1998 OPEL FRONTERA center console
[x] Cancel search: center consolePage 814 of 6000

5A–4
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
normal braking when a malfunction has occurred in the
ABS.
The EHCU has a self-diagnosing function which can
indicate faulty circuits during diagnosis.
The EHCU is mounted on the engine compartment front
right side. It consists of a Motor, Plunger Pump, Solenoid
Valves and Check Valve.
On the outside, the relay box containing a motor relay and
a valve relay is installed.
Solenoid Valves: Reduces or holds the caliper fluid
pressure for each front disc brake or both rear disc brakes
according to the signal sent from the EHCU.
Reservoir: Temporarily holds the brake fluid that returns
from the front and rear disc brake caliper so that pressure
of front disc brake caliper can be reduced smoothly.
Plunger Pump: Feeds the brake fluid held in the reservoir
to the master cylinder.
Motor: Drives the pump according to the signal from
EHCU.
Check Valve: Controls the brake fluid flow.
ABS Warning Light
821RW033Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System have
an amber “ABS” warning light in the instrument panel.
The “ABS” warning light will illuminate if a malfunction in
the Anti-lock Brake System is detected by the Electronic
Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU). In case of an electronic
malfunction, the EHCU will turn “ON” the “ABS” warning
light and disable the Anti-lock braking function.
The “ABS” light will turn “ON” for approximately three
seconds after the ignition switch is to the “ON” position.
If the “ABS” light stays “ON” after the ignition switch is the
“ON” position, or comes “ON” and stays “ON” while
driving, the Anti-lock Brake System should be inspected
for a malfunction according to the diagnosis procedure.
Wheel Speed Sensor
It consists of a sensor and a rotor. The sensor is attached
to the knuckle on the front wheels and to the axle shaft
bearing holder on the rear wheels.
The rotor is press-fit in the axle shaft.The flux generated from electrodes magnetized by a
magnet in the sensor varies due to rotation of the rotor,
and the electromagnetic induction generates alternating
voltage in the coil. This voltage draws a “sine curve” with
the frequency proportional to rotor speed and it allows
detection of wheel speed.
G-Sensor
The G-sensor installed inside the center console detects
the vehicle deceleration speed and sends a signal to the
EHCU. In 4WD operation, all four wheels may be
decelerated in almost the same phase, since all wheels
are connected mechanically.
This tendency is noticeable particularly on roads with low
friction coefficient, and the ABS control is adversely
affected.
The G-sensor judges whether the friction coefficient of
road surface is low or high, and changes the EHCU’s
operating system to ensure ABS control.
Normal and Anti-lock Braking
Under normal driving conditions, the Anti-lock Brake
System functions the same as a standard power assisted
brake system. However, with the detection of wheel
lock-up, a slight bump or kick-back will be felt in the brake
pedal. This pedal “bump” will be followed by a series of
short pedal pulsations which occurs in rapid succession.
The brake pedal pulsation will continue until there is no
longer a need for the anti-lock function or until the vehicle
is stopped. A slight ticking or popping noise may be heard
during brake applications when the Anti-lock features is
being used.
When the Anti-lock feature is being used, the brake pedal
may rise even as the brakes are being applied. This is
also normal. Maintaining a constant force on the pedal
will provide the shortest stopping distance.
Brake Pedal Travel
Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System may
be stopped by applying normal force to the brake pedal.
Although there is no need to push the pedal beyond the
point where it stops or holds the vehicle, by applying more
force the pedal will continue to travel toward the floor.
This extra brake pedal travel is normal.
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Several acronyms and abbreviations are commonly used
throughout this section:
ABS
Anti-lock Brake System
CKT
Circuit
DLC
Data Link Connector
EHCU
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit
FL
Front Left
Page 851 of 6000

5A–41 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
The DLC is located behind the center console
350RV010
Keep #12 terminal connected with #4 terminal or # 5
terminal (GND) during DTC display. (If #12 terminal
is separated from #4 terminal or # 5 terminal (GND)
during display, display will stop.)
2. DTC display:
DTC is displayed by blinking warning light.
Double-digit display.
First, normal DTC 12 is displayed three times and
then any other DTCs are displayed three times. (If
no other DTCs have been stored, the display of DTC
12 will be repeated.)
3. How to erase code:
Conduct brake switch ON/OFF operation 6 or more
times within 3 seconds of self-diagnosis startup.
The code cannot be erased if more than 3 seconds
have passed since self-diagnosis startup, or if
self-diagnosis has started with brake switched on
(brake pedal depressed).
B05RW005
Page 875 of 6000

5B–3 ANTI–LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
G-Sensor
Removal
350RX001
1. Remove center console.
Refer to Consoles in Body and Accessories
section.
2. Remove clip from G-sensor connector (1), then
disconnect connector.
3. Remove G-sensor assembly fixing bolt (2).
4. Remove G-sensor assembly (3).
Inspection and Repair
Refer to Chart B-5 in Brake Control System section.
Installation
1. Install G-sensor assembly (3).
Care should be taken so that the G-sensor is not
installed in the wrong direction.
2. Install G-sensor assembly fixing bolt (2).
Tighten the fixing bolt to the specified torque.
Torque : 10 Nꞏm (1.0kgꞏm/87 lb in)
3. Install G-sensor wiring connector (1).
4. Install center console.
Refer to Consoles in Body and Accessories
section.
Page 1059 of 6000

6B–6
ENGINE COOLING
Draining and Refilling Cooling
System
Before draining the cooling system, inspect the system
and perform any necessary service to ensure that it is
clean, does not leak and is in proper working order. The
engine coolant (EC) level should be between the “MIN”
and “MAX” lines of reserve tank when the engine is cold.
If low, check for leakage and add EC up to the “MAX” line.
There should not be any excessive deposit of rust or
scales around the radiator cap or radiator filler hole, and
the EC should also be free from oil.
Replace the EC if excessively dirty.
1. Completely drain the cooling system by opening the
drain plug (2) at the bottom of the radiator.
110RW002
2. Remove the radiator cap.
WARNING: TO AVOID THE DANGER OF BEING
BURNED, DO NOT REMOVE THE CAP WHILE THE
ENGINE AND RADIATOR ARE STILL HOT.
SCALDING FLUID AND STEAM CAN BE BLOWN OUT
UNDER PRESSURE.
3. Disconnect all hoses from the EC reserve tank.
Scrub and clean the inside of the reserve tank with
soap and water. Flush it well with clean water, then
drain it. Install the reserve tank and hoses.
4. Refill the cooling system with the EC using a solution
that is at least 50 percent antifreeze but no more than
70 percent antifreeze.
5. Fill the radiator to the base of the filler neck.
Fill the EC reserve tank to “MAX” line when the engine
is cold.
6. Block the drive wheels and firmly apply the parking
brake. Shift an automatic transmission to “P” (Park)
or a manual transmission to neutral.
7. Remove the radiator cap. Start the engine and warm
it up at 2,500
3,000 rpm for about 30 minutes.
8. When the air comes out from the radiator filler neck
and the EC level has gone down, replenish with the
EC. Repeat this procedure until the EC level does not
go down. Then stop the engine and install the radiator
cap. Let the engine cool down.9. After the engine has cooled, replenish with EC up to
the “MAX” line of the reserve tank.
10. Start the engine. With the engine running at 3,000
rpm, make sure there is no running water sound from
the heater core (behind the center console).
11. If the running water sound is heard, repeat steps 8 to
10.
Page 1455 of 6000

6E–338
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
RPM. A failure in the MAF sensor or circuit will set DTC
P0101, DTC P0102, or DTC P0103.
0007
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP sensor signal voltage to the PCM varies from below
2 volts at idle (high vacuum) to above 4 volts with the
ignition ON, engine not running or at wide-open throttle
(low vacuum).
The MAP sensor is used to determine the following:
Manifold pressure changes while the linear EGR flow
test diagnostic is being run. Refer to
DTC P0401.
Engine vacuum level for other diagnostics.
Barometric pressure (BARO).
If the PCM detects a voltage that is lower than the
possible range of the MAP sensor, DTC P0107 will be set.
A signal voltage higher than the possible range of the
sensor will set DTC P0108. An intermittent low or high
voltage will set DTC P1107 or DTC P1106, respectively.
The PCM can detect a shifted MAP sensor. The PCM
compares the MAP sensor signal to a calculated MAP
based on throttle position and various engine load factors.
If the PCM detects a MAP signal that varies excessively
above or below the calculated value, DTC P0106 will set.
055RW004
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
The powertrain control module (PCM) is located in the
passenger compartment below the center console. The
PCM controls the following:
Fuel metering system.
Transmission shifting (automatic transmission only).
Ignition timing.
On-board diagnostics for powertrain functions.
The PCM constantly observes the information from
various sensors. The PCM controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The PCM performs the
diagnostic function of the system. It can recognize
operational problems, alert the driver through the MIL
(Service Engine Soon lamp), and store diagnostic trouble
codes (DTCs). DTCs identify the problem areas to aid the
technician in making repairs.
This engine uses 2 different control modules:
IPCM-6KT for automatic transmission-equipped
vehicles.
ISFI-6 for manual transmission-equipped vehicles.
PCM Function
The PCM supplies either 5 or 12 volts to power various
sensors or switches. The power is supplied through
resistances in the PCM which are so high in value that a
test light will not light when connected to the circuit. In
some cases, even an ordinary shop voltmeter will not give
an accurate reading because its resistance is too low.
Therefore, a digital voltmeter with at least 10 megohms
input impedance is required to ensure accurate voltage
readings. Tool J 39200 meets this requirement. The PCM
controls output circuits such as the injectors, IAC, cooling
fan relays, etc., by controlling the ground or the power
feed circuit through transistors of following device.
Output Driver Module (ODM)
Page 2266 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–21
NOTE: To use the DTC again to identify a problem, you
will need to reproduce the fault or the problem. This may
require a new test drive or just turning the ignition on (this
depends on the nature of the fault).
1. IF you have a Tech2:
1. Connect the Tech2 if it is still not connected
GOTHROUGH Tech2 OBD II CONNECTION.
2. Push “F4” and answer “Yes” to the question “Do
you really want to clear the codes?”
a. When a malfunction remains as it is the Tech2
displays “4L30E CODES NOT CLEARED”. This
means that the problem is still there or that the
recovery was not done. Please GOTO DTC
CHECK.
b. When a malfunction has been repaired and the
recovery is done. The Tech2 displays “4L30E
CODES CLEARED”.
2. IF you have no Tech2:
To clear the DTC, remove Fuse “Stop, A/T CONT”
(C–14, 15A) for at least 10 seconds.
DTC Check
1. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) have been identified
by Tech2.
2. You have written the list of the DTCs. The order of the
malfunctions has no meanings for this PCM. Usually
only one or two malfunctions should be set for a given
problem.
3. Check directly the DTCs you identified. The DTCs are
sorted by number. Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) Identification in this section.
PCM Precaution
The PCM can be damaged by:
1. Electrostatic discharge
2. The short circuit of some terminals to voltage or to
ground.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage Description:
1. Electronic components used to control systems are
often designed to carry very low voltage, and are very
susceptible to damage caused by electrostatic
discharge. It is possible for less than 100 volts of
static electricity to cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as
4,000 volts for a person to even feel the zap of a static
discharge.2. There are several ways for a person to become
statically charged. The most common methods of
charging are by friction and induction. An example of
charging by friction is a person sliding across a car
seat, in which a charge of as much as 25,000 volts
can build up. Charging by induction occurs when a
person with well insulated shoes stands near a highly
charged object and momentarily touches ground.
Charges for the same polarity are drained off, leaving
the person highly charged with the opposite polarity.
Static charges of either type can cause damage,
therefore, it is important to use care when handling
and testing electronic components.
NOTICE: To prevent possible electrostatic
discharge damage:
1. Do not touch the PCM connector pins or soldered
components on the PCM circuit board.
2. Be sure to follow the guidelines listed below if
servicing any of these electronic components:
3. Do not open the replacement part package until it is
time to install the part.
4. Avoid touching electrical terminals of the part.
5. Before removing the part from its package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
6. Always touch a known good ground before handling
the part. This step should be repeated before
installing the part if the part has been handled while
sliding across the seat, while sitting down from a
standing position or while walking some distance.
Information On PCM
1. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is located in
the center console and is the control center of the
electronic transmission control system.
2. The PCM must be maintained at a temperature below
185
F (85C) at all times. This is most essential if the
vehicle is put through a paint baking process. The
PCM will become inoperative if its temperature
exceeds 85
C (185F). Therefore, it is
recommended that the PCM be removed or that
temporary insulation be placed around the PCM
during the time the vehicle is in a paint oven or other
high temperature process.
3. The PCM is designed to process the various inputs
and then respond by sending the appropriate
electrical signals to control transmission upshift,
downshift, shift feel and torque converter clutch
engagement.
4. The PCM constantly interprets information from the
various sensors, and controls the systems that affect
transmission and vehicle performance. By analyzing
operational problems, the PCM is able to perform a
diagnostic function by displaying DTC(s) and aid the
technician in making repairs.
Intermittent Conditions
If the Tech2 displays a diagnostic trouble code as
intermittent, or if after a test drive a DTC does not
reappear though the detection conditions for this DTC are
present, the problem is most likely a faulty electrical
Page 3380 of 6000

EXTERIOR/INTERIOR TRIM8J–1
BODY AND ACCESSORIES
EXTERIOR / INTERIOR TRIM
CONTENTS
Service Precaution 8J–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dash Side Trim Panel 8J–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Assist Grip 8J–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parts Location 8J–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal and Installation 8J–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Consoles 8J–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Consoles and Associated Parts 8J–4. . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Door Trim Panel 8J–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Door Trim Panel and Associated
Parts 8J–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Door Trim Panel 8J–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Door Trim Panel and Associated
Parts 8J–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Door Mirror 8J–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Door Mirror and Associated Parts 8J–13. . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Luggage Side and Quarter Upper Trim Cover
(Long Wheel Base) 8J–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Luggage Side, Quarter Upper Trim Cover
and Associated Parts 8J–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Luggage Side and Quarter Upper Trim Cover
(Short Wheel Base) 8J–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Luggage Side, Quarter Upper Trim Cover
and Associated
Parts 8J–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Center Pillar and Roof Side Trim Cover
(Long Wheel Base) 8J–20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Center Pillar, Roof Side Trim Cover and
Associated Parts 8J–20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Roof Side Trim Cover (Short Wheel Base) 8J–22. . Roof Side Trim Cover and Associated
Parts 8J–22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Pillar Trim Cover 8J–23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Pillar Trim Cover and Associated
Parts 8J–23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–23
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Center Pillar Assist Grip 8J–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parts Location 8J–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal and Installation 8J–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Assist Grip 8J–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parts Location 8J–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal and Installation 8J–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filler Lid Opener Cable 8J–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filler Lid Opener Cable
and Associated Parts 8J–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filler Door 8J–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parts Location 8J–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rocker Protector (Without Wheel
Opening Extension) 8J–27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rocker Protector (Without Wheel
Opening Extension) and Associated Parts 8J–27
Removal 8J–27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wheel Opening Extension and Rocker
Protector Assembly 8J–28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wheel Opening Extension, Rocker Protector
Assembly and Associated Parts 8J–28. . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mud Flaps (With Wheel Opening Extension) 8J–31
Mud Flaps (With Wheel Opening Extension)
and Associated Parts 8J–31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8J–31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ventilation Assembly 8J–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ventilation Assembly and Associated Parts 8J–32
Removal 8J–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8J–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 3383 of 6000
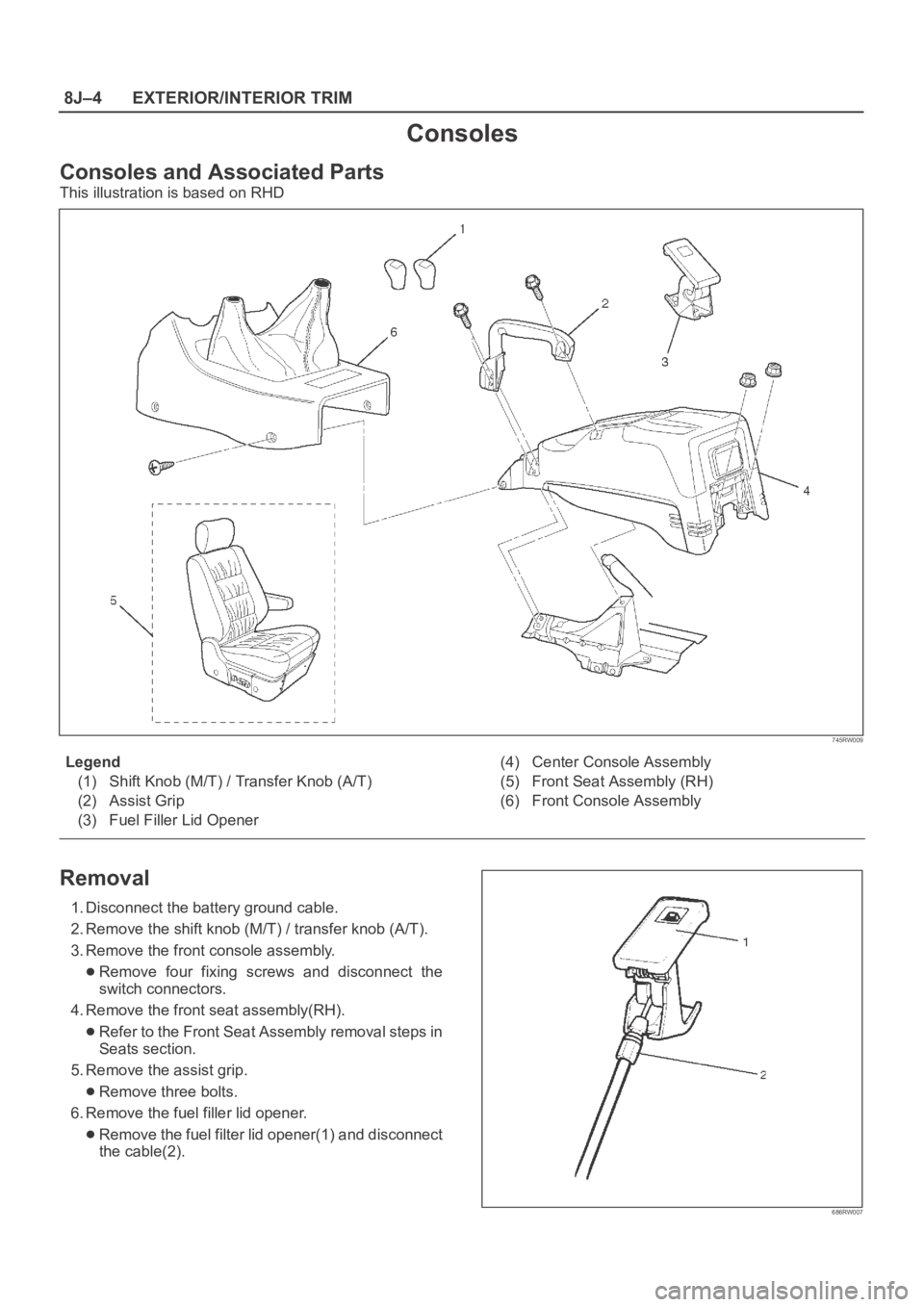
8J–4EXTERIOR/INTERIOR TRIM
Consoles
Consoles and Associated Parts
This illustration is based on RHD
745RW009
Legend
(1) Shift Knob (M/T) / Transfer Knob (A/T)
(2) Assist Grip
(3) Fuel Filler Lid Opener(4) Center Console Assembly
(5) Front Seat Assembly (RH)
(6) Front Console Assembly
Removal
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
2. Remove the shift knob (M/T) / transfer knob (A/T).
3. Remove the front console assembly.
Remove four fixing screws and disconnect the
switch connectors.
4. Remove the front seat assembly(RH).
Refer to the Front Seat Assembly removal steps in
Seats section.
5. Remove the assist grip.
Remove three bolts.
6. Remove the fuel filler lid opener.
Remove the fuel filter lid opener(1) and disconnect
the cable(2).
686RW007