1998 JAGUAR X308 valve
[x] Cancel search: valvePage 1503 of 2490
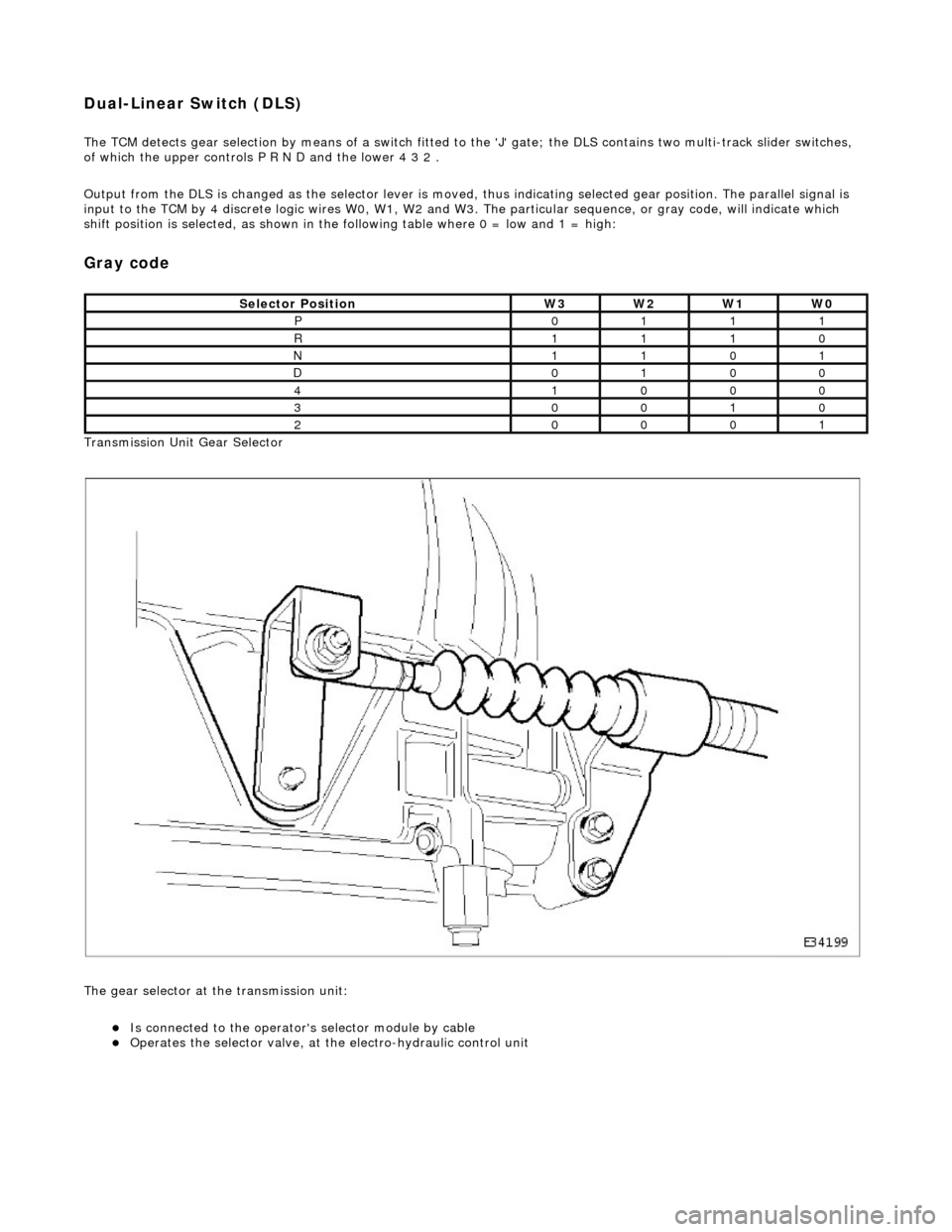
Dual-Linear Switch (DLS)
The TCM detects gear selection by means of a switch fitted to the 'J' gate; the DLS contains two multi-track slider switches,
of which the upper controls P R N D and the lower 4 3 2 .
Output from the DLS is changed as the select or lever is moved, thus indicating selected gear position. The parallel signal is
input to the TCM by 4 discrete logic wires W0, W1, W2 and W3. The particular sequence, or gray code, will indicate which
shift position is selected, as shown in the following table where 0 = low and 1 = high:
Gray code
Transmission Unit Gear Selector
The gear selector at the transmission unit:
Is connected to the operator's selector module by cable Operates the selector valve, at the electro-hydraulic control unit
Selector PositionW3W2W1W0
P0111
R1110
N1101
D0100
41000
30010
20001
Page 1688 of 2490

Fuel System - General Inform
ation - Fuel System
Description an
d Operation
The fuel tank is mounted across the vehicle behind the passenger compartment bulkhead.
Fuel is drawn by the fuel pump from the tank and then supplied to the two fuel rails, via a filter.
Fuel injectors are installed in the fuel ra ils on each side of the intake manifold.
The amount of fuel injected into th e engine is controlled by the ECM.
A cross-over pipe connects the two fuel ra ils together at the front of the manifold.
A test valve in the cross-over pipe allo ws the fuel rail to be pressurized and de-pressurized during the servicing and
troubleshooting procedures.
A pressure regulator on the rear of the right fuel rail controls the pressure in the fuel rails.
A return line directs excess fuel from the pressure regulator back to the fuel tank.
Operation and service procedures
The fuel injector
s, rails, pres
sure regulator and, wher e fitted, supercharger are described in greater detail in Section 303-04
together with servicing procedures.
The fuel tank, pump, fuel level senders and fuel lines are similarly covered in Section 310-01.
Page 1689 of 2490

Fuel System - General Information - Fuel System Pre
ssure Check
Gen
eral Procedures
WARNING: Working on the fuel system re sults in fuel and fuel vapor being present in the atmosphere. Fuel vapor is
extremely flammable, hence great care must be taken whilst working on the fuel system. Adhere strictly to the following
precautions:
D
o not smoke in the work area
Di
splay
NO SMOKING signs around the work area
D
isconnect the battery before
working on the fuel system
Av
oid sparks
Make sure sui
table fire ex
tinguishers are at hand
Make sure absor
bent material is at
hand to soak up any spillage
Make sure the work area is
well ventilated
M
ake sure that the gauge is correctly conn
ected, and that all connections are secure BEFORE starting the engine
DO N
OT
disconnect the gauge from the schrader valve while the engine is running
Make su
re the schrader valve reseals once the gauge is disconnected
• NOTE: Depending on the design of the ga uge set, there may be a drain valve and tube. Make sure this valve is closed, and
the drain tube placed in a suitable container BEFORE connecting the gauge to the schrader valve.
1. Make sure the vehi
cle is in
Park for vehicles with automatic
transmission, Neutral for vehicles with manual transmission.
2. Apply the parking brake.
3. Place suitable absorbent material around the schrader valve to
absorb any spillage when connecting the gauge set.
4. Remove the protective cap from the schrader valve.
5. Connect the gauge, using adaptors if required.
6. Remove the absorbent material and dispose of safely.
7. Disconnect and plug the vacuum hose from the pressure
regulator.
8. Start the engine and record the fuel pressure reading.
As a gui
de, the fuel pressu
re should be approximately 3.0
bar (44.1 psi) with the regulator disconnected.
9. With the engine still running, reconnect the vacuum hose to
the pressure regulator an d record the reading.
Th
e pressure should dr
op to approximately 2.6 bar (38
psi) when the vacuum hose is reconnected.
10. Switch off the engine.
11. Place more absorbent material around the schrader valve.
12. Where fitted, open the drain valve and allow the fuel from the
gauge and line to flow into the container to depressurize the
system.
13. Disconnect and remove the gauge set and any adaptors.
14. Clean up any fuel which may have been spilt and remove the
absorbent material. Dispose of safely.
15. Refit and secure the protective cap to the schrader valve.
16. Reconnect the fuel pressure regulator vacuum hose.
17. Start the engine and make sure there are no leaks.
Page 1690 of 2490
Fuel System - General Information - Fuel System Pressure Rele
ase
Gen
e
ral Procedures
S p
ecial Tool(s)
Tes
t
Equipment - Fuel Pressure Relief
310-058 (TE 7635A or JD 209)
1. WARNING: BEFORE PROCEEDING, IT IS ESSENTIAL THAT
THE WARNING NOTES GIVEN IN SECTION 100-00 (UNDER THE
HEADING 'SAFETY PRECAUTIONS') ARE READ AND
UNDERSTOOD.
Open engine compartment and fi t paintwork protection sheets.
2. Carefull
y remove left
hand engine cover, taking care not to
damage the plasti c fixings or the rubber inserts.
3. WA
RNING: MAKE SURE EQUIPMENT BLEED / DRAIN
VALVE IS CLOSED.
• NOTE: Place a cloth under the valve to collect any spillage.
Depressurize fuel system.
Make sure ignition i s
switched off.
R
e
move cap from Schrader valve.
Pla
c
e a closed container, su
itable for collecting fuel,
adjacent to vehicle.
R e
move lid from container.
Conne
ct
fuel injection pressu
re test equipment 310-058
(TE 7635A or other suitable type).
Insert drain / bleed tu be i
nto fuel container.
R
e
ad and follow manufacturer's instructions to
depressurize fuel system.
4. Store drained f u
el safely and make
sure container lid is closed
securely.
5. Remove equipment and discard cloth from beneath the valve.
6. Install valve cap.
7. Install left hand engine cover.
Page 1691 of 2490
Fuel System - Gener
al Information - Fuel Tank Draining
Gen
eral Procedures
1.
WARNING: BEFORE PROCEEDING, IT IS ESSENTIAL THAT
THE WARNING NOTES GIVEN IN SECTION 100-00 (UNDER THE
HEADING 'SAFETY PRECAUTIONS') ARE READ AND
UNDERSTOOD.
Remove the battery. Refer to operation 86.15.01.
2. De
pressurise the fuel system.
E
nsure that the ignition is
switched off and remove the
valve cap from the fuel cross-over pipe. Place a cloth
under the valve to collect any spillage.
Pla
ce a closed container, su
itable for collecting fuel,
adjacent to the vehicle. Remove the lid.
3. Conne
ct the fuel injection pressu
re test equipment JD 209 (or
other suitable type). Insert the drain / bleed tube into the fuel
container. Follow the manufa cturer's instructions and
depressurise the fuel system.
4. Store the drained fuel safely and ensure that the lid is closed
securely. Remove the equipmen t and discard the cloth from
beneath the valve. Refit the valve cap.
5. Use a suitable fuel storage tank er / pump system to drain the
vehicle tank as described below.
6. Connect a ground cable betw een the vehicle and drain
equipment and connect both to a suitable earth point.
7. At the engine bay bulkhead, lo cate the quick fit connecto
r
between the underfloor fuel feed pipe and the fuel pulse
damper.
Pla
ce a cloth under the pipes
to absorb any spillage.
D
isconnect the fuel feed hose
at the quick fit connector,
using special tool JD 182.
Conne
ct the fuel drain equipment to the underfloor fuel
feed pipe.
8. Drain the fuel tank in accordance with the equipment
manufacturers instructions.
Page 1693 of 2490

Filler Cap and P
ipe
The fuel
filler cap with bayonet-type fixi
ng is located beneath a remote-release sp ring-latched lid on the rear saddle panel
on the left-hand-side of the vehicle.
Fuel Pum
p
The fu
el pump(s) is energized by an ECM co
ntrolled relay. Fuel is drawn by this pu mp and supplied to the fuel injectors via
the fuel line, filter and fuel rails.
Servicing of the fuel pump re quires fuel tank removal.
Ev
aporative Loss Flange Assembly
The evaporative-loss flan
ge asse
mbly is mounted centrally on top of the tank. The flange assembly consists of a removeable
steel cap which mounts the evaporative emissions system vapor outlet valves and, if applicable, a pressure sensor. The
external electrical supply to th e fuel pump(s) is also made via a connector on the flange.
The flange assembly is fixed to the tank by a locking ring which is turned usin g special tool JD-174. A seal is fitted between
the flange assembly and the tank. Three di fferent flange assemblies are applicable according to the evaporative emission
system fitted to the vehicle. The fl ange size and fixing are identical fo r the three systems, as described.
Removal of the evaporative flange assembly is necessary to gain access to th e fuel pump(s) and other internal components.
To remove the evaporative fl ange assembly the fuel tank must first be removed.
The evaporative flange variant assemblies are described, together with service information, in Section 303-13.
Fuel R
eturn
Excess fuel
is directed back to
the fuel tank via a return line.
Fuel Pum
p Relay
The
fuel pump relay,
under control of the ECM, switches power to the fuel pump motor.
I
nertia Fuel Shutoff (IFS) Switch
The IF
S switch is located in the right-hand
side footwell behind the footboard carpet . When activated the switch isolates the
ignition system and fuel pump, releases any locked doors and disables unnecessary electrical systems. The system can be
reset by pressing down the flexible cover on the top of the switch.
• NOTE: The doors will not unlock if the IFS switch is tripped when the ignition switch is in position '0'.
Page 1753 of 2490
Climate Co
ntrol System - General In
formation - Climate Control System
Description an
d Operation
CAUTION: Observe all relevant safety requirements. Wear suitable eye and skin protection Do not mix HFC 134A and
CFC 12 refrigerants. Do not vent refrigerant directly to atmosphere and always use Jaguar approved recovery, recycle and
recharge equipment. Note the amount of recovered refrigerant; it will indicate the state of the system.
Working Practices
Be aware o
f, and comply with al
l health and safety requirements , whether they be legislative or common sense. This applies
to conditions set both for the operator and workshop.
Before commencing any repair or service procedure, disconnect the vehicle battery ground lead and protect the vehicle,
where appropriate, from dirt or damage.
Work in a well ventilated, clean and tidy area.
Keep all components and tools clean.
Recovery, recycle and recharge equipment must meet, or ex ceed, the requirements detailed in the Specification sub-
section.
Handling Refrigerant
We
ar eye protection at all times. Use gloves and keep all
skin covered that may come into contact with refrigerant.
Should refrigerant come into co ntact with eyes or skin, wash the affected area with cool water and seek medical advice; do
not attempt to treat the condition yourself.
Avoid breathing refrigerant vapor; it may cause irritation to the respiratory system.
CAUTION: Never use high pressure comp ressed air to flush out a system. Under certain ci rcumstances a combination
of HFC 134A refrigerant, compressed air and a source of combus tion (welding and brazing operations in the vicinity), may
result in an explosion and the release of potentially toxic compounds.
HFC 134A and CFC 12 refrigerants must neve r come into contact with each other. They will form an inseparable mixture
which can only be disposed of by incineration.
Do not vent refrigerant directly to atmo sphere; always use Jaguar approved recove ry equipment. Never depress the charge
or discharge port valves to check for the pr esence of refrigerant.
HFC 134A refrigerant is fully recycleable and it may be 'cleaned' by the recovery equipment and therefore re-used following
removal from a system.
Page 1756 of 2490
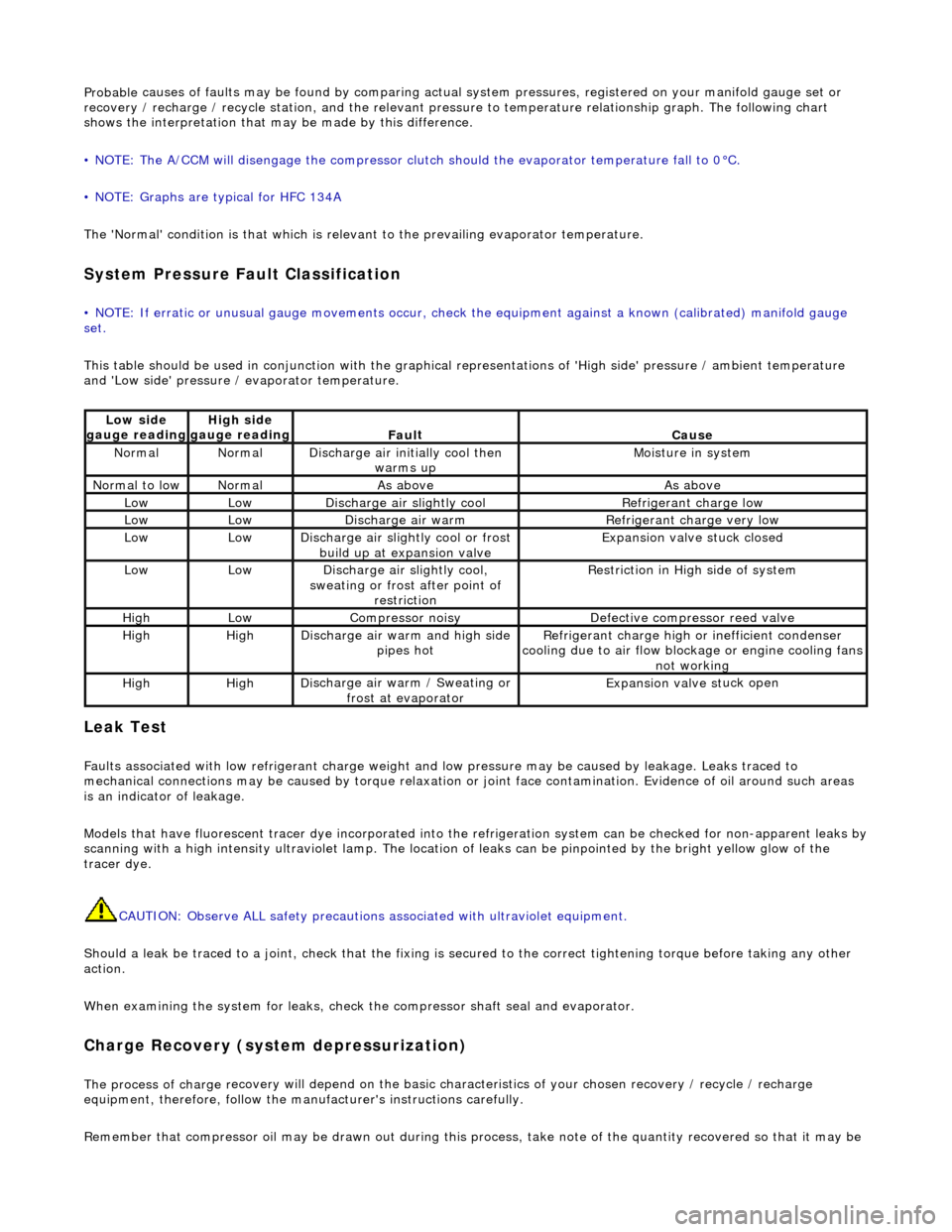
Probable
causes of faults may be found by comparing actual
system pressures, registered on your manifold gauge set or
recovery / recharge / recycle station, and the relevant pressure to temperature relationship graph. The following chart
shows the interpretation that ma y be made by this difference.
• NOTE: The A/CCM will disengage the compressor clutch should the evaporator temperature fall to 0°C.
• NOTE: Graphs are typical for HFC 134A
The 'Normal' condition is that which is relevant to the prevailing evaporator temperature.
System Pressure Fault Classification
• NOTE
: If erratic or unusual gauge move
ments occur, check the equipment against a known (calibrated) manifold gauge
set.
This table should be used in conjunction with the graphical representations of 'High side' pressure / ambient temperature
and 'Low side' pressure / evaporator temperature.
Leak
Test
F
a
ults associated with low re
frigerant charge weight and low pressure ma y be caused by leakage. Leaks traced to
mechanical connections may be caused by to rque relaxation or joint face contamination. Evidence of oil around such areas
is an indicator of leakage.
Models that have fluorescent tracer dye incorporated into the refrigeration system can be checke d for non-apparent leaks by
scanning with a high intensity ultraviolet lamp. The location of leaks can be pinpointed by the bright yellow glow of the
tracer dye.
CAUTION: Observe ALL safety precautions associated with ultraviolet equipment.
Should a leak be traced to a joint, check that the fixing is secured to the correct tightening torque before taking any other
action.
When examining the system for leaks, chec k the compressor shaft seal and evaporator.
Charge Re
covery (system depressurization)
The process of
charge r
ecovery will depe
nd on the basic characteristics of your chosen recovery / recycle / recharge
equipment, therefore, follow the manu facturer's instructions carefully.
Remember that compressor oil may be drawn out during this process, take note of the quantity recovered so that it may be
Lo
w side
gauge reading
High s i
de
gauge reading
Fau l
t
Cause
No
r
mal
No
r
mal
Di
sc
harge air initially cool then
warms up
Mois
ture in system
N
ormal
to low
No
r
mal
As aboveAs above
LowLowD
i
scharge air slightly cool
Ref
r
igerant charge low
LowLowDi
scharge air warm
Refr
igerant charge very low
LowLowDi
scharge air slightly cool or frost
build up at expansion valve
Expansion valve st
uck closed
LowLowDi
scharge air slightly cool,
sweating or frost after point of restriction
Restri
ction in High side of system
HighLowCompressor noisyDe
fe
ctive compressor reed valve
HighHighD
i
scharge air warm and high side
pipes hot
Refri
gerant charge high or inefficient condenser
cooling due to air flow blockage or engine cooling fans
not working
HighHighD i
scharge air warm / Sweating or
frost at evaporator
Expans ion valve st
uck open