1998 JAGUAR X308 evaporative
[x] Cancel search: evaporativePage 1113 of 2490

The intake elbow di
rects the metered airflow from the electronic throttle outlet (und
erside of the throttle body) into the
intake of the supercharger.
The supercharger by-pass valve assembly is bolted to the intake elbow. The butterfly valve inside the assembly is opened
by a diaphragm actuator operated by vacu um feed from the elbow. At closed or partially open throttle positions, the
butterfly valve opens, allowing th e airflow from the two charge air cooler inlets to be directed back to the supercharger inlet .
This action inhibits the supercharging e ffect and reduces engine torque to non supercharged levels. Progressive opening of
the throttle causes the by-pass valve to gradually close.
On the right-hand side of the elbow a la rge diameter pipe connects to the brake servo. On the left-hand side the smaller
pipe supplies vacuum control for the evaporative emissions system valves.
Emissions from the engine part load breather (bank 1) and pu rged fuel vapor from the EVAP valve are drawn via a common
T piece into the left-hand side of the intake elbow. Re-cir culated exhaust gas enters the intake elbow via the EGR valve
which is mounted directly on the rear of the elbow. Where the EGR system is not used, a blanking plate is fitted.
The fuel system and emission control systems are described more fully in the relevant sections.
Fuel Pressure Regula
tion and
Cruise Control Vacuum Feed
The inlet v
acuum feed fo
r the fuel rail pressure regula tor and the cruise control system is taken from the supercharger
outlet duct. The feed pipe is located below the large charge air cooler coolant filler plug.
Superchar
ger
and associated components
Inta
ke Elbow and Bypass
Page 1148 of 2490
Evaporative E
missions - Evaporative Emissions
Description an
d Operation
To reduce the emission of fuel vapour, th e fuel tank is vented to atmosphere through activated charcoal adsorption canister
(s) which collects the fuel droplets. The ch arcoal is periodically purged of fuel when the EVAP Canister Purge Valve opens
the vapour line between the canister(s) and the air intake induct ion elbow. This action allows manifold depression to draw
air through the canister atmospheric vent, taking up the deposited fuel from the charcoal adsorber and burning the resulting
fuel vapour in the engine.
The EVAP Canister Purge Valve is controlled by the engine management system ECM. Purging is carried out in accordance
with the engine management fu eling strategy (see below).
The fuel tank vapour outlet is via a removeable flange assemb ly on the top surface of the tank. The vapour storage canister
or canisters are fitted on the underside of the vehicle below the rear seats.
There are three variants of the evaporativ e system. All systems use the charcoal adsorber storage canisters and purge valve
and operate as described above. The specific features of each system are described below. The evaporative systems are
designated as :
sin g
le canister system
ru
nn
ing loss system
ru
nn
ing loss with On-board Re-fueling Vapour Recovery (ORVR) system
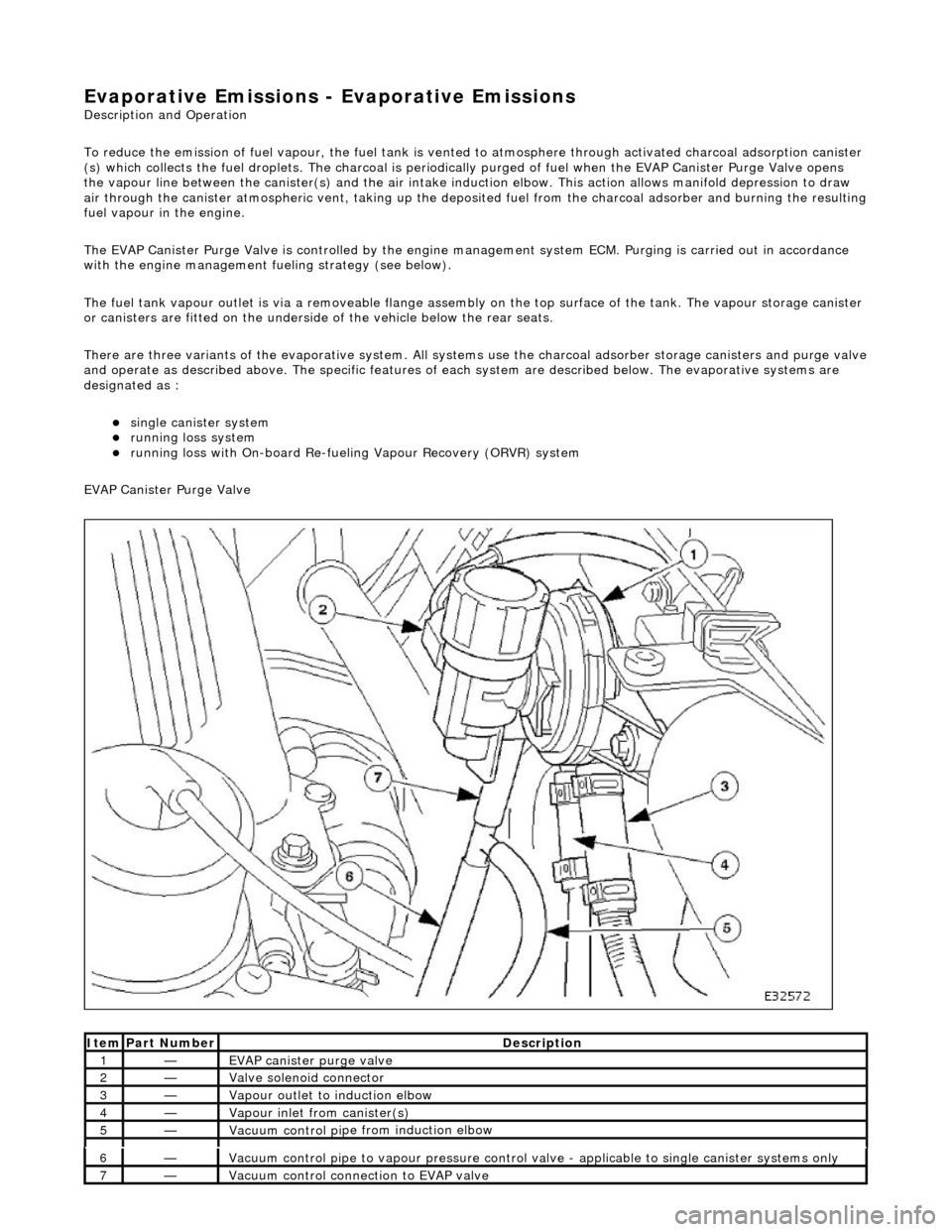
EVAP Canister Purge Valve
Ite
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—EVAP canister purge v
alve
2—Valve s
olenoid connector
3—Vapour outlet to indu
ction elbow
4—Vapour
inlet from canister(s)
5—Vacuum contro
l pi
pe from induction elbow
6—Vacuum contro
l pi
pe to vapour pressure control va
lve - applicable to single canister systems only
7—Vacuum
control connection to EVAP valve
Page 1149 of 2490

The E
VAP canister purge valve controls th
e flow rate of fuel vapour drawn into the engine during the canister purge
operation. The valve is opened by a vacu um feed from the induction elbow : the vacu um feed is controlled by the integral
valve solenoid and is applied when the so lenoid is energised. The solenoid is pulsed on (energised) and off by a fixed
frequency (100Hz) variable pulse width control signal (pulse width modulation). By varying the pulse on to off time, the
ECM controls the duty cycle of the valve (time that the valve is open to time closed) and thus the vapour flow rate to the
engine.
With no ECM signal applied to the va lve solenoid, the valve remains closed.
Can
ister Purge Operation
The
following pre-conditions are ne
cessary for purging to commence :
aft
er battery disconnection/reconnection, engine
management adaptations must be re-instated.
engine has run for
at least 8 seconds.
engi
ne coolant temperature is not less than 70 °C.
engine
not running in the fuel
cut off condition (eg overrun).
t
he adaptive fuel correction
function has not registered a rich or lean failure
t
he evaporative emission leak test has not failed
no faults have been diagnosted in th
e rel
evant sensor and valve circuits -
Air Flow Meter (AFM), Engine Coolant
Temperature sensor, Evaporativ e Canister Purge valve and Canister Close Valve (CCV).
If these conditions have been satisfied, purging is started. If any failures are registered, purging is inhibited.
The canister(s) is purged during each driv e cycle at various rates in accordance with the prevailing engine conditions. The
engine management software st ores a map of engine speed (RPM) against engine load (grams of air inducted / rev). For
any given engine speed and load, a vapour purge rate is assigned (purge rate increases with engine speed and load).
The preset purge rates are base d on the assumption of a vapour concentratio n of 100%. The actual amount of vapour is
measured by the closed loop fueling system : the input of evaporative fuel into the engine causes the outputs from the
upstream oxygen sensors to change, the am ount of change providing a measure of the vapour concentration. This feedback
causes the original purge rate to be adju sted and also reduces the amount of fuel input via the injectors to maintain the
correct air to fuel ratio.
Engine speed/load mapping and the corresp onding purge rates are different for single canister, running loss and ORVR
evaporative systems.
Page 1150 of 2490
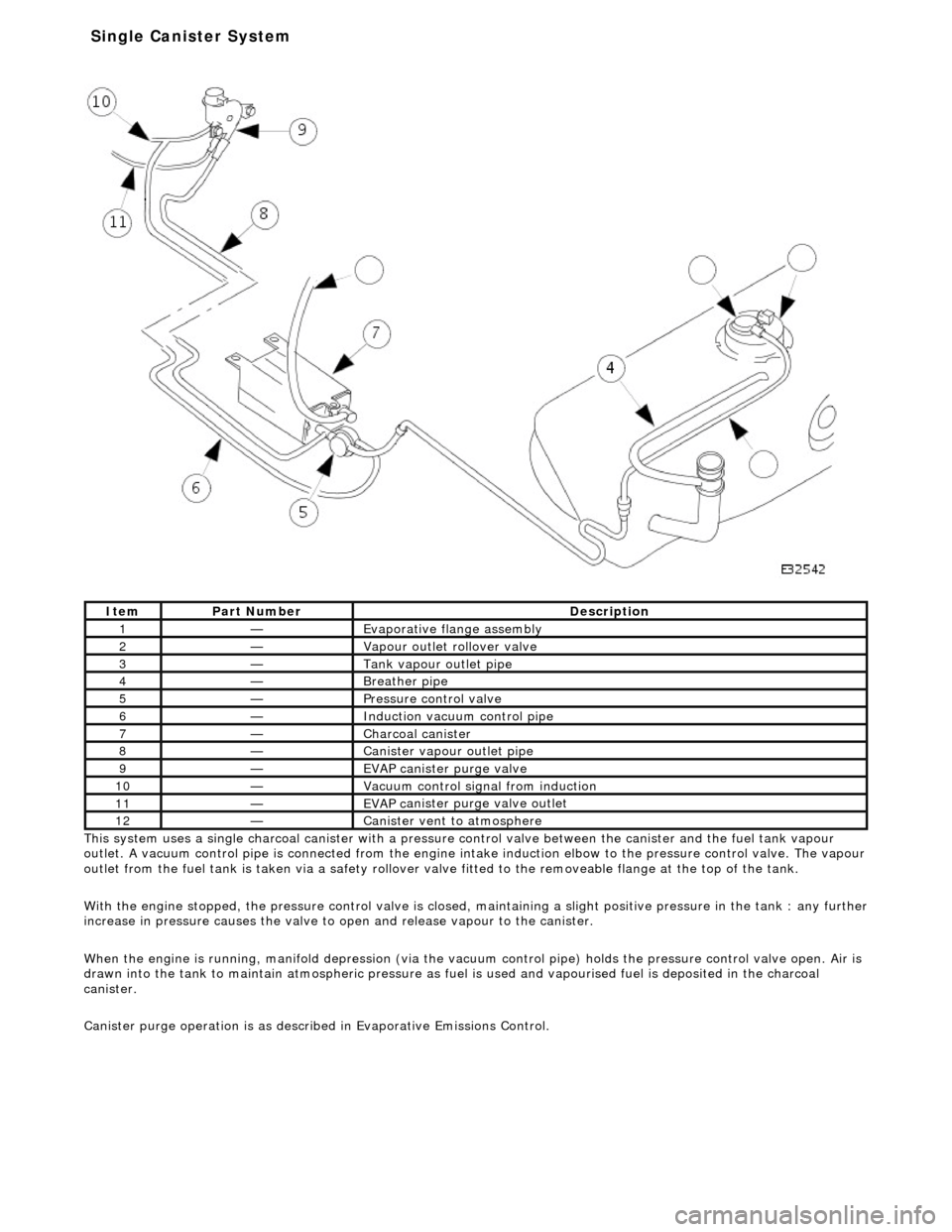
Thi s
system uses a single charcoal canister with a pressure
control valve between the canister and the fuel tank vapour
outlet. A vacuum control pipe is connecte d from the engine intake induction elbow to the pressure control valve. The vapour
outlet from the fuel tank is taken via a safety rollover valve fitted to the re moveable flange at the top of the tank.
With the engine stopped, the pressure control valve is closed, maintaining a slight positive pre ssure in the tank : any further
increase in pressure causes the valve to open and release vapour to the canister.
When the engine is running, manifold depr ession (via the vacuum control pipe) holds the pressure control valve open. Air is
drawn into the tank to maintain atmospheric pressure as fuel is used and vapourised fuel is deposited in the charcoal
canister.
Canister purge operation is as described in Evaporative Emissions Control.
It e
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—Evaporative flan
ge assembly
2—Vapour outlet rol
lover valve
3—Tank vapour outlet pipe
4—Breather
pipe
5—Pressure control valve
6—Induct
ion vacuum control pipe
7—Charcoal can
i
ster
8—Canister vapour outlet pipe
9—EVAP canister purge v
a
lve
10—Vacuu
m
control sign
al from induction
11—EVAP ca
nister purge valve outlet
12—Canist
er vent
to atmosphere
Single Ca
nister System
Page 1151 of 2490
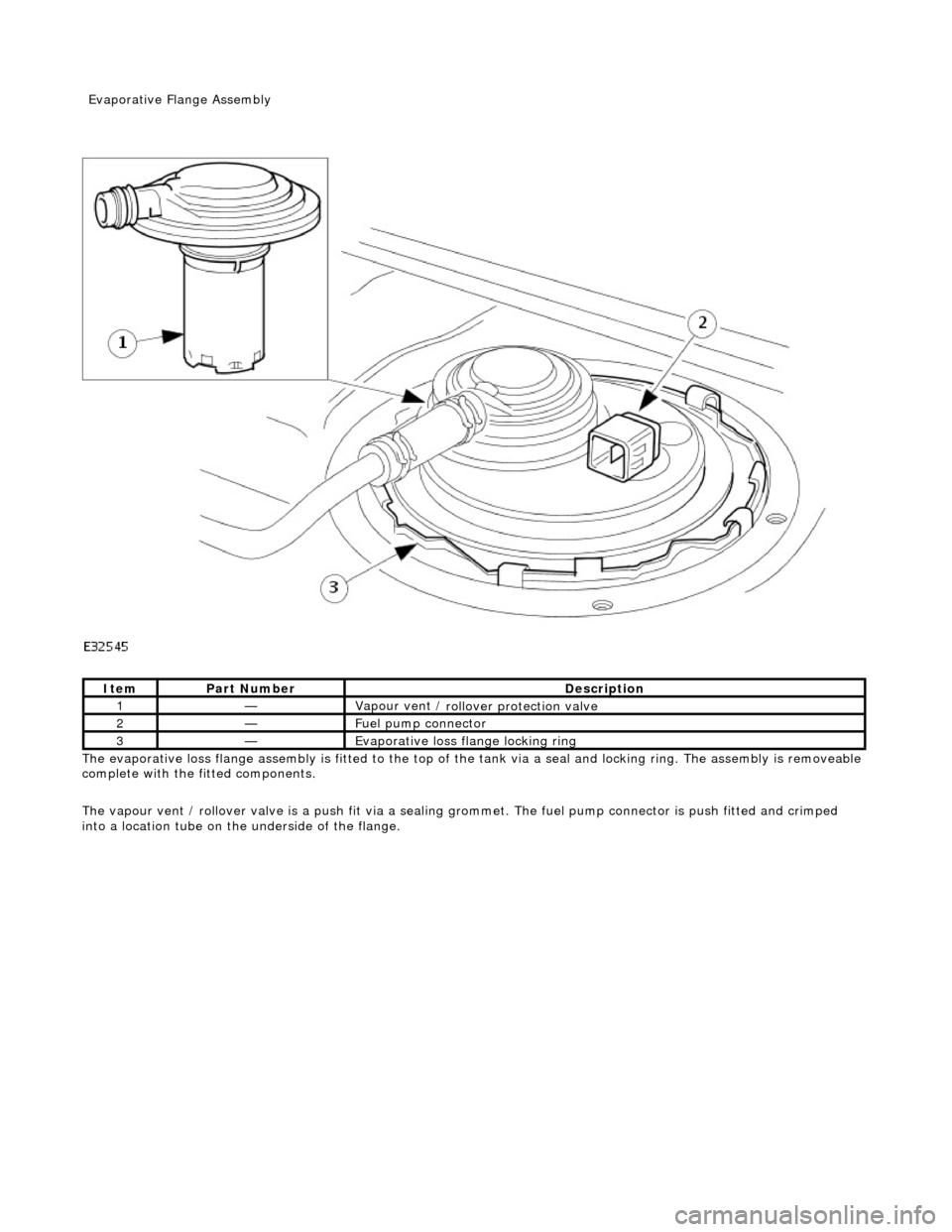
The evaporative l
oss flange assembly is fitted to the top of the tank via a seal and locking ring. The assembly is removeable
complete with the fitted components.
The vapour vent / rollover valve is a push fit via a sealing grommet. The fuel pump connector is push fitted and crimped
into a location tube on the underside of the flange.
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1—Vapour vent /
rollover protection valve
2—Fue
l pump connector
3—Evaporative loss flange locking rin
g
Evaporative Flang
e Assembly
Page 1152 of 2490
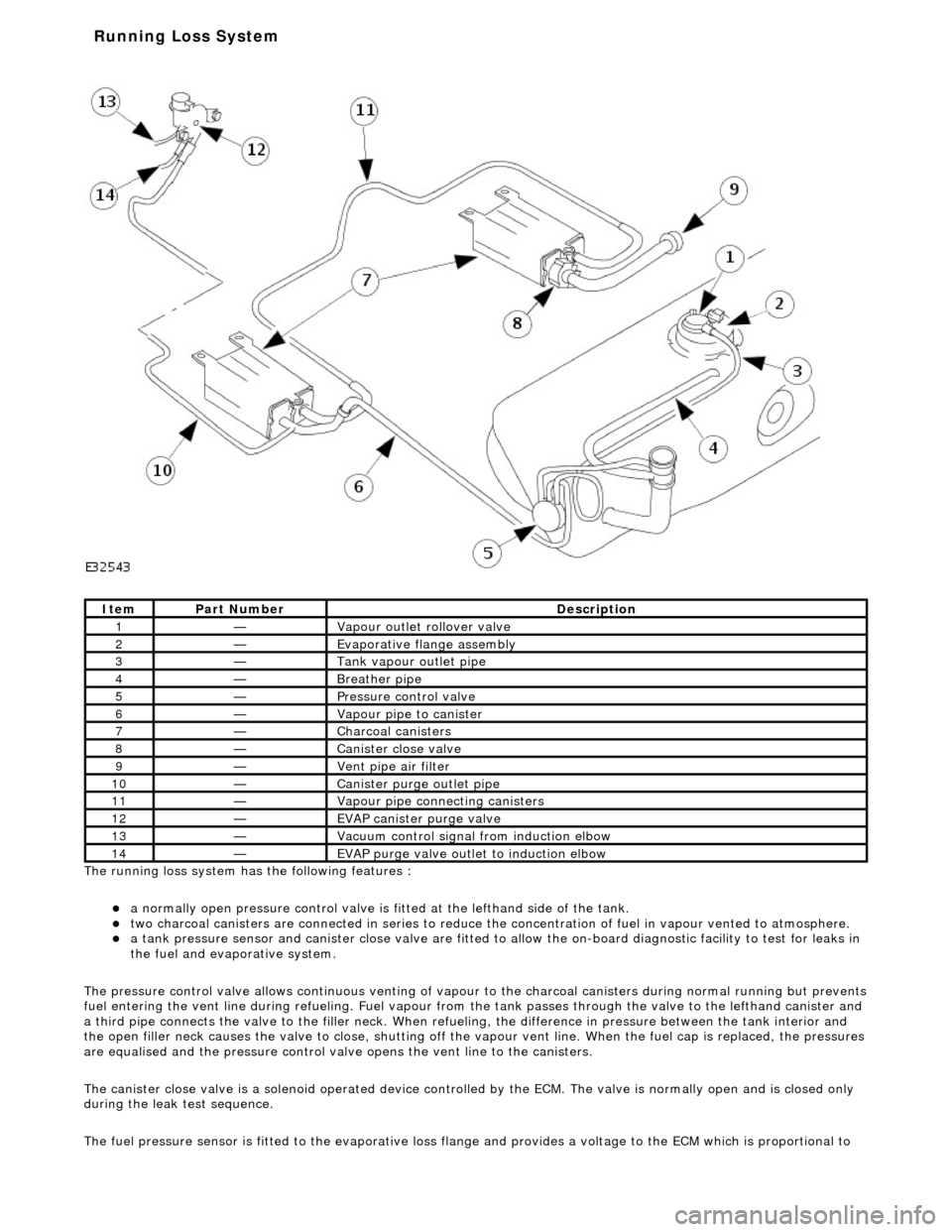
The ru nning loss
system has the following features :
a
normall
y open pressure control valve is fi
tted at the lefthand side of the tank.
two charcoal
canisters are connected in series to reduce th
e concentration of fuel in vapour vented to atmosphere.
a t
ank pressure sensor and canister close
valve are fitted to allow the on-board di agnostic facility to test for leaks in
the fuel and evaporative system.
The pressure control valve allows continuo us venting of vapour to the charcoal canisters during normal running but prevents
fuel entering the vent line duri ng refueling. Fuel vapour from the tank passes through the valve to the lefthand canister and
a third pipe connects the valve to the fill er neck. When refueling, the difference in pressure betw een the tank interior and
the open filler neck causes the valve to cl ose, shutting off the vapour vent line. Wh en the fuel cap is replaced, the pressures
are equalised and the pressure control valve opens the vent line to the canisters.
The canister close valve is a solenoid operated device controlled by the ECM. The valve is normally open and is closed only
during the leak test sequence.
The fuel pressure sensor is fitted to th e evaporative loss flange and provides a volt age to the ECM which is proportional to
Ite
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—Vapour outl
et rol
lover valve
2—Evaporative flan
ge assembly
3—Tank vapour outlet pipe
4—Breather pipe
5—Pressure control
valve
6—Vapour pipe to canister
7—Charcoal cani
sters
8—Cani
st
er close valve
9—Vent pi
pe ai
r filter
10—Canister purge ou
tlet pipe
11—Vapour pipe conn
ecting canisters
12—EVAP canister purge v
a
lve
13—Vacuu
m
control signal from induction elbow
14—EVAP pu
rge valve outlet to induction elbow
Running Loss Sys
tem
Page 1153 of 2490
tank vapou
r pressure.
Canister purge operation is as described in Evaporative Emissions Control.
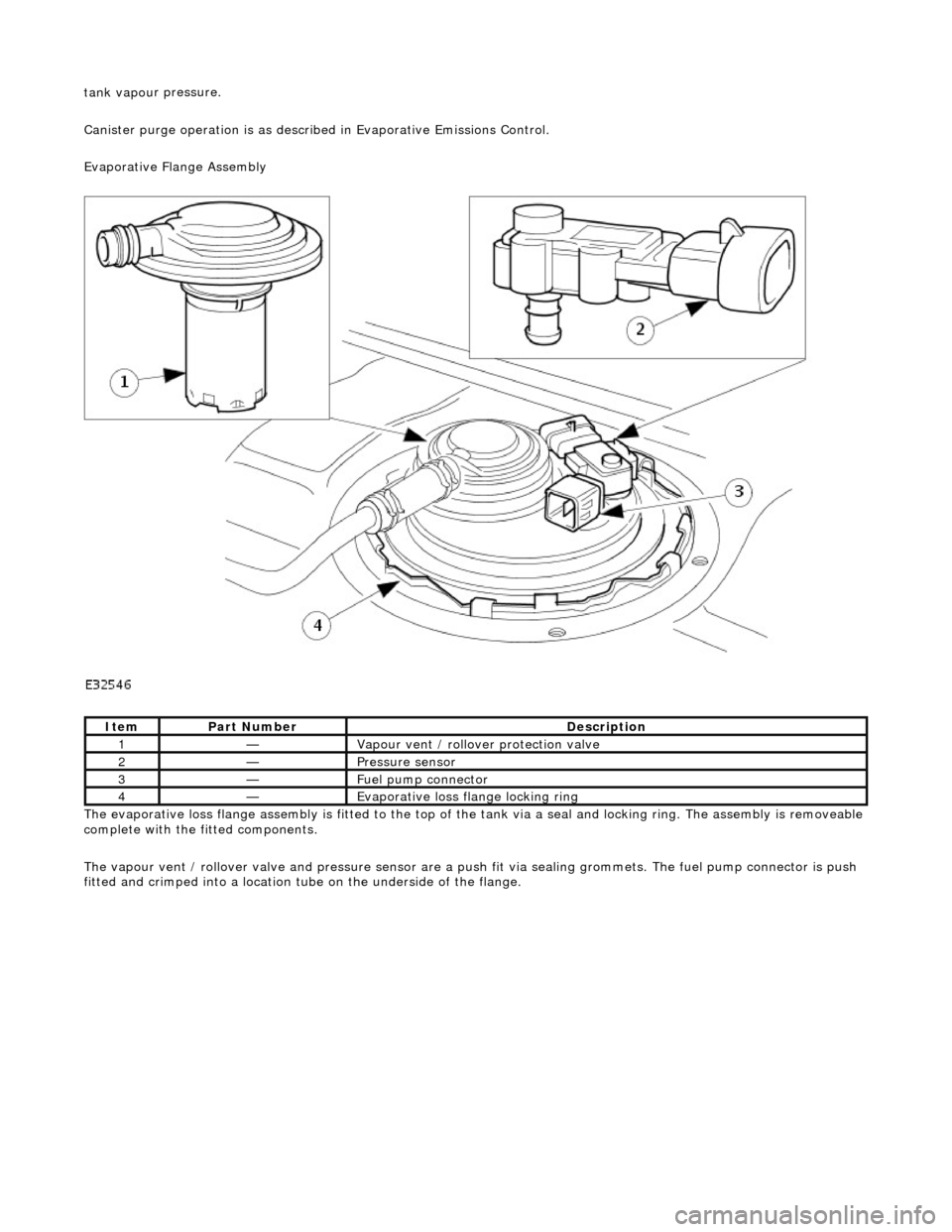
Evaporative Flange Assembly
The evaporative loss flange assembly is fitted to the top of the tank via a seal and locking ring. The assembly is removeable
complete with the fitted components.
The vapour vent / rollover valve and pressure sensor are a pu sh fit via sealing grommets. The fuel pump connector is push
fitted and crimped into a location tu be on the underside of the flange.
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1—Vapour vent /
rollover protection valve
2—Pres
sure sensor
3—Fue
l pump connector
4—Evaporative loss flange locking rin
g
Page 1156 of 2490
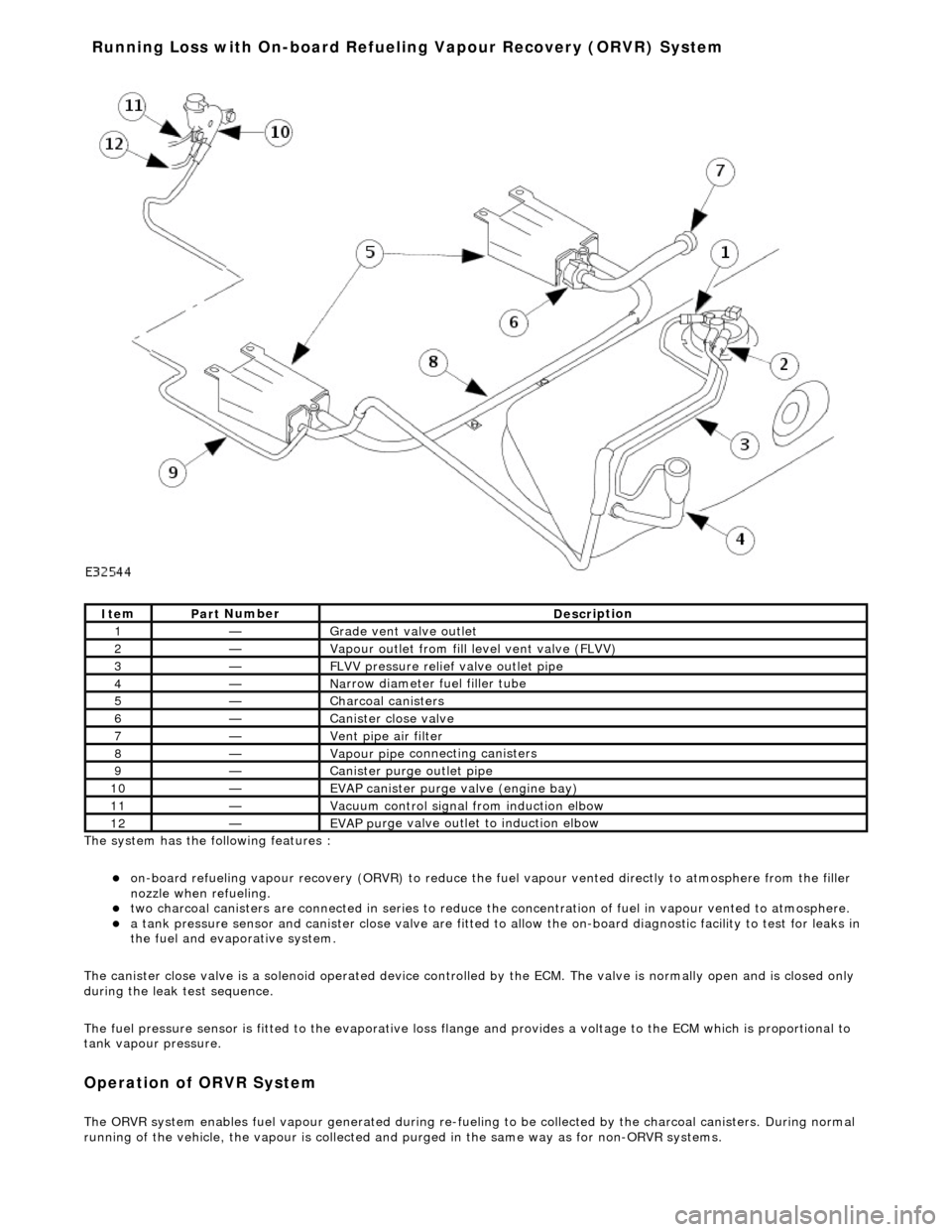
The system has the
following features :
o
n
-board refueling vapour recovery (ORVR) to reduce the fu
el vapour vented directly to atmosphere from the filler
nozzle when refueling.
two ch arcoal
canisters are connected in series to reduce th
e concentration of fuel in vapour vented to atmosphere.
a t
ank pressure sensor and canister close
valve are fitted to allow the on-board di agnostic facility to test for leaks in
the fuel and evaporative system.
The canister close valve is a solenoid operated device controlled by the ECM. The valve is normally open and is closed only
during the leak test sequence.
The fuel pressure sensor is fitted to th e evaporative loss flange and provides a volt age to the ECM which is proportional to
tank vapour pressure.
Op era
tion of ORVR System
The ORVR system enabl
e
s fuel vapour generated during re-fueling to be collected by
the charcoal canisters. During normal
running of the vehicle, the vapour is collected and purged in the same way as for non-ORVR systems.
Ite
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—Grade vent
valve outl
et
2—Vapour outl
et from fil
l level vent valve (FLVV)
3—F
L
VV pressure relief valve outlet pipe
4—N
a
rrow diameter fuel filler tube
5—Charcoal can
i
sters
6—Cani
st
er close valve
7—Vent pi
pe ai
r filter
8—Vapour pipe
conn
ecting canisters
9—Canister purge ou
tlet pipe
10—EVAP canister purge v a
lve (engine bay)
11—Vacuu
m
control signal from induction elbow
12—EVAP pu
rge valve outlet to induction elbow
Running Loss with On-board R
efuelin
g Vapour Recovery (ORVR) System