1998 OPEL FRONTERA diagram
[x] Cancel search: diagramPage 4992 of 6000

6E–335 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
General Description
General Description (PCM and
Sensors)
58X Reference PCM Input
The powertrain control module (PCM) uses this signal
from the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor to calculate
engine RPM and crankshaft position at all engine speeds.
The PCM also uses the pulses on this circuit to initiate
injector pulses. If the PCM receives no pulses on this
circuit, DTC P0337 will set. The engine will not start and
run without using the 58X reference signal.
A/C Request Signal
This signal tells the PCM when the A/C mode is selected
at the A/C control head. The PCM uses this to adjust the
idle speed before turning “ON” the A/C clutch. The A/C
compressor will be inoperative if this signal is not
available to the PCM.
Refer to
A/C Clutch Circuit Diagnosis for A/C wiring
diagrams and diagnosis for the A/C electrical system.
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor provides a signal
used by the powertrain control module (PCM) to calculate
the ignition sequence. The CKP sensor initiates the 58X
reference pulses which the PCM uses to calculate RPM
and crankshaft position.
Refer to
Electronic Ignition System for additional
information.
0013
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor and
Signal
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor sends a CMP signal
t o t h e P C M . T h e P C M u s e s t h i s s i g n a l a s a “ s y n c p u l s e ” t otrigger the injectors in the proper sequence. The PCM
uses the CMP signal to indicate the position of the #1
piston during its power stroke. This allows the PCM to
calculate true sequential fuel injection (SFI) mode of
operation. If the PCM detects an incorrect CMP signal
while the engine is running, DTC P0341 will set. If the
CMP signal is lost while the engine is running, the fuel
injection system will shift to a calculated sequential fuel
injection mode based on the last fuel injection pulse, and
the engine will continue to run. As long as the fault is
present, the engine can be restarted. It will run in the
calculated sequential mode with a 1-in-6 chance of the
injector sequence being correct.
Refer to
DTC P0341 for further information.
0014
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor (a resistor which changes value based on
temperature) mounted in the engine coolant stream. Low
coolant temperature produces a high resistance of
100,000 ohms at –40
C (–40F). High temperature
causes a low resistance of 70 ohms at 130
C (266F).
The PCM supplies a 5-volt signal to the ECT sensor
through resistors in the PCM and measures the voltage.
The signal voltage will be high when the engine is cold and
low when the engine is hot. By measuring the voltage, the
PCM calculates the engine coolant temperature. Engine
coolant temperature affects most of the systems that the
PCM controls.
Tech 2 displays engine coolant temperature in degrees.
After engine start-up, the temperature should rise steadily
to about 85
C (185F). It then stabilizes when the
thermostat opens. If the engine has not been run for
several hours (overnight), the engine coolant
temperature and intake air temperature displays should
be close to each other. A hard fault in the engine coolant
sensor circuit will set DTC P0177 or DTC P0118. An
intermittent fault will set a DTC P1114 or P1115.
Page 5006 of 6000

6E–349 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Damage during re-gapping can happen if the gapping
tool is pushed against the center electrode or the
insulator around it, causing the insulator to crack.
When re-gapping a spark plug, make the adjustment
by bending only the ground side terminal, keeping the
tool clear of other parts.
”Heat shock” breakage in the lower insulator tip
generally occurs during several engine operating
conditions (high speeds or heavy loading) and may be
caused by over-advanced timing or low grade fuels.
Heat shock refers to a rapid increase in the tip
temperature that causes the insulator material to
crack.
Spark plugs with less than the recommended amount of
service can sometimes be cleaned and re-gapped , then
returned to service. However, if there is any doubt about
the serviceability of a spark plug, replace it. Spark plugs
with cracked or broken insulators should always be
replaced.
A/C Clutch Diagnosis
A/C Clutch Circuit Operation
A 12-volt signal is supplied to the A/C request input of the
PCM when the A/C is selected through the A/C control
switch.
The A/C compressor clutch relay is controlled through the
PCM. This allows the PCM to modify the idle air control
position prior to the A/C clutch engagement for better idle
quality. If the engine operating conditions are within their
specified calibrated acceptable ranges, the PCM will
enable the A/C compressor relay. This is done by
providing a ground path for the A/C relay coil within the
PCM. When the A/C compressor relay is enabled,
battery voltage is supplied to the compressor clutch coil.
The PCM will enable the A/C compressor clutch
whenever the engine is running and the A/C has been
requested. The PCM will not enable the A/C compressor
clutch if any of the following conditions are met:
The throttle is greater than 90%.
The engine speed is greater than 6315 RPM.
The ECT is greater than 119C (246F).
The IAT is less than 5C (41F).
The throttle is more than 80% open.
A/C Clutch Circuit Purpose
The A/C compressor operation is controlled by the
powertrain control module (PCM) for the following
reasons:
It improvises idle quality during compressor clutch
engagement.
It improvises wide open throttle (WOT) performance.
It provides A/C compressor protection from operation
with incorrect refrigerant pressures.
The A/C electrical system consists of the following
components:
The A/C control head.
The A/C refrigerant pressure switches.
The A/C compressor clutch.
The A/C compressor clutch relay.
The PCM.
A/C Request Signal
This signal tells the PCM when the A/C mode is selected
at the A/C control head. The PCM uses this to adjust the
idle speed before turning on the A/C clutch. The A/C
compressor will be inoperative if this signal is not
available to the PCM.
Refer to
A/C Clutch Circuit Diagnosis for A/C wiring
diagrams and diagnosis for A/C electrical system.
General Description (Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) System)
EGR Purpose
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is use to
reduce emission levels of oxides of nitrogen (NOx). NOx
emission levels are caused by a high combustion
temperature. The EGR system lowers the NOx emission
levels by decreasing the combustion temperature.
057RW002
Linear EGR Valve
The main element of the system is the linear EGR valve.
The EGR valve feeds small amounts of exhaust gas back
into the combustion chamber. The fuel/air mixture will be
diluted and combustion temperatures reduced.
Linear EGR Control
The PCM monitors the EGR actual positron and adjusts
the pintle position accordingly. The uses information from
the following sensors to control the pintle position:
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
Throttle position (TP) sensor.
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor.
Linear EGR Valve Operation and Results
of Incorrect Operation
The linear EGR valve is designed to accurately supply
EGR to the engine independent of intake manifold
vacuum. The valve controls EGR flow from the exhaust
Page 5404 of 6000

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 6D – 1
ENGINE ELECTRICAL
CONTENTS
Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–1
General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–1
Diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–1
On Vehicle Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–3
Main Data and Specification . . . . . . . . . . 6D–4
Starting System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–5
General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–5
On Vehicle Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–7
Starter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–7
Unit Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–8Charging System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–15
General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–15
Diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–16
Unit Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–17
Main Data and Specification . . . . . . . . . . 6D–22
QOS4 Preheating System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–23
General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–23
System Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6D–23
Inspection of QOS4 System Operation . . 6D–24
BATTERY
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
DIAGNOSIS
There are six battery fluid caps at the top of the battery.
These are covered by a paper label.
The battery is completely sealed except for the six
small vent holes at the side. These vent holes permit
the escape of small amounts of gas generated by the
battery.
This type of battery has the following advantages over
conventional batteries:1. There is no need to add water during the entire
service life of the battery.
2. The battery protects itself against overcharging.
The battery will refuse to accept an excessive
charge.
(A conventional battery will accept an excessive
charge, resulting in gassing and loss of battery
fluid.)
3. The battery is much less vulnerable to self-
discharge than a conventional type battery.
1. VISUAL INSPECTION (Step 1)
Inspect the battery for obvious physical damage, such
as a cracked or broken case, which would permit
electrolyte loss.
Replace the battery if obvious physical damage is
discovered during inspection.
Check for any other physical damage and correct it as
necessary. If not, proceed to Step 2.
2. HYDROMETER CHECK (Step 2)
There is a built-in hydrometer (Charge test indicator) at
the top of the battery. It is designed to be used during
diagnostic procedures.
Before trying to read the hydrometer, carefully clean the
upper battery surface.
If your work area is poorly lit, additional light may be
necessary to read the hydrometer.
a. BLUE RING OR DOT VISIBLE – Go to Step 4.
b. BLUE RING OR DOT NOT VISIBLE – Go to
Step 3.3. FLUID LEVEL CHECK (Step 3)
The fluid level should be between the upper level line
and lower level line on side of the battery.
a. CORRECT FLUID LEVEL – Charge the battery.
b. BELOW LOWER LEVEL – Replace battery.
4. VOLTAGE CHECK (Step 4)
(1) Put voltmeter test leads to battery terminals.
a. VOLTAGE IS 12.4V OR ABOVE – Go to Step 5.
b. VOLTAGE IS UNDER 12.4V – Go to procedure
(2) below.
(2) Determine fast charge amperage from
specification. (See Main Data and Specifications in
this section.)
Fast charge battery for 30 minutes at amperage
rate no higher than specified value.
Take voltage and amperage readings after charge.
a. VOLTAGE IS ABOVE 16V AT BELOW 1/3 OF
AMPERAGE RATE – Replace battery.
Page 5426 of 6000
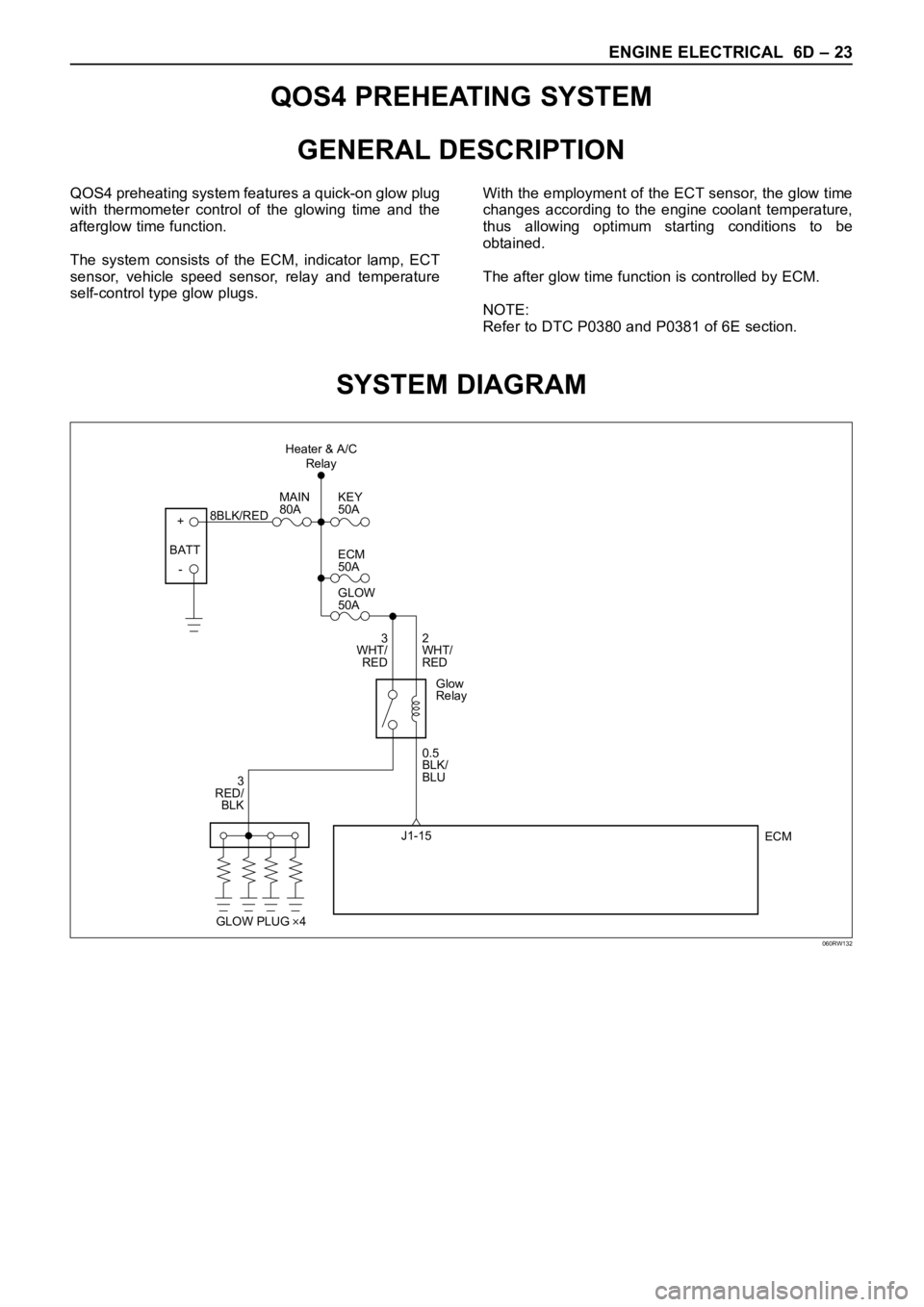
ENGINE ELECTRICAL 6D – 23
QOS4 PREHEATING SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
QOS4 preheating system features a quick-on glow plug
with thermometer control of the glowing time and the
afterglow time function.
The system consists of the ECM, indicator lamp, ECT
sensor, vehicle speed sensor, relay and temperature
self-control type glow plugs.With the employment of the ECT sensor, the glow time
changes according to the engine coolant temperature,
thus allowing optimum starting conditions to be
obtained.
The after glow time function is controlled by ECM.
NOTE:
Refer to DTC P0380 and P0381 of 6E section.
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
+
-KEY
50A
ECM
50A
GLOW
50A
2
WHT/
RED
0.5
BLK/
BLU
ECM J1-15 3
WHT/
RED
3
RED/
BLKMAIN
80A
8BLK/RED
Glow
Relay
GLOW PLUG 4
BATTHeater & A/C
Relay
060RW132
Page 5430 of 6000
6E–1 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
4JX1–TC 3.0L ENGINE
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CONTENTS
Specification 6E–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tightening Specifications 6E–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagrams and Schematics 6E–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Wiring Diagram (1 of 6) 6E–8. . . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Wiring Diagram (2 of 6) 6E–9. . . . . . . . . . . .
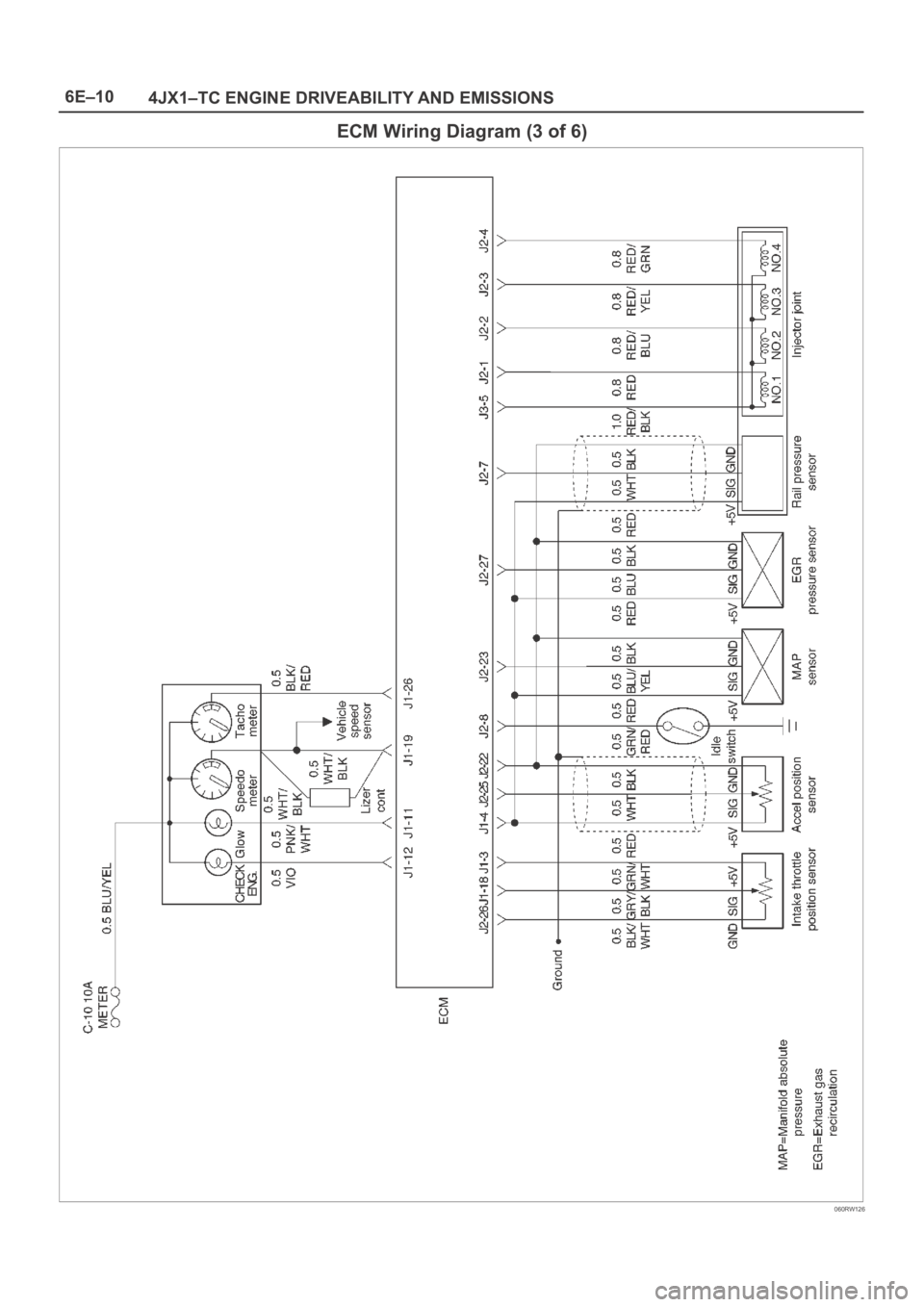
ECM Wiring Diagram (3 of 6) 6E–10. . . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Wiring Diagram (4 of 6) 6E–11. . . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Wiring Diagram (5 of 6) 6E–12. . . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Wiring Diagram (6 of 6) 6E–13. . . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Pinouts 6E–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Pinout Table, 32-Way Connector – J1
RED – Upper 6E–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Pinout Table, 32-Way Connector – J1
RED – Lower 6E–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Pinout Table, 32-Way Connector – J2
BLUE – Upper 6E–16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Pinout Table, 32-Way Connector – J2
BLUE – Lower 6E–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Pinout Table, 5-Way Connector – J3 6E–18
Component Locator 6E–19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Sensors and Miscellaneous Component
Locators 6E–21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Abbreviations Charts 6E–23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnosis 6E–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Strategy-Based Diagnostics 6E–24. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Strategy-Based Diagnostics 6E–24. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC Stored 6E–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No DTC 6E–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Matching Symptom 6E–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intermittents 6E–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Trouble Found 6E–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying Vehicle Repair 6E–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Service Information 6E–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serviceability Issues 6E–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Visual/Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection 6E–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Basic Knowledge of Tools Required 6E–25. . . . . .
Serial Data Communications 6E–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Class II Serial Data Communications 6E–25. . . . .
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) 6E–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
On-Board Diagnostic Tests 6E–25. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Comprehensive Component Monitor
Diagnostic Operation 6E–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Common OBD Terms 6E–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
The Diagnostic Executive 6E–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC Types 6E–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying Vehicle Repair 6E–27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Reading Flash Diagnostic Trouble Codes 6E–27.
Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes Using
a TECH 2 6E–28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tech 2 Scan Tool 6E–29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Getting Started 6E–30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC Modes 6E–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC Information Mode 6E–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Injector Test 6E–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EGR Valve Test 6E–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rail Pressure Control Valve Test 6E–32. . . . . . . . .
Injector Balance Test 6E–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Data Programming in Case of ECM Change 6E–32
Rail Pressure Sensor Programming 6E–33. . . . . .
Injector Group Sign Programming
(Injector Change) 6E–33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check 6E–35.
Circuit Description 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Control Module ECM Diagnosis 6E–39. . . .
Multiple ECM Information Sensor DTCS Set 6E–39
Circuit Description 6E–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) Diagnosis 6E–41
Tech 2 Data Definitions and Ranges 6E–41. . . . . . .
Typical Scan Data Values 6E–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Conditions 6E–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4JX1-TC Engine (Automatic and Manual
Transmission) 6E–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) 6E–44. . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) “ON”
Steady 6E–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit description 6E–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Cranks But Will Not Run 6E–49. . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System
Check 6E–52. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–52. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Diagnostic Trouble Codes 6E–54. . . . . . . . . . .
ECM Diagnostic Trouble Codes 6E–54. . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0107
(Flash DTC 34)
MAP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–56. . . . . . . . . .
Page 5437 of 6000
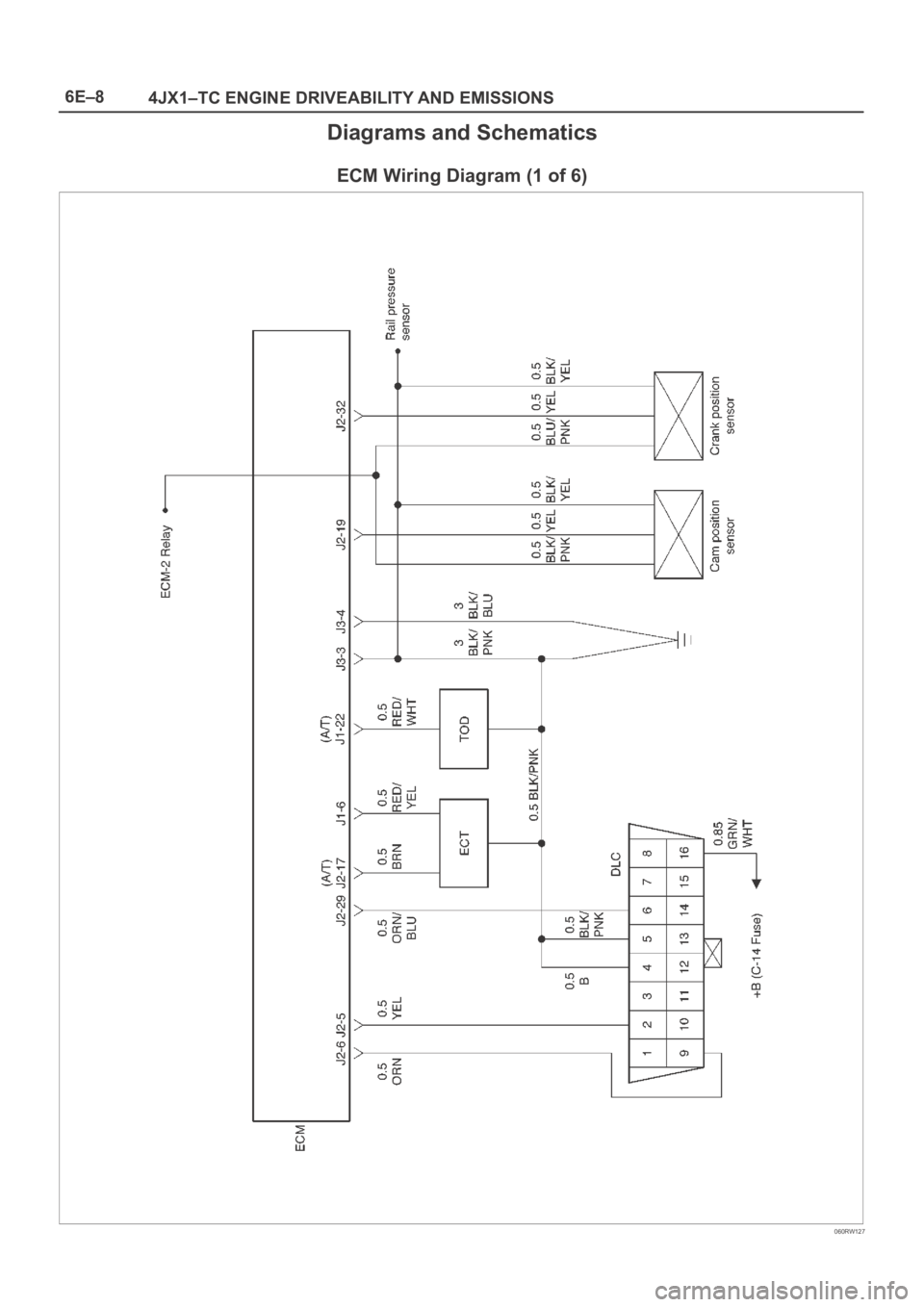
6E–8
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagrams and Schematics
ECM Wiring Diagram (1 of 6)
060RW127
Page 5438 of 6000
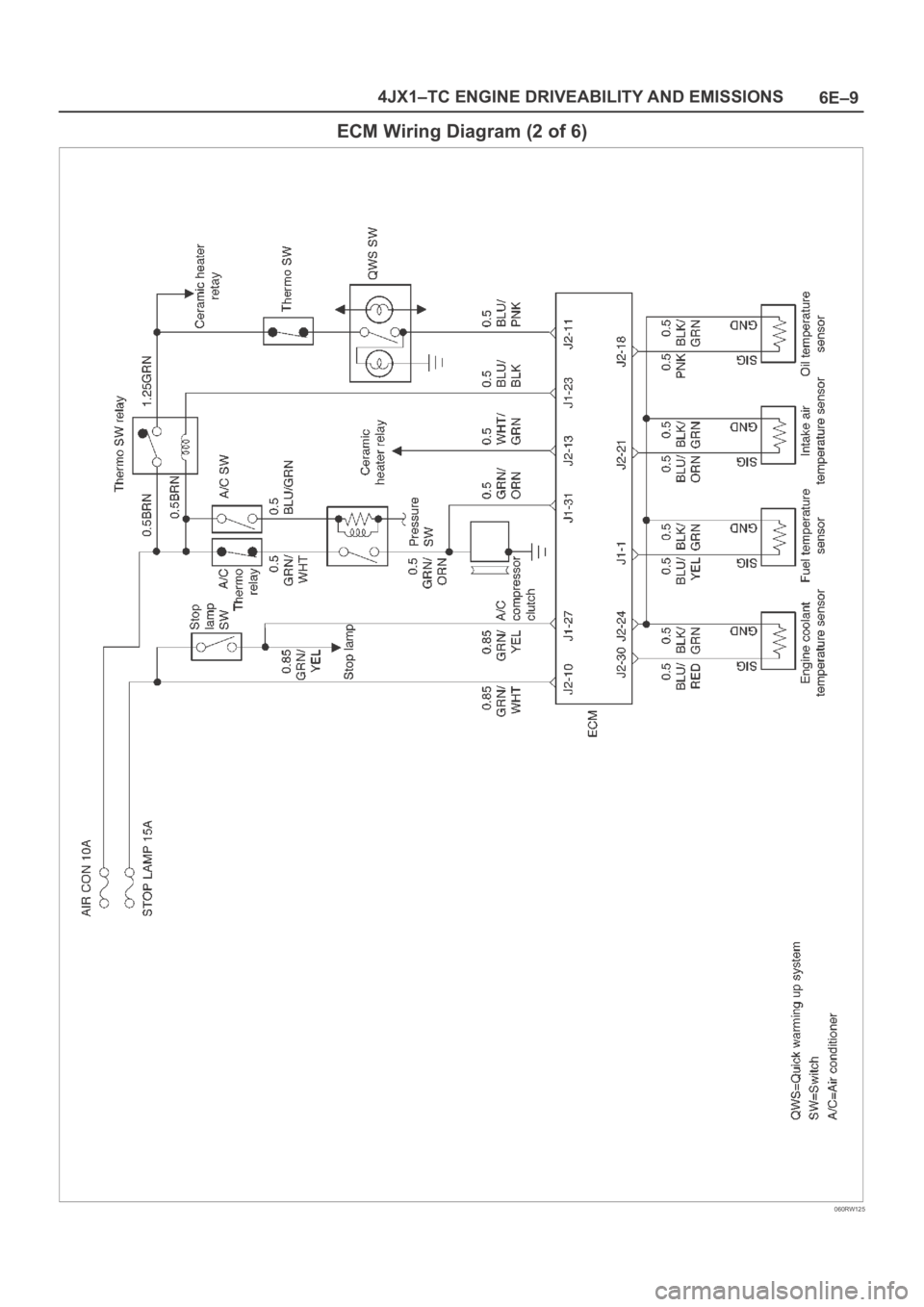
6E–9 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ECM Wiring Diagram (2 of 6)
060RW125
Page 5439 of 6000
6E–10
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ECM Wiring Diagram (3 of 6)
060RW126