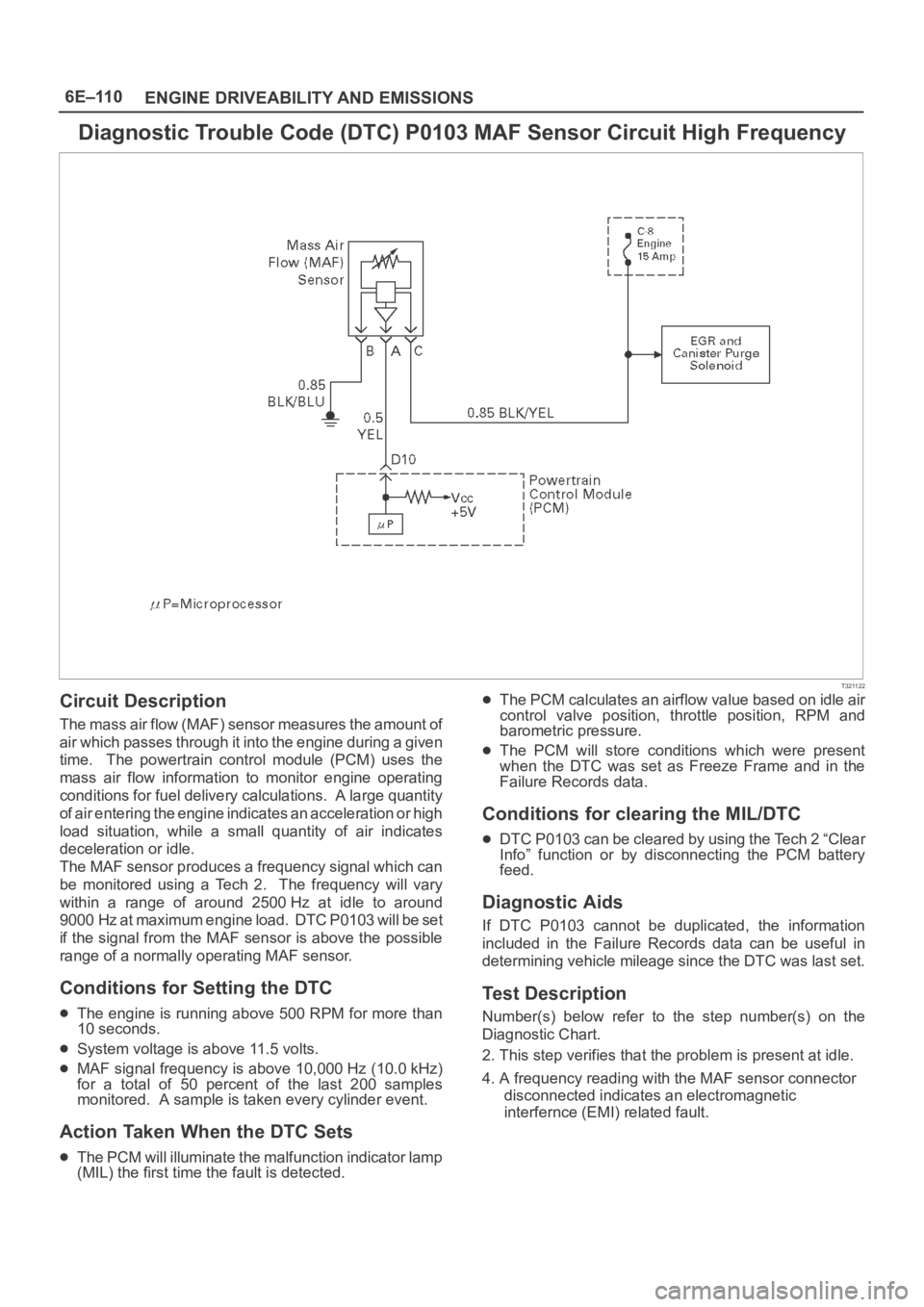
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0103 MAF Sensor Circuit High Frequency
T321122
Circuit Description
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of
air which passes through it into the engine during a given
time. The powertrain control module (PCM) uses the
mass air flow information to monitor engine operating
conditions for fuel delivery calculations. A large quantity
of air entering the engine indicates an acceleration or high
load situation, while a small quantity of air indicates
deceleration or idle.
The MAF sensor produces a frequency signal which can
be monitored using a Tech 2. The frequency will vary
within a range of around 2500 Hz at idle to around
9000 Hz at maximum engine load. DTC P0103 will be set
if the signal from the MAF sensor is above the possible
range of a normally operating MAF sensor.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The engine is running above 500 RPM for more than
10 seconds.
System voltage is above 11.5 volts.
MAF signal frequency is above 10,000 Hz (10.0 kHz)
for a total of 50 percent of the last 200 samples
monitored. A sample is taken every cylinder event.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM calculates an airflow value based on idle air
control valve position, throttle position, RPM and
barometric pressure.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0103 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
If DTC P0103 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. This step verifies that the problem is present at idle.
4. A frequency reading with the MAF sensor connector
disconnected indicates an electromagnetic
interfernce (EMI) related fault.
Page 4769 of 6000
6E–112
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
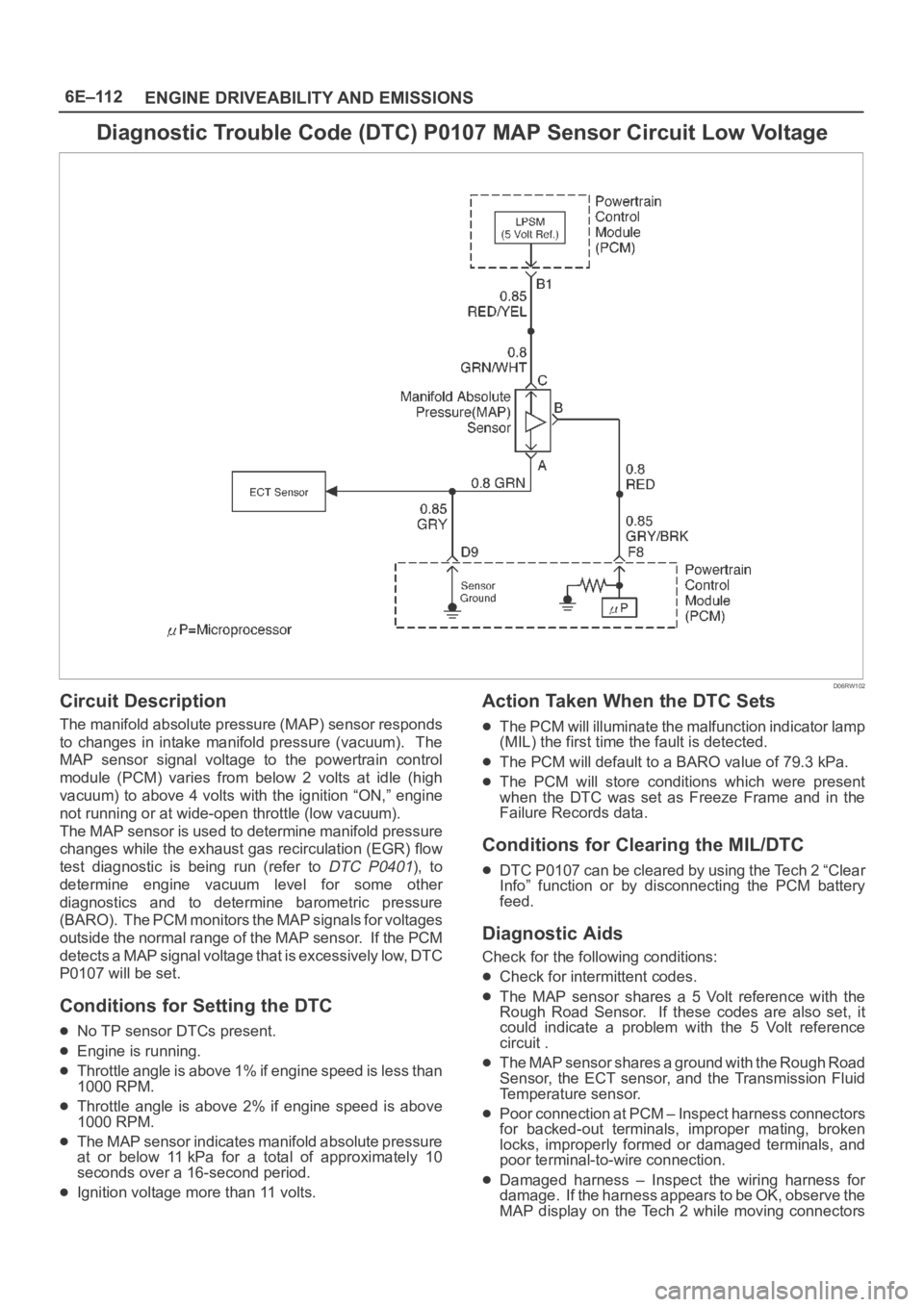
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0107 MAP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
D06RW102
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP sensor signal voltage to the powertrain control
module (PCM) varies from below 2 volts at idle (high
vacuum) to above 4 volts with the ignition “ON,” engine
not running or at wide-open throttle (low vacuum).
The MAP sensor is used to determine manifold pressure
changes while the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) flow
test diagnostic is being run (refer to
DTC P0401), to
determine engine vacuum level for some other
diagnostics and to determine barometric pressure
(BARO). The PCM monitors the MAP signals for voltages
outside the normal range of the MAP sensor. If the PCM
detects a MAP signal voltage that is excessively low, DTC
P0107 will be set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No TP sensor DTCs present.
Engine is running.
Throttle angle is above 1% if engine speed is less than
1000 RPM.
Throttle angle is above 2% if engine speed is above
1000 RPM.
The MAP sensor indicates manifold absolute pressure
at or below 11 kPa for a total of approximately 10
seconds over a 16-second period.
Ignition voltage more than 11 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will default to a BARO value of 79.3 kPa.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0107 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Check for intermittent codes.
The MAP sensor shares a 5 Volt reference with the
Rough Road Sensor. If these codes are also set, it
could indicate a problem with the 5 Volt reference
circuit .
The MAP sensor shares a ground with the Rough Road
Sensor, the ECT sensor, and the Transmission Fluid
Temperature sensor.
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors