1998 ISUZU TROOPER Rear axle
[x] Cancel search: Rear axlePage 768 of 3573

4D2±1 TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
DRIVELINE/AXLE
TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
CONTENTS
Service Precaution 4D2±1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transfer Case Assembly 4D2±2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 4D2±2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 4D2±3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transfer Rear Oil Seal 4D2±5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transfer Rear Oil Seal and Associated
Parts 4D2±5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 4D2±5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 4D2±5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TOD ECU 4D2±7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 4D2±7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 4D2±7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Unit Repair 4D2±8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection 4D2±8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transfer Case 4D2±9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 4D2±9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 4D2±9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 4D2±10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transfer Cover Assembly 4D2±12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 4D2±12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 4D2±12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 4D2±14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transfer Case Assembly Clutch Pack and
Clutch Cam 4D2±16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 4D2±16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Disassembly 4D2±16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Sprocket and Mechanical Lock 4D2±18. . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 4D2±18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 4D2±18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output Shafts and Shift Control Shaft 4D2±20. . . . . .
Disassembled View 4D2±20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 4D2±21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transfer Case 4D2±23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 4D2±23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 4D2±24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection and Repair 4D2±26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transfer Case 4D2±30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 4D2±30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 4D2±30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output Shafts and Shift Control Shaft 4D2±34. . . . . .
Disassembled View 4D2±34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 4D2±34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Sprocket and Mechanical Lock 4D2±37. . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 4D2±37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 4D2±37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clutch Pack and Clutch Cam 4D2±39. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 4D2±39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 4D2±39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Main Data and Specifications 4D2±41. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Special Tools 4D2±43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Service Precaution
WARNING: I F S O E Q U IPPED WITH A
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS),
REFER TO THE SRS COMPONENT AND WIRING
LOCATION VIEW IN ORDER TO DETERMINE
WHETHER YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR
NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS
WIRING. WHEN YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE
ON OR NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS
WIRING, REFER TO THE SRS SERVICE
INFORMATION. FAILURE TO FOLLOW WARNINGS
COULD RESULT IN POSSIBLE AIR BAG
DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY, OR
OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS SYSTEM REPAIRS.CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
ISUZU will call out those fasteners that require a
replacement after removal. ISUZU will also call out
the fasteners that require thread lockers or thread
sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED, do not
use supplemental coatings (Paints, greases, or other
corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners or
fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such coatings
adversely affect the fastener torque and the joint
clamping force, and may damage the fastener. When
you install fasteners, use the correct tightening
sequence and specifications. Following these
instructions can help you avoid damage to parts and
systems.
Page 814 of 3573

5A±4
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
normal braking when a malfunction has occurred in the
ABS.
The EHCU has a self-diagnosing function which can
indicate faulty circuits during diagnosis.
The EHCU is mounted on the engine compartment front
right side. It consists of a Motor, Plunger Pump, Solenoid
Valves and Check Valve.
On the outside, the relay box containing a motor relay and
a valve relay is installed.
Solenoid Valves: Reduces or holds the caliper fluid
pressure for each front disc brake or both rear disc brakes
according to the signal sent from the EHCU.
Reservoir: Temporarily holds the brake fluid that returns
from the front and rear disc brake caliper so that pressure
of front disc brake caliper can be reduced smoothly.
Plunger Pump: Feeds the brake fluid held in the reservoir
to the master cylinder.
Motor: Drives the pump according to the signal from
EHCU.
Check Valve: Controls the brake fluid flow.
ABS Warning Light
821RW033Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System have
an amber ªABSº warning light in the instrument panel.
The ªABSº warning light will illuminate if a malfunction in
the Anti-lock Brake System is detected by the Electronic
Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU). In case of an electronic
malfunction, the EHCU will turn ªONº the ªABSº warning
light and disable the Anti-lock braking function.
The ªABSº light will turn ªONº for approximately three
seconds after the ignition switch is to the ªONº position.
If the ªABSº light stays ªONº after the ignition switch is the
ªONº position, or comes ªONº and stays ªONº while
driving, the Anti-lock Brake System should be inspected
for a malfunction according to the diagnosis procedure.
Wheel Speed Sensor
It consists of a sensor and a rotor. The sensor is attached
to the knuckle on the front wheels and to the axle shaft
bearing holder on the rear wheels.
The rotor is press-fit in the axle shaft.The flux generated from electrodes magnetized by a
magnet in the sensor varies due to rotation of the rotor,
and the electromagnetic induction generates alternating
voltage in the coil. This voltage draws a ªsine curveº with
the frequency proportional to rotor speed and it allows
detection of wheel speed.
G-Sensor
The G-sensor installed inside the center console detects
the vehicle deceleration speed and sends a signal to the
EHCU. In 4WD operation, all four wheels may be
decelerated in almost the same phase, since all wheels
are connected mechanically.
This tendency is noticeable particularly on roads with low
friction coefficient, and the ABS control is adversely
affected.
The G-sensor judges whether the friction coefficient of
road surface is low or high, and changes the EHCU's
operating system to ensure ABS control.
Normal and Anti-lock Braking
Under normal driving conditions, the Anti-lock Brake
System functions the same as a standard power assisted
brake system. However, with the detection of wheel
lock-up, a slight bump or kick-back will be felt in the brake
pedal. This pedal ªbumpº will be followed by a series of
short pedal pulsations which occurs in rapid succession.
The brake pedal pulsation will continue until there is no
longer a need for the anti-lock function or until the vehicle
is stopped. A slight ticking or popping noise may be heard
during brake applications when the Anti-lock features is
being used.
When the Anti-lock feature is being used, the brake pedal
may rise even as the brakes are being applied. This is
also normal. Maintaining a constant force on the pedal
will provide the shortest stopping distance.
Brake Pedal Travel
Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System may
be stopped by applying normal force to the brake pedal.
Although there is no need to push the pedal beyond the
point where it stops or holds the vehicle, by applying more
force the pedal will continue to travel toward the floor.
This extra brake pedal travel is normal.
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Several acronyms and abbreviations are commonly used
throughout this section:
ABS
Anti-lock Brake System
CKT
Circuit
DLC
Data Link Connector
EHCU
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit
FL
Front Left
Page 845 of 3573

5A±35 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Symptom Diagnosis
The symptoms that cannot be indicated by the warning
light can be divided in the following five categories:
1. ABS works frequently but vehicle does not
decelerate.
2. Uneven braking occurs while ABS works.
3. The wheels lock during braking.4. Brake pedal feel is abnormal.
5. Braking sound (from EHCU) is heard while not
braking.
These are all attributable to problems which cannot be de-
tected by EHCU self-diagnosis. Use the customer com-
plaint and a test to determine which symptom is present.
Then follow the appropriate flow chart listed below.
NoSymptomDiagnostic Flow ChartsNo.Sym tomWithout TECH 2With TECH 2
1ABS works frequently but vehicle does not decelerate.Chart A±1Chart TA±1
2Uneven braking occurs while ABS works.Chart A±2Ð
3The wheels are locked.Chart A±3Chart TA±3
4Brake pedal feel is abnormal.Chart A±4Ð
5Braking sound (from EHCU) is heard while not braking. Chart A±5Chart TA±5
Chart A±1 ABS Works Frequently But Vehicle Does Not Decelerate
StepActionYe sNo
11. Turn key off.
2. G Sensor connector and EHCU connector disconnected.
Is there continuity between EHCU terminals 26 and 8?
Go to Step 2Go to Step 3
2Connect EHCU connector.
Is there continuity between the G sensor and the EHCU?
Go to Step 3
Repair circuit.
Go to Step 1
3Is the G sensor normal? (Refer to chart B-5)
Go to Step 4
Replace G
sensor.
Go to Step 11
4Is braking force distribution normal between the front and rear of
the vehicle?
Go to Step 5
Repair brake
parts.
Go to Step 11
5Are axle parts installed normally?Go to Step 6Repair axle parts.
Go to Step 11
6Is there play in each wheel speed sensor?Repair wheel
speed sensor.
Go to Step 11
Go to Step 7
7Is there damage, or powered iron sticking to each wheel speed
sensor/sensor ring?Replace sensor
or sensor ring.
Go to Step 11
Go to Step 8
8Is the output of each wheel speed sensor normal? (Refer to chart
C-1 or TC-1)
Go to Step 9
Replace wheel
speed sensor or
repair harness.
Go to Step 11
9Is the input of transmission normal? (Refer to chart C-2 or TC-2)
Go to Step 10
Replace switch or
repair harness.
Go to Step 11
Page 878 of 3573

5B±6ANTI±LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor and Associated Parts
350RW008
Legend
(1) Speed Sensor Connector
(2) Sensor Cable Fixing Bolt(3) Clip (11 pieces)
(4) Speed Sensor
(5) Sensor Fixing Bolt
Removal
1. Remove speed sensor connector.
2. Remove clip.
3. Remove sensor cable fixing bolt.
4. Remove sensor fixing bolt.
5. Remove speed sensor.
350RS035
Inspection and Repair
1. Check the speed sensor pole piece for presence of
foreign materials; remove any dirt, etc.2. Check the pole piece for damage, and replace the
speed sensor if necessary.
3. Check the speed sensor cable for a short or an open,
and replace with a new one if necessary. To check for
cable short or open, bend or stretch the cable while
checking for continuity.
4. Check the sensor ring for damage including tooth
chipping. If damaged replace the axle shaft assembly.
Refer to Front Hub and Disc in Drive Shaft System
section.
Installation
1. Install the speed sensor and take care not to hit the
speed sensor pole piece during installation.
2. Install the sensor fixing bolt and tighten it to the
specified torque.
Torque : 18 N´m (1.8kg´m/13 lb ft)
3. Install the sensor cable fixing bolt and tighten it to the
specified torque.
Torque : 24 N´m (2.4kg´m/18 lb ft)
NOTE: Confirm that the cable is not twisted when
connecting the speed sensor cable.
4. Install clip.
5. Install speed sensor connector.
Page 883 of 3573
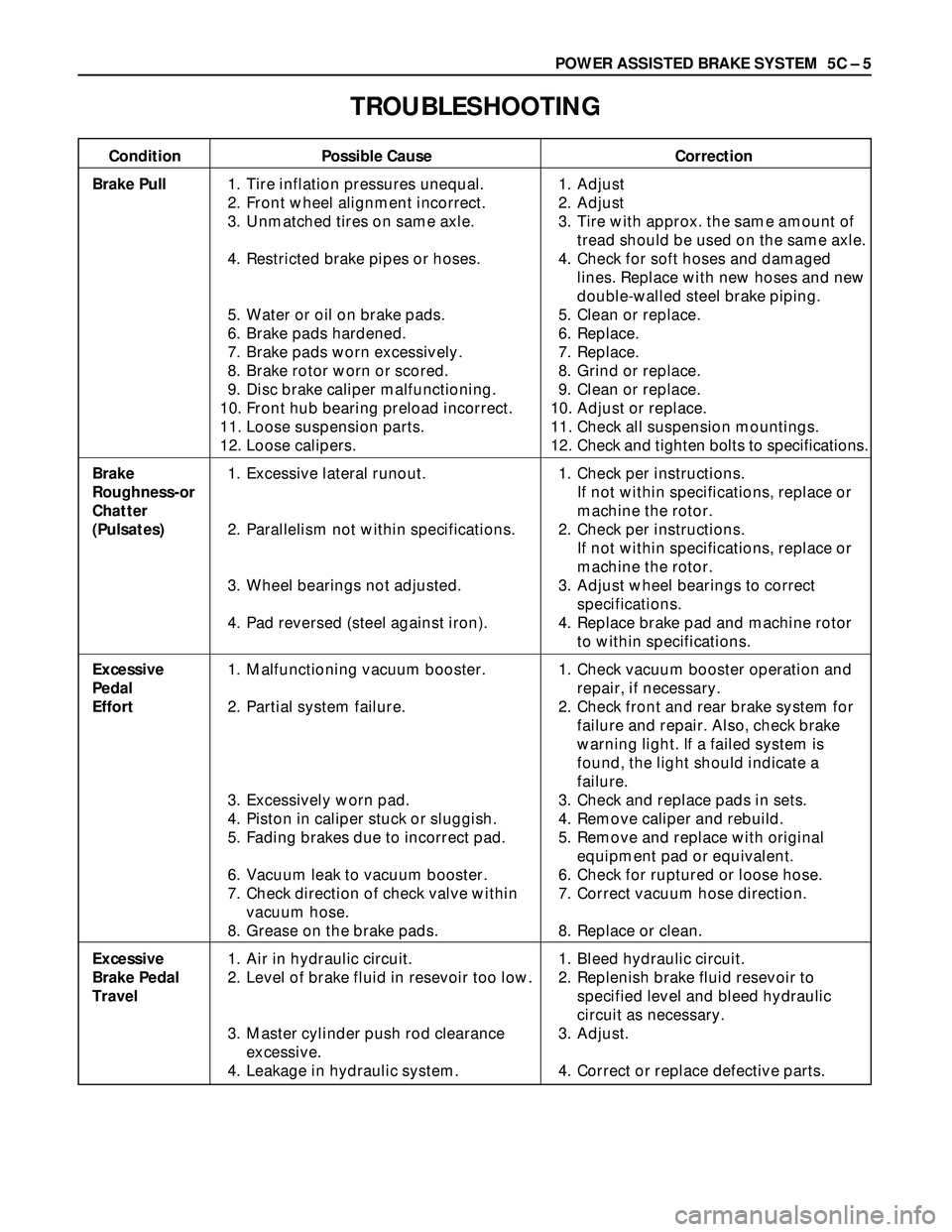
POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM 5C – 5
TROUBLESHOOTING
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Brake Pull1. Tire inflation pressures unequal. 1. Adjust
2. Front wheel alignment incorrect. 2. Adjust
3. Unmatched tires on same axle. 3. Tire with approx. the same amount of
tread should be used on the same axle.
4. Restricted brake pipes or hoses. 4. Check for soft hoses and damaged
lines. Replace with new hoses and new
double-walled steel brake piping.
5. Water or oil on brake pads. 5. Clean or replace.
6. Brake pads hardened. 6. Replace.
7. Brake pads worn excessively. 7. Replace.
8. Brake rotor worn or scored. 8. Grind or replace.
9. Disc brake caliper malfunctioning. 9. Clean or replace.
10. Front hub bearing preload incorrect. 10. Adjust or replace.
11. Loose suspension parts. 11. Check all suspension mountings.
12. Loose calipers. 12. Check and tighten bolts to specifications.
Brake 1. Excessive lateral runout. 1. Check per instructions.
Roughness-orIf not within specifications, replace or
Chattermachine the rotor.
(Pulsates)2. Parallelism not within specifications. 2. Check per instructions.
If not within specifications, replace or
machine the rotor.
3. Wheel bearings not adjusted. 3. Adjust wheel bearings to correct
specifications.
4. Pad reversed (steel against iron). 4. Replace brake pad and machine rotor
to within specifications.
Excessive 1. Malfunctioning vacuum booster. 1. Check vacuum booster operation and
Pedal repair, if necessary.
Effort2. Partial system failure. 2. Check front and rear brake system for
failure and repair. Also, check brake
warning light. If a failed system is
found, the light should indicate a
failure.
3. Excessively worn pad. 3. Check and replace pads in sets.
4. Piston in caliper stuck or sluggish. 4. Remove caliper and rebuild.
5. Fading brakes due to incorrect pad. 5. Remove and replace with original
equipment pad or equivalent.
6. Vacuum leak to vacuum booster. 6. Check for ruptured or loose hose.
7. Check direction of check valve within 7. Correct vacuum hose direction.
vacuum hose.
8. Grease on the brake pads. 8. Replace or clean.
Excessive 1. Air in hydraulic circuit. 1. Bleed hydraulic circuit.
Brake Pedal 2. Level of brake fluid in resevoir too low. 2. Replenish brake fluid resevoir to
Travelspecified level and bleed hydraulic
circuit as necessary.
3. Master cylinder push rod clearance 3. Adjust.
excessive.
4. Leakage in hydraulic system. 4. Correct or replace defective parts.
Page 890 of 3573

5C – 12 POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM
27. Depress the brake pedal to check if you feel
“sponginess” after the air has been removed from
all wheel cylinders and calipers. If the pedal feels
“spongy”, the entire bleeding procedure must be
repeated.
28. After the bleeding operation is completed on each
individual wheel, check the level of brake fluid in
the reservoir and replenish up to the “MAX” level if
necessary.
29. Attach the reservoir cap.
•If the diaphragm inside the cap is deformed,
reform it and install.
30. Stop the engine.
FLUSHING BRAKE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
It is recommended that the entire hydraulic system be
thoroughly flushed with clean brake fluid whenever
new parts are installed in the hydraluic system.
Approximately one quart of fluid is required to flush
the hydraulic system.
The system must be flushed if there is any doubt as to
the grade of fluid in the system or if fluid has been
used which contains the slightest trace of mineral oil.
All rubber parts that have been subjected to a
contaminated fluid must be replaced.
BRAKE PIPES AND HOSES
The hydraulic brake system components are
interconnected by special steel piping and flexible
hoses. Flexible hoses are used between the frame and
the front calipers, the frame and rear axle case and the
rear axle and the rear calipers.
When the hydraulic pipes have been disconnected for
any reason, the brake system must be bled after
reconnecting the pipe; refer to “Bleeding Brake
Hydraulic System” in this section.
BRAKE HOSE INSPECTION
The brake hoses should be inspected at least twice a
year. The brake hose assembly should be checked for
road hazard, cracks and chafing of the outer cover,
and for leaks and blisters. Inspect for proper routing
and mounting of the hose. A brake hose that rubs on
suspension components will wear and eventually fail.
A light and mirror may be needed for an adequate
inspection. If any of the above conditions are
observed on the brake hose, adjust or replace the
hose as necessary.
CAUTION:
Never allow brake components such as calipers to
hang from the brake hoses, as damage to the hoses
may occur.
Page 902 of 3573

5C – 24 POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM
DISC BRAKES
The disc brake assembly consists of a caliper, piston, rotor, pad assembly and support bracket. The
caliper assembly has a single bore and is mounted to the support bracket with 2 mounting bolts. The
support bracket allows the caliper to move laterally against the rotor. The caliper is a one-piece casting
with the inboard side containing the piston bore. A square cut rubber seal is located in a groove in the
piston bore which provides the hydraulic seal between the piston and the cylinder wall.
NOTE:
1) Replace all components included in repair kits used to service this caliper.
2) Lubricate rubber parts with clean brake fluid to ease assembly.
3) If any hydraulic component is removed or disconnected, it may be necessary to bleed all or part of
the brake system.
4) Replace pads in axle sets only.
5) The torque values specified are for dry, unlubricated fasteners.
6) Perform service operation a clean bench free from all mineral oil materials.
OPERATION
Hydraulic pressure, created by applying the brake pedal, is converted by the caliper to a stopping force.
This force acts equally against the piston and the bottom of the caliper bore to move the piston outward
and to move (slide) the caliper inward resulting in a clamping action on the rotor. This clamping action
forces the linings against the rotor, creating friction to stop the vehicle.
Front disc brakes
Rear disc brakes
Page 903 of 3573

POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM 5C – 25
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BRAKE HOSE REPLACEMENT
1
24
2
3
12
4
5
3
Front/Rear Caliper Brake Hose
Removal Steps
1. Brake pipe
2. Clip
3. Bolt and gasket
4. HoseInstallation Steps
To install, follow the removal steps in the
reverse order.
Rear Axle Brake Hose
Removal Steps
1. Brake pipe
2. Clip
3. Brake pipe
4. Bolt
5. HoseInstallation Steps
To install, follow the removal steps in the
reverse order.