Page 777 of 2053
1F3 -- 20 OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
FUEL PUMP
1 Fuel Injection Pump
2 Pressure Line 13N∙m (10 lb-ft) ..............
3 Suction Line
4 Hose Clip Replace........................5 Gasket Replace..........................
6 Spring Lock Washer
7 Hexagon Nuts
8 Fuel Pump
Page 780 of 2053
OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F3 -- 23
D AEW OO M Y_2000
5. Opening pressure test :
Open the valve (3) and slowly operate the hand le-
ver at tester (approx. 1 stroke / second) and mea-
sure opening pressure.
New Nozzle115 -- 125bar
Used NozzleMin. 100bar
Difference Between NozzlesMax. 5bar
Notice
If out of standard, repair the injection nozzle.
6. Leak test
Slowly operate the hand lever at the tester until get a
pressure of approx. 90bar. Maintain this pressure
for more than 20 seconds and within this period no
drop of fuel should build up at the nozzle tip.
Page 785 of 2053
1F3 -- 28 OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
7. Check the fuel injection nozzle and adjust opening
pressure if necessary.
Opening pressure adjustment
Disassemble the fuel injection nozzle and replace
the steel washer (2).
Notice
Each 0.05mm thickness of the washer results in a
pressure difference of approx. 3bar.
Page 803 of 2053
1F3 -- 46 OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Removal Procedure
1. Position then no.1 cylinder at 15_ATDC.
Notice
Do not rotate the engine in opposition direction of
engine rotation.
2. Remove the connecting rod (9).
3. Disconnect the vacuum lines (13, 14).
4. Remove the accelerator control damper (10).
(Manual transmission vehicle)
5. Remove the suction line (16) and pressure line (4).
6. Remove the banjo bolt (1) and then remove the seal
(2) and fuel line (3).
7. Remove the plastic clip (8) on the injection line.
8. Disconnect the injection lines (15) from the injection
pump (25).
9. Remove the banjo bolt (1) and then remove the seal
(7) and return line (5).
Page 806 of 2053
OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F3 -- 49
D AEW OO M Y_2000
5. Coat the new seal (23) with engine oil and install it.
6. Insert the fuel injection pump (25) and tighten the
bolts (22).
Tightening Torque23 N∙m (17 lb-ft)
7. Remove the locking screw (32).
8. Tighten the bolt(12).
Tightening Torque23 N∙m (17 lb-ft)
9. Insert the washer (21) and tighten the bolts (20) and
then remove the assembly cage (29).
Tightening Torque46 N∙m (34 lb-ft)
10. Connect the fuel pipes.
Return Line46 N∙m (34 lb-ft)
Fuel Injection Line18 N∙m (13 lb-ft)
Fuel feed Line13 N∙m (10 lb-ft)
Suction and Pressure Line13 N∙m (10 lb-ft)
Notice
Replace the seal.
Box Wrench Insert 000 589 77 03 00
Page 808 of 2053
OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F3 -- 5
D AEW OO M Y_2000
VACUUM CONTROLSYSTEM TEST
1 Ventilation (To Passenger Compartment)
2 Engine Cut -- Off Valve (Ignition Key Switch)
3 Auto-- locking Hub Solenoid Valve
4 Engine Stop Valve Unit
5 PLA Vacuum Unit (Idle Speed Adjustment)6Engine
7 Vacuum Pump
830_Thermovalve
9 Fuel Injection Pump
Test Data
Idle Speed IncreaseAt least 100 rpm at approx. 500mbr
Permissible Pressure Drop of System400 -- 500mbar approx. 1 min.
Page 1096 of 2053
5A-2 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
SSANGYONG MY2002
OPERATORS INTERFACES
There are three operator interfaces as the following;
•Gear Shift Control Lever
Driving Mode Selector
Indicator Light
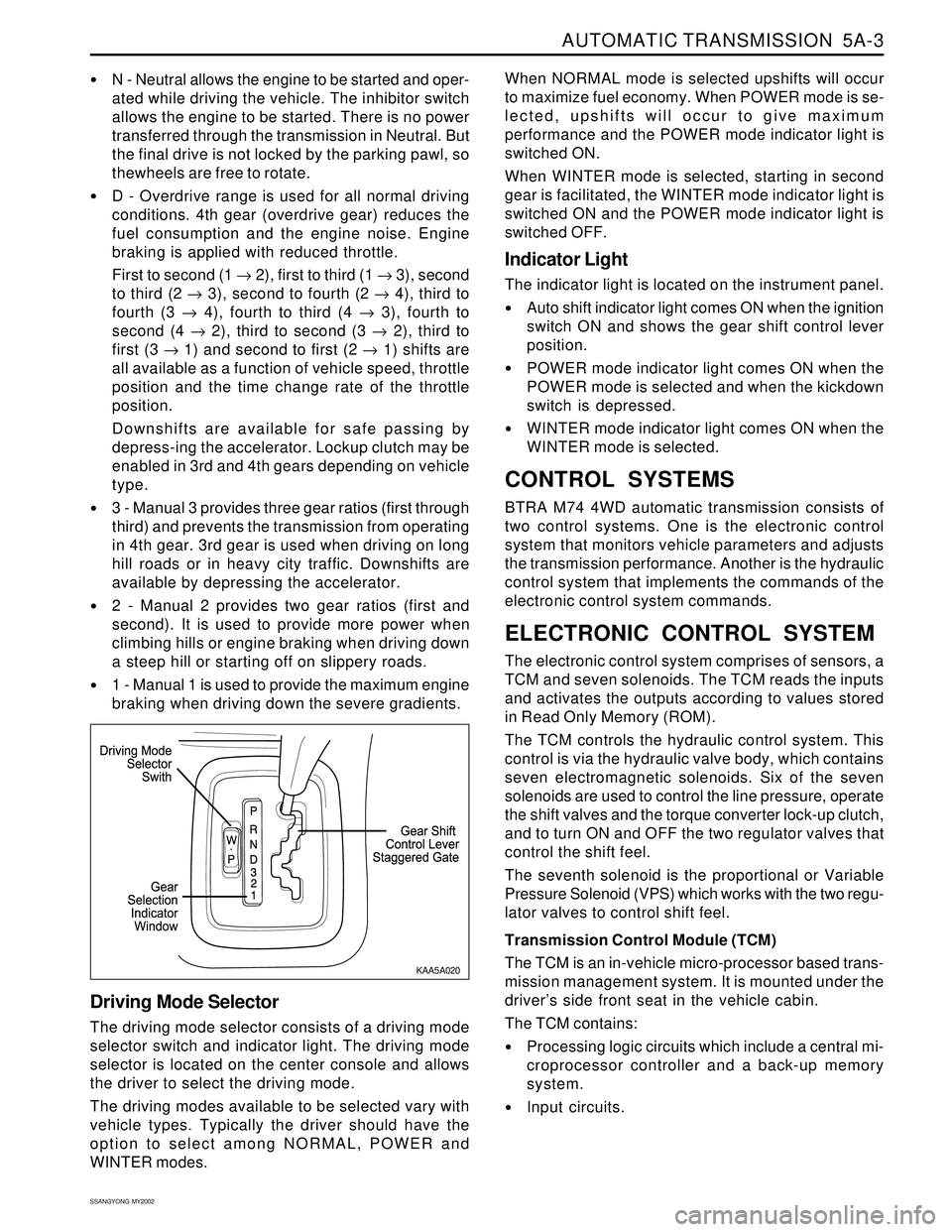
Gear Shift Control lever
The transmission uses a conventional shift control lever.
The gear shift control lever can be moved from one
position to another within the staggered configuration
of the shift control lever gate to positively indicate the
gear selection.
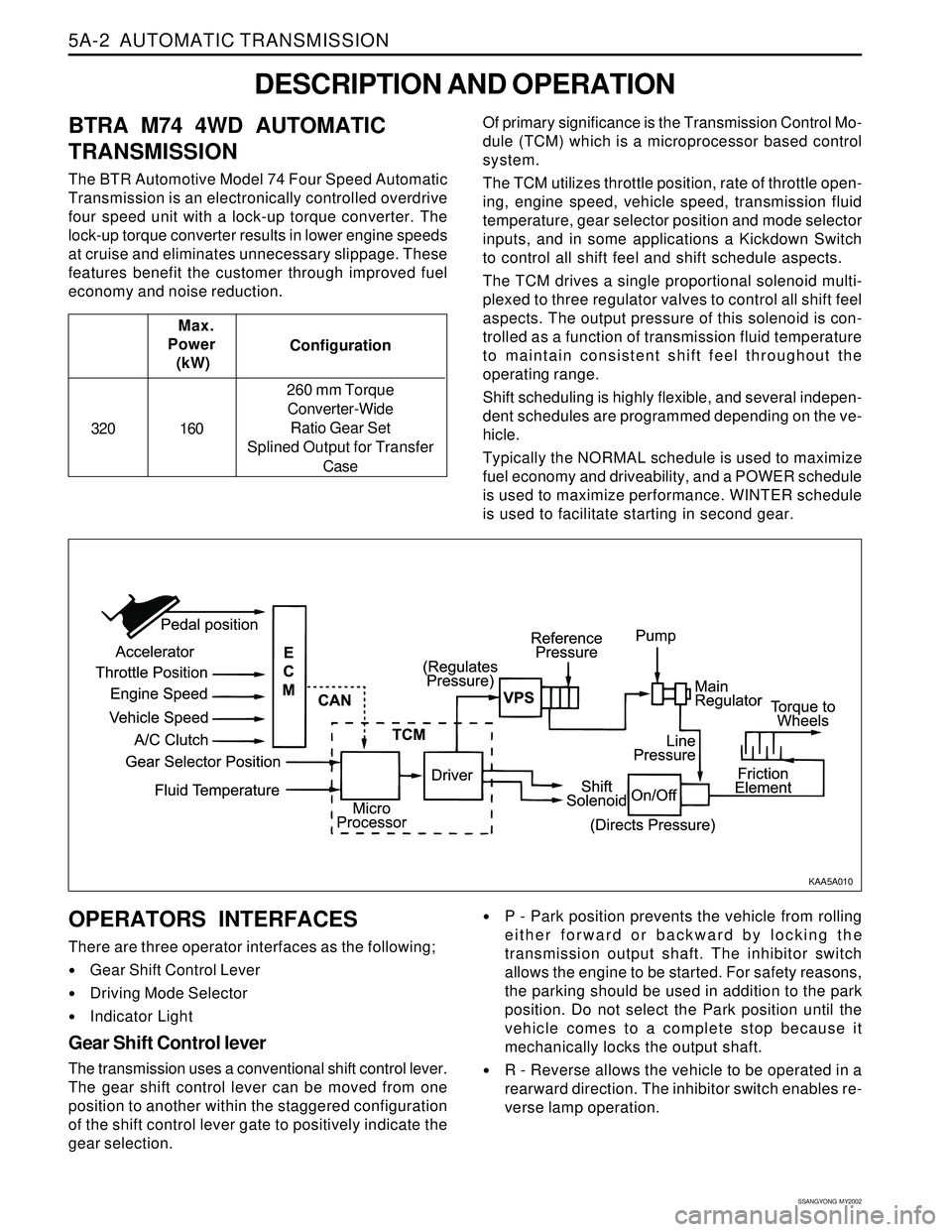
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BTRA M74 4WD AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
The BTR Automotive Model 74 Four Speed Automatic
Transmission is an electronically controlled overdrive
four speed unit with a lock-up torque converter. The
lock-up torque converter results in lower engine speeds
at cruise and eliminates unnecessary slippage. These
features benefit the customer through improved fuel
economy and noise reduction.Of primary significance is the Transmission Control Mo-
dule (TCM) which is a microprocessor based control
system.
The TCM utilizes throttle position, rate of throttle open-
ing, engine speed, vehicle speed, transmission fluid
temperature, gear selector position and mode selector
inputs, and in some applications a Kickdown Switch
to control all shift feel and shift schedule aspects.
The TCM drives a single proportional solenoid multi-
plexed to three regulator valves to control all shift feel
aspects. The output pressure of this solenoid is con-
trolled as a function of transmission fluid temperature
to maintain consistent shift feel throughout the
operating range.
Shift scheduling is highly flexible, and several indepen-
dent schedules are programmed depending on the ve-
hicle.
Typically the NORMAL schedule is used to maximize
fuel economy and driveability, and a POWER schedule
is used to maximize performance. WINTER schedule
is used to facilitate starting in second gear. Configuration Max.
Power
(kW)
320 160260 mm Torque
Converter-Wide
Ratio Gear Set
Splined Output for Transfer
Case
P - Park position prevents the vehicle from rolling
either forward or backward by locking the
transmission output shaft. The inhibitor switch
allows the engine to be started. For safety reasons,
the parking should be used in addition to the park
position. Do not select the Park position until the
vehicle comes to a complete stop because it
mechanically locks the output shaft.
R - Reverse allows the vehicle to be operated in a
rearward direction. The inhibitor switch enables re-
verse lamp operation.
KAA5A010
Page 1097 of 2053
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-3
SSANGYONG MY2002
N - Neutral allows the engine to be started and oper-
ated while driving the vehicle. The inhibitor switch
allows the engine to be started. There is no power
transferred through the transmission in Neutral. But
the final drive is not locked by the parking pawl, so
thewheels are free to rotate.
D - Overdrive range is used for all normal driving
conditions. 4th gear (overdrive gear) reduces the
fuel consumption and the engine noise. Engine
braking is applied with reduced throttle.
First to second (1 → 2), first to third (1 → 3), second
to third (2 → 3), second to fourth (2 → 4), third to
fourth (3 → 4), fourth to third (4 → 3), fourth to
second (4 → 2), third to second (3 → 2), third to
first (3 → 1) and second to first (2 → 1) shifts are
all available as a function of vehicle speed, throttle
position and the time change rate of the throttle
position.
Downshifts are available for safe passing by
depress-ing the accelerator. Lockup clutch may be
enabled in 3rd and 4th gears depending on vehicle
type.
3 - Manual 3 provides three gear ratios (first through
third) and prevents the transmission from operating
in 4th gear. 3rd gear is used when driving on long
hill roads or in heavy city traffic. Downshifts are
available by depressing the accelerator.
2 - Manual 2 provides two gear ratios (first and
second). It is used to provide more power when
climbing hills or engine braking when driving down
a steep hill or starting off on slippery roads.
1 - Manual 1 is used to provide the maximum engine
braking when driving down the severe gradients.When NORMAL mode is selected upshifts will occur
to maximize fuel economy. When POWER mode is se-
lected, upshifts will occur to give maximum
performance and the POWER mode indicator light is
switched ON.
When WINTER mode is selected, starting in second
gear is facilitated, the WINTER mode indicator light is
switched ON and the POWER mode indicator light is
switched OFF.
Indicator Light
The indicator light is located on the instrument panel.
Auto shift indicator light comes ON when the ignition
switch ON and shows the gear shift control lever
position.
POWER mode indicator light comes ON when the
POWER mode is selected and when the kickdown
switch is depressed.
WINTER mode indicator light comes ON when the
WINTER mode is selected.
CONTROL SYSTEMS
BTRA M74 4WD automatic transmission consists of
two control systems. One is the electronic control
system that monitors vehicle parameters and adjusts
the transmission performance. Another is the hydraulic
control system that implements the commands of the
electronic control system commands.
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The electronic control system comprises of sensors, a
TCM and seven solenoids. The TCM reads the inputs
and activates the outputs according to values stored
in Read Only Memory (ROM).
The TCM controls the hydraulic control system. This
control is via the hydraulic valve body, which contains
seven electromagnetic solenoids. Six of the seven
solenoids are used to control the line pressure, operate
the shift valves and the torque converter lock-up clutch,
and to turn ON and OFF the two regulator valves that
control the shift feel.
The seventh solenoid is the proportional or Variable
Pressure Solenoid (VPS) which works with the two regu-
lator valves to control shift feel.
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
The TCM is an in-vehicle micro-processor based trans-
mission management system. It is mounted under the
driver’s side front seat in the vehicle cabin.
The TCM contains:
Processing logic circuits which include a central mi-
croprocessor controller and a back-up memory
system.
Input circuits.
Driving Mode Selector
The driving mode selector consists of a driving mode
selector switch and indicator light. The driving mode
selector is located on the center console and allows
the driver to select the driving mode.
The driving modes available to be selected vary with
vehicle types. Typically the driver should have the
option to select among NORMAL, POWER and
WINTER modes.
KAA5A020