1998 JAGUAR X308 vin
[x] Cancel search: vinPage 463 of 2490
No
ise
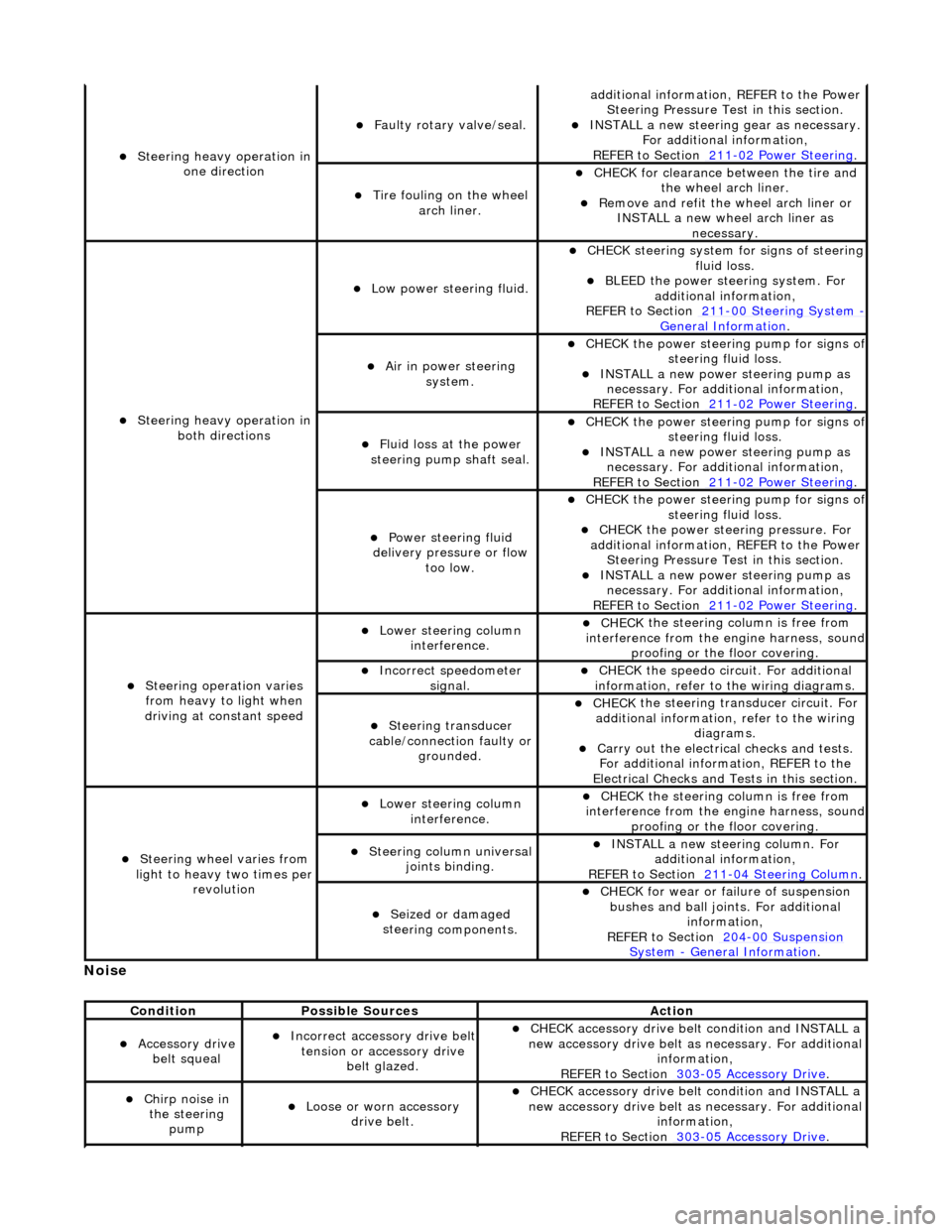
S
teering heavy operation in
one direction
F
aulty rotary valve/seal.
addi
tional information, REFER to the Power
Steering Pressure Test in this section.
INST
ALL a new steering
gear as necessary.
For additional information,
REFER to Section 211
-0
2 Power Steering
.
Ti
re fouling on the wheel
arch liner.
CHECK for
clearance be
tween the tire and
the wheel arch liner.
R
emove and refit the wheel arch liner or
INSTALL a new wheel arch liner as necessary.
S
teering heavy operation in
both directions
Low power steer
ing fluid.
CHE
CK steering system
for signs of steering
fluid loss.
BLEE
D the power steering system. For
additional information,
REFER to Section 211
-0
0 Steering System
- General Informati
on
.
Ai
r in power steering
system.
CHECK
the power steering pump for signs o
f steering fl
uid loss.
INST
ALL a new power steering pump as
necessary. For additi onal information,
REFER to Section 211
-0
2 Power Steering
.
Fluid loss at the power
steering pump shaft seal.
CHECK
the power steering pump for signs o
f steering fl
uid loss.
INST
ALL a new power steering pump as
necessary. For additi onal information,
REFER to Section 211
-0
2 Power Steering
.
Power steeri
ng fluid
delivery pressure or flow too low.
CHECK
the power steering pump for signs o
f steering fl
uid loss.
CHECK
the power stee
ring pressure. For
additional information, REFER to the Power Steering Pressure Test in this section.
INST
ALL a new power steering pump as
necessary. For additi onal information,
REFER to Section 211
-0
2 Power Steering
.
Steeri
ng operation varies
from heavy to light when
driving at constant speed
Lower steeri
ng column
interference.
CHECK
the steering co
lumn is free from
interference from the en gine harness, sound
proofing or the floor covering.
Incorre
ct sp
eedometer
signal.
CHECK
the speedo circ
uit. For additional
information, refer to the wiring diagrams.
Steeri
ng transducer
cable/connection faulty or grounded.
CHECK
the steering transducer circuit. For
additional information, refer to the wiring diagrams.
Carry ou
t the electrical checks and tests.
For additional information, REFER to the
Electrical Checks and Tests in this section.
Steeri
ng wheel varies from
light to heavy two times per revolution
Lower steeri
ng column
interference.
CHECK
the steering co
lumn is free from
interference from the en gine harness, sound
proofing or the floor covering.
Steeri
ng column universal
joints binding.
IN
STALL a new steering column. For
additional information,
REFER to Section 211
-0
4 Steering Column
.
Seized or damaged
ste
ering components.
CHECK
for wear or failure of suspension
bushes and ball join ts. For additional
information,
REFER to Section 204
-00
Suspension
Sy
stem
- General
Information
.
Cond
ition
Possib
le Sources
Acti
on
Acce
ssory drive
belt squeal
Incorre
ct accessory drive belt
tension or accessory drive belt glazed.
CHECK
accessory drive belt condition and INSTALL a
new accessory drive belt as necessary. For additional
information,
REFER to Section 303
-0
5 Accessory Drive
.
Chir
p noise in
the steering pump
Loose or worn accessory dr
ive belt.
CHECK
accessory drive belt condition and INSTALL a
new accessory drive belt as necessary. For additional
information,
REFER to Section 303
-0
5 Accessory Drive
.
Page 467 of 2490

High
-pitched sound like rubbing a clean window.
Squea
l
Continu
ous, high-pitched sound like runn
ing finger nails across a chalkboard.
Tap
Ligh
t, hammering sound like tapping pencil on edge
of table. May be rhythmic or intermittent.
Weep
Continu
ous mid-range sound (lower frequency
than squeal, higher frequency than groan).
Whir/
Whine
High
-pitched buzzing sound, like
an electric motor or drill.
Whistle
Sharp, shril
l sound, like wi
nd passing a small opening.
Description of Specific St eer
ing System Noise Types
Bel
t Squeal
Belt squea
l is a high frequency air-born
e noise generated by slippage of the ribbe d Vee belt on the power steering pump
pulley. Squeal increases with system loading and at the end of lock.
Clonk
Cl
onk is a structure-borne nois
e heard as a loose-sounding rattle or vibration coming from the steering column. Clonk can
be identified by driving and turning over cobblestones, rough roads, or high frequency bumps such as 25-50 mm tall tar
strips. Clonk requires a tie-rod load impact.
Column Knoc
k
Col
umn knock is a loose-sounding rattle or
vibration generated by the steering column shaft contacting other portions of the
column assembly. The noise is both audible and tactile. Column knock is generate d by driving over cobblestones or rough
pavement. It is not necessary to turn the steering wheel to create this noise.
Column Ra
ttle
Co
lumn rattle is a metallic sounding no
ise created when applying a highly impuls ive force to the steering wheel. Column
rattle is often used to combine the more general group of column noises includin g clonk and column knock. Column rattle
noises can be caused by clonk, knock, l oose column components, bonus parts etc. A series of parked, straight-line driving,
and cornering test should be carried out to isolate the source/sources.
Gr
inding/Scrape
Gr
inding is a low frequency noise in the column when the st
eering wheel is turned. Is generally caused by interference
between moving components such as the st eering wheel to steering column shroud.
Gr
unt (Squawk)
Grunt
is a "honking" sound elicited when coming off one of
the steering stops. Grunt is generally excited during parking
manoeuvres with a low to me dium speed steering input.
Squea
k
Page 468 of 2490

Hiss (Swish)
Hiss or Val
ve Hiss is a high-frequency so
und coming from the steering gear when the system is loaded. It is a rushing or
"swish" noise that doesn't change frequency with RPM. Hiss is the general noise generated by the flow of hydraulic fluid
through restrictions in the steer ing system. Restrictions include the rotary stee ring valve, power steering tubes, connectors,
tuning orifices, etc. Hiss can be air- borne and structure-borne, but the structure-borne path through the steering
intermediate shaft is usually dominant.
Moan (Groan)
Moan is the general structu r
e-borne noise of the steering system. Moan is primarily transmitted to the driver via the body
structure through the pump mount, engine mounts, power steering lines and power steering brackets. On some vehicles,
moan is a load humming noise, often present when the wheel is turned and the system is loaded. It may change frequency
with engine RPM and if the sy stem is loaded or unloaded.
Rack Knock (R
ack Slap)
CAU
T
ION: DO NOT attempt to adjust the stee
ring gear yoke. Failure to follow this instruction will result in the steering
gear warranty to become invalid.
Rack Knock is a rattle sound an d steering wheel vibration caused by separation of the steering gear and pinion while driving
over bumps. It is a structure-borne noise transmitted throug h the intermediate shaft and column. Rack knock can also be
heard as a "thump" or impact noise that occurs with the vehicle stationary when the steering wheel is released from a
loaded position and allowed to return to rest . Noise occurs with the engine on or off.
Rattles
Ra
ttles are noises caused by knocking or hitting with components in the steering system. Steering rattles can occur in the
engine compartment, the suspension, or the passenger compartment . Rattles can be caused by loose parts, movable and
flexible parts, and improper clearances.
Squea k
s/Scrapes
Squeaks/Scrapes are noises due
to fri
ction or component rubbi
ng anywhere in the steering system. Squeaks/Scrapes have
appeared in steering linkages and jo ints, in column components and in co lumn and steering wheel trim parts.
Weep
We
ep is an air-borne noise, occasionally
generated when turning the steering across lock at a constant rate. When present
on a vehicle the noise, once initiated can often be maintained across a large proportion of the available steering movement.
Whistle
Wh
istle is similar to hiss but is louder and of a higher frequency. It is also more
of a pure tone noise than hiss. Whistle is
air-borne and is generated by a high flow rate of hydraulic fluid through a small restriction.
Zip
Zip n
o
ise is the air-borne noise
generated by power steerin g pump cavitation when power steering fluid does not flow freely
through the suction hose from the rese rvoir to the pump. Zip primarily occurs during cold weather at start-up.
Steering System Vibrations and Harshne
ss
Buzz
Buzz is a tactile rotary vi
bration felt in
the steering wheel for slow steering inputs. Buzz can also be called a grinding feel
and it is closely related to grunt and is caused by high system gain with low damping. Buzz is generally excited during
parking manoeuvres with low to medium speed steering input.
Page 472 of 2490

Steering System - General Information - Power Steeri
ng System Flushing
Gen
e
ral Procedures
• NOTE: If heavy steering or contamination within the power steering system is found, it is necessary to carry out the
system flush procedure as detailed below. If any components have been replaced in the power steering system the
procedure below must be carried out in full.
• NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur, but the essential information is always correct.
1. Remove the power steering fluid reservoir cap.
2. Using a suitable syringe, remove the power steering fluid from
the power steering fluid reservoir.
3. CAUTIO
N: Be prepared to
collect escaping fluids.
• NOTE: Note the orientation of the clip. Detach the power steeri ng fluid reservoir.
De
tach but do not remove the power steering fluid
reservoir.
Re lea
se the power steering fluid return hose from the
power steering fluid reservoir.
If a qui
ck release coupling is fitted to the power
steering return ho se, release the powe r steering fluid
return hose from the coupling by removing the clip.
4. CAUTIO
N: Be prepared to
collect escaping fluids.
• NOTE: Make sure that all openings are sealed. Use new
blanking caps.
Using a suitable blanking cap, cap the power steering
reservoir return pipe.
5. CAUTIO
N: Be prepared to
collect escaping fluids.
• NOTE: Make sure the extended pipe is not kinked or twisted
and is correctly secure d with hose clips.
Attach a suitable pipe to the power steering return hose to
allow the fluid to drain.
Page 479 of 2490

Power Steering - Power Steering
Description an
d Operation
Parts List
The power steering system is a rack and pinion design, with an engine-dri ve n pump providing the steering assistance. The
system features variable steering assistance with vehicle spee d, a variable ratio steering rack, and a hydraulic control valve
which has a torsion bar arrangement giving improved center feel to the steering.
Absolute cleanliness must be observed wh en replenishing the fluid or dismantling any part of the system. If any major
component is renewed a new fluid rese rvoir must be fitted. New fluid from a sealed container must be used.
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1—Steeri
ng rack assembly
2—Power as
sisted steering pump
3—F
luid reservoir
4—F
luid cooler
5—Hoses and pipework
6—In-
line quick-fit connector
Page 482 of 2490

P a
rts List
The variable ratio rack:
Incorporates teeth
of varying pitch and angle of contact, giving a variable pi
tch circle diameter which is a minimum
at the center of the rack and a maximum at the ends.
R e
duces excessive response to on-center stee
ring inputs during motorway driving.
Causes the steering action to become pro
gressively more
direct as the stee ring wheel is turned from the center
position.
Allows a low n u
mber of turns of the
steering wheel from lock to lock.
Ite
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—Steeri
ng rack
2—Tooth contact an
gle at
center of rack
3—Tooth c o
ntact angle
at ends of rack
Variable Ratio Steering Rack
Page 486 of 2490

P a
rts List
The supply and return pipes are secured to the hydraulic control valve housing by a latch-plate having a single fixing screw.
The latch-plate is captive to the supply pipe. Each pipe has an O-ri ng which is a serviceable item.
In-Line Quick-Fit Connector
Parts List
Ite
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—Return
pipe (RH drive)
2—Supply pipe (RH
drive)
3—Latc
h-plate
4—Latch-
plate securing screw
It
e
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—Qu
ic
k-fit connector
2—Return
pipe
Latch
-Plate Location
Page 491 of 2490

DO NOT DRIVE THE VEHICLE WITH THE TEST EQUIPMENT INSTALLED.
With the control valve CLOSED the pump maximum output pressure can be checked.
Remov
ing Test Equipment
T
o remove the test equipment:
Install a hose clamp
on the
reservoir to pump hose.
Re
moving the test equipmen
t is a reversal of the installation instructions.
Install a new O-r
ing to the PAS pump high
pressure outlet to hose connection.
Inst
all the original hose to the PAS pump.
R
emove the clamp from the reservoir to pump hose.
Top-up the reservoi
r fluid.
B
leed the PAS system; refe
r to this section.
Refer to PDU
User Guide
T
he PDU will diagnose all electrical components of the system.
Before changing a component, chec k fuse No. 12 (10A) in the left-hand heelboard fu se box. However, if this fuse is faulty a
number of other components wi ll also fail to function.