1998 JAGUAR X308 brake sensor
[x] Cancel search: brake sensorPage 429 of 2490

Anti-Lock Control -
Lubri
cants, Fluids, Sealants and Adhesives
Torques
Brake Tube, Hoses and Bracket Torques
CAUTI
ON: Replacement of
nuts and bolts: Various thread-locking devices are used on nuts and bolts throughout the
vehicle. These devices restrict the number of times a nut or bolt can be used. See section 100-00 for information.
UnitS
pecification
Brake flu
id
ITT Supe
r Dot 4
Com
ponent
Nm
Bol
t - front wheel speed sensor
8-
10
Bolt
- rear wheel speed sensor
8-
10
Bo
lt - hydraulic control unit to bracket
8-
10
Bolt -
hydraulic control unit bracket to body
10
-14
Hub rotor nut2
70-330
Com
ponent
Nm
Bleed n
ipple - front
4-
6
Bleed n
ipple - rear
8-1
1
Hose to fr
ont caliper
10
-14
Hose banjo to rear caliper -
bolt
30
-40
M1
0 hose locknut
15
-20
M10
brake tube female-nut
13
-17
M10
brake tube male-nut
13
-17
M12
brake tube male-nut
15
-20
M18
brake tube male-nut
22
-28
Brake tube clip retention
-bracket to body
4-
6
Page 430 of 2490

Anti-Lock Control - Anti-Lock Control
Description and Operation
Wheel Spe
ed Sensors
Each
wheel is monitored by a wheel speed se n
sor, to detect the speed of movement of
a toothed gear that is driven by the
wheel. Signal's generate d by the toothed gear passing th e sensor are sent to the ABS/TCCM to communicate the speed of
wheel rotation and any rapid change of wheel speed.
The frequency of the sinusoidal output voltag e signal from the sensor, is proportional to road wheel rotational speed and the
number of teeth on the toothed gear. The amplitude of the volt age is dependent upon the 'air gap' between the sensor and
toothed wheel, therefore it is important that this preset gap remains clear and undisturbed.
Ite
m
De
scr
iption
1Pe
dal Housi
ng / Booster - refer to 206-07
2Vac
u
um Hose - refer to 206-07
3Mas
t
er Cylinder / Reservoir - refer to 206-06
4Pri
m
ary Brake Circuit - refer to 206-06
5Sec
ondary Brake Circuit - refer to 206-06
6Hydraulic
Pump / Motor Unit
7ABS/Traction
Control Control Module (ABS/TCCM)
8Hydraulic Cont
rol Unit (HCU)
6/
7/
8
Br
ak
e Control Modulator
9Brake
Di
sc - refer to 206-03 or 206-04
10Brake
Cali
per - refer to 206-03/206-04
11Wh
ee
l Speed Sensor
12ABS Warning Lamp
13Brake
Fl
uid Level Warning-Lamp - refer to 206-06
Page 432 of 2490

It is a reciprocating two
-circuit pu
mp in which one brake circuit is as signed to each pump circuit.
It supplies th
e fluid pressure and vo
lume to supply the brake circuits under ABS and Traction control.
The pump is driven by an electri
c motor, with the pump
housing incorporating two lo w pressure accumulators and
damping chambers for each brake circuit.
The ac cu
mulator stores the pressure and smooths out the output pu
lses from the pump.
ABS Warning Lamp
The sys
tem will be set in a fail-safe mode if a problem is de
tected; a warning lamp on the instrument panel will notify the
driver there is a problem.
Anti-Lock Braking Sy
stem (ABS)
The AB
S components are combined with
an hydraulic booster and a tandem master cylinder to provide a two circuit braking
system. The system comprises, four wheel speed sensor s, a brake control modulator and an ABS warning lamp.
Should a wheel start to lock-up during braking a signal tr ansmitted from the wheel speed sensor to the brake control
modulator will start the hydraulic pump. The brake control modula tor will close the input valve of the line connected to the
locked-wheel to stop any increase in fluid pressure to the br ake caliper. If this fails to prevent the wheel locking, the
pressure in the caliper will be decreased by opening the return valve until th e wheel starts accelerating again. The fluid
pressure from the return va lve is directed into the low pressure accumulator, housed in the pump.
From the low pressure accumulator, fl uid is pumped through the damping cham ber to the brake master cylinder. The
pressure to the brake caliper will then be increased in small steps to maintain maximum adhesion between the tire and road
surface. This is achieved by closing the return valve, and opening the input valve and using the hydraulic pump to increase
the pressure.
Although the system senses all four wheels independently, the rear wheels are regulated as a pair. If a sensor on a rear
wheel detects a wheel decelerating rapidly, then the fluid pressure to both wheels is reduced. The fluid pressure is then
dictated by the wheel having the lowe st adhesion with the road surface.
The ABS system will be set in a fail-safe mode if a problem is detected; a warn ing lamp on the instrument panel will notify
the driver there is a problem. The brake system will still operate conventionally and with the same standard of performance
as a vehicle not equipped with ABS.
Automa tic Stability Control (ASC)
Th
e ASC utilizes the ABS sensing arrangement to provide the maximum traction force to propel the vehicle.
The ASC is switched on when the engine is started. The system can be switched off by pressing the 'ASC OFF' (the switched
is marked 'TRAC OFF' on vehicles fitted with traction control). The switch, which is situated in the center console switchpack,
lights up to warn that the system is sw itched off. An 'ASC' amber warning light flashes on the instrument panel when the
system detects a spinning wheel.
The ASC system uses engine intervention to reduce the torque delivered to the drive wheels to prevent them spinning.
Engine torque is re duced in three ways:
The
throttle is moved towards the closed position.
The ignition is retarded. F
u
el is cut-off at the cylinder injectors.
Wheel spin is detected by the wheel sp eed sensors and communicated to the AB S/TCCM. The ABS/TCCM uses information
from the controller area network (CAN) to calculate the torque that the engine should produce to stop the wheel spinning.
Torque reductions are then requested from the engine control module (ECM ) through the CAN. The throttle is then
positioned to provide the target torque, which has been calculated to prevent wheel spin. During the transient phase of
torque reduction the fuel is cut-off and th e ignition retarded Both the fuel cut-off an d ignition retard will be restored to
normal when the throttle is set to its new position.
The ASC uses a brake control modulator with six solenoid va lves: three normally open inlet valves and three normally
Page 1111 of 2490

the
intake elbow provide connections for vacuum actuators and are also used to redirect emissions into the engine.
On the right-hand side of the elbow a la rge diameter pipe connects to the brake servo. The smaller pipe provides a vacuum
feed to the fuel rail pressure regulator and throttle cruise control system. On the le ft-hand side of the elbow the front pipe
supplies vacuum control for the evaporative emissions system valves.
Emissions from the engine part load breather (bank 2) and pu rged fuel vapor from the EVAP valve are drawn via a common
T piece into the left-hand side of the intake elbow. Re-cir culated exhaust gas enters the intake elbow via the EGR valve
which is mounted directly on the rear of the elbow : where the EGR system is not used, a blanking plate is fitted.
The fuel system, throttle and emission control system s are described more fully in the relevant sections.
Intake Manifold
Filtered air from the vehicle's intake ducting is metered by th e electronic throttle and distributed to the two cylinder banks
via an integral intake manifold.
The intake manifold is manufactured in plastic with integral plastic fuel rails and metal-thread inserts; the very smooth
internal surfaces give excellent air flow.
Individual ducts lead off a central chamber to the inlet valves of each cylinder.
Silicon-rubber gaskets, loca ted in channels in the intake manifold, seal th e joints between the ducts and the cylinder heads.
Engine Ventilation
The e
ngine is ventilated through two brea
thers; a part-load breather and a full-load breather, one on each camshaft cover.
The outlet hose for the part-load breather is connected between the bank 2 camshaft cover and the intake elbow. The full-
load outlet hose is connected from the bank 1 camshaft cover to the intake duct between the MAF sensor assembly and the
throttle body.
Constructed in plastic, the hoses incorporate O-ring seal s and quick-release connectors; refer to Section 303-01.
I
ntake Air Distribution and Filtering - Supercharged Vehicles
Ai
r is supplied to the supercharger via an
intake cleaner/duct, throttle assembly and intake elbow which are similar to those
used for normally aspirated engines. The su percharger delivers pressurized air to two separate charge air cooler units, each
unit being mounted on the cy linder bank which it supplies. Pr essurized cooled air is fed from the charge air coolers directly
into each inlet port.
Page 1206 of 2490
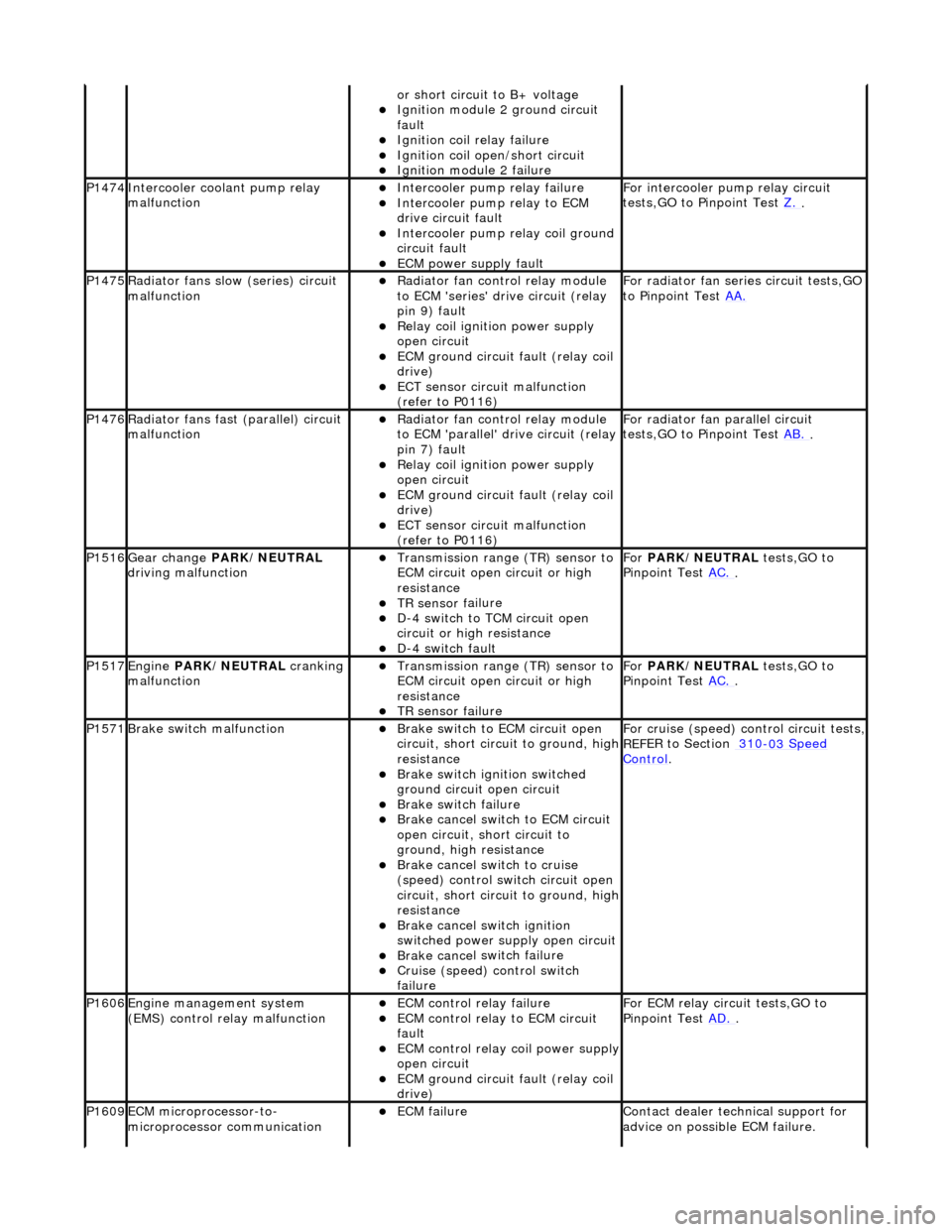
or sho
rt circuit to B+ voltage
Ignition modul
e
2 ground circuit
fault
Ignition coil relay fai
lure
Ignition coil
open/short
circuit
Ignition modul
e
2 failure
P1474Int
e
rcooler coolant pump relay
malfunction
Intercooler pump relay failure
Intercooler pump relay
to ECM
drive circuit fault
Intercooler pump relay coi
l ground
circuit fault
ECM power supply f
ault
F
or i
ntercooler pump relay circuit
tests,GO to Pinpoint Test Z.
.
P1475Ra
diator fans slow
(series) circuit
malfunction
R a
diator fan control relay module
to ECM 'series' drive circuit (relay
pin 9) fault
Relay coil ignition power supply
o p
en circuit
ECM ground circuit fault (relay coil
drive)
ECT se ns
or circuit malfunction
(refer to P0116)
F o
r radiator fan seri
es circuit tests,GO
to Pinpoint Test AA.
P1476Ra
diator fans fast (parallel) circuit
malfunction
R a
diator fan control relay module
to ECM 'parallel' drive circuit (relay
pin 7) fault
Relay coil ignition power supply
o p
en circuit
ECM ground circuit faul
t (relay coil
drive)
ECT sens
or circuit malfunction
(refer to P0116)
F or radi
ator fan parallel circuit
tests,GO to Pinpoint Test AB.
.
P1516Gear change PARK
/NEUTRAL
driving malfunction
Transmission range (T
R) sensor to
ECM circuit open circuit or high
resistance
TR sensor f
ailure
D-
4
switch to TCM circuit open
circuit or high resistance
D-4 swi
tch fault
For
PARK/NEUTRAL tests,GO to
Pinpoint Test AC.
.
P1517Engine PA
RK/NEUTRAL
cranking
malfunction
Transmissi on range (T
R) sensor to
ECM circuit open circuit or high
resistance
TR sensor f
ailure
Fo
r
PARK/NEUTRAL tests,GO to
Pinpoint Test AC.
.
P1571Brake swit
ch malfunction
Brake sw
it
ch to ECM circuit open
circuit, short circ uit to ground, high
resistance
Brake sw it
ch ignition switched
ground circuit open circuit
Brake sw it
ch failure
Brake ca
ncel
switch to ECM circuit
open circuit, short circuit to
ground, high resistance
Brake ca nce
l switch to cruise
(speed) control switch circuit open
circuit, short circ uit to ground, high
resistance
Brake cance
l switch ignition
switched power supply open circuit
Brake ca nce
l switch failure
Cru
i
se (speed) control switch
failure
For cru i
se (speed) control circuit tests,
REF
E
R to Section 310
-03
Sp
eed
Control.
P1606Engine
m
anagement system
(EMS) control relay malfunction
ECM co ntrol rel
ay failure
ECM c
o
ntrol relay to ECM circuit
fault
ECM co ntrol rel
ay coil power supply
open circuit
ECM ground circuit faul t (relay coil
drive)
F or ECM
relay circuit tests,GO to
Pinpoint Test AD.
.
P1609EC
M microprocessor-to-
microprocessor communication
ECM failu r
e
Contact deal
er techni
cal support for
advice on possible ECM failure.
Page 1272 of 2490

3.3. Gradient: Under specific speeds and loads
4. 4. Cruise: During cruise control
5. 5. Manual: Shift map when the LH side of the 'J gate' is used
Three specific condition shift maps have a higher priority than the two base shift maps and will intervene when appropriate
conditions prevail for traction, gradient or cruise.
When traction control (engine or brake system derived) is operational the TCM will implement the traction map to maximise
control of wheel slip.
The gradient maps are intended to enhance vehicle drivability when towing or climbing a gradient. The TCM will implement
the maps when increased driving resistan ce is detected and enhanced drivability, cooling and increa sed performance is
appropriate.
The cruise map is intended to minimize unwanted gearshifts and 'hunting' and is activated when cruising near to the set
speed, or resuming.
Connector Pins Identification
Connector Pin Identity Chart for EM007
Pin NumberCircuit Function
001Pressure regulator 2
002Mode switch status
003Not used
004Pressure regulator #4
005Pressure regulator #1
006Power ground
007Not used
008Rotary switch L2
009Rotary switch L4
010 to 011Not used
012Mode switch Pin B (Sport)
013D to 4 switch
014Input speed sensor (-)
015Output speed sensor (screen)
016Output speed sensor (+)
017Not used
018Kickdown switch (where used)
019 to 020Not used
021Analogue ground
022Fluid temperature sensor
023Input speed sensor (screen)
024 to 025Not used
026B+
027Not used
028Digital ground
029Pressure regulator #3
Page 1390 of 2490

Stator, intermediate and output shafts. Three epicyclic geartrains. Six multi-disc clutch/brake packs. Two freewheels (One-way clutches). Hydraulic pump. Parking lock assembly. Electro-hydraulic control unit. Internal harness and 13 pin connector with bayonet lock.
Hydraulic pump
This engine driven pump is located at the front of the transmission casing and provides pressure for the hydraulic
functions.
Supplies fluid under pressure to the torq ue converter, geartrain, electro-hydraulic control unit and the lubrication
circuit.
Draws fluid from the fluid pa n below the transmission casing, through a filter.
Parking lock
This component prevents movement of th e vehicle by engaging a fixed pawl with the parking lock gear located on the
output shaft. The pawl is engaged by movi ng the gear selector lever to the park (P) position.
Electro-hydraulic control unit
This unit, mounted in the transmission lower case, converts signals, mechanical from the J-gate and electrical from the
TCM, into hydraulic functions.
The following components ar e assembled to the unit:
Selector valve. Shift plate. Control valve - modulating pressure. Control valve - shift pressure. Solenoid valve 1 <-> 2 and 4 <-> 5 shift. Solenoid valve 3 <-> 4 shift. Solenoid valve 2 <-> 3 shift. Solenoid valve - converter lock-up. Speed sensors (2). Temperature sensor.
Speed sensors
There are two speed sensors within the transmission assembly which provide input to the TCM. These inputs, when used in
conjunction with CAN data relative to engine speed (from ECM) and road speed (from ABS), are used to electronically
control the transmission.
Temperature sensor
The output from this sensor allows the TCM to compensate for the affect of fluid temperature on shift time and quality
Control Systems
Hydraulic Control
The selector valve is operated directly by the J-gate and directs fluid flow for P R N D.
Of the four solenoid valves, 3 control shifts and 1 controls converter lock-up. One control valve controls modulating pressure
and the other shift pressure.
Regulating valves are used to maintain/control pressure for lu brication, normal operating functions, and the supply to the
control valves and shift valves.
Page 1989 of 2490

Wiring Harnesses - Wiring Harness
Description and Operation
Introduction
CAUTION: Do not use any other heat shrink sleeve other than the approved glue lined heat shrink sleeve mentioned
in the repair procedure.
The purpose of this document is to promote quick and efficient minor repair to harness connectors or cables using approved
methods and the wiring harness repair kit. Repairs may only be made to cables and connectors which have been
mechanically, not electrically damaged. It also applies wher e the whole extent of the damage can be clearly identified and
rectified.
Care and neatness are essential requir ements in making a perfect repair.
Caution:
At the time of this first issue of the Harness Repair Guide, do not approve re pairs to any of the following circuits:
Any media orientated system transport network harnesses. Supplement restraint system (SRS) firing circuits (Air bags). Link lead assembles, which are unique to safety critical circuits such as anti-lock brake system (ABS) and
thermocouple circuits. An example of this is the ABS wheel speed sensors with moulded connectors.
4. Screened cables, leads and wiring harness(s).
If any harness(s) with defective electrical connector te rminals or wires from the above circuits are a concern,
new components must be installed.
Repair Kit
CAUTION: Where the repair procedure indica tes that a glue lined heat shrink sleeve should be applied, apply sufficient
heat to the glue lined heat shrink to melt the glue in order to provide a water tight seal. Do not over heat the glue lined
heat shrink sleeve so that the wiring harness insulation becomes damaged.
The wiring harness repair kit has been produced which comprises:
Pre-terminated wiring harness(s) of different sizes and types Three sizes of butt splice connectors A selection of colored cable identification sleeves Two sizes of glue lined heat shrink sleeves Crimping pliers A wire cutter and insulation stripper An electrical connector terminal extraction handle and tips
A suitable heat source, fo r shrinking heat shrink sleeves will be required.
The pre-insulated diamond grip range of el ectrical connector terminals and in-line, butt splice connectors contained within
the wiring harness repair kit are the only acceptable product for the repairs of wi ring harnesses. The butt connectors not
only grip the wire but also the insu lation, making a very secure joint.
If an electrical connector terminal is not included in the wiring harness repair kit then approval for the repair is NOT given
and in these circumstances a new wi ring harness must be installed.
Pre-Terminated Wiring Harness( s) and Butt Splice Connectors
All pre-terminated wiring harness(s) and butt splice connectors in the wiring harness repair kit are contained in bags which
can be resealed after use. Each bag is marked with the part number of the items stored within the bag. Each storage
compartment in the wiring harness repair kit is identified with the corresponding part number. Make sure that pre-
terminated wiring harness(s) and connectors are not mixed up it is advisable to only open one bag at a time and to reseal