1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO turn signal
[x] Cancel search: turn signalPage 233 of 2053

1F1 -- 70 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Acceleration Pedal Position Sensor 1 Inspection
1. Turn the ignition switch to “ON” position.
2. Measure the signal voltage between the ECM pin No. 47 and No. 31 while operating the accelerator pedal as follow-
ing conditions.
DNot depress the pedal (closed throttle position)
DFully depress the pedal (full throttle with kick down)
Condition of Throttle Valve
Specified Value (V)
Closed Throttle Valve0.3 ~ 0.7
Fully Depressed Throttle Valve4.3 ~ 4.8
Notice:If measured value is not within the specified value, check the pedal valve sensor and the supply voltage to
APP 1 sensor.
Acceleration Pedal Position Sensor 2 Inspection
1. Turn the ignition switch to “ON” position.
2. Measure the signal voltage between the ECM pin No. 48 and No. 50 while operating the accelerator pedal as follow-
ing conditions.
DNot depress the pedal (closed throttle position)
DFully depress the pedal (full throttle with kick down)
Condition of Throttle Valve
Specified Value (V)
Closed Throttle Valve0.1 ~ 0.4
Fully Depressed Throttle Valve2.1 ~ 2.5
Notice:If measured value is not within the specified value, check the pedal valve sensor and the supply voltage to
APP sensor 2.
Page 246 of 2053

M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 83
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
81
Bank 1 system short
term fuel trim adaptation
below lean threshold
When recognition the value
less than nominal control
threshold, it means that when
big deviation in control range
of adaptation values through
fuel and air mixture formation
93
Bank 1 system short
term fuel trim adaptation
above rich threshold
When recognition the value
more than nominal control
threshold, it means that when
big deviation in control range
of adaptation values through
fuel and air mixture formation
96
Bank 1 system short
term fuel trim at rich
stopWhen recognition the short
term fuel trim that more than
nominal threshold
97
Bank1 system short
term fuel trim at lean
stopWhen recognition the short
term fuel trim that less than
nominal threshold
DInspection the intake air leakage
DIns
pection the injectionquantities with
98
Bank 1 system idle
adaptation failure (above
rich threshold)When recognition the long
term fuel trim exceeds rich
threshold
DInspectiontheinjectionquantitieswith
injector block or leakage
DInspection the exhaust leakage
DInspection the ECM
99
Bank 1 system idle
adaptation failure (below
rich threshold)When recognition the long
term fuel trim exceeds lean
threshold
p
100
Bank 1 system learning
control failure (rich, low
load)When recognition the long
term fuel trim exceeds rich
threshold
101
Bank 1 system learning
control failure (lean, low
load)When recognition the long
term fuel trim exceeds lean
threshold
102
Bank 1 system learning
control failure (rich, high
load)When recognition the long
term fuel trim exceeds rich
threshold
103
Bank 1 system learning
control failure (rich, low
load)When recognition the long
term fuel trim exceeds lean
threshold
Circuit Description
In order to control emissions, a catalytic converter is used to covert harmful emissions into harmless water vapor and
carbon dioxide. The ECM has the ability to monitor this process by using a oxygen sensor. The oxygen sensor pro-
duces and output signal which indicates the storage capacity of the catalyst. This in turn indicates the catalyst’s ability
to convert exhaust emission effectively. If the oxygen sensor pigtail wiring, connector, or terminal is damaged. Do not
attempt to repair the wiring, connector, or terminals. In order for the sensor to function properly, it must have a clean air
reference provided to it. This clean air reference is obtained by way of the oxygen sensor wire(s). Any attempt to repair
the wires, connector, or terminal and degrade the oxygen sensor performance.
Page 247 of 2053

1F1 -- 84 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Oxygen Sensor Signal Voltage Inspection
1. Maintain the engine speed is at idle while the coolant temperature is over 80°C.
2. Measure the oxygen sensor signal voltage between the ECM terminal No. 16 and No. 17.
Specified Value
-- 0.2 ~ 1.0 v
Notice:If the measured value is not within the specified value, the possible cause may be in cable, oxygen sensor or
ECM
Oxygen Sensor Heating Voltage Inspection
1. Maintain the engine speed is at idle while the coolant temperature is over 80°C.
2. Measure the oxygen sensor signal voltage between the ECM terminal No. 11 and No. 9.
Specified Value
11 ~ 14 v
Notice:If the measured value is not within the specified value, the possible cause may be in cable, oxygen sensor or
ECM
Oxygen sensor Heating Current Consumption Inspection
1. Turn the ignition switch to “ON” position.
2. Measure the oxygen sensor heating current consumption between the ECM terminal No. 9 and No. 5.
Specified Value
0.2~2.0A
Notice:If the measured value is not within the specified value, the possible cause may be in cable, oxygen sensor or
ECM
Page 257 of 2053
1F1 -- 94 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
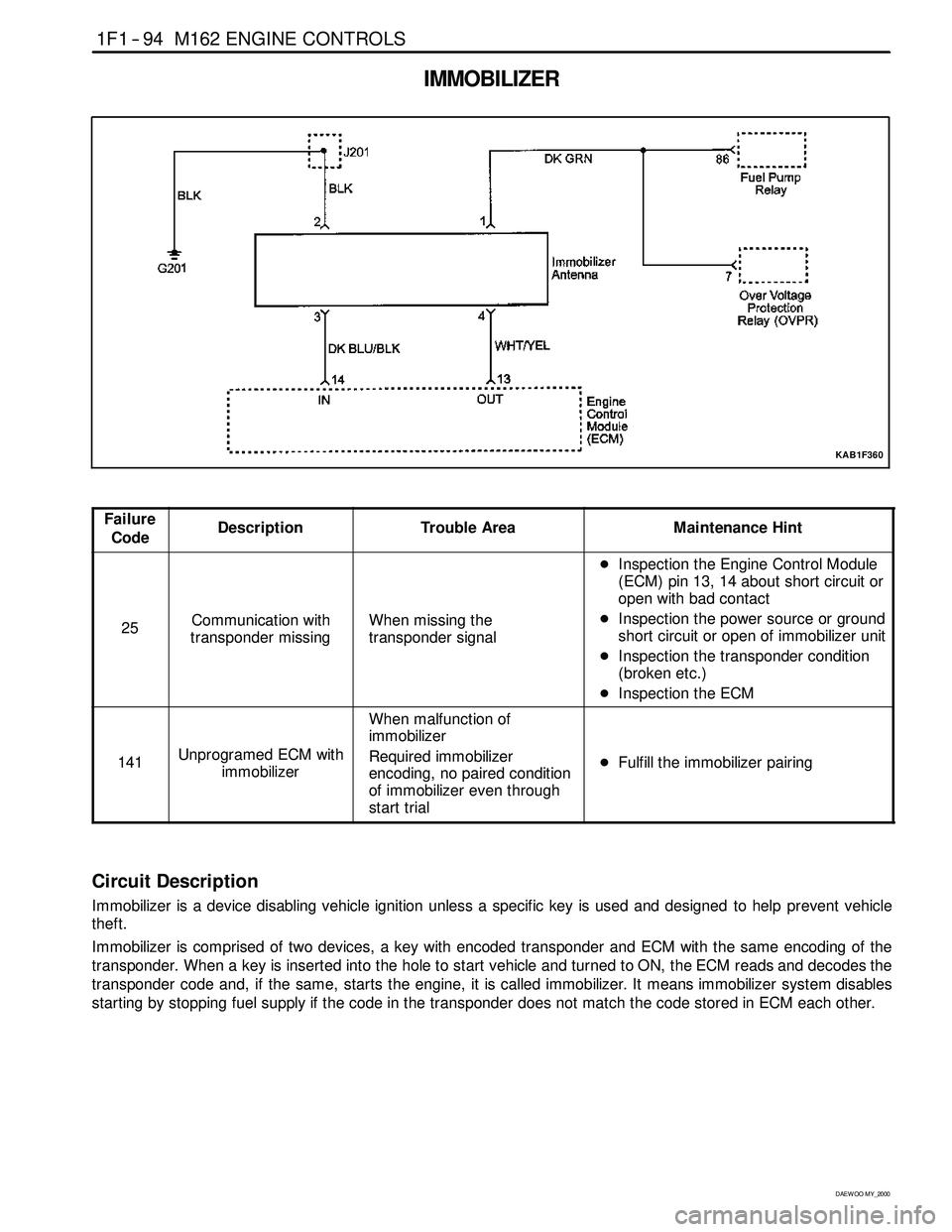
IMMOBILIZER
KAB1F360
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
25Communication with
transponder missingWhen missing the
transponder signal
DInspection the Engine Control Module
(ECM) pin 13, 14 about short circuit or
open with bad contact
DInspection the power source or ground
short circuit or open of immobilizer unit
DInspection the transponder condition
(broken etc.)
DInspection the ECM
141Unprogramed ECM with
immobilizer
When malfunction of
immobilizer
Required immobilizer
encoding, no paired condition
of immobilizer even through
start trial
DFulfill the immobilizer pairing
Circuit Description
Immobilizer is a device disabling vehicle ignition unless a specific key is used and designed to help prevent vehicle
theft.
Immobilizer is comprised of two devices, a key with encoded transponder and ECM with the same encoding of the
transponder. When a key is inserted into the hole to start vehicle and turned to ON, the ECM reads and decodes the
transponder code and, if the same, starts the engine, it is called immobilizer. It means immobilizersystem disables
starting by stopping fuel supply if the code in the transponder does not match the code stored in ECM each other.
Page 436 of 2053
1F2 -- 14 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
DIAGNOSIS
FAILURE CODE DIAGNOSIS
CLEARING FAILURE CODES
Notice:To prevent Engine Control Module (ECM) damage, the key must be OFF when disconnecting or reconnecting
the power to the ECM (for example battery cable, ECM pigtail connector, ECM fuse, jumper cables, etc.)
Parameters listed in the table may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other
factors. If a failure code is displayed during the “TROUBLE CODE” in scan tool check mode, check the circuit for the
code listed in the table below. For details of each code, turn to the page referred to under the “See Page” for the re-
spective “Failure Code” in the below table.
Failure codes should be cleared after repairs have been completed.
FAILURE CODES TABLE
Failure
codeSee
PageDescription
001F2 -- 66Engine coolant temperature sensor low voltage
011F2 -- 66Engine coolant temperature sensor high voltage
021F2 -- 66Engine coolant temperature sensor plausibility
031F2 -- 62Intake air temperature sensor low voltage
041F2 -- 62Intake air temperature sensor high voltage
051F2 -- 62Intake air temperature sensor plausibility
061F2 -- 66Engine coolant temperature insufficient for closed loop fuel control
081F2 -- 38System voltage too low
091F2 -- 62Mass air flow sensor plausibility
101F2 -- 62Mass air flow sensor low voltage
111F2 -- 62Mass air flow sensor high voltage
171F2 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor signal failure (no engine revolution signal)
181F2 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor signal failure (rpm > max. value)
191F2 -- 27Camshaft position senosr signal : No.1 cylinder recognition failure
201F2 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor signal failure (gap recognition failure)
211F2 -- 90Transmission coding failure
231F2 -- 88CAN communication failure : ASR/MSR
241F2 -- 88CAN communication failure : ABS
251F2 -- 94Communication with transponder missing
261F2 -- 88CAN communication failure : TCU (A/T only)
291F2 -- 89CAN communication failure : ID 200h not plausible
301F2 -- 89CAN communication failure : ID 208h not plausible
311F2 -- 89CAN communication failure : communication initialization failure
321F2 -- 77Engine rpm output circuit short circuit to battery
331F2 -- 77Engine rpm output circuit short circuit to ground or open
341F2 -- 43Fuel pump relay short circuit to battery
351F2 -- 43Fuel pump relay short circuit to ground or open
Page 458 of 2053

1F2 -- 40 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
FUEL SYSTEM
The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating condi-
tions. The fuel is delivered to the engine by the individual fuel injectors mounted into the intake manifold near each
cylinder.
The main fuel control sensors are the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor and the oxygen (O2) sensors.
The MAF sensor monitors the mass flow of the air being drawn into the engine. An electrically heated element is
mounted in the intake air stream, where it is cooled by the flow of incoming air. Engine Control Module (ECM) modu-
lates the flow of heating current to maintain the temperature differential between the heated film and the intake air at a
constant level. The amount of heating current required to maintain the temperature thus provides an index for the
mass air flow. This concept automatically compensates for variations in air density, as this is one of the factors that
determines the amount of warmth that the surrounding air absorbs from the heated element. MAF sensor is located
between the air filter and the throttle valve.
Under high fuel demands, the MAF sensor reads a high mass flow condition, such as wide open throttle. The ECM
uses this information to enrich the mixture, thus increasing the fuel injector on-- time, to provide the correct amount of
fuel. When decelerating, the mass flow decreases. This mass flow change is sensed by the MAF sensor and read by
the ECM, which then decreases the fuel injector on-- time due to the low fuel demand conditions.
The O2 sensors are located in the exhaust pipe before catalytic converter. The O2 sensors indicate to the ECM the
amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas, and the ECM changes the air/fuel ratio to the engine by controlling the fuel
injectors. The best air/fuel ratio to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7 to 1, which allows the catalytic converter to
operate most efficiently. Because of the constant measuring and adjusting of the air/fuel ratio, the fuel injection system
is called a “closed loop” system.
The ECM uses voltage inputs from several sensors to determine how much fuel to provide to the engine. The fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions, called ‘‘modes”.
Starting Mode
When the ignition is turned ON, the ECM turns the fuel pump relay on for 1 second. The fuel pump then builds fuel
pressure. The ECM also checks the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor and the Throttle Position (TP) sensor
and determines the proper air/fuel ratio for starting the engine. This ranges from 1.5 to 1 at -- 36°C(--33°F) coolant
temperature to 14.7 to 1 at 94°C (201°F) coolant temperature. The ECM controls the amount of fuel delivered in the
starting mode by changing how long the fuel injector is turned on and off. This is done by ‘‘pulsing” the fuel injectors for
very short times.
Run Mode
The run mode has two conditions called ‘‘open loop” and ‘‘closed loop”.
Open Loop
When the engine is first started and it is above 690 rpm, thesystem goes into “open loop” operation. In “open loop”, the
ECM ignores the signal from the HO2S and calculates the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the ECT sensor and the
MAF sensor. The ECM stays in “open loop” until the following conditions are met:
DThe O2 has a varying voltage output, showing that it is hot enough to operate properly.
DThe ECT sensor is above a specified temperature (22.5°C).
DA specific amount of time has elapsed after starting the engine.
Closed Loop
The specific values for the above conditions vary with different engines and are stored in the Electronically Erasable
Programmable Read -- Only Memory (EEPROM). When these conditions are met, thesystem goes into “closed loop”
operation. In “closed loop”, the ECM calculates the air/fuel ratio (fuel injector on-- time) based on the signals from the
O2 sensors. This allows the air/fuel ratio to stay very close to 14.7 to 1.
Acceleration Mode
The ECM responds to rapid changes in throttle position and airflow and provides extra fuel.
Deceleration Mode
The ECM responds to changes in throttle position and airflow and reduces the amount of fuel. When deceleration is
very fast, the ECM can cut off fuel completely for short periods of time.
Page 475 of 2053

M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2 -- 57
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F240
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
104Throttle position sensor
1 low voltageTPS 1 short circuit to ground
or open
105Throttle position sensor
1 high voltageTPS 1 short circuit to power
108Throttle position sensor
2 low voltageTPS 2 short circuit to ground
or open
109Throttle position sensor
2 high voltageTPS 2 short circuit to powerDMonitoring the actual values through
scantool
116Throttle actuator
learning control failureWhen actuator adaption
fluctuation or not meet the
conditionscantool
DInspection the ECM pin 84, 85, 87,
112, 67, 68 about short circuit or open
with bad contact
119Throttle valve return
spring failureWhen return spring defective
of actuator
withbadcontact
DInspection the throttle valve actuator
DInspection the ECM
121Throttle actuator failureWhen supply voltage of the
actuator short circuit to power
InspectiontheECM
123
Different mass air flow
sensor signal with
throttle position sensorWhen shut down of output
driver
125Both throttle position
sensor failureWhen defective of both
potentiometers
Page 476 of 2053

1F2 -- 58 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
126
Throttle position sensor
1 not plausible with
Throttle position sensor
2
When difference between
TPS 1 and TPS 2DMonitoring the actual values through
scan tool
DIns
pection the ECMpin 84, 85, 87,
127High permanent throttle
signalWhen failure of wiring
harness or actuator
DInspectiontheECMpin84,85,87,
112, 67, 68 about short circuit or open
with bad contact
Itiththttlltt
185
Mass air flow sensor
and throttle position
sensor failureWhen difference between
MAF and TPS signal
DInspection the throttle valve actuator
DInspection the ECM
Circuit Description
The ECM supplies a 5 volt reference signal and a ground to the TP sensor. The TP sensor sends a voltage signal back
to the ECM relative to the throttle plate opening. The voltage signalwill vary from approximately 0.3 ~ 0.9 volts at
closed throttle, to over 4.0 ~ 4.6 volts at Wide Open Throttle (WOT).
The TP sensors serve for engine load control according to the drive pedal command. Load adjustments independent of
the drive pedal command can be implemented; such functions are, for instance, idle control, speed control, drive slip
control, load shock damping, and similar functions.
When the actuator current fails, the throttle valve is returned to emergency operating position by a spring. The throttle
valve position, thereby the actuator drive position checkback is provided by two potentiometers. The motor positions
the throttle valve against the return spring force. Motor and return spring are two separate energy sources. Each of
them is able to position the throttle valve in emergency position alone. Throttle valve position checkback and monitor-
ing is provided by two actual value potentiometers connected to the engine control electronics.
Throttle Actuator Inspection
1. Turn the ignition switch to “ON” position.
2. Measure the TPS 1 signal voltage at the ECM pin No. 87 and TPS 2 signal voltage at the ECM pin No. 85.
Pedal PositionSpecified Value
TPS1Closed0.3 ~ 0.9 vTPS1Opened4.0 ~ 4.6 v
TPS2Closed4.0 ~ 4.6 vTPS2Opened0.3 ~ 0.9 v
Throttle Actuator DC Motor Inspection
1. Turn the ignition switch to “ON” position.
2. Measure the signal voltage between the ECM pin No. 67 and No. 68.
Application
Specified Value
Ignition “ON”0.8 ~ 2.3 v
Engine StatusIdling1.0 ~ 2.5 v
(Coolant temperature is over 70°C)
Throttle Actuator DC Motor Resistance
1. Turn the ignition switch to “OFF” position.
2. Measure the resistance between the ECM pin No. 67 and No. 68.
Specified Value
<10Ω