1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 504 of 2053

1F2 -- 86 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
YAA1F830
The Engine Control Module (ECM), located inside the right side kick panel, is the control center of the fuel injection
system. It constantly looks at the information from various sensors and controls the systems that affect the vehicle’s
performance. Engine rpm and air mass are used to measure the air intake quantity resulting in fuel injection metering.
The ECM also performs the diagnostic functions of the system. It can recognize operational problems, store failure
code(s) which identify the problem areas to aid the technician in making repairs.
There are no serviceable parts in the ECM. The calibrations are stored in the ECM in the Programmable Read Only
Memory (PROM).
The ECM supplies either 5 or 12 volts to power the sensors or switches. This is done through resistance in the ECM
which are so high in value that a test light will not come ON when connected to the circuit. In some cases, even an
ordinary shop voltmeter will not give and accurate reading because its resistance is too low. You must use a digital
voltmeter with a 10 Mohm input impedance to get accurate voltage readings. The ECM controls output circuits such as
the ignition coils, the fuel injectors, the fuel pump relay, the camshaft actuator, the canister purge valve, etc., by con-
trolling the ground circuit.
Page 516 of 2053

1F2 -- 98 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
YAA1F180
14. Turn the roll over valves counterclockwise at an
angle of 90 degrees.
15. Turn the lock ring counterclockwise.
16. Remove and discard the gasket.
17. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
YAA1F700
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
Removal and Installation Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the fuel pressure test connector.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque
25 NSm (18 Ib-ft)
YAA1F720
Caution: The fuel system is under pressure. To
avoid fuel spillage and the risk of personal injury or
fire, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system pres -
sure before disconnecting the fuel lines.
3. Relieve the fuel pressure in fuel supply system by
pressing the service valve.
YAA1F730
4. Disconnect the vacuum hose.
5. Disconnect the circlip and remove the fuel pressure
regulator.
6. Apply the oil to O-ring lightly and then replace it.
7. Perform a leak test of the fuel pressure regulator
with the engine off and the ignition on.
8. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
Page 518 of 2053

1F2 -- 100 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
YAA1F770
Notice:Before removal, the fuel rail assembly may be
cleaned with a spray-type cleaner, following package in-
structions. Do not immerse the fuel rails in liquid clean-
ing solvent. Use care in removing the fuel rail assembly
to prevent damage to the electrical connectors and in-
jector spray tips. Prevent dirt and other contaminants
from entering open lines and passages. Fittings should
be capped and holes plugged during service.
Important:If an injector becomes separated from the
rail and remains in the cylinder head, replace the injector
O-ring seals and the retaining clip.
12. Remove the injectors and the fuel rail carefully.
13. Remove the fuel injector retainer clips.
14. Remove the fuel injectors by pulling them down and
out.
15. Discard the fuel injector O-rings.
16. Lubricate the new fuel injector O-rings with engine
oil. Install the new O-rings on the fuel injectors.
17. Perform a leak check of the fuel rail and fuel injec-
tors.
18. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
YAA1F780
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
Removal and Installation Procedure
1. Relieve the coolant system pressure.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Disconnect the engine coolant temperature sensor
connector.
Notice:Take care when handling the engine coolant
temperature sensor. Damage to the sensor will affect
the proper operation of the fuel injection system.
4. Remove the engine coolant temperature sensor
from the pump hosing.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque
30 NSm (22 Ib-ft)
5. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
Page 536 of 2053

D AEW OO M Y_2000
SECTION 1
ENGINE
SECTION 1A3 (OM600 ENGINE)
GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications 1A3 -- 1............................
Engine Specifications 1A3-- 1.....................
Sectional View 1A3 -- 3............................
OM662LA Engine 1A3-- 3........................
OM661LA Engine 1A3-- 5........................
Performance Curve 1A3-- 7........................
OM662LA Engine 1A3-- 7........................
OM661LA Engine 1A3-- 8........................
Special Tools 1A3 -- 9.............................Special Tools Table 1A3-- 9.......................
Diagnosis 1A3 -- 10................................
Oil Leak Diagnosis 1A3-- 10.......................
Compression Pressure Test 1A3-- 11..............
Cylinder Pressure Leakage Test 1A3-- 13...........
General Information 1A3 -- 15......................
Cleanliness and Care 1A3 -- 15....................
On-- Engine Service 1A3-- 15......................
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationOM662LAOM661LA
Engine TypeFour -- Stroke DieselFour -- Stroke Diesel
Displacement (CC)28742299
Cylinder (Bore x Stroke)(mm)89 x 92.489 x 92.4
Fuel Injection / Ignition SystemPES 5 M55 C320 RS 168PES 5 M55 C320 RS 167
Compression Ratio22 :122 :1
Number of Cylinders54
Camshaft Valve ArrangementSOHCSOHC
Camshaft Drive TypeChain -- DriveChain-- Drive
Max. Output (ps/rpm)120 / 4000101 / 4000
Max. Torque (kgSm/rpm)25.5 / 400021.5 / 2400
Firing Order1--2--4--5--31--3--4--2
Injection TimingBTDC 18_±10_BTDC 18_±10_
Valve Timing
(t2lift)
IntakeOpen/CloseAT DC 11 . 3 3_/ ABDC 17_AT DC 11 . 3 3_/ ABDC 17_g
(at 2mm lift)ExhaustOpen/CloseBBDC 28_/ BTDC 15.25_BBDC 28_/ BTDC 15.25_
Valve Clearance AdjustmentAutomatic ControlAutomatic Control
Page 537 of 2053

1A3 -- 2 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
D AEW OO M Y_2000
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS (Cont’d)
ApplicationOM662LAOM661LA
Idle Speed (rpm)720 -- 820750 -- 850
Fuel Injection Pressure (bar)135 -- 143135 -- 143
Oil Capacity (liter)8.0 -- 9.56.5 -- 8.0
Lubrication TypeForced by Gear PumpForced by Gear Pump
Oil Filter TypeCombined Full-- Flow and Partial
Flow FilterCombined Full-- Flow and Partial
Flow Filter
FuelDieselDiesel
Page 545 of 2053

1A3 -- 10 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
D AEW OO M Y_2000
DIAGNOSIS
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. On some occasions a fluid leak may be
difficult to locate or repair. The following procedures may
help you in locating and repairing most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine oil,
automatic transmission fluid, power steering fluid,
etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large sheet
of paper.
2.2 Wait a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate loca-
tion of the leak by the drippings on the paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas that
are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be necessary
to clean the suspected area with a degreaser, steam
or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at normal
operating temperature and varying speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol-- type powder (such as foot powder)
to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating condi-
tions.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer to
the manufacturer ’s directions when using the kit.
1. Pour the specified amount of dye into the engine oil fill
tube.
2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions as
directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The dyed
fluid willappear as a yellow path leading to the
source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpointed and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must be
determined n order for it to be repaired properly. If a gas-
ket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent, the new
gasket will not repair the leak. Thebent flange must be
repaired also. Before attempting to repair a leak, check
for the following conditions and correct them as they
may cause a leak.
Gaskets
DThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
DThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
DThe fasteners are tightened improperly or the threads
are dirty or damaged.
DThe flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
DThere are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
DThe gasket is damaged or worn.
DThere is cracking or porosity of the component.
DAn improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
DThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
DThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
DThe seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
DThe seal is damaged or worn.
DImproper installation is evident.
DThere are cracks in the components.
DThe shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
DA loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal wear.
Page 549 of 2053
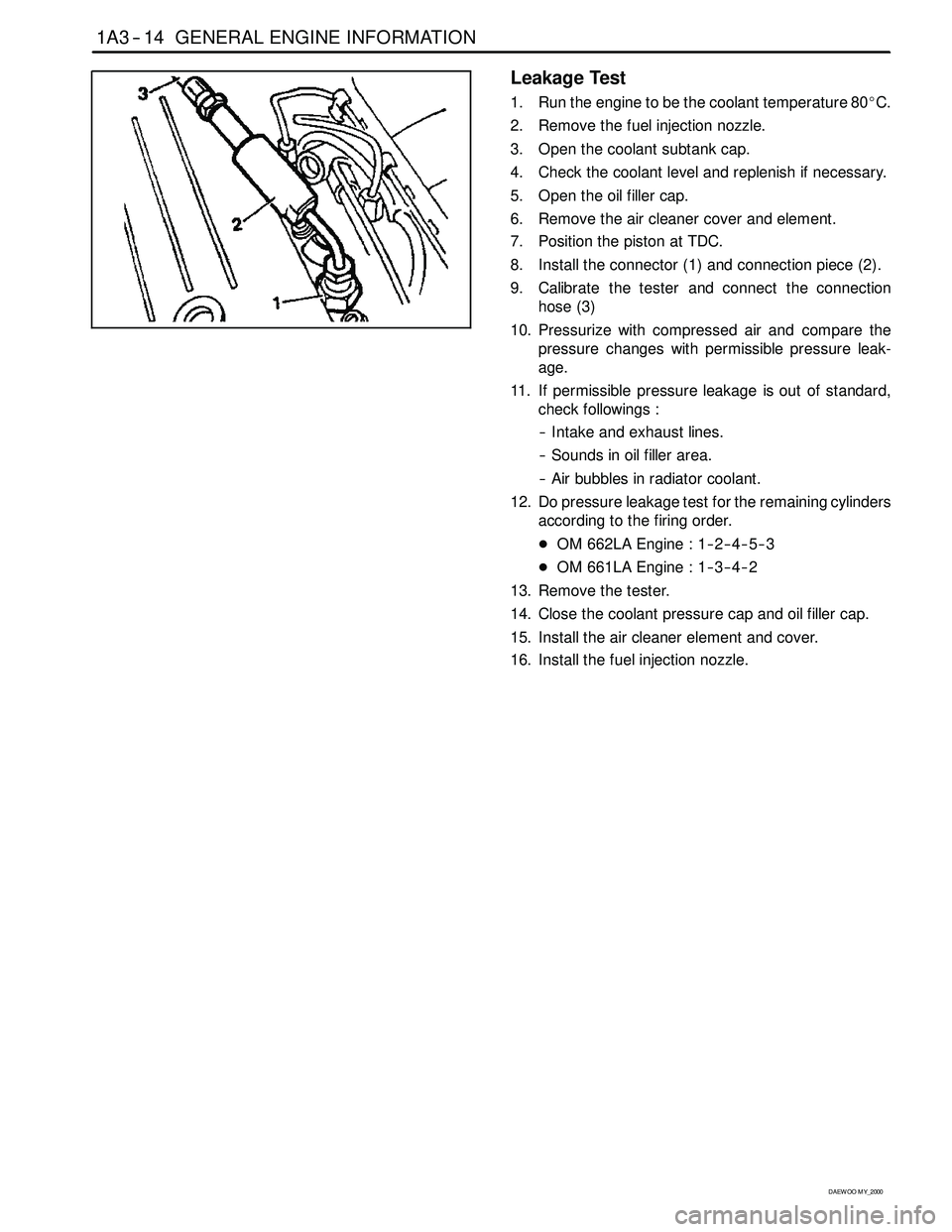
1A3 -- 14 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Leakage Test
1. Run the engine to be the coolant temperature 80_C.
2. Remove the fuel injection nozzle.
3. Open the coolant subtank cap.
4. Check the coolant level and replenish if necessary.
5. Open the oil filler cap.
6. Remove the air cleaner cover and element.
7. Position the piston at TDC.
8. Install the connector (1) and connection piece (2).
9. Calibrate the tester and connect the connection
hose (3)
10. Pressurize with compressed air and compare the
pressure changes with permissible pressure leak-
age.
11. If permissible pressure leakage is out of standard,
check followings :
-- Intake and exhaust lines.
-- Sounds in oil filler area.
-- Air bubbles in radiator coolant.
12. Do pressure leakage test for the remaining cylinders
according to the firing order.
DOM 662LA Engine : 1-- 2-- 4-- 5-- 3
DOM 661LA Engine : 1-- 3-- 4-- 2
13. Remove the tester.
14. Close the coolant pressure cap and oil filler cap.
15. Install the air cleaner element and cover.
16. Install the fuel injection nozzle.
Page 550 of 2053

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A3 -- 15
D AEW OO M Y_2000
GENERAL INFORMATION
CLEANLINESS AND CARE
An automobile engine is a combination of many ma-
chined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with toler-
ances that are measured in the ten-- thousanths of an
inch. When any internal engine parts are serviced, care
and cleanliness are important. A liberal coating of en-
igne oil should be applied to friction areas during assem-
bly, to protect and lubricate the surfaces on initial
operation. Proper cleaning and protection of machined
surfaces and friction areas is part fo the repair proce-
dure. This is considered standard shop practice even if
not specifically stated.
Whenever valve train components are removed for ser-
vice, they should be kept in order. They should be
installed in the same locations, and with the same mat-
ing surfaces, as when they were removed.
Battery cables should be disconnected before any major
work is performed on the engine. Failure to disconnectcables may result in damage to wire harness or other
electrical parts.
ON-- ENGINE SERVICE
Caution: Disconnect the negative battery cable be -
fore removing or installing any electrical unit, or
when a tool or equipment could easily come in con-
tact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnect -
ing this cable will help prevent personal injury and
damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in
LOCK unless otherwise noted.
Notice:Any time the air cleaner is removed, the intake
opening should be covered. Thiswill protect against ac-
cidental entrance of foreign material, which could follow
the intake passage into the cylinder and cause exten-
sive damage when the engine is started.