1998 JAGUAR X308 evaporative
[x] Cancel search: evaporativePage 1078 of 2490
• NO
TE: When performing electrical voltag
e or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter (DMM) accurate to 3
decimal places, and with an up-t o-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the
DMM leads into account.
• NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic ro utines involving pinpoint tests.
Sym
ptom Chart
Sy
m
ptom
Possib
l
e source
Acti
o
n
Engine
cranks, but does
not fire
Secu
rit
y system /Immobiliser
engaged
Harness Fue l
system
ECM fault
Contact deal er techni
cal support for
information on security system. Check fuel
system pressure,
REFER to: Fuel System Pressure Check
(310
-
00 Fuel System - Genera l Information, General
Procedures).
For ECM tests,
REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls
(303
-14
Electronic Engine Co ntrols, Diagnosis and
Testing).
Engine cranks and
fi
res, but will not
start
Fu
el pump relay
Fuel
pump
Cyl
i
nder compression loss
(short-term. Refer to bulletin; 303-52)
Engine coolan t
temperature
(ECT) sensor
Spark plugs fouled, gapp
ed
incorrectly
Ignition coil fail
ure(s)
Check f
o
r water ingress into
spark plug wells
HT sho rt to ground (tracking)
check rubber
boots for
cracks/damage
Fo
r fuel pump relay tests,
REFER to: Fuel Charging and Controls
(303
-04
Fuel Charging and Controls, Diagnosis and Testing).
Check fuel pressure,
REFER to: Fuel System Pressure Check
(310
-
00 Fuel System - Genera l Information, General
Procedures).
For compression loss, REFER to the technical service bulletins. For ECT sensor tests,
REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls
(303
-14
Electronic Engine Co ntrols, Diagnosis and
Testing).
For spark plug tests, GO to Pinpoint Test B.
.
For ign i
tion system tests, GO to Pinpoint Test
A.
.
Diff
icult to start cold
Batt
ery Fuel
pump
Cyl
i
nder compression loss
(short-term. Refer to bulletin; 303-52)
Spark plugs fouled, gapp
ed
incorrectly
F o
r battery information,
REFER to: Battery and Cables
(414
-01 Battery,
Mounting and Cables, Description and Operation).
Check fuel pressure.
REFER to: Fuel System Pressure Check
(310
-
00 Fuel System - Genera l Information, General
Procedures).
For compression loss, REFER to the technical service bulletins. For spark plug tests, GO to
Pinpoint Test B.
. For ig
nition system tests, GO
to Pinpoint Test A.
.
Diff
icult to start hot
Roc
h
ester valve
Injec
t
or leak
Purge
val
ve
Fue
l
pump
Engine coolan
t
temperature
(ECT) sensor
F or R
ochester
valve test,
REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls
(303
-14
Electronic Engine Co ntrols, Diagnosis and
Testing).
For injector leak test, REFER to technical
service bulletins. Check fuel pressure. For evaporative emissions components,
REFER to: Evaporative Emissions
(303
-13
Evaporative Emissions, Diagnosis and Testing).
For ECT sensor tests,
REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls
(303
-14
Electronic Engine Co ntrols, Diagnosis and
Testing).
D iff
icult to start after hot soak
(vehicle standing after engine has reached operating temperature)
Roc h
ester valve
Injec
t
or leak
Purge
val
ve
Fue
l
pump
Engine coolan
t
temperature
(ECT) sensor
F or R
ochester
valve test,
REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls
(303
-14
Electronic Engine Co ntrols, Diagnosis and
Testing).
For injector leak test, REFER to technical service bulletins. Check fuel pressure,
REFER to: Fuel System Pressure Check
(310
-
00 Fuel System - Genera l Information, General
Procedures).
Page 1079 of 2490
F
or evaporative emissions components,
REFER to: Evaporative Emissions
(30
3-13
Evaporative Emissions, Diagnosis and Testing).
For ECT sensor tests,
REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls
(30
3-14
Electronic Engine Co ntrols, Diagnosis and
Testing).
Engine stalls
soon after start
F
uel pump relay
ECM relay
Harness damage Fue
l pump
Engine coolan
t temperature
(ECT) sensor
Fue
l lines
F
uel pressure regulator
Air leakage
Check f
or DTCS. For fuel pump and ECM relay
tests,
REFER to: Fuel Charging and Controls
(30
3-04
Fuel Charging and Controls, Diagnosis and Testing).
Check fuel pressure.
REFER to: Fuel System Pressure Check
(31
0-
00 Fuel System - Genera l Information, General
Procedures).
For ECT sensor tests,
REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls
(30
3-14
Electronic Engine Co ntrols, Diagnosis and
Testing).
For fuel line information,
REFER to: Fuel Tank and Lines
(31
0-01 Fuel
Tank and Lines, Description and Operation).
For fuel pressure regulator,
REFER to: Fuel Charging and Controls
(30
3-04
Fuel Charging and Controls, Diagnosis and Testing).
For intake system information,
REFER to: Intake Air Distribution and Filtering
(30
3-12 Intake Air Distribution and Filtering,
Description and Operation).
Engine hesi
tates/poor acceleration
Fue
l pump
Air leakage
F
uel pressure regulator
Fue
l lines
Harness damage Throttl
e sensors
Throttl
e motor
Spark
plugs fouled, gapped
incorrectly
Ignition coil
failure(s)
Check f
or water ingress into
spark plug wells
HT sho
rt to ground (tracking)
check rubber boots for cracks/damage
Exhaus
t gas recirculation (EGR)
(SC only)
Chec
k fuel pressure,
REFER to: Fuel System Pressure Check
(31
0-
00 Fuel System - Genera l Information, General
Procedures).
For intake system information,
REFER to: Intake Air Distribution and Filtering
(30
3-12 Intake Air Distribution and Filtering,
Description and Operation). For fuel pressure regulator,
REFER to: Fuel Charging and Controls
(30
3-04
Fuel Charging and Controls, Diagnosis and Testing).
For fuel lines information,
REFER to: Fuel Tank and Lines
(31
0-01 Fuel
Tank and Lines, Description and Operation).
For throttle position se nsor and throttle motor
relay tests,
REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls
(30
3-14
Electronic Engine Co ntrols, Diagnosis and
Testing).
For spark plug tests, GO to Pinpoint Test B.
.
For ign
ition system tests, GO to Pinpoint Test
A.
. F
or EGR information,
REFER to: Engine Emission Control
(30
3-08
Engine Emission Cont rol, Description and
Operation).
Engine ba
ckfires
Fue
l pump
Fue
l lines
Air leakage
Mass ai
r flow (MAF) sensor
Spark plugs
Check f
or water ingress into
spark plug wells
HT sho
rt to ground (tracking)
check rubber boots for cracks/damage
Chec
k fuel pressure,
REFER to: Fuel System Pressure Check
(31
0-
00 Fuel System - Genera l Information, General
Procedures).
For fuel pump and lines,
REFER to: Fuel Tank and Lines
(31
0-01 Fuel
Tank and Lines, Description and Operation).
For intake system,
REFER to: Intake Air Distribution and Filtering
(30
3-12 Intake Air Distribution and Filtering,
Description and Operation). For MAF sensor tests,
Page 1098 of 2490
Engine Emission
Control - Exhaus
t Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve
Remo
val and Installation
Remov
a
l
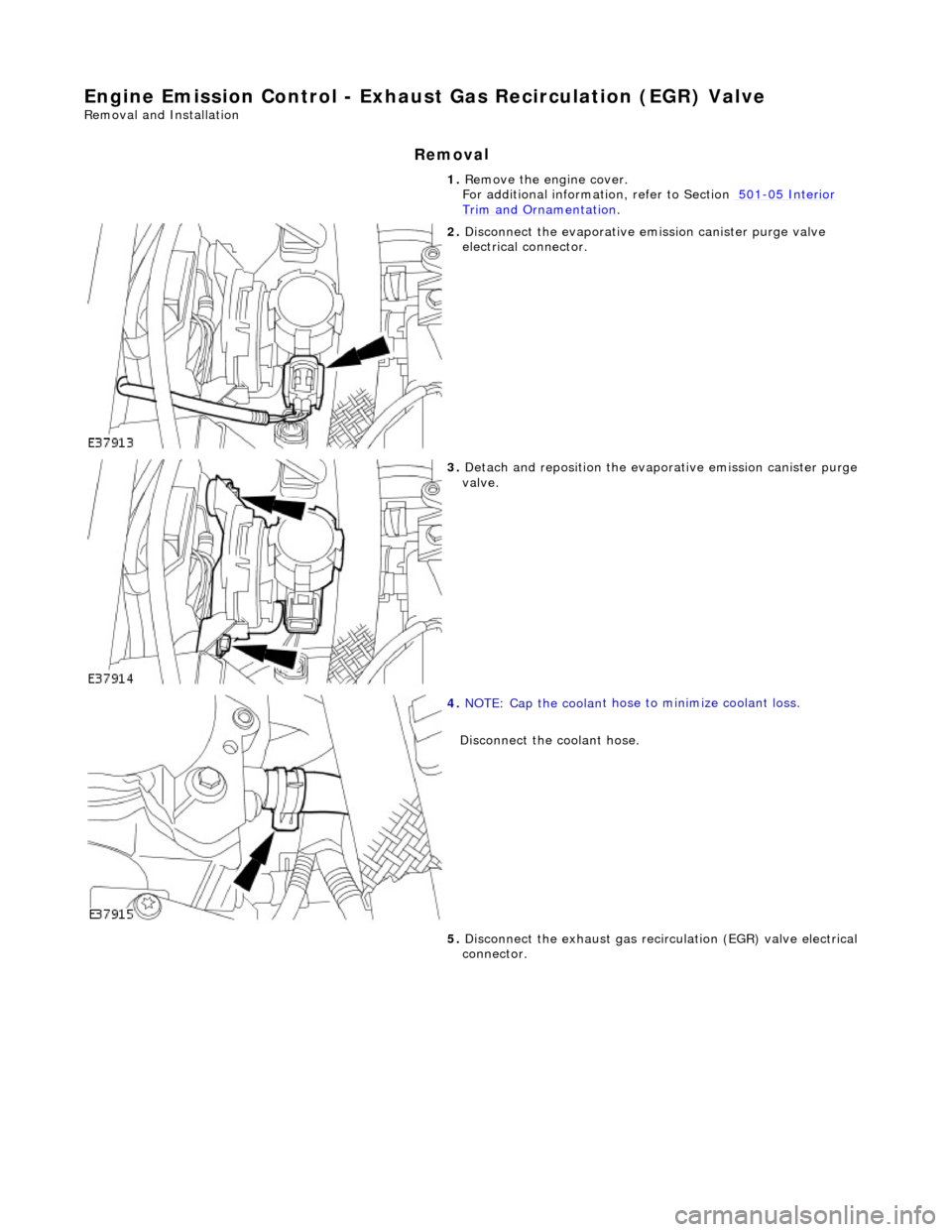
1.
Re
move the engine cover.
For additional informat ion, refer to Section 501
-05
Interior
Trim and Ornamen
t
ation
.
2. Disc
onnect the evaporative emission canister purge valve
electrical connector.
3. Detac
h and reposition the evaporative emission canister purge
valve.
4. NOTE : Cap the coolan
t hose
to minimize coolant loss.
Disconnect the coolant hose.
5. Disconnect the exhaust gas recirc ulation (EGR) valve electrical
connector.
Page 1101 of 2490
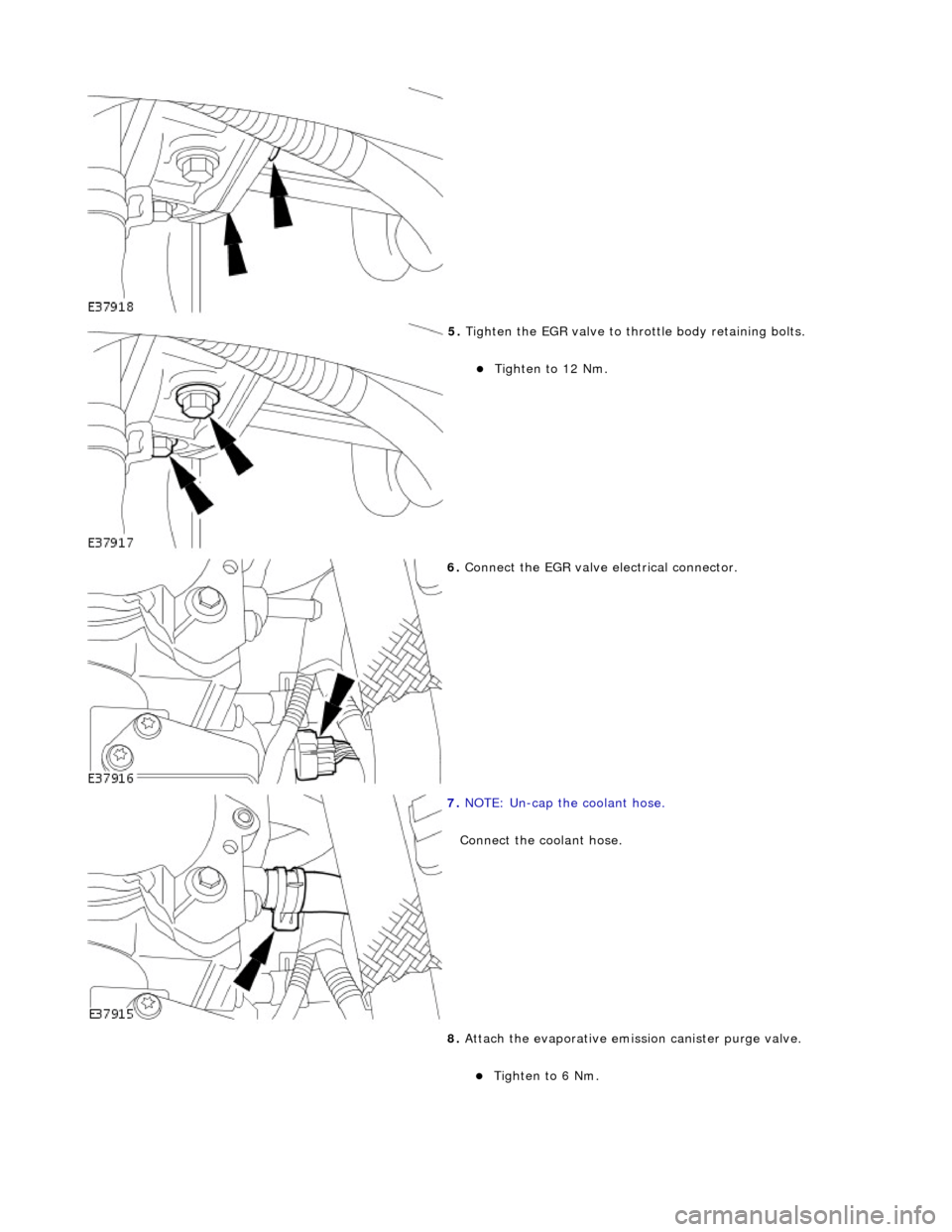
5. Tigh
ten the EGR valve to throttle body retaining bolts.
Tigh
ten to 12 Nm.
6. Con
nect the EGR valve electrical connector.
7. NO
TE: Un-cap the coolant hose.
Connect the coolant hose.
8. Attach the evaporative emission canister purge valve.
Tigh
ten to 6 Nm.
Page 1102 of 2490

9.
Connect
the evaporative emission canister purge valve
electrical connector.
10. Check and if necessary to p up the cooling system.
11. Install the engine cover.
For additional informat ion, refer to Section 501
-05
Interior
Trim and Ornament
ation
.
Page 1103 of 2490
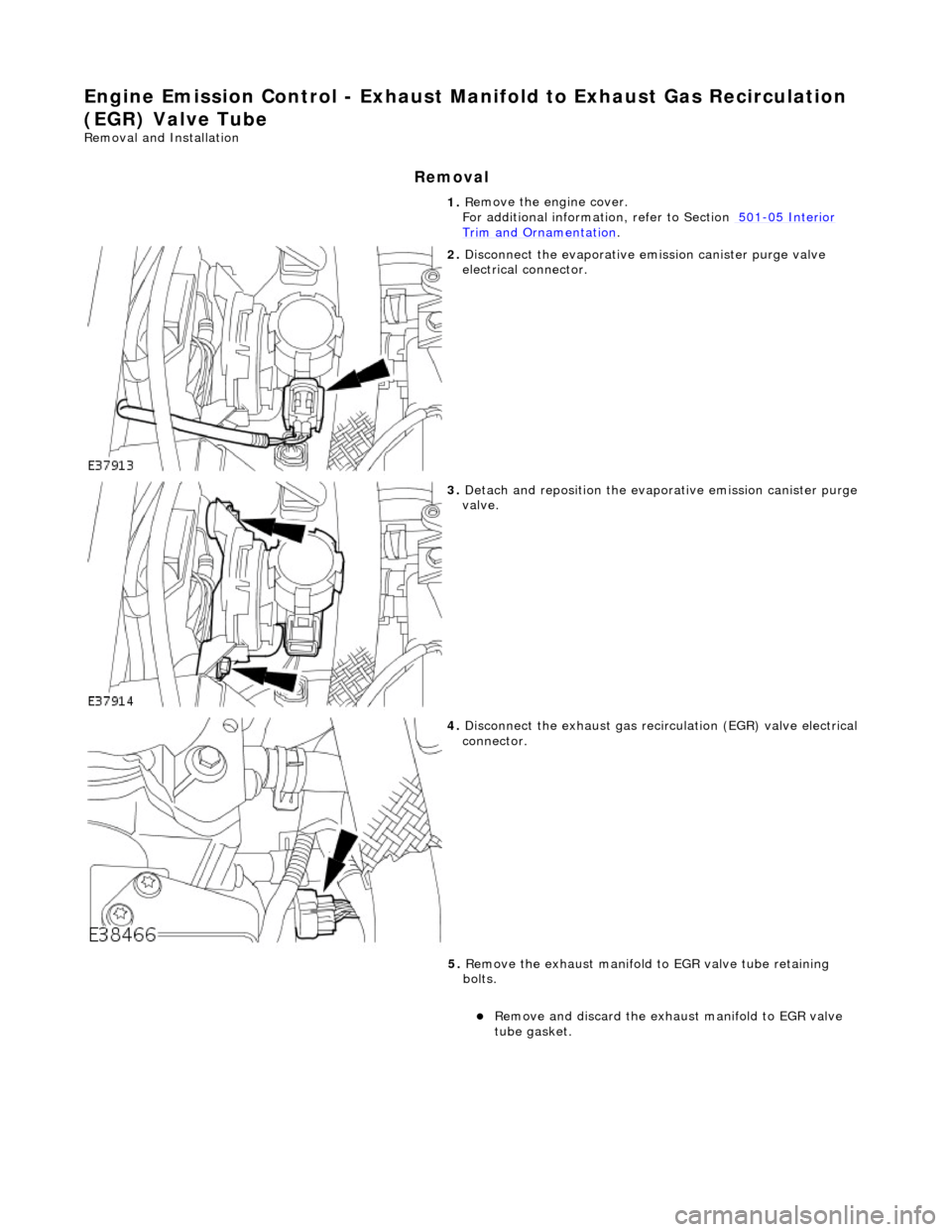
E
ngine Emission Control - Exhaust Ma
nifold to Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) Valve Tube
Re
moval and Installation
Remov
al
1.
R
emove the engine cover.
For additional informat ion, refer to Section 501
-0
5 Interior
Trim and Ornamen
tation
.
2. Di
sconnect the evaporative emission canister purge valve
electrical connector.
3. De
tach and reposition the evaporative emission canister purge
valve.
4. Di
sconnect the exhaust gas recirc
ulation (EGR) valve electrical
connector.
5. Remove the exhaust manifold to EGR valve tube retaining
bolts.
Remove an
d discard the exhaust manifold to EGR valve
tube gasket.
Page 1105 of 2490
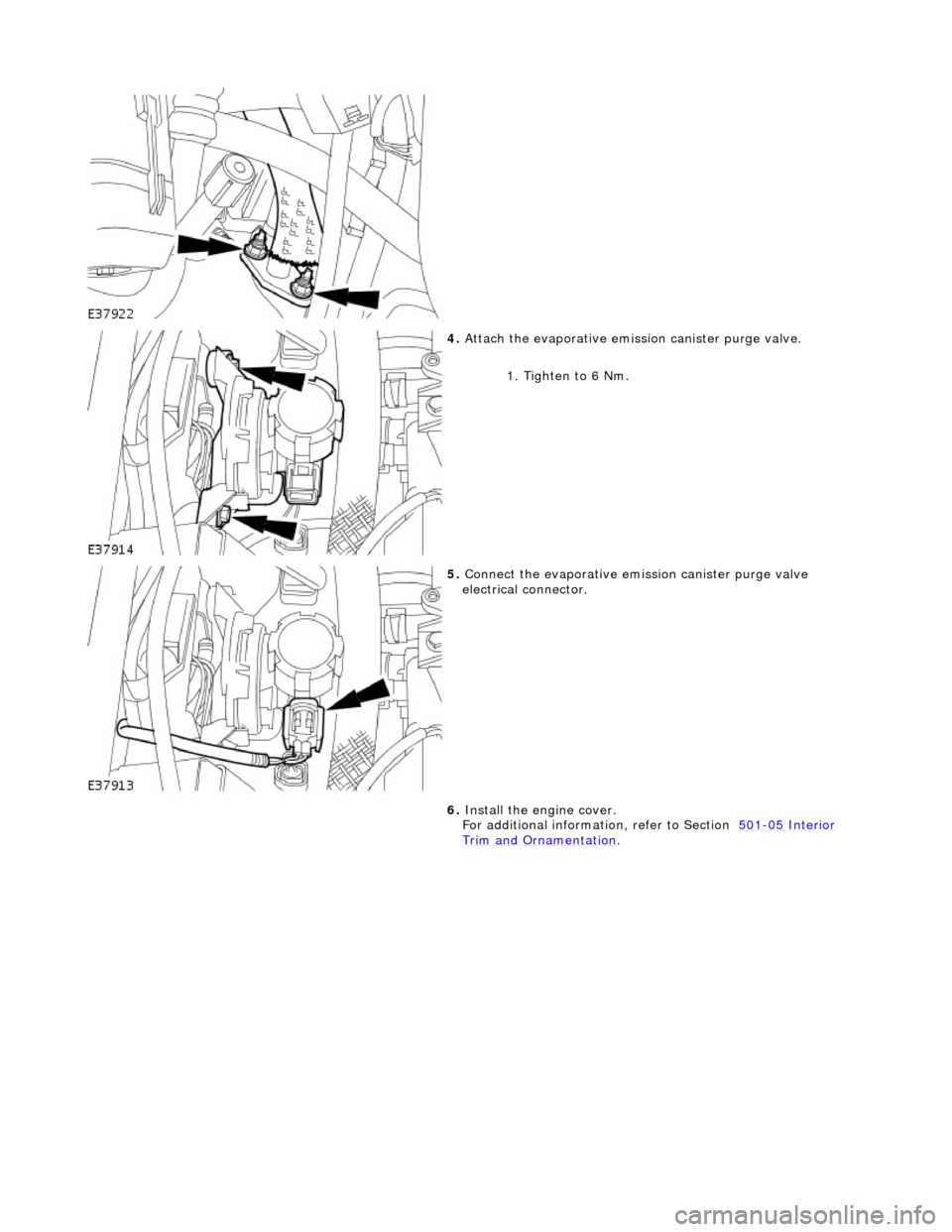
4.
Att
ach the evaporative emission canister purge valve.
1. Tighten to 6 Nm.
5. Conne
ct the evaporative emission canister purge valve
electrical connector.
6. Install the engine cover.
For additional informat ion, refer to Section 501
-0
5 Interior
Trim and Ornamen
tation
.
Page 1111 of 2490

the
intake elbow provide connections for vacuum actuators and are also used to redirect emissions into the engine.
On the right-hand side of the elbow a la rge diameter pipe connects to the brake servo. The smaller pipe provides a vacuum
feed to the fuel rail pressure regulator and throttle cruise control system. On the le ft-hand side of the elbow the front pipe
supplies vacuum control for the evaporative emissions system valves.
Emissions from the engine part load breather (bank 2) and pu rged fuel vapor from the EVAP valve are drawn via a common
T piece into the left-hand side of the intake elbow. Re-cir culated exhaust gas enters the intake elbow via the EGR valve
which is mounted directly on the rear of the elbow : where the EGR system is not used, a blanking plate is fitted.
The fuel system, throttle and emission control system s are described more fully in the relevant sections.
Intake Manifold
Filtered air from the vehicle's intake ducting is metered by th e electronic throttle and distributed to the two cylinder banks
via an integral intake manifold.
The intake manifold is manufactured in plastic with integral plastic fuel rails and metal-thread inserts; the very smooth
internal surfaces give excellent air flow.
Individual ducts lead off a central chamber to the inlet valves of each cylinder.
Silicon-rubber gaskets, loca ted in channels in the intake manifold, seal th e joints between the ducts and the cylinder heads.
Engine Ventilation
The e
ngine is ventilated through two brea
thers; a part-load breather and a full-load breather, one on each camshaft cover.
The outlet hose for the part-load breather is connected between the bank 2 camshaft cover and the intake elbow. The full-
load outlet hose is connected from the bank 1 camshaft cover to the intake duct between the MAF sensor assembly and the
throttle body.
Constructed in plastic, the hoses incorporate O-ring seal s and quick-release connectors; refer to Section 303-01.
I
ntake Air Distribution and Filtering - Supercharged Vehicles
Ai
r is supplied to the supercharger via an
intake cleaner/duct, throttle assembly and intake elbow which are similar to those
used for normally aspirated engines. The su percharger delivers pressurized air to two separate charge air cooler units, each
unit being mounted on the cy linder bank which it supplies. Pr essurized cooled air is fed from the charge air coolers directly
into each inlet port.