1998 OPEL FRONTERA weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 1736 of 6000

ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 3
SERVICE INFORMATION
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATION
Engine type Diesel, four cycle water cooled inline
Camshaft type DOHC
Number of cylinders 4
Bore x stroke (mm) 95.4 x 104.9
Total piston displacement (cc) 2999
Compression ratio (to 1) 19.0
For Europe : 18.5
Engine weight (dry) N (kg/lb) 2492 (254/560) (A/T)
For Europe : 2422 (247/545) (A/T)
2649 (270/593) (M/T)
For Europe : 2697 (275/606) (M/T)
Engine idling speed (Reference) RPM 720
Compression pressure kpa (kg/cm
2/psi)-rpm 3040 (31/441)-200
Firing order 1–3–4–2
VALVE SYSTEM
Intake valves open at: B.T.D.C. 3°
close at: A.B.D.C. 57.6°
Exhaust valves open at: B.B.D.C. 56.5°
close at: A.T.D.C. 5°
Valve clearance (at cold) mm (in)
intake: 0.15 (0.006)
exhaust: 0.25 (0.01)
Oil filter Full flow and bypass combined type
Oil capacity (Original factory fill or rebuilt engine) 9.0 liters (7.9 US quarts)
Oil capacity (Service change)
with filter change 6.0 liters (6.3 US quarts)
without filter change 5.0 liters (5.3 US quarts)
Oil cooler Water cooled type
Inter cooler Air cooled type
Turbocharger method
Control method Wastegate control
Lubrication Pressurized control
Cooling method Coolant cooled
Crankshaft
As tufftriding (Nitrizing treatment) is applied to increase
crankshaft strength, crankpins and journals should not
be reground.
Piston Cooling
An oiling jet device for piston cooling is provided in the
lubricating oil circuit from the cylinder block oil gallery
via a check valve.
Take care not to damage any oiling jet when removing
and installing piston and connecting assembly.
Fuel Injection System
The injection system is oil rail type.
Quick On Start 4 System
QOS4 preheating system which features a quick-on
glow plug with thermometer control of the glowing time
and the afterglow time function, is applied.
Page 1737 of 6000
6A – 4 ENGINE MECHANICAL
Engine Cooling
Starting System
Cooling system Coolant forced circulation
Radiator (2 tube in row) Tube type corrugated
Heat radiation capacity J/h (kcal/h) 318 x 10
6(76000)
Heat radiation area m
2(ft2) 15.63 (1.454)
Front area m
2(ft2) 0.309 (2.029)
Dry weight N (kg/lb) 83 (8.5/18.7)
Radiator cap
Valve opening pressure kPa (kg/cm
2/ psi) 93.3 – 122.7 (0.95 – 1.25/13.5 – 17.8)
Coolant capacity lit (Imp.qt./US qt.) M/T 2.5 (2.2/2.6) A/T 2.4 (2.1/2.5)
Coolant pump Centrifugal impeller type
Pulley ratio (to 1) 1.2
Coolant total capacity lit (Imp.qt./US qt.) 9.3 (8.2/9.8)
Model HITACHI S14-0
Rating
Vo l t a ge V 1 2
Output kW 2.8
Time sec 30
Number of teeth of pinion 9
Rotating direction (as viewed from pinion) Clockwise
Weight (approx.) N(kg/lb) 49 (5.0/11)
No-load characteristics
Voltage/current V/A 11/160 or less
Speed rpm 4000 or more
Load characteristics
Voltage/current V/A 8.76/300
Torque Nꞏm(kgꞏm/lbꞏft) 7.4 (0.75/5.4) or more
Speed rpm 1700 or more
Locking characteristics
Voltage/current V/A 2.5/1100 or less
Torque Nꞏm(kgꞏm/lbꞏft) 18.6 (1.9/14) or more
Page 1738 of 6000
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 5
Charging System
Model (HITACHI) LR190-750B LR1100 – 731
Rated voltage V 12
Rated output A 90 100
Rotation direction
Clockwise
(As viewed from pulled)
Pulley effective diameter mm (in) 69 (2.72)
Weight N (kg/lb) 52 (5.3/11.7)
Page 1822 of 6000

ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 89
3. Measure the oil clearance between the connecting
rod and the crankshaft.
1) Remove the connecting rod cap nuts and the
rod caps.
Arrange the removed rod caps in the cylinder
number order.
2) Clean the rod bearings and the crankshaft pins.
3) Carefully check the rod bearings.
If even one bearing is found to be damaged or
badly worn, the entire bearing assembly must be
replaced as a set. Reinstall the bearings in their
original positions.
Apply plastigage to the crank pin.
4) Reinstall the rod caps to their original positions.
5) Tighten the cap nuts in 2 steps, using angular
tightening method as shown in the following
specifications.
1st step: 29 Nꞏm (3.0 kgꞏm/22 lb ft)
2nd step: 45°– 60°NOTE: Do not allow the crankshaft to rotate
6) Remove the rod caps.
7) Measure the smallest width of the plastigage
and determine the oil clearance. If the oil
clearance exceeds the limit, replace the rod
bearings as a set.
8) Clean the plastigage from the bearings and the
crankshaft pins
Standard: 0.022 – 0.042 mm (0.0009 – 0.0017 in)
Limit: 0.100 mm (0.0039 in)
REASSEMBLY
1. Connecting Rod
2. Piston
3. Piston Pin
1) Apply a coat of engine oil to the piston pin and
the piston pin hole.
4. Piston Pin Snap Ring
1) Try to insert the piston pin into the piston pin
hole with normal finger pressure.
2) Weight each piston and connecting rod
assembly.
3) Select piston and connecting rod combinations
so that the weight variation of the different four
assemblies is held within the specified limits.
Variance in weight after assembly: Less than 3g
(0.1058 oz)
NOTE: When changing piston/connecting rod
combinations, do not change the piston/piston pin
combination.
4) Attach the piston to the connecting rod with the
piston front mark (2) and the connecting rod
front mark (3) on the same side.
014RW055
012RW075
014RW077
Page 2207 of 6000
7A–53 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
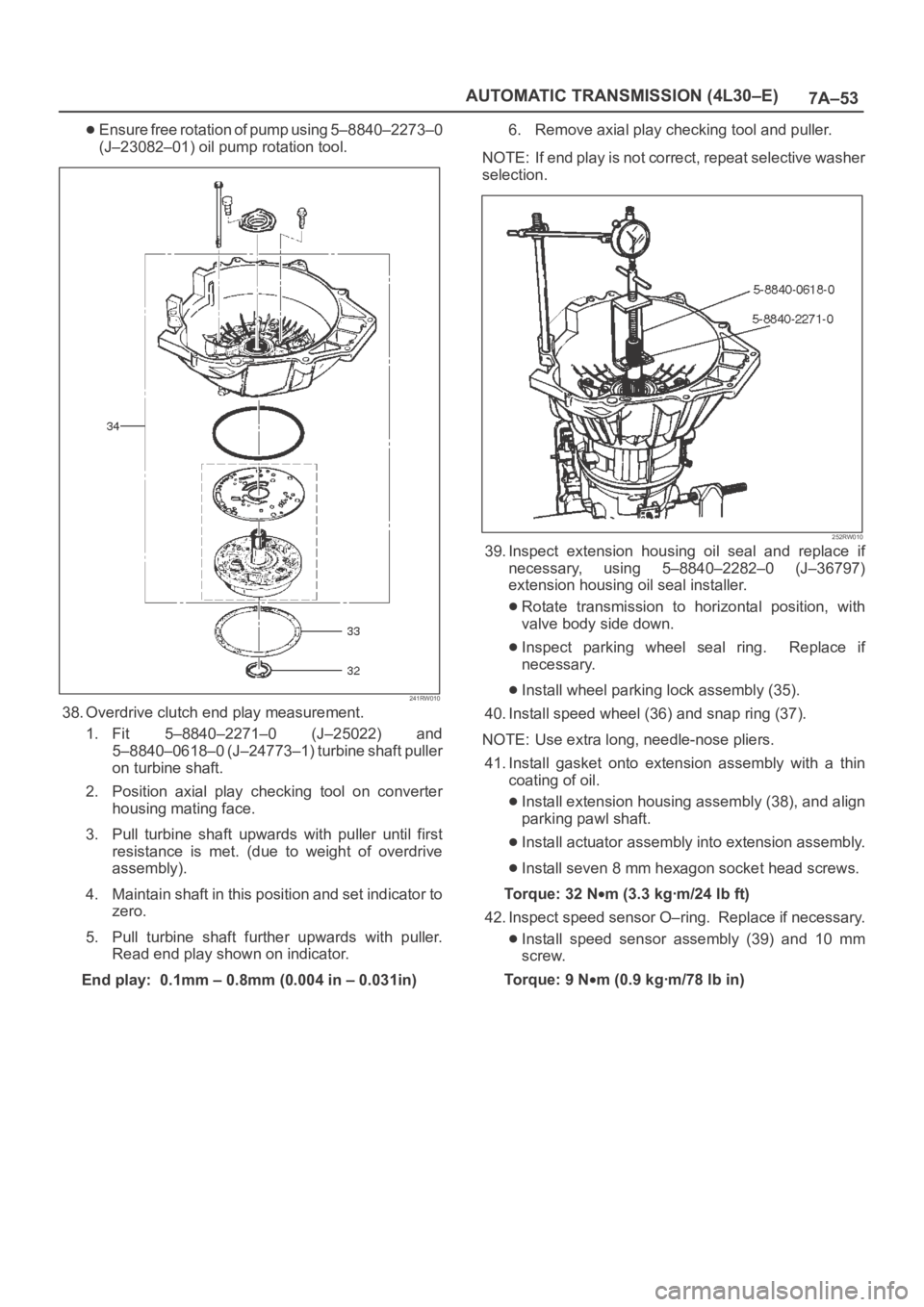
Ensure free rotation of pump using 5–8840–2273–0
(J–23082–01) oil pump rotation tool.
241RW010
38. Overdrive clutch end play measurement.
1. Fit 5–8840–2271–0 (J–25022) and
5–8840–0618–0 (J–24773–1) turbine shaft puller
on turbine shaft.
2. Position axial play checking tool on converter
housing mating face.
3. Pull turbine shaft upwards with puller until first
resistance is met. (due to weight of overdrive
assembly).
4. Maintain shaft in this position and set indicator to
zero.
5. Pull turbine shaft further upwards with puller.
Read end play shown on indicator.
End play: 0.1mm – 0.8mm (0.004 in – 0.031in)6. Remove axial play checking tool and puller.
NOTE: If end play is not correct, repeat selective washer
selection.
252RW010
39. Inspect extension housing oil seal and replace if
necessary, using 5–8840–2282–0 (J–36797)
extension housing oil seal installer.
Rotate transmission to horizontal position, with
valve body side down.
Inspect parking wheel seal ring. Replace if
necessary.
Install wheel parking lock assembly (35).
40. Install speed wheel (36) and snap ring (37).
NOTE: Use extra long, needle-nose pliers.
41. Install gasket onto extension assembly with a thin
coating of oil.
Install extension housing assembly (38), and align
parking pawl shaft.
Install actuator assembly into extension assembly.
Install seven 8 mm hexagon socket head screws.
To r q u e : 3 2 N
m (3.3 kgꞏm/24 lb ft)
42. Inspect speed sensor O–ring. Replace if necessary.
Install speed sensor assembly (39) and 10 mm
screw.
To r q u e : 9 N
m (0.9 kgꞏm/78 lb in)
Page 3971 of 6000
4A2A–2
DIFFERENTIAL (REAR 220mm)
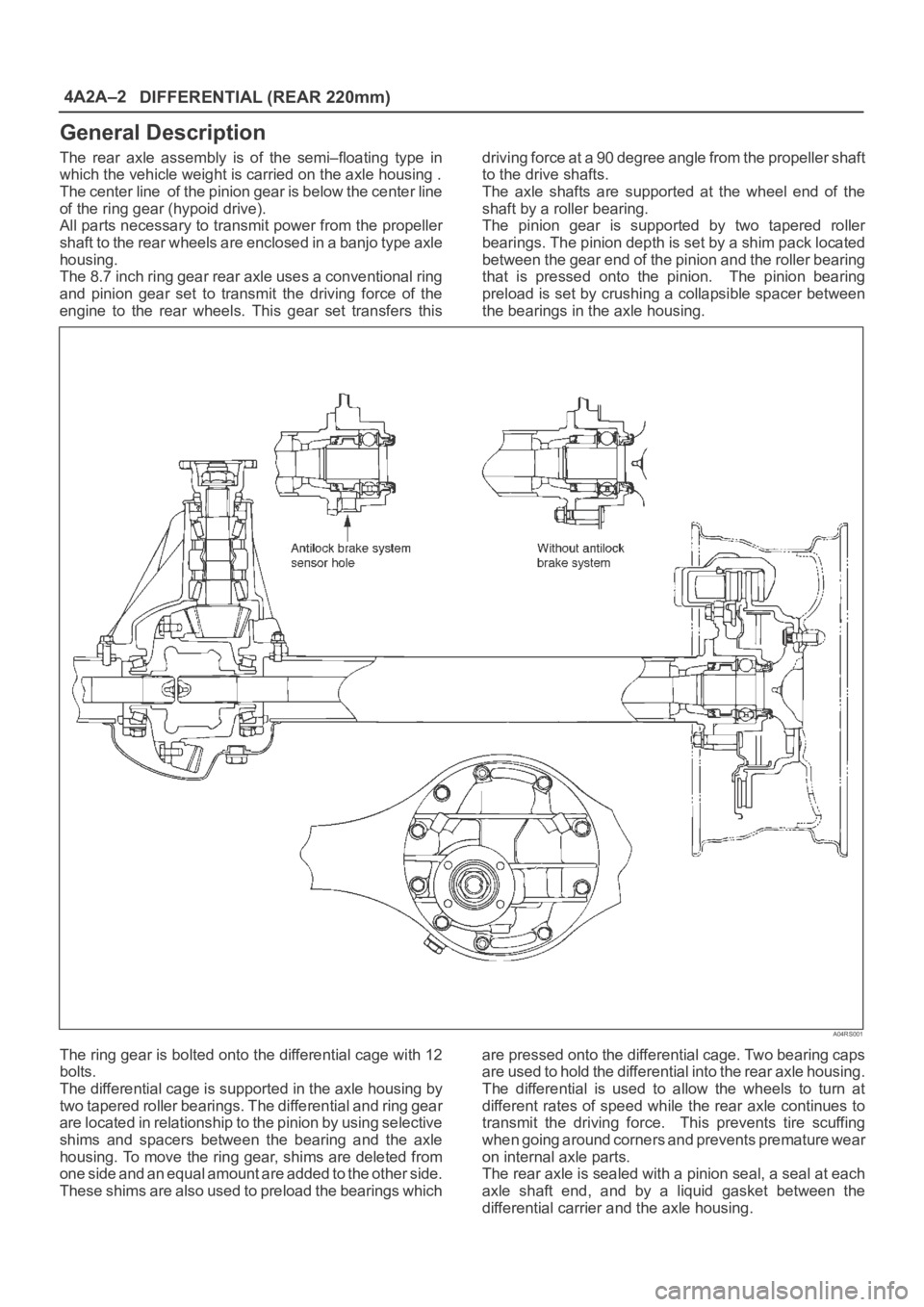
General Description
The rear axle assembly is of the semi–floating type in
which the vehicle weight is carried on the axle housing .
The center line of the pinion gear is below the center line
of the ring gear (hypoid drive).
All parts necessary to transmit power from the propeller
shaft to the rear wheels are enclosed in a banjo type axle
housing.
The 8.7 inch ring gear rear axle uses a conventional ring
and pinion gear set to transmit the driving force of the
engine to the rear wheels. This gear set transfers thisdriving force at a 90 degree angle from the propeller shaft
to the drive shafts.
The axle shafts are supported at the wheel end of the
shaft by a roller bearing.
The pinion gear is supported by two tapered roller
bearings. The pinion depth is set by a shim pack located
between the gear end of the pinion and the roller bearing
that is pressed onto the pinion. The pinion bearing
preload is set by crushing a collapsible spacer between
the bearings in the axle housing.
A04RS001
The ring gear is bolted onto the differential cage with 12
bolts.
The differential cage is supported in the axle housing by
two tapered roller bearings. The differential and ring gear
are located in relationship to the pinion by using selective
shims and spacers between the bearing and the axle
housing. To move the ring gear, shims are deleted from
one side and an equal amount are added to the other side.
These shims are also used to preload the bearings whichare pressed onto the differential cage. Two bearing caps
are used to hold the differential into the rear axle housing.
The differential is used to allow the wheels to turn at
different rates of speed while the rear axle continues to
transmit the driving force. This prevents tire scuffing
when going around corners and prevents premature wear
on internal axle parts.
The rear axle is sealed with a pinion seal, a seal at each
axle shaft end, and by a liquid gasket between the
differential carrier and the axle housing.
Page 4010 of 6000
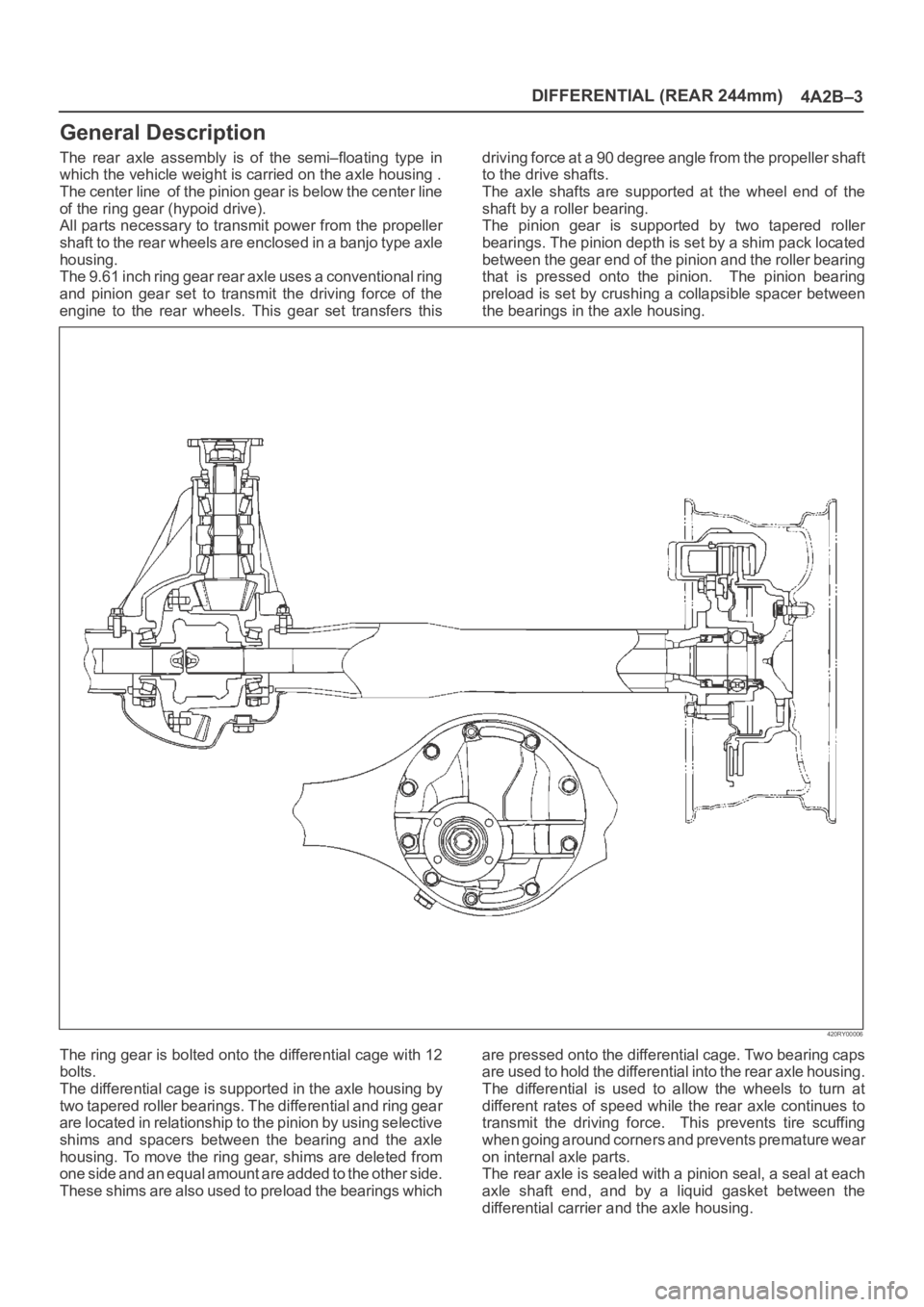
DIFFERENTIAL (REAR 244mm)
4A2B–3
General Description
The rear axle assembly is of the semi–floating type in
which the vehicle weight is carried on the axle housing .
The center line of the pinion gear is below the center line
of the ring gear (hypoid drive).
All parts necessary to transmit power from the propeller
shaft to the rear wheels are enclosed in a banjo type axle
housing.
The 9.61 inch ring gear rear axle uses a conventional ring
and pinion gear set to transmit the driving force of the
engine to the rear wheels. This gear set transfers thisdriving force at a 90 degree angle from the propeller shaft
to the drive shafts.
The axle shafts are supported at the wheel end of the
shaft by a roller bearing.
The pinion gear is supported by two tapered roller
bearings. The pinion depth is set by a shim pack located
between the gear end of the pinion and the roller bearing
that is pressed onto the pinion. The pinion bearing
preload is set by crushing a collapsible spacer between
the bearings in the axle housing.
420RY00006
The ring gear is bolted onto the differential cage with 12
bolts.
The differential cage is supported in the axle housing by
two tapered roller bearings. The differential and ring gear
are located in relationship to the pinion by using selective
shims and spacers between the bearing and the axle
housing. To move the ring gear, shims are deleted from
one side and an equal amount are added to the other side.
These shims are also used to preload the bearings whichare pressed onto the differential cage. Two bearing caps
are used to hold the differential into the rear axle housing.
The differential is used to allow the wheels to turn at
different rates of speed while the rear axle continues to
transmit the driving force. This prevents tire scuffing
when going around corners and prevents premature wear
on internal axle parts.
The rear axle is sealed with a pinion seal, a seal at each
axle shaft end, and by a liquid gasket between the
differential carrier and the axle housing.
Page 4606 of 6000
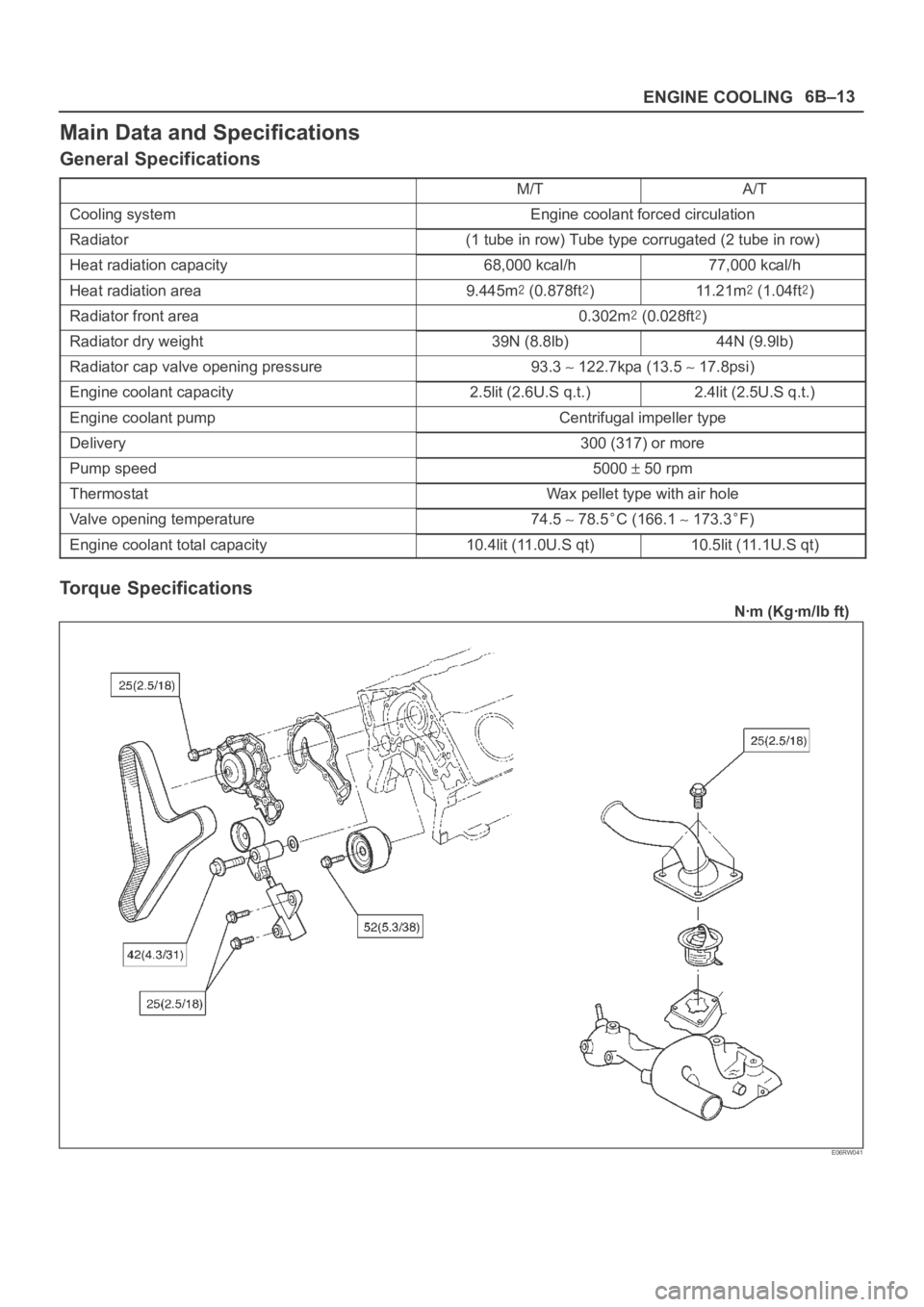
ENGINE COOLING6B–13
Main Data and Specifications
General Specifications
M/TA/T
Cooling systemEngine coolant forced circulation
Radiator(1 tube in row) Tube type corrugated (2 tube in row)
Heat radiation capacity68,000 kcal/h77,000 kcal/h
Heat radiation area9.445m (0.878ft)11 . 2 1 m (1.04ft)
Radiator front area0.302m (0.028ft)
Radiator dry weight39N (8.8lb)44N (9.9lb)
Radiator cap valve opening pressure93.3 122.7kpa (13.5 17.8psi)
Engine coolant capacity2.5lit (2.6U.S q.t.)2.4lit (2.5U.S q.t.)
Engine coolant pumpCentrifugal impeller type
Delivery300 (317) or more
Pump speed5000 50 rpm
ThermostatWax pellet type with air hole
Valve opening temperature74.5 78.5C (166.1 173.3F)
Engine coolant total capacity10.4lit (11.0U.S qt)10.5lit (11.1U.S qt)
Torque Specifications
Nꞏm (Kgꞏm/lb ft)
E06RW041